【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
[全部文件] 那张截图中的文件为本资料所有内容,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763











Abstract
Pneumatic manipulator is a robot which is based on Pressure-driven. The robot is the combination of expertise and expertise of an anthropomorphic machine electro-mechanical device, not simply instead of manual labor. It owns both the rapid response to the environment state and the ability of a long continuous operation, high accuracy, and the resistance to harsh environments. It is mainly used to crawl at a fixed program, and carry objects and operate tools automatically. So Pneumatic Manipulator can reduce labor intensity, improve production efficiency. However, its disadvantages are obvious. Pneumatic Manipulator getting the precise positioning is very difficult, especially achieving multi-point positioning to anywhere because of the great compressibility of gas. Also, the compressibility limits a load to be too heavy. Traditional pneumatic system only relies on the set position of the mechanical giving location and reliable positioning and velocity which relies on a single one-way throttle. So it is often unable to meet many requirements of the automatic control equipment.
After a deep study, we found that the pneumatic flip robot on the current production line can only be achieved crawling and flip function once in a movement process whose efficiency is too low. So we design a pneumatic flip robot which can achieve the two crawling and flipping in a motion process. There is no doubt that the pneumatic flip robot can improve work efficiency and speed up the production efficiency.
Key words: pneumatic devices; robot; turning device; clip bottle;
目 录
摘 要
Abstract
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 引言 1
1.2气动机械手的发展 1
1.2.1国外气动机械手状况 1
1.2.2国内气动机械手情况 3
1.3发展趋势 3
1.3.1重复高精度 3
1.3.2模块化 3
1.3.3无给油化 4
1.3.4 机电气一体化 4
1.4 机械手夹持部件结构示意图 4
1.4.1 外夹持型机械手 4
1.4.2 内夹持型机械手 5
1.5国内外气动机械手设计举例 5
1.5.1与模具切割相结合 5
1.5.2 机械手虚拟样机 6
1.5.3 高精度机械手 6
第2章 气动翻转机械手总体设计 8
2.1 抓取系统的初步设计 8
2.2 翻转系统的初步设计 8
2.2.1 锥齿轮电机翻转 8
2.2.2 链轮链条气缸翻转 9
2.2.3 翻转方案选择 9
2.3气动翻转机械手的三维建模、装配思路 10
2.3.1各部分零件设计 10
2.3.2 气动翻转机械手的运动学仿真 10
2.3.3 研究思路方案、可行性分析及预期成果 11
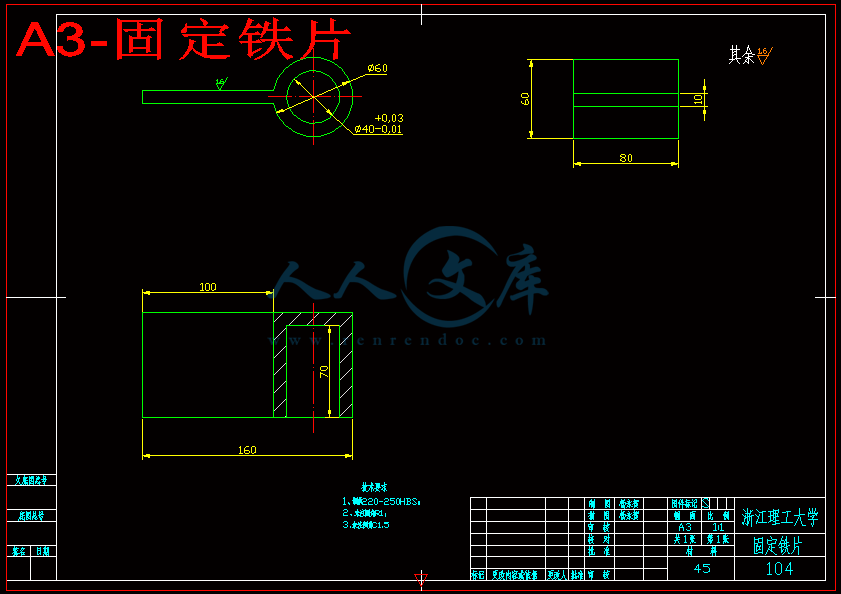
第3章 气动翻转机械手重要零部件设计校核及其装配 12
3.1气缸的设计和校核 12
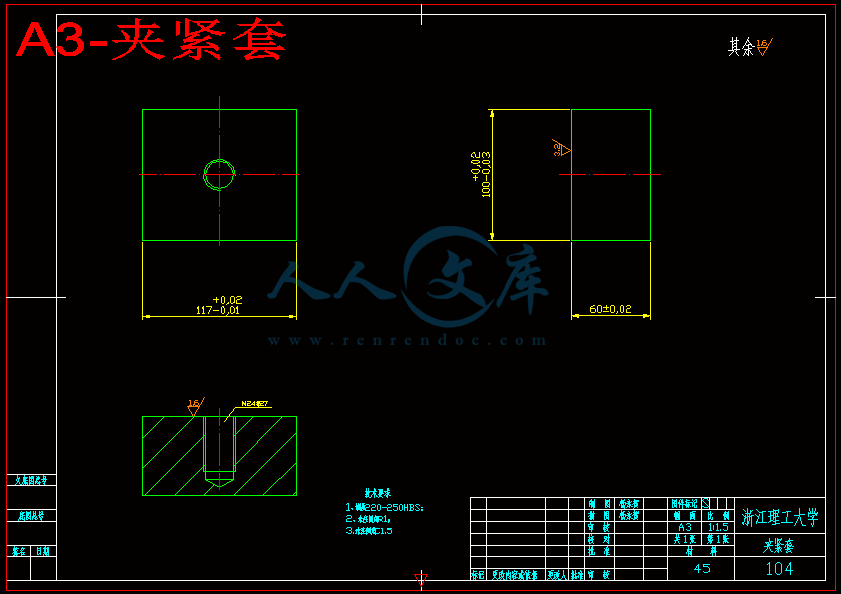
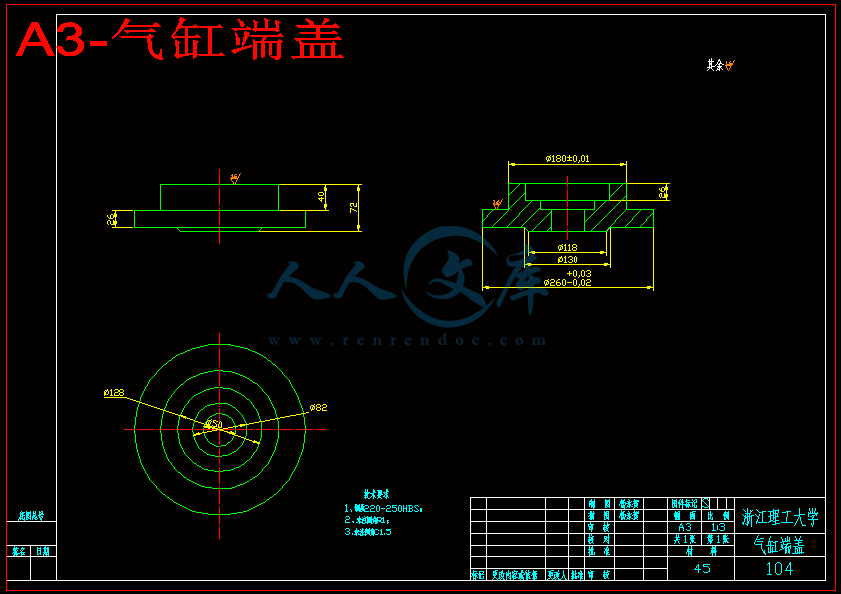
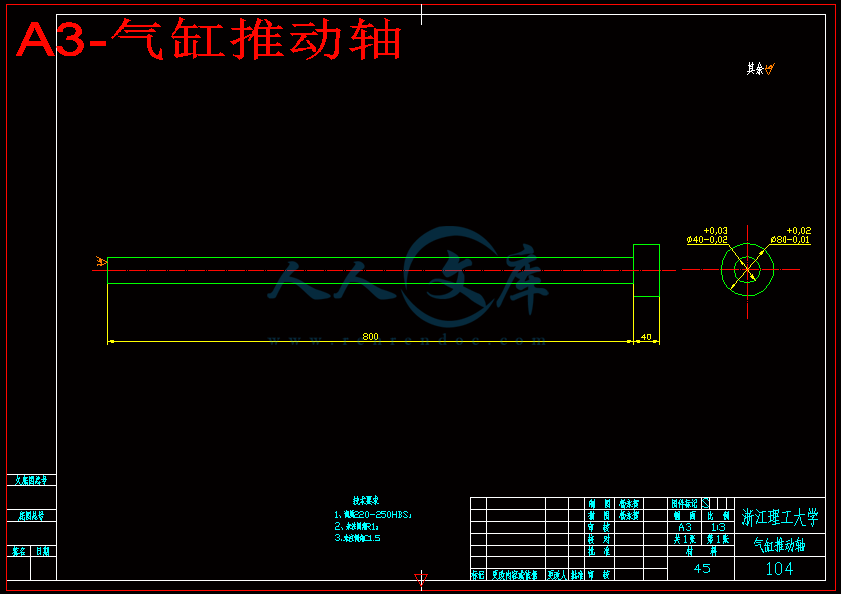
3.1.1 夹紧系统气缸设计和校核 12
3.1.2 翻转系统气缸设计和校核 14
3.2齿轮设计和校核 15
3.2.1齿轮参数的选择 15
3.2.2齿轮几何尺寸确定 15
3.2.3齿根弯曲疲劳强度计算 16
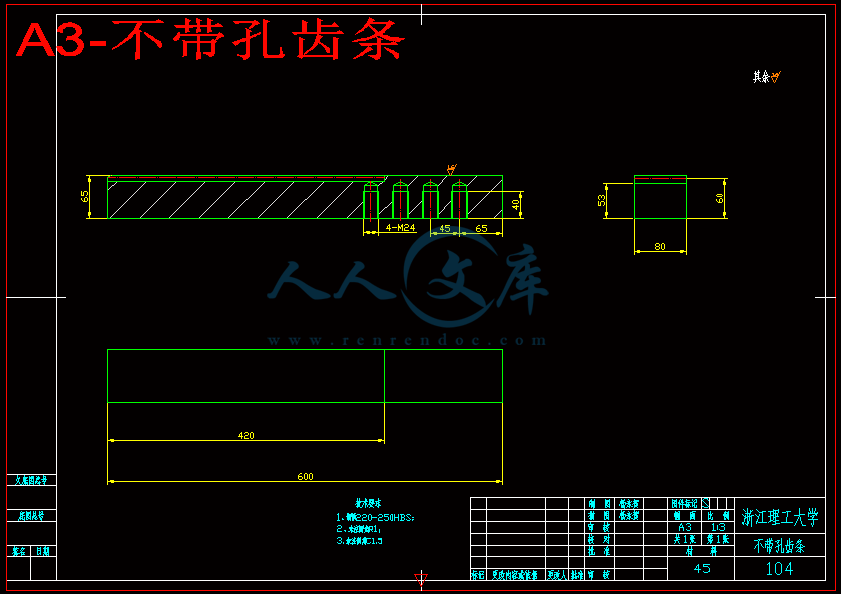
3.3齿条的设计和校核 18
3.3.1齿条的设计 18
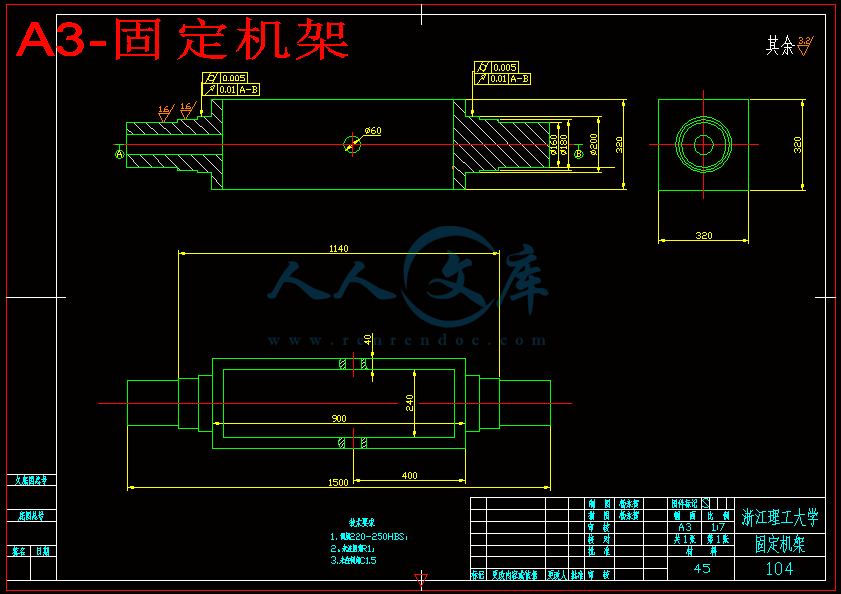
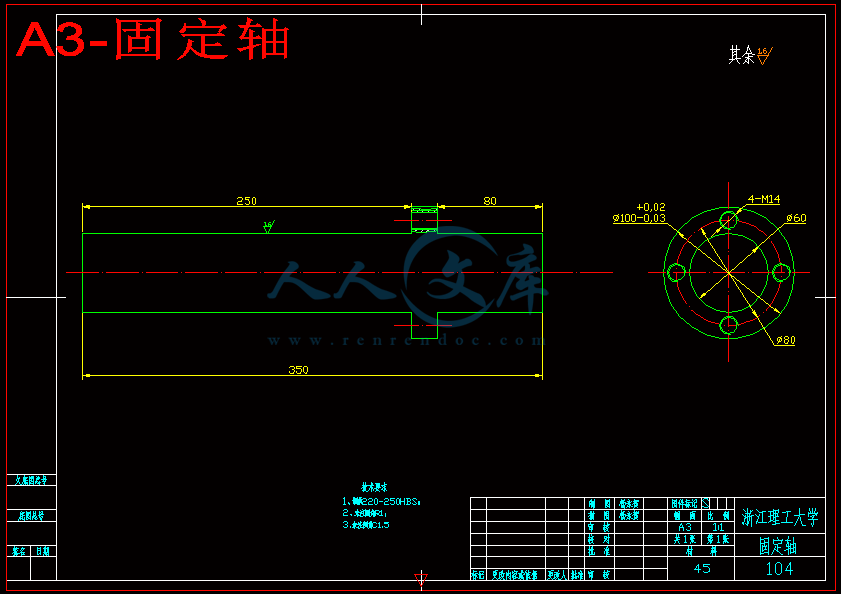
3.4 固定机架上的轴设计和校核 20
3.4.1求输入轴上的功率、转速和转矩 20
3.4.2求作用在齿轮上的力 20
3.4.3 初步确定轴的最小直径 21
3.4.4轴的结构设计 21
3.4.5精确校核轴的疲劳强度 23
3.5圆锥滚子轴承的设计和校核 25
3.6键连接设计和校核 26
3.6.1输入轴键计算 26
3.6.2中间轴键计算 26
3.6.3输出轴键计算 27
3.7联轴器的设计和校核 27
第4章 三维建模和运动仿真 29
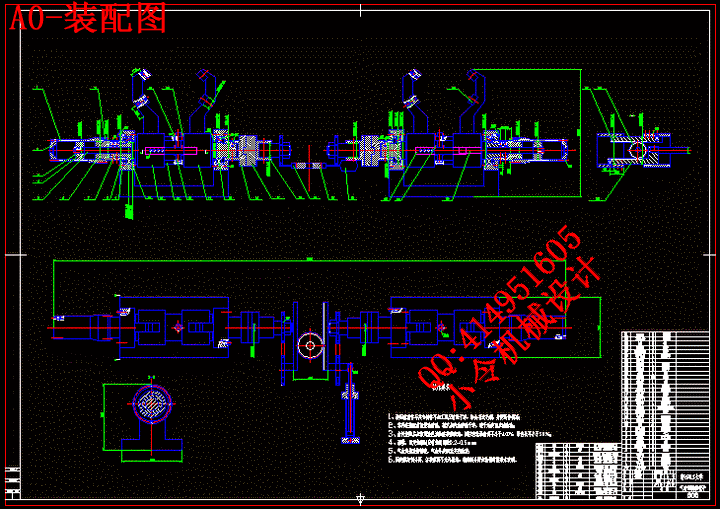
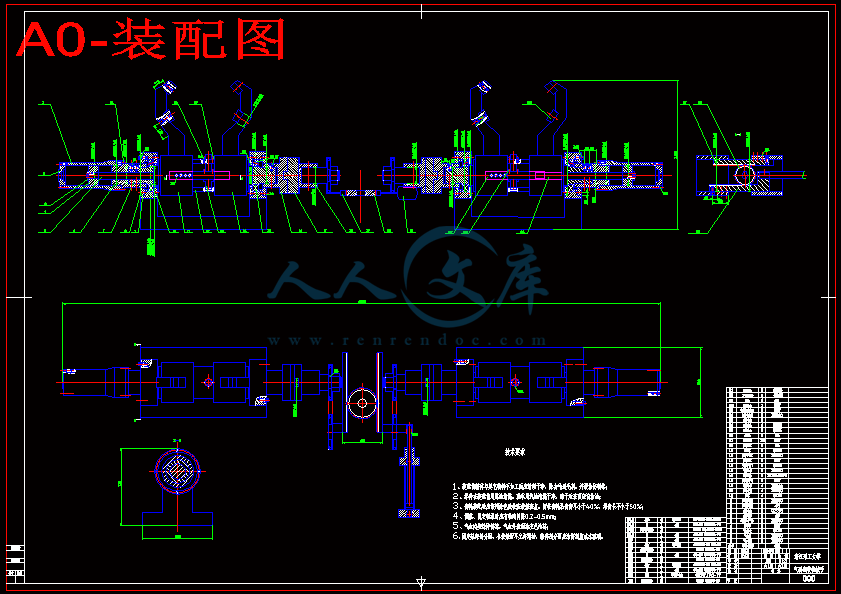
4.1 整体装配图 29
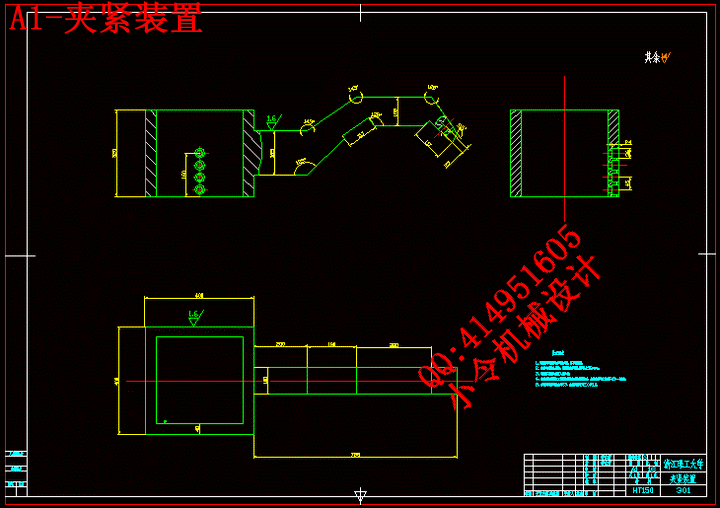
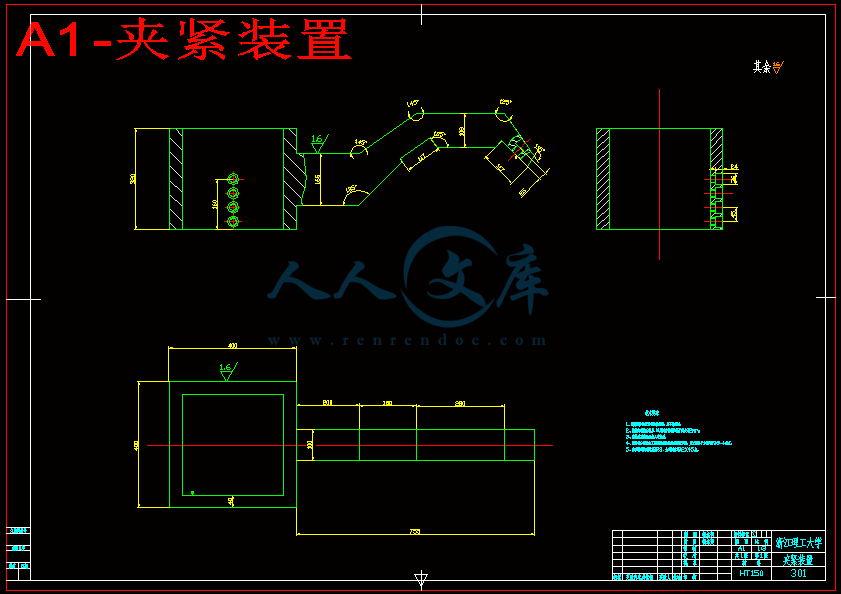
4.2夹紧系统装配图 29
4.3气缸推动和翻转系统装配图 30
4.4 气缸推动夹紧装置系统装配图 30
第5章 总结与展望 32
5.1总结 32
5.2展望 32
参考文献 33
致 谢 35
第1章 绪论
1.1 引言
近20年来,气动技术的应用领域迅速拓宽,尤其是在各种自动化生产线上得到广泛应用。电气可编程控制技术与气动技术相结合, 使整个系统自动化程度更高, 控制方式更灵活, 性能更加可靠; 气动机械手、柔性自动生产线的迅速发展, 对气动技术提出了更多更高的要求;由于气动脉宽调制技术具有结构简单、抗污染能力强和成本低廉等特点, 国内外都在大力研发气动机械手。
1.2气动机械手的发展
1.2.1国外气动机械手状况
从各国的行业统计资料来看, 近30多年来, 气动行业发展很快。20世纪70年代, 液压与气动元件的产值比约为9:1, 而30多年后的今天, 在工业技术发达的欧美、日本等国家, 该比例已达到6:4, 甚至接近5:5。
90年代初,有布鲁塞尔皇家军事学院Y.Bando教授领导的综合技术部开发研制的电子气动机器人--"阿基里斯"六脚勘测员,也被称为FESTO的"六足动物"[12]。Y.Bando教授采用了世界上著名的德国FESTO生产的气动元件、可编程控制器和传感器等,创造了一个在荷马史诗中最健壮最勇敢的希腊英雄--阿基里斯。它能在人不易进入的危险区域、污染或放射性的环境中进行地形侦察。六脚电子气动机器人的上方安装了一个照相机来探视障碍物,能安全的绕过它,并在行走过程中记录和收集数据。六脚电子气动机器人行走的所有程序由FPC101-B可编程控制器控制,FPC101-B能在六个不同方向控制机器人的运动,最大行走速度0.1m/s。通常如果有三个脚与地面接触,机器人便能以一种平稳的姿态行走,六脚中的每一个脚都有三个自由度,一个直线气缸把脚提起、放下,一个摆动马达控制脚伸展、退回,另一个摆动马达则负责围绕脚的轴心作旋转运动。每个气缸都装备了调节速度用的单向节流阀,使机械驱动部件在运动时保持平稳,即在无级调速状态下工作。控制气缸的阀内置在机器人体内,由FPC101-B可编程控制器控制。当接通电源时,气动阀被切换到工作状态位置,当关闭电源时,他们便回到初始位置。此外,操作者能在任何一点
上停止机器人的运动,如果机器人的传感器在它的有效范围内检测到障碍物,机器人也会自动停止。
由汉诺威大学材料科学研究院设计的气动攀墙机器人,它能在两个相互垂直的表面上行走(包括从地面到墙面或者从墙面到天花板上)。该机器人轴心的圆周边上装备着等距离(根据步距设置)的吸盘和气缸,一组吸盘吸力与另一组吸盘吸力的交替交换,类似脚踏似的运动方式,使机器人产生旋转步进运动。这种攀墙式机器人可被用于工具搬运或执行多种操作,如在核能发电站、高层建筑物气动机械手位置伺服控制系统的研究或船舶上进行清扫、检验和安装工作。机器人用遥控方式进行半自动操作,操作者只需输入运行的目标距离,然后计算机便能自动计算出必要的单步运行。操作者可对机器人进行监控。
国外的设计人员对于机械手的设计理念已经非常成熟。Wright等人分析比较了机械手与人手抓取系统,并把机械手分成与机器人手臂和控制系统相兼容、安全抓取和握持对象、准确的完成复杂性任务三种类别。许多工厂的机械手的例子和机械手设计指导方针也被描述进去了。Pham等人总结了机械手在不同应用环境下设计方案应该如何选择。在他们的研究中,影响机械手如何选择的变量如下:(a)成分,(b)任务,(c)环境,(d)机械臂和控制条件。“成分”这个变量包括几何、形状、重量、表面质量和温度,这些因素都需要考虑好。对于可重构系统,他们以形状和大小为标准又把这个变量分成了其他家族。对于“任务”这个变量,除了机械手的类型、不同组成部分的数量、准确性及周期需要考虑外,还有主要的操作处理如抓取、握持、移动和放置都要考虑。在合适的地方设计核实的机械手,必须考虑所有的因素,而且验证性的测试必须要多做。为了减少疲劳效应,pham等人开发了一个用于选择机械手的专家系统。瑞典EIET ROIUX 公司于最近创造一种新产品一一气动机械手。这种机械手以压缩空气为动力, 小巧灵便,它装在一个圆形竖柱上, 该圆柱又能上下移动0 至150 mm , 左右移动350mm,机械手的最高速度为1000m/s,定位精度为500m/s;两个机械手各能举起5kg重物。
1.2.2国内气动机械手情况
我国改革开放以来,气动行业发展很快。1986年至2003年间,气动元件产值的年第增率达24.2,高于中国机械工业产值平均年递增率10的水平。虽然市场和应用发展迅速,但是我国的气动技术与欧美、日本等国相比,还存在着相当大的差距。我国在气动技术的研究与开发的方面,缺乏先进的仪器与设备,研究开发手段落后,技术力量差,每年问世的新产品数量极其有限。在许多开发与研究领域还是空白,因此必须跟踪国外气动技术的最新发展动向,以减小差距,提高我国气动技术的水平。
1.3发展趋势
1.3.1重复高精度
精度是指机器人、机械手到达指定点的精确程度, 它与驱动器的分辨率以及反馈装置有关。重复精度是指如果动作重复多次, 机械手到达同样位置的精确程度重复精度比精度更重要, 如果一个机器人定位不够精确, 通常会显示一个固定的误差, 这个误差是可以预测的, 因此可以通过编程予以校正。重复精度限定的是一个随机误差的范围, 它通过一定次数地重复运行机器人来测定。随着微电子技术和现代控制技术的发展, 以及气动伺服技术走出实验室和气动伺服定位系统的成套化。气动机械手的重复精度将越来越高, 它的应用领域也将更广阔, 如核工业和军事工业等。
1.3.2模块化
有的公司把带有系列导向驱动装置的气动机械手称为简单的传输技术, 而把模块化拼装的气动机械手称为现代传输技术。模块化拼装的气动机械手比组合导向驱动装置更具灵活的安装体系。它集成电接口和带电缆及气管的导向系统装置, 使机械手运动自如。由于模块化气动机械手的驱动部件采用了特殊设计的滚珠轴承, 使它具有高刚性、高强度及精确的导向精度。优良的定位精度也是新一代气动机械手的一个重要特点。模块化气动机械手使同一机械手可能由于应用不同的模块而具有不同的功能, 扩大了机械手的应用范围, 是气动机械手的一个重要的发展方向。智能阀岛的出现对提高模块化气动机械手和气动机器人的性能起到了十分重要的支持作用。因为智能阀岛本来就是模块化的设备, 特别是紧凑型CP 阀岛, 它对分散上的集中控制起了十分重要的作用, 特别对机械手中的移动模块。
1.3.3无给油化
为了适应食品、医药、生物工程、电子、纺织、精密仪器等行业的无污染要求, 不加润滑脂的不供油润滑元件已经问世。随着材料技术的进步, 新型材料(如烧结金属石墨材料) 的出现, 构造特殊、用自润滑材料制造的无润滑元件, 不仅节省润滑油、不污染环境, 而且系统简单、摩擦性能稳定、成本低、寿命长。
1.3.4 机电气一体化
由“可编程序控制器-传感器-气动元件”组成的典型的控制系统仍然是自动化技术的重要方面;发展与电子技术相结合的自适应控制气动元件, 使气动技术从“开关控制” 进入到高精度的“ 反馈控制”; 省配线的复合集成系统, 不仅减少配线、配管和元件, 而且拆装简单, 大大提高了系统的可靠性。
而今, 电磁阀的线圈功率越来越小, 而PLC 的输出功率在增大, 由PLC直接控制线圈变得越来越可能。气动机械手、气动控制越来越离不开PLC, 而阀岛技术的发展, 又使PLC 在气动机械手、气动控制中变得更加得心应手。
1.4 机械手夹持部件结构示意图
1.4.1 外夹持型机械手
图1-2为一种较简单平行开闭手爪的结构。气缸的活塞有压缩空气驱动,通过活塞杆7上的支点轴2带动拨叉3转动,再通过传动轴4使手爪1沿导向槽做平行移动,图中为双作用气缸,也可为单作用气缸返回运动靠弹簧完成。该结构的特点是重量轻,体积小,最小型重量为75g,最大型为300g,因此,可以与小型机械手配套使用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号