摘 要
塑料注射模具是成型塑料的一种重要工艺装备,通过对液压管路三通塑料模具设计,能够全面的了解塑料模具设计的基本原则、方法.并能较为熟练的使用Proe4.0、AUTOCAD软件进行塑料模具设计,提高自己的绘图能力。为今后从事设计工作打下了坚实的基础。
随着现代工业发展的需要,塑料制品在工业、农业、日常生活和军事等各个领域的应用范围越来越广,质量要求也越来越高,中国已经成为全球最大的塑料市场之一,塑料制品产量全球第二。为了做到高质、高效、低成本,从而提高市场占有率,注塑模具的开发、设计、加工与CAD/CAE/CAM技术相结合具有重大意义。
本次主要设计是对液压管路三通注射模的设计, 重点对塑件的成型原理、原料选用和注射技术进行分析。通过根据形状、尺寸、精度及表面质量要求的分析结果,确定所需的模塑成型方案,制品的后加工、分型面的选择、型腔的数目和排列、成型零件的结构、浇注系统等。
关键词:注塑模;模具结构;侧型芯;工艺方案
Abstract
Plastic injection mold is an important technological equipment of plastic forming, based on the hydraulic piping tee plastic mold design, can fully understand the basic principles, methods of plastic mold design. And can be used more skilled Proe4.0, AUTOCAD software for plastic mold design, improve their ability to draw. Engaged in the design for the future work laid a solid foundation.
With the needs of the development of modern industry, plastic products in industry, agriculture, military and other fields of daily life and the application scope is more and more wide, the quality requirements also more and more high, China has become one of the world's largest plastics market, plastic products production in the world's second. In order to achieve high quality, high efficiency, low cost, and improve the market share, injection mold development, design, processing combined with CAD/CAE/CAM technology is of great significance.
The main design is the design of injection mold hydraulic piping tee, focus on the forming principle of plastic parts, raw materials selection and injection technology were analyzed. By according to the shape, size, precision and surface quality requirement analysis, to determine the required molding solutions, products after processing, the choice of the parting surface, cavity number and arrangement, the structure of molding parts, pouring system, etc.
Key words: injection mold; The mold structure; The side core; The processing plan
目 录
前言 1
1 研究概况 1
1.1国外研究现状.........................................................................................................1
1.2国内研究现状.........................................................................................................1
2 塑件制品分析 2
2.1 明确制品设计要求 2
2.2 明确制品批量 3
2.3 材料选择及性能 3
2.3.1 材料选择 3
2.4 成型设备 4
2.5 拔模斜度 4
2.6 计算制品的体积和质量 5
2.6.1表面质量的分析 5
2.6.2塑件的体积重量 5
3 注射机及成型方案的确定 6
3.1 注射机的确定 6
3.2 成型方案的确定 6
3.2.1 成型设备的选择 6
3.2.2成型的特点 7
3.2.3成型的原理 7
3.2.4成型过程 7
4 型腔数的确定及分型面的选择 9
4.1 型腔数的确定 9
4.2 分型面的选择 10
4.2.1 分型面的主要选择原则 10
4.3 确定型腔的排列方式 11
4.4 标准模架的选用 11
5 成型零部件的设计与计算 13
5.1 凸模设计 13
5.2 凹模的设计 13
5.3 成型零件工作尺寸的计算 14
5.3.1 模腔工作尺寸的计算 14
6 浇注系统的设计 13
6.1 主流道设计 16
6.2分主流道的设计 16
6.3 浇口的设计 17
6.4 平衡进料 17
6.5冷料穴设计 18
7 排气与冷却系统的设计 13
7.1 冷却系统设计的原则 18
7.2 冷却水路的计算 19
7.3 排气系统的设计 20
8 顶出与抽芯机构的设计 20
8.1 推杆复位装置 20
8.2 抽芯机构的选择 21
8.3 抽芯距的计算 21
8.4斜导柱抽芯的设计 21
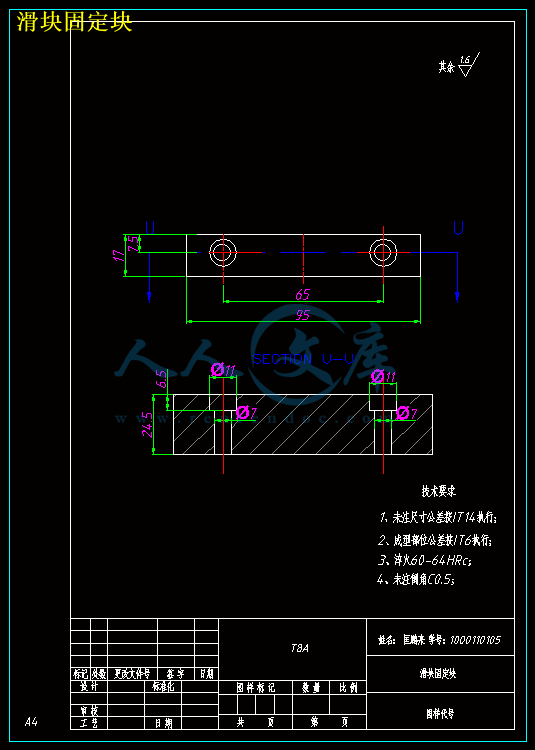
8.5滑块的设计 23
8.5侧向分型与抽芯机构三维效果图如下所示: 23
9 导向机构的设计 24
9.1 导向、定位机构的主要功能 24
9.2导向机构的设计 24
9.2.1 导柱的设计 24
10 注塑机与模具各参数的校核 25
10.1 工艺参数的校核 25
10.2 模具安装尺寸的校核 26
10.2.1 喷嘴的校核 26
10.2.2 定位圈尺寸的校核 26
10.2.3 模具外形尺寸的校核 26
10.2.4 模具厚度的校核 26
10.2.5 安装参数的校核 26
10.3 开模行程的校核 27
11 模具安装和试模 27
12 主要成型零件加工工艺 28
13 结论……………………………………………………………… 30
谢 辞 32
参考文献 33
前言
注射成型也称为注射或注塑,是热塑性塑料的一种重要成型方法。到现在为止,有超过1/3的塑料原材料,是通过注射成型工业加工的,除氟塑料外,几乎所有的热塑性塑料都可以采用此成型方法。它的特点是生产周期短、生产效率高的、易自动化,因此广泛应用于塑料制品的生产。现在塑料成型生产中,塑料制件的质量与塑料成型模具、塑料成型设备和塑料成型工艺密切相关。在这三要素中,塑料成型模具的质量最为关键,他的功能是双重的:赋予塑料熔体以期望的形状、性能、质量;冷却并推出成型的塑件。模具是决定最终产品的性能、规格、形状以及尺寸精度的载体,塑料成型模具是使塑料成型生产过程顺利进行、保证塑料成型质量不可缺少的工艺装备,是体现塑料成型设备高效率、高性能和合理先进塑料成型工艺的具体实施者,也是新产品开发的决定环节。由此可见,周而复始地获得符合技术经济要求及质量稳定的塑料制件,塑料成型模具的优劣是关键,它最能反映出整个塑料成型生产过程的技术含量以及经济效益。因此,注射成型的模具设计制造成为当今社会模具发展的热点,己发展成为热塑性塑料最主要的成型加工方法。
















 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号