【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
[全部文件] 那张截图中的文件为本资料所有内容,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763





摘 要
在社会不断发展的今天,机器人在工业现场中的应用也越来越广泛,用机器的力量代替人力,而将人类从繁重的体力劳动中解放出来是历史发展的趋势。
近十几年来,机器人的开发不仅越来越优化,而且涵盖了许多领域,应用的范畴十分广阔。
在工业上,自动控制系统有着广泛的应用,如工业自动化机床控制,计算机系统,机器人等。而工业机器人是相对较新的电子设备,它正开始改变现代化工业面貌。
本设计的机械手是基于提高劳动生产率、产品质量和经济效益,减轻工人劳动强度而设计的。在某些劳动条件极其恶劣的条件下,工人难以用手工工作,可用本机械手代替人力劳动。
本设计为四自由度圆柱坐标型工业机械手,其工作方向为两个直线方向和两个旋转方向。
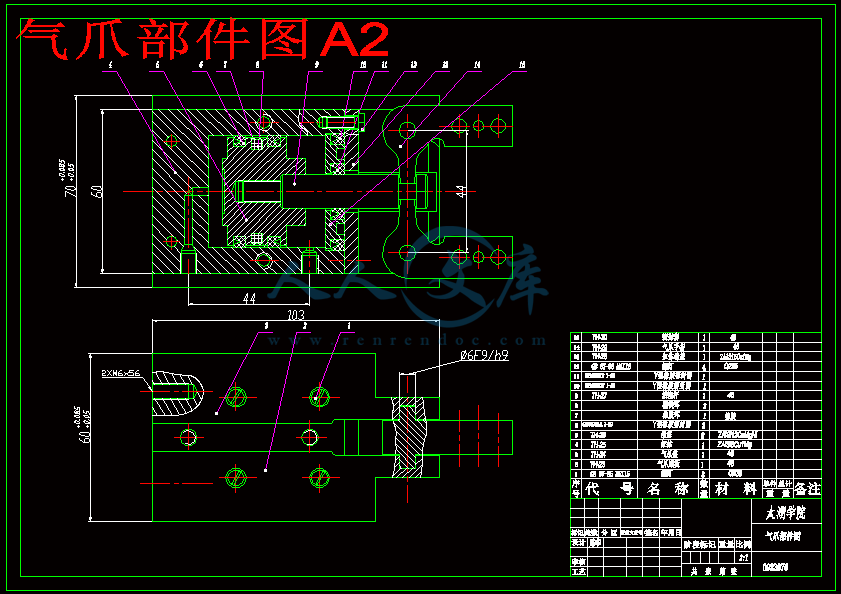
本设计中的四自由度棒料搬运机械手,主要是针对质量少于2KG的圆形棒料的搬运。通过气爪手指的不同选择可满足直径小于60mm的棒料的搬运。
在控制器的作用下,机械手执行将工件从一条流水线拿到另一条流水线并把工件翻转过来这一简单的动作。
关键词:四自由度;机械手;搬运;工业机器人
Abstract
Today that develop continuously in the society, The robot are more and more Using at industry scene application. Replaces the manpower with the machine strength, It‘s the historical development tendency that liberates the humanity from the arduous physical labor.
In the recent several years, the robot development not only more and more optimizes, but also moreover has covered many domains.
Industrially, automatic control systems are found in numerous applications, such as automation machine tool control, computer systems and robotics. Industrial robots are relatively new electromechanical devices that are beginning to change the appearance of modern industry.
This paper design for enhances the labor productivity, product quality, economic efficiency and reduces the worker labor intensity. Some job working at extremely bad environment, that people can’t work in hand, so the robots can replace worker to do it.
This scheme introduced a cylindrical robot for four degree of freedom. It is composed of two linear axes and two rotary axis current
This paper mainly use at the transporting of circular good material that quality is short to 2KG. The different fingernail finger was Choice for transporting the good material that diameter is smaller than 60mm.
Under controller function the robot move the components from one assembly line to other assembly line and turn over it in space, perform relatively simple takes.
Key words: four degrees of freedom; robot; transporting; Industrial robot
目 录
摘 要 IV
Abstract V
目 录..............................................................................................................................................................VII
1 绪论 1
1.1 工业机器人的技术与发展 1
1.2 本设计中的四自由度棒料搬运机械手所实现的功能 2
1.3 本设计中的四自由度棒料搬运机械手设计的意义 2
2 机械手的总体设计 3
2.1设计要求 3
2.2 机械手的组成 3
2.3 总方案的拟定 4
2.4机器人的工作空间 4
2.5 机械手驱动系统的设计 5
2.5.1 机械手驱动器 5
2.5.2 机械手传动机构 5
3 机械手的传动设计 7
3.1 滚珠丝杠的选择 7
3.2 谐波齿轮减速器参数的确定 8
4 机械手的各电机选择 12
4.1 机械手手臂升降步进点击的选择 12
4.2 机械手底座回转驱动电动机的选择 14
5 机械手各气动件的设计计算 18
5.1 气爪夹紧力的起算与气爪的选择 18
5.1.1 气爪夹紧力的要求 18
5.1.2 缸径的确定 19
5.1.3 行程的确定 20
5.1.4 气缸的动速度 20
5.1.5 摆动气缸的选择 21
5.2 手臂伸缩气缸的选择 23
6 机器人控制系统的设置 26
6.1 机械手控制器的选择 26
6.2 机械手控制系统的特点及对控制功能的基本要求 26
6.3 控制系统的总体设计 27
7 手臂验算与机械手参数...........................................................................................................................29
7.1 手臂平衡的验算 29
7.2 机械手参数 30
8 结论与展望 31
8.1 结论 31
8.2 不足之处及未来展望 31
致 谢 32
参考文献 33
1 绪论
1.1 工业机器人的技术与发展
机器人(又称机械手,机械人,英文名称:Robot),在人类科技发展史上其来有自,早在三国时代,诸葛亮发明的木牛流马即是古代中国人的智能结晶。随着近代的工业革命,机器产业的不断发展成为近代工业的主要支柱。
机器人的研究从一开始就是拟人化的,所以才有机械手、机械臂的开发与制作,也是为了以机械来代替人去做人力所无法完成的劳作或探险。但近十几年来,机器人的开发不仅越来越优化,而且涵盖了许多领域,应用的范畴十分广阔。
工业机器人是典型的机电一体化高技术产品。在许多生产领域,它对于提高生产自动化水平,提高劳动生产率、产品质量和经济效益,改善工人劳动条件的作用日见显著。不少劳动条件恶劣、生产要求苛刻的场合,工业机器人代替人力劳动已是必然的趋势。
工业机器人是一种机体独立,动作自由度较多,程序可灵活变更,能任意定位,自动化程度高的自动操作机械。主要用于加工自动线和柔性制造系统中传递和装卸工件或夹具。
工业机器人以刚性高的手臂为主体,与人相比,可以有更快的运动速度,可以搬运更重的东西,而且定位精度相当高,它可以根据外部来的信号,自动进行各种操作。
工业机器人的发展,由简单到复杂,由初级到高级逐步完善,它的发展过程可分为三代:
第一代工业机器人就是目前工业中大量使用的示教再现型工业机器人,它主要由手部、臂部、驱动系统和控制系统组成。它的控制方式比较简单,应用在线编程,即通过示教存贮信息,工作时读出这些信息,向执行机构发出指令,执行机构按指令再现示教的操作。
第二代工业机器人是带感觉的机器人。它具有寻力觉、触觉、视觉等进行反馈的能力。其控制方式较第一代工业机器人要复杂得多,这种机器人从1980年开始进入了实用阶段,不久即将普及应用。
第三代工业机器人即智能机器人。这种机器人除了具有触觉、视觉等功能外,还能够根据人给出的指令认识自身和周围的环境,识别对象的有无及其状态,再根据这一识别自动选择程序进行操作,完成规定的任务。并且能跟踪工作对象的变化,具有适应工作环境的功能。这种机器人还处于研制阶段,尚未大量投入工业应用。
世界上工业机器人萌芽于50年代的美国,经过40多年的发展,已被不断地应用于人类社会很多领域,正如计算机技术一样,机器人技术正在日益改变着我们的生产方式。
进入90年代,世界机器人工业继续稳步增长,每年增长率保持在10%左右,世界上已拥有机器人数量达到70万台左右,1992、1993年世界机器人市场曾一度出现小的低谷,近年除日本外,欧美机器人市场也开始复苏,并日益兴旺。与全球机器人市场一样,中国机器人市场也逐渐活跃,1997年上半年,我国从事机器人及相关技术产品研制、生产的单位已达200家,研制生产的各类工业机器人约有410台,其中已用于生产的约占3/4。目前全国约有机器人用户500家,拥有的工业机器人总台数约为1200台,其中从40家外国公司进口的各类机器人占2/3以上,并每年以100~150台的速度增加。
从机器人的应用与发展来看,在很多方面工业机器人代替人力劳动已是必然的趋势,工业机器人将来必定有广阔的发展前景。
1.2 本设计中的四自由度棒料搬运机械手所实现的功能
本设计中的四自由度棒料搬运机械手,主要是针对质量少于2KG的圆形棒料的搬运。
本设计中的机械手有四个自由度,由底座的旋转,手臂的升降,手臂的伸缩,手爪的旋转组成。本设计中的机械手是一种通用型棒料搬运机械手。通过气爪手指的不同选择可满足小于直径60mm的棒料的搬运。通过示教再现或程序的直接控制可实现在机械手工作范围内把棒料从指定点搬运到另一指定点,并把棒料翻转过来。通过对机械手的相应控制还可实现对棒料的排列。
1.3 本设计中的四自由度棒料搬运机械手设计的意义
机器人工程是近二十多年迅速发展起来的,目前已应用与许多生产领域。由目前的发展状况看,在可预见的将来它将在生产中扮演越来越重要的角色。本机械手就是基于此并为提高劳动生产率、产品质量和经济效益,减轻工人劳动强度而设计的。在某些劳动条件极其恶劣的条件下,工人难以用手工工作,可用本机械手代替人力劳动。在社会不断发展的今天,机器人在工业现场中的应用也越来越广泛,用机器的力量代替人力,而将人类从繁重的体力劳动中解放出来是历史发展的趋势。
2 机械手的总体设计
2.1 设计要求
要求:本毕业设计要求学生掌握机器人或工业机械手的结构及工作原理,实现机械手的上升、下移、左移、右移抓紧和放松等多个自由度,完成一四自由度搬运机器人设计,要求所设计机器人能抓取一定质量的工件并到达规定的地点。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号