1000L-min大流量液压实验台设计【原创含9张CAD图带开题报告】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:10233042
类型:共享资源
大小:1002.12KB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2018-06-25
上传人:QQ14****9609
认证信息
个人认证
郭**(实名认证)
陕西
IP属地:陕西
100
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
min
流量
液压
实验
试验
设计
原创
cad
开题
报告
讲演
呈文
- 资源描述:
-
1000L-min大流量液压实验台设计【含9张CAD图带开题报告+外文翻译】
【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】图纸预览详情如下:
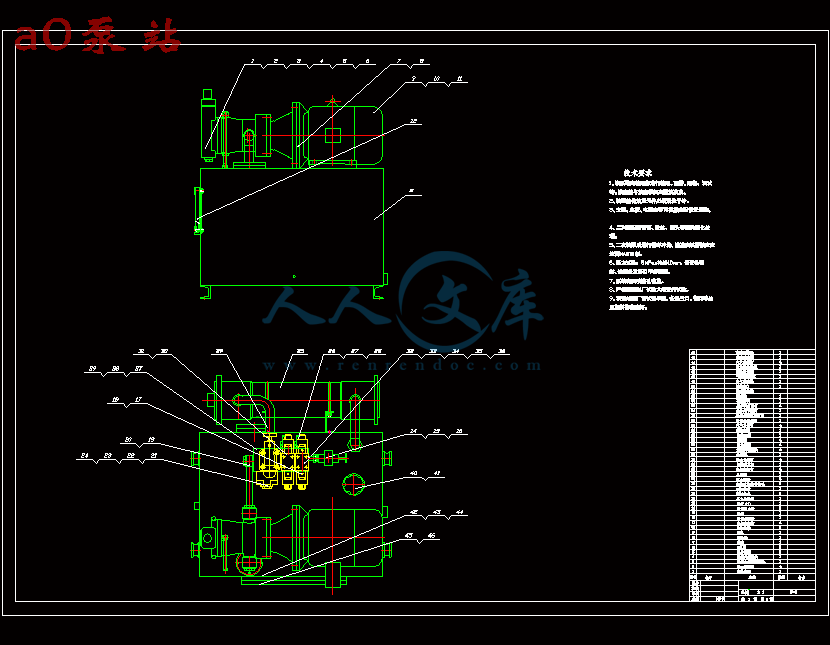


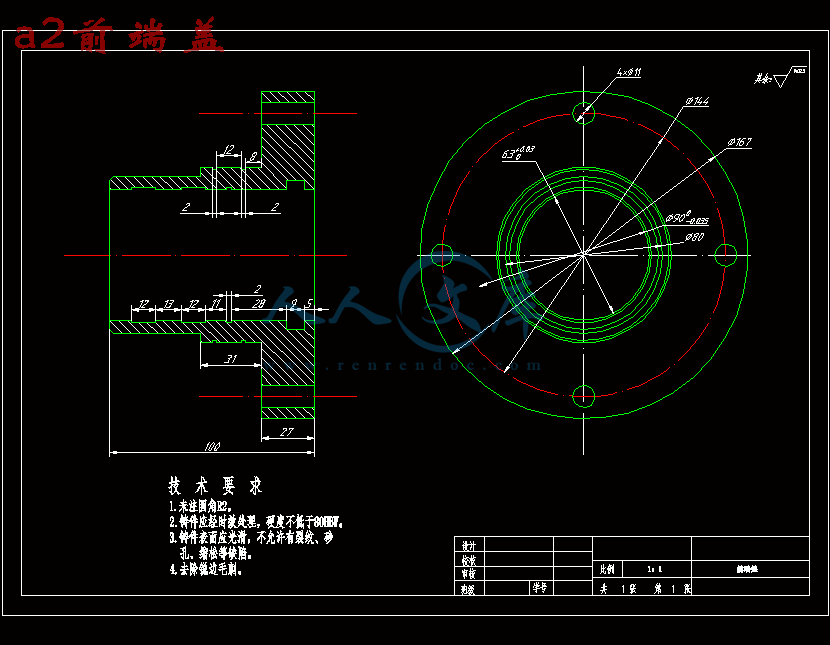


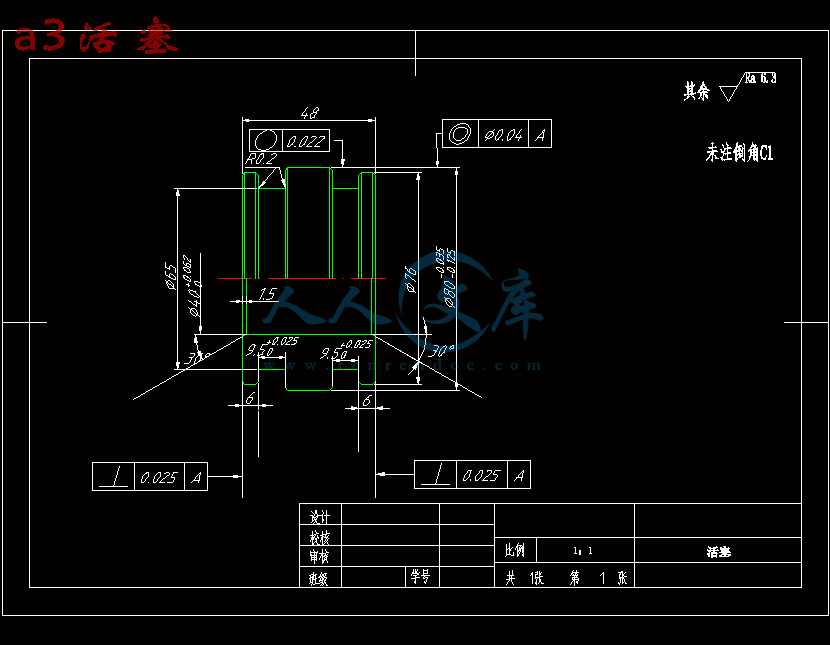






- 内容简介:
-
1课题申报表指导教师 职称 教研室申报课题名称 1000L/min 大流量液压实验台设计课题类型 工程设计类 课题来源 A.教师科研课题简介设计为适用于大流量液压阀的实验台。主要进行整机总体方案设计,包括液压系统设计、增压缸设计和绘图。 课题要求(包括所具备的条件)1)学生应该具有相应的机械制造专业的相关知识、CAD 或 PRO/E软件的操作和一定的英语翻译能力。2)教师提供相关零件图,相关参考书、工具书、设计手册等书目。课题工作量要求1)与课题有关的外文文献翻译不少于 4000 汉字;2)设计说明书的字数不少于 20000 字;3)毕业答辩图纸总量不少于 3 张 A0 图纸,其中包括计算机辅助绘图的工作量;4)主要参考文献不少于 15 篇(包括 2 篇以上外文文献)。教研室审定意见课题符合教学大纲要求,难度适中,工作量合适;同意作为毕业设计课题。教研室主任签名:学 院审定意见同意教学院长签名:说明:1、该表为毕业设计(论文)课题申报时专用,由选题教师填写,经教研室讨论、教研室主任签名,报学院审定,教学院长签名后生效。2、课题类型填:工程设计类;理论研究类;应用(实验)研究类;软件设计类;其它。3、课题来源填:教师科研;社会生产实践;教学;其它2任 务 书1.毕业设计的背景:大流量的安全阀实验,在理论与实践方面均相对较为落后,远不及大流量安全阀的发展速度,对流量在 300L/min 以上的安全阀,只有少数国家具有实验能力,由于没有实验能力,首先无法对国外进口设备进行有效检测,还阻碍的大流量安全阀和液压支架的发展,因此大冲击流量液压试验台对大流量安全阀的检测,提高大流量安全阀的可靠性有着重要意义。2.毕业设计(论文)的内容和要求:1)与课题有关的外文文献翻译不少于 4000 汉字;2)设计说明书的字数不少于 20000 字;3)毕业答辩图纸总量不少于 3 张 A0 图纸;4)主要参考文献不少于 15 篇(包括 2 篇以上外文文献)。3.主要参考文献:1 赵丽娟,李鸿岩液压支架用大流量安全阀发展综述J现代制造技术与装备,2009(1)2 孙玲,李鸿岩液压支架用大流量安全阀研究J 辽宁工程技术大学学报,2009(S2)3 王慧,隗金文液压支架用大流量安全阀动态特性的数字仿真J煤矿机械,1990(5)4 高扬新型液压支架用液控单向阀系统动态特性的分析与研究D,郑州大学,20075 熊诗波,章迪寰液压支架冲击阀动态特性分析煤炭学报,1991(4)6 王慧,郑祥林液压支架用大流量安全阀动态设计阜新矿业学院学报(自然科学版)J,1991(3)7 谢腾飞,赵继云等液压支架大流量安全阀动态性能试验方法研究J液压与气动,2010.(12)8 Rihardzoel. New and developing areas in modeling and simulation from a european perspectiveJ.System Simulation and Scientific Computing,1999.39 曾庆良,万丽荣,张鑫大流量安全阀的动态特性分析与计算机仿真J煤矿机械 1999(8) 10 杜岚松充气式安全阀气体弹簧非线性特性分析J太原理工大学学报,2004(3)4.毕业设计(论文)进度计划(以周为单位):1 查阅与毕业设计课题相关的资料2 提交开题报告3 进行毕业实习,并提交实习报告4 对课题资料进行整理,提交整体设计方案5 与指导老师讨论设计方案,确定最终方案6 展开具体的设计计算与校核,绘制相应设计草图7 展开具体的设计计算与校核,绘制相应设计草图8 绘制相应设计正式图纸9 绘制相应设计正式图纸10 撰写毕业设计论文草稿11 撰写毕业设计论文草稿12 图纸及论文修改并提交13 答辩教研室审查意见:同意室主任签名: 2018 年 3 月 2 日4学院审查意见:教学院长签名: 年 月 日开题报告课题名称 1000L/min 大流量液压实验台设计课题来源 A.教师科研 课题类型 工程设计类5选题的背景及意义我国是一个富煤的国家,是我国的支柱产业之一,作为在机械化采煤过程中的重要设备,液压支架可以有效的支撑和控制工作面的顶板,隔离踩空区,因此在煤炭生产中的作用是至关重要的。由于在采煤过程中,地质环境不是不会变动的,地质变动会使顶板下沉,立柱上部压力增加,这时立柱下腔压力迅速增加,液控单向阀反向锁死,在压力到达安全阀开启压力的情况下,安全阀开启,是乳化液溢流,支架下降,其过载保护作用。在普通情况下,流量在 100L/min 以上的安全阀被称为大流量安全阀,当立柱内压力过高时,安全阀开启溢流,保护了液压系统,但是随着矿井越来越深,冲击地压的问题也愈发突出。当冲击地压发生时,顶板压力急剧增,对液压支架系统产生巨大的载荷冲击,而液压支架系统并不能承受如此大的压力,就需要安全阀溢流卸载,从而限制最高压力,避免发生事故,保证工人的安全。目前国外安全阀流量已达 3000L/min,而我国也已经出现流量为 1000L/min 的大流量安全阀,并且还在不断发展进步之中,但缺乏适应大流量安全阀试验的实验台。研究内容拟解决的主要问题(1)在研究现有安全阀试验方法的基础上,确定试验台的设计方案(2)设计液压系统,对主要液压元件进行选择和设计(3)绘制装配图6研究方法技术路线首先根据设计题目明确设计任务,了解大流量实验台的工作原理,工作环境以及国内外发展现状,理清设计思路和确定方向,拟定初步设计方案。其次,根据设计任务书给定参数和技术要求对大流量实验台整体结构设计,对于大流量实验台各部分结构,要经过严格的设计,计算和校核。满足可靠性设计,使用周期等要求。在设计过程中要按照制定的工作流程,运用各种方法和多门学科知识。在大流量实验台设计时,拟定详细方案,分析其性能。明确各部分的结构。研究的总体安排和进度计划1 查阅与毕业设计课题相关的资料2 提交开题报告3 进行毕业实习,并提交实习报告4 对课题资料进行整理,提交整体设计方案5 与指导老师讨论设计方案,确定最终方案6 展开具体的设计计算与校核,绘制相应设计草图7 展开具体的设计计算与校核,绘制相应设计草图8 绘制相应设计正式图纸9 绘制相应设计正式图纸10 撰写毕业设计论文草稿11 撰写毕业设计论文草稿12 图纸及论文修改并提交13 答辩7主要参考文献1 赵丽娟,李鸿岩液压支架用大流量安全阀发展综述J现代制造技术与装备,2009(1)2 孙玲,李鸿岩液压支架用大流量安全阀研究J 辽宁工程技术大学学报,2009(S2)3 王慧,隗金文液压支架用大流量安全阀动态特性的数字仿真J煤矿机械,1990(5)4 高扬新型液压支架用液控单向阀系统动态特性的分析与研究D,郑州大学,20075 熊诗波,章迪寰液压支架冲击阀动态特性分析煤炭学报,1991(4)6 王慧,郑祥林液压支架用大流量安全阀动态设计阜新矿业学院学报(自然科学版)J,1991(3)7 谢腾飞,赵继云等液压支架大流量安全阀动态性能试验方法研究J液压与气动,2010.(12)8 Rihardzoel. New and developing areas in modeling and simulation from a european perspectiveJ.System Simulation and Scientific Computing,1999.9 曾庆良,万丽荣,张鑫大流量安全阀的动态特性分析与计算机仿真J煤矿机械 1999(8) 10 杜岚松充气式安全阀气体弹簧非线性特性分析J太原理工大学学报,2004(3)指导教师意 见对“文献综述”的评语: 文献综述深入全面 对总体安排和进度计划的评语 : 进度安排恰当合理,同意开题 指导教师签名:2018 年 4 月 10 日 教研室意见 学院意见同意教研室主任签名:2018 年 4 月 28 日教学院长签名:年 月 日8设计指导记录第一次指导记录:解释论文题目,互留联系方式讲毕业论文应交作业及具体要求、参考文献要求同学回去广泛搜集资料,确定框架思路推荐了一些查阅资料的网站以及方法。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 1 月 15 日第二次指导记录:开学后的第一次会议定在 3 月 2 号上午十点,首先是对实习报告,实习鉴定表的材料的上交;其次是把自己搜集的资料,查找的翻译文章让老师查阅,方便了解毕设的思路;最后老师针对个人毕业设计题目,进行设计方向的指导,大致确定研究设计方向。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 3 月 2 日9第三次指导记录:任务书下发,开始写开题报告老师经任务书在学校的毕业生系统中下达,根据任务书中的要求,开始书写开题报告,分析说明开题报告的写法和注意事项(研究背景、目的意义、课题研究现状和趋势、本文研究技术路线和研究方法,主要解决问题),讨论研究各位同学题目的框架和研究内容。对开题报告中需要注意的一些关键点,老师做了简单介绍和举例。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 3 月 6 日第四次指导记录:检查开题报告撰写进度,讲解点评开题报告初稿。老师针对所写开题报告,指出需要修改内容,包括选题的背景和意义在介绍时,字数偏少,内容方面没有点题,偏离所设计题目。研究内容拟解决的主要问题这个方面中,缺少主导思想,没有写出本次设计中所需要着重设计的方面,没有表现出此次设计存在的社会意义。研究方法技术路线缺少细节介绍,只是流程似的阐述设计步骤,总的来说,整体需要修改。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 3 月 14 日 10第五次指导记录:根据上周老师对开题报告提出的建议,把需要修改的地方,通过查阅资料参考其他结论性文章,对内容做了添加和修改。老师审阅了修改后的开题报告,内容方面大致可以了,对开题报告的格式还需要按照模板加以修改。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 3 月 20 日第六次指导记录:修改完成的开题报告经老师审阅,内容和格式方面大致没有问题,经老师同意,将开题报告上传至学校官网的毕业生系统。将大致翻译的外文文献的文档让老师查阅,在内容翻译的方法上存在一定问题,有待修改。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 3 月 25 日第七次指导记录:对外文翻译的内容加以审阅,在格式方面加以规范化,要求按照论文格式加以修改。指导地点 XXXX 2018 年 3 月 30 日18Belt Conveying Systems Development of driving systemAmong the methods of material conveying employed,belt conveyors play a very important part in the reliable carrying of material over long distances at competitive costConveyor systems have become larger and more complex and drive systems have also been going through a process of evolution and will continue to do soNowadays,bigger belts require more power and have brought the need for larger individual drives as well as multiple drives such as 3 drives of 750 kW for one belt(this is the case for the conveyor drives in Chengzhuang Mine)The ability to control drive acceleration torque is critical to belt conveyors performance An efficient drive system should be able to provide smooth,soft starts while maintaining belt tensions within the specified safe limitsFor load sharing on multiple drivestorque and speed control are also important considerations in the drive systems design. Due to the advances in conveyor drive control technology,at present many more reliableCost-effective and performance-driven conveyor drive systems covering a wide range of power are available for customers choices1.1 Analysis on conveyor drive technologies11 Direct drivesFull-voltage startersWith a full-voltage starter design,the conveyor head shaft is direct-coupled to the motor through the gear driveDirect full-voltage starters are adequate for relatively low-power, simple-profile conveyorsWith direct full-voltage startersno control is provided for various conveyor loads anddepending on the ratio between fu11- and no-1oad power requirements,empty starting times can be three or four times faster than full loadThe maintenance-free starting system is simple,low-cost and very reliableHowever, they cannot control starting torque and maximum stall torque;thereforethey are limited to the low-power, simple-profile conveyor belt drivesReduced-voltage startersAs conveyor power requirements increase,controlling the applied motor torque during the acceleration period becomes increasingly importantBecause motor torque 1s a function of voltage,motor voltage must be controlledThis can be achieved through reduced-voltage starters by employing a silicon controlled rectifier(SCR)A common starting method with SCR reduced-voltage starters is to apply low voltage initially to take up conveyor belt slackand then to apply a timed linear ramp up to full voltage and belt speed However, this starting method will not produce constant conveyor belt accelerationWhen acceleration is completethe SCRs, which control the applied voltage to the electric motor are locked in full conduction, providing fu11-line voltage to the motor Motors with higher torque and pullup torque,can provide better starting torque when 19combined with the SCR starters, which are available in sizes up to 750 KWWound rotor induction motorsWound rotor induction motors are connected directly to the drive system reducer and are a modified configuration of a standard AC induction motorBy inserting resistance in series with the motors rotor windingsthe modified motor control system controls motor torqueFor conveyor starting,resistance is placed in series with the rotor for low initial torqueAs the conveyor accelerates,the resistance is reduced slowly to maintain a constant acceleration torqueOn multiple-drive systemsan external slip resistor may be left in series with the rotor windings to aid in load sharingThe motor systems have a relatively simple designHowever, the control systems for these can be highly complex,because they are based on computer control of the resistance switchingToday,the majority of control systems are custom designed to meet a conveyor systems particular specificationsWound rotor motors are appropriate for systems requiring more than 400 kW DC motorDC motorsavailable from a fraction of thousands of kW ,are designed to deliver constant torque below base speed and constant kW above base speed to the maximum allowable revolutions per minute(r/min)with the majority of conveyor drives, a DC shunt wound motor is usedWherein the motors rotating armature is connected externallyThe most common technology for controlling DC drives is a SCR device which allows for continual variable-speed operationThe DC drive system is mechanically simple, but can include complex custom-designed electronics to monitor and control the complete systemThis system option is expensive in comparison to other soft-start systemsbut it is a reliable, cost-effective drive in applications in which torque,1oad sharing and variable speed are primary considerationsDC motors generally are used with higher-power conveyors,including complex profile conveyors with multiple-drive systems,booster tripper systems needing belt tension control and conveyors requiring a wide variable-speed range12 Hydrokinetic couplingHydrokinetic couplings,commonly referred to as fluid couplingsare composed of three basic elements; the driven impeller, which acts as a centrifugal pump;the driving hydraulic turbine known as the runner and a casing that encloses the two power componentsHydraulic fluid is pumped from the driven impeller to the driving runner, producing torque at the driven shaftBecause circulating hydraulic fluid produces the torque and speed,no mechanical connection is required between the driving and driven shaftsThe power produced by this coupling is based on the circulated fluids amount and density and the torque in proportion to input speedBecause the pumping action within the fluid coupling depends on centrifugal forcesthe output speed is less than the input speedReferred to as slipthis normally is 20between l% and 3%Basic hydrokinetic couplings are available in configurations from fractional to several thousand kW Fixed-fill fluid couplings Fixed-fill fluid couplings are the most commonly used soft-start devices for conveyors with simpler belt profiles and limited convex/concave sectionsThey are relatively simple,1ow-cost,reliable,maintenance free devices that provide excellent soft starting results to the majority of belt conveyors in use todayVariable-fill drain couplingsDrainable-fluid couplings work on the same principle as fixed-fill couplingsThe couplings impellers are mounted on the AC motor and the runners on the driven reducer high-speed shaftHousing mounted to the drive base encloses the working circuit The couplings rotating casing contains bleed-off orifices that continually allow fluid to exit the working circuit into a separate hydraulic reservoirOil from the reservoir is pumped through a heat exchanger to a solenoid-operated hydraulic valve that controls the filling of the fluid couplingTo control the starting torque of a single-drive conveyor system,the AC motor current must be monitored to provide feedback to the solenoid control valveVariable fill drain couplings are used in medium to high-kW conveyor systems and are available in sizes up to thousands of kW The drives can be mechanically complex and depending on the control parameters the system can be electronically intricateThe drive system cost is medium to high, depending upon size specifiedHydrokinetic scoop control driveThe scoop control fluid coupling consists of the three standard fluid coupling components:a driven impeller, a driving runner and a casing that encloses the working circuitThe casing is fitted with fixed orifices that bleed a predetermined amount of fluid into a reservoirWhen the scoop tube is fully extended into the reservoir, the coupling is l00 percent filledThe scoop tube, extending outside the fluid coupling,is positioned using an electric actuator to engage the tube from the fully retracted to the fully engaged positionThis control provides reasonably smooth acceleration ratesto but the computer-based control system is very complexScoop control couplings are applied on conveyors requiring single or multiple drives from l50 kW to 750 kW.13 Variable-frequency control(VFC)Variable frequency control is also one of the direct drive methodsThe emphasizing discussion about it here is because that it has so unique characteristic and so good performance compared with other driving methods for belt conveyor VFC devices Provide variable frequency and voltage to the induction motor, resulting in an excellent starting torque and acceleration rate for belt conveyor drivesVFC drivesavailable from fractional to several thousand(kW ), are electronic controllers that rectify AC line power to DC and,through an 21inverter, convert DC back to AC with frequency and voltage contro1VFC drives adopt vector control or direct torque control(DTC)technology,and can adopt different operating speeds according to different loadsVFC drives can make starting or stalling according to any given S-curvesrealizing the automatic track for starting or stalling curvesVFC drives provide excellent speed and torque control for starting conveyor beltsand can also be designed to provide load sharing for multiple driveseasily VFC controllers are frequently installed on lower-powered conveyor drives,but when used at the range of medium-high voltage in the pastthe structure of VFC controllers becomes very complicated due to the limitation of voltage rating of power semiconductor devices,the combination of medium-high voltage drives and variable speed is often solved with low-voltage inverters using step-up transformer at the output,or with multiple low-voltage inverters connected in seriesThree-level voltage-fed PWM converter systems are recently showing increasing popularity for multi-megawatt industrial drive applications because of easy voltage sharing between the series devices and improved harmonic quality at the output compared to two-level converter systems With simple series connection of devicesThis kind of VFC system with three 750 kW /23kV inverters has been successfully installed in ChengZhuang Mine for one 27-km long belt conveyor driving system in following the principle of three-level inverter will be discussed in detail2 Neutral point clamped(NPC)three-level inverter using IGBTsThree-level voltage-fed inverters have recently become more and more popular for higher power drive applications because of their easy voltage sharing features1ower dv/dt per switching for each of the devices,and superior harmonic quality at the outputThe availability of HV-IGBTs has led to the design of a new range of medium-high voltage inverter using three-level NPC topologyThis kind of inverter can realize a whole range with a voltage rating from 23 kV to 41 6 kV Series connection of HV-IGBT modules is used in the 33 kV and 41 6 kV devices The 23 kV inverters need only one HV-IGBT per switch 2,3.21 Power sectionTo meet the demands for medium voltage applicationsa three-level neutral point clamped inverter realizes the power sectionIn comparison to a two-level inverterthe NPC inverter offers the benefit that three voltage levels can be supplied to the output terminals,so for the same output current quality,only 1/4 of the switching frequency is necessaryMoreover the voltage ratings of the switches in NPC inverter topology will be reduced to 1/2and the additional transient voltage stress on the motor can also be reduced to 1/2 compared to that of a two-level inverterThe switching states of a three-level inverter are summarized in Table 1UV and 22W denote each of the three phases respectively;P N and O are the dc bus pointsThe phase U,for example,is in state P(positive bus voltage)when the switches S1u and S2u are closed,whereas it is in state N (negative bus voltage) when the switches S3u and S4u are closedAt neutral point clamping,the phase is in O state when either S2u or S3u conducts depending on positive or negative phase current polarity,respectivelyFor neutral point voltage balancing,the average current injected at O should be zero22 Line side converterFor standard applicationsa l2-pulse diode rectifier feeds the divided DC-link capacitorThis topology introduces low harmonics on the line sideFor even higher requirements a 24-pulse diode rectifier can be used as an input converterFor more advanced applications where regeneration capability is necessary, an active frontend converter can replace the diode rectifier, using the same structure as the inverter23 Inverter controlMotor Contro1Motor control of induction machines is realized by using a rotor fluxoriented vector controllerFig2 shows the block diagram of indirect vector controlled drive that incorporates both constant torque and high speed field-weakening regions where the PW M modulator was used In this figure,the command flux is generated as function of speedThe feedback speed is added with the feed forward slip command signal . the resulting frequency signal is integrated and then the unit vector signals(cos and sin )are generatedThe vector rotator generates the voltage and angle commands for the PW M as shownPWM ModulatorThe demanded voltage vector is generated using an elaborate PWM modulatorThe modulator extends the concepts of space-vector modulation to the three-level inverterThe operation can be explained by starting from a regularly sampled sine-triangle comparison from two-level inverterInstead of using one set of reference waveforms and one triangle defining the switching frequency, the three-level modulator uses two sets of reference waveforms Ur1 and Ur2 and just one triangleThus, each switching transition is used in an optimal way so that several objectives are reached at the same timeVery low harmonics are generatedThe switching frequency is low and thus switching losses are minimizedAs in a two-level inverter, a zero-sequence component can be added to each set of reference waveform s in order to maximize the fundamental voltage componentAs an additional degree of freedom,the position of the reference waveform s within the triangle can be changedThis can be used for current balance in the two halves of the DC-1ink233 Testing resultsAfter Successful installation of three 750 kW /23 kV three-level inverters for one 27 km long belt conveyor driving system in Chengzhuang MineThe performance of the whole VFC system was testedFig3 is taken from the test,which shows the excellent characteristic of the belt conveyor driving system with VFC controllerFig3 includes four curvesThe curve 1 shows the belt tensionFrom the curve it can be find that the fluctuation range of the belt tension is very smal1Curve 2 and curve 3 indicate current and torque separatelyCurve 4 shows the velocity of the controlled beltThe belt velocity have the“s”shape characteristicA1l the results of the test show a very satisfied characteristic for belt driving system4 ConclusionsAdvances in conveyor drive control technology in recent years have resulted in many more reliableCost-effective and performance-driven conveyor drive system choices for users Among these choices,the Variable frequency control (VFC) method shows promising use in the future for long distance belt conveyor drives due to its excellent performancesThe NPC three-level inverter using high voltage IGBTs make the Variable frequency control in medium voltage applications become much more simple because the inverter itself can provide the medium voltage needed at the motor terminals,thus eliminating the step-up transformer in most applications in the pastThe testing results taken from the VFC control system with NPC three1evel inverters used in a 27 km long belt conveyor drives in Chengzhuang Mine indicates that the performance of NPC three-level inverter using HV-IGBTs together with the control strategy of rotor field-oriented vector control for induction motor drive is excellent for belt conveyor driving system24带式输送机及其牵引系统 在运送大量的物料时,带式输送机在长距离的运输中起到了非常重要的竞争作用。输送系统将会变得更大、更复杂,而驱动系统也已经历了一个演变过程,并将继续这样下去。如今,较大的输送带和多驱动系统需要更大的功率,比如 3 驱动系统需要给输送带750KW (成庄煤矿输送机驱动系统的要求)。控制驱动力和加速度扭矩是输送机的关键。一个高效的驱动系统应该能顺利的运行,同时保持输送带张紧力在指定的安全极限负荷内。为了负载分配在多个驱动上,扭矩和速度控制在驱动系统的设计中也是很重要的因素。由于输送机驱动系统控制技术的进步,目前更多可靠的低成本和高效驱动的驱动系统可供顾客选择 1。1 带式输送机驱动1.1 带式输送机驱动方式全电压启动 在全电压启动设计中,带式输送机驱动轴通过齿轮传动直接连接到电机。直接全压驱动没有为变化的传送负载提供任何控制,根据满载和空载功率需求的比率,空载启动时比满载可能快34倍。此种方式的优点是:免维护,启动系统简单,低成本,可靠性高。但是,不能控制启动扭矩和最大停止扭矩。因此,这种方式只用于低功率,结构简单的传送驱动中。降压启动 随着传送驱动功率的增加,在加速期间控制使用的电机扭矩变得越来越重要。由于电机扭矩是电压的函数,电机电压必须得到控制,一般用可控硅整流器(SCR) 构成的降压启动装置,先施加低电压拉紧输送带,然后线性的增加供电电压直到全电压和最大带速。但是,这种启动方式不会产生稳定的加速度,当加速完成时,控制电机电压的SCR 锁定在全导通,为电机提供全压。此种控制方式功率可达到750kW。绕线转子感应电机 绕线转子感应电机直接连接到驱动系统减速机上,通过在电机转子绕组中串联电阻控制电机转矩。在传送装置启动时,把电阻串联进转子产生较低的转矩,当传送带加速时,电阻逐渐减少保持稳定增加转矩。在多驱动系统中,一个外加的滑差电阻可能将总是串联在转子绕组回路中以帮助均分负载。该方式的电机系统设计相对简单,但控制系统可能很复杂,因为它们是基于计算机控制的电阻切换。当今,控制系统的大多数是定制设计来满足传送系统的特殊规格。绕线转子电机适合于需要400kW以上的系统。直流(DC)电机 大多数传送驱动使用DC 并励电机,电机的电枢在外部连接。控制DC 驱动技术一般应用SCR装置,它允许连续的变速操作。DC 驱动系统在机械上是简单的,但设计的电子电路,监测和控制整个系统,相比于其他软启动系统的选择是昂贵的,但在转矩、负载均分和变速为主要考虑的场合,它又是一个可靠的,节约成本的方式。DC 电25机一般使用在功率较大的输送装置上,包括需要输送带张力控制的多驱动系统和需要宽变速范围的输送装置上。1.2 液力偶合器流体动力偶合器通常被称为液力偶合器,由三个基本单元组成:充当离心泵的叶轮,推进水压的涡轮和装进两个动力部件的外壳。流体从叶轮到涡轮,在从动轴产生扭矩。由于循环流体产生扭矩和速度,在驱动轴和从动轴之间不需要任何机械连接。这种连接产生的动力决定于液力偶合器的充液量,扭矩正比于输入速度。因在流体偶合中输出速度小于输入速度,其间的差值称为滑差,一般为1 %3 %。传递功率可达几千千瓦。固定充液液力偶合器 固定充液液力偶合器是在结构较简单和仅具有有限的弯曲部分的输送装置中最常用的软启动装置,其结构相对比较简单,成本又低,对现在使用的大多数输送机能提供优良的软启动效果。可变充液液力偶合器 也称为限矩型液力偶合器。偶合器的叶轮装在AC 电机上,涡轮装在从动减速器高速轴上,包含操作部件的轴箱安装在驱动基座。偶合器的旋转外壳有溢出口,允许液体不断地从工作腔中流出进入一个分离的辅助腔,油从辅助腔通过一个热交换器泵到控制偶合器充液量的电磁阀。为了控制单机传动系统的启动转矩,必须监测AC 电机电流,给电磁阀的控制提供反馈。可变充液液力偶合器可使用在中大功率输送系统中,功率可达
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号