摘 要
我国塑料模具工业从起步到现在,经历了半个世纪,有了很大发展,模具水平有了较大的提高。由于模具生产产品具有精度高,复杂性高,一致性好,生产效率高消耗低等优点。所以现代工业中将会起到更大的作用,得到更多的应用。我的塑料发展至今,已能生产精度高达2微米的精密,多工位级进模,工位数最多已达160个,寿命1~2亿次。
模具时现代工业发展的基础,许多产业的发展都离不开模具行业的支持。用模具生产制造所表现出来的的高精度,高复杂程度,高一致性,高生产率和低消耗,是其他加工制造方法所不能比拟的。在模具工业的总产值中塑料模具约占33%。不同的塑料成型方法使得模具原理和结构不通。按照成型方法的不通,塑料模具分为:注塑模具,压塑模具,吹塑模具等。注塑模具主要用于热塑性塑料制品的成型中占有很大比重。现代工业中,消费品外壳的色彩,手感,和精度,厚度等提出了新要求。塑料外壳设计成为重要的一环。设计合理的注塑模具将得到越来越多的应用。
现代注塑模具的设计方法目前为了应付当前多样化的要求,缩短产品只在周期以缺德最佳的竞争优势,模具设计中都引用了CAD/CAE计算机一体化制造技术,以提高产品质量,降低成本,增加竞争力,一般而言,一件完整理想的工业产品,其制造流程为现有原创型的概念设计出原件,配合计算机辅助工程分析技术,再依据分析结果修改测试,最后再依据设计图经由计算机辅助制造,进行产品自动化生产在模具设计生产,以上整个过程均在计算机上进行。
在模具设计生产过程中,应用Pro/ENGINEER软件进行模具结构设计-模具型腔-型芯二维设计-工艺准备-模具型腔,型芯设计三维造型等。
随着计算机技术和网络技术取得了突破性的成就,模具设计越来越多地使用CAD/CAM技术。在产品生产之前,使用这些新技术来进行模具的设计和改善,是现代设计必然趋势在现实生活里,手机已经成为人们的一个生活必须品,现代的手机已经不再仅仅是一个工具同时一时装饰品,所以做出的不管是手机机身还是手机壳都需要美观大方,因此加工工艺就显得非常重要。所以在对手机壳的模具设计时不仅要考虑成型,还需要考虑成型后的美观。因此在模具的设计过程中多方兼顾。
关键字:手机;模具设计;注射模;斜导柱;侧抽芯。
Abstract
Plastic mold industry in China from the beginning to now, has experienced half a century, has made great development, mould level has greatly improved. Because the mold production product has high accuracy, high complexity, good consistency and high efficiency low consumption etc. So modern industry will play a greater role, get more applications. Precision plastic development up to now, I have been able to produce as much as 2 micron precision, multi-station progressive die, has reached the maximum number of stations in 160, life 1 ~ 200 million times.
Mould the basis for the development of modern industry, many industry's development cannot leave the mould industry support. With mold manufacturing of high precision, high complexity, high consistency, high productivity and low consumption, is can't be matched by other methods of processing and manufacturing. In the mold industry plastic mould accounted for about 33% of the total output. Different methods of plastic molding makes mold principle and structure. According to the forming method of impassability, plastic mold is divided into: injection mold, compression mold, blow molding mould, etc. In the injection mold is mainly used for thermoplastic plastics molding occupies a large proportion. In modern manufacturing, consumer goods shell color, feel, and precision, thickness, etc. Put forward new requirements. Plastic shell design become important one annulus. Reasonable design of injection mould will be applied more and more.
Modern design method of injection mould at present in order to cope with the current diversified requirements, shorten the product by the wicked the best competitive advantage, only in the cycle of mould design reference the CAD/CAE technology of computer integrated manufacturing, in order to improve the product quality, reduce cost, increase the competitiveness, in general, a complete ideal industrial products, the concept of the manufacturing process for existing original type original design, with computer aided engineering analysis techniques, according to the results of analysis, modifying test again, and then on the basis of design through computer aided manufacturing, automated production in the mold design production, more than the whole process are conducted on the computer.
In the mold design and production process, the application of Pro/ENGINEER software to design the mould structure - the mold - core of two-dimensional design process to prepare - mold cavity, core design three dimensional modeling, etc.
Along with the computer technology and network technology has achieved breakthrough and mold design are increasingly using CAD/CAM technology. Before production, the use of these new technologies for the design of the mould and improvement, is an inevitable trend in the modern design in real life, mobile phones have become a people living necessities, modern mobile phone is no longer just a tool for decoration at the same time, so the mobile body or following needs to be beautiful and easy, so the processing technology is very important. So when opponents casing mold design should not only consider the forming, also need to consider after molding. Therefore, in the mold design process to two or morethings.
Key words:Cell phones, mold design, injection mould, inclined guide pillar, side core-pulling
目录
引言 1
第一章 塑件分析 2
1.1 材料的分析 2
1.2 塑件相关参数的设计 2
1.2.1 注射温度的影响 2
1.3 塑件原料的分析 3
1.3.1 PC塑料的干燥 3
1.3.2注射温度 3
1.3.3注射压力 3
1.3.4注射速度 3
1.3.5模具温度 4
1.4 体积及质量计算 4
1.4.1 体积的计算 4
1.4.2 质量及面积的计算 4
第二章 型腔数目的确定 6
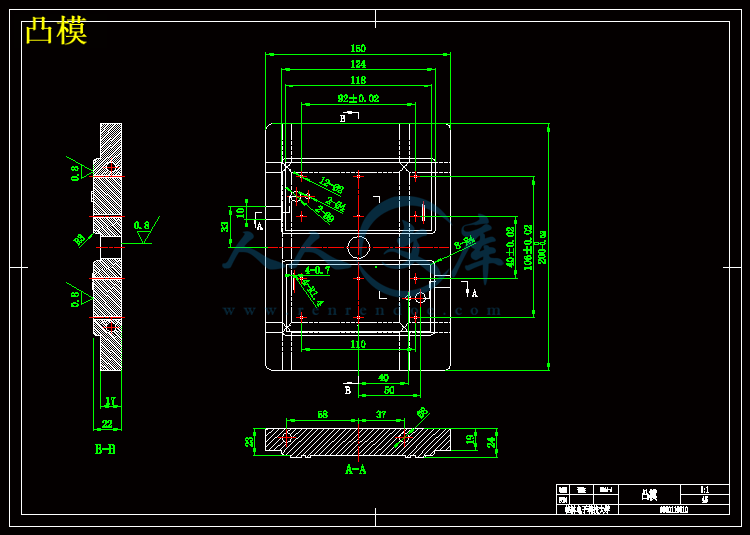
第三章 成型零部件的设计 7
3.1 型腔尺寸的计算 7
3.2 型芯尺寸的计算 7
第四章 注射机的选择 9
第五章 注射机的校核 10
5.1注射机注射容量校核 10
5.2注射机锁模力校核 10
5.3注射机注射压力校核 10
5.4注射机模具厚度校核 11
5.5注射机最大开模行程校核 11
第六章 分型面的选择 13
6.1 分形面的形式 13
6.2 分型面的选择 13
第七章 浇注系统的设计 15
7.1 分流道的设计原则 15
7.2 分流道的设计 16
7.3 分流道的尺寸的设计 17
第八章 浇口的设计 18
8.1浇口位置选择的仿真 19
8.2 直接浇口的直径设计 19
8.3 点浇口直径设计 20
第九章 冷却系统的设计 21
9.1 冷却系统设计原则 21
9.2 冷却系统的结构形式 21
9.3 冷却系统的计算 21
9.4冷却时间计算 22
9.5 用水量M的计算 23
9.6 成型周期计算 23
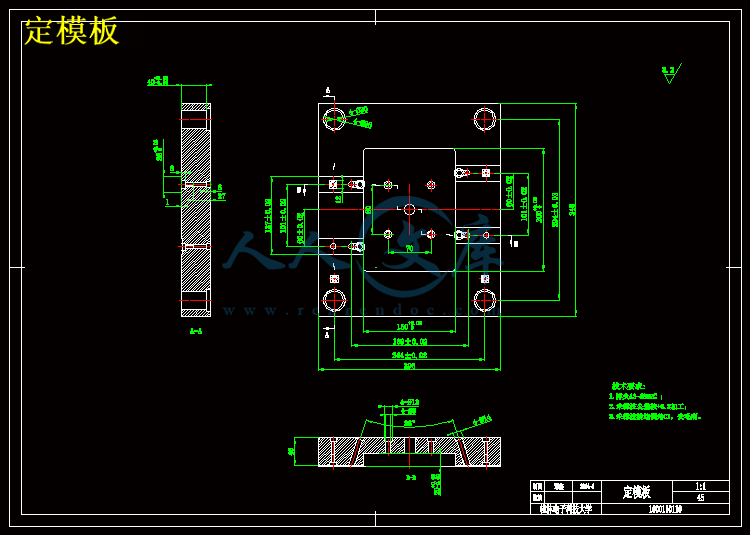
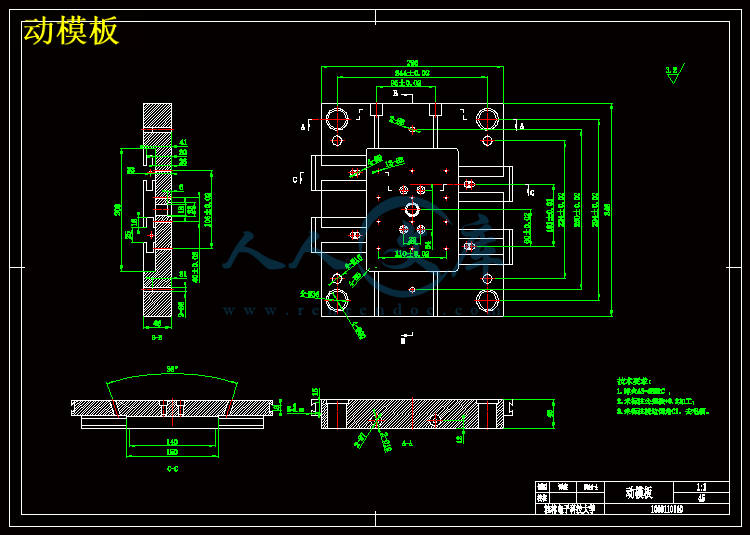
第十章 模具材料选择 25
第十一章 模具主要参数的计算 26
11.1 脱模力的计算 26
11.2 初始脱模力 26
11.3 推杆直径计算 27
11.4 推杆的应力校核 27
11.5 推板的厚度计算 28
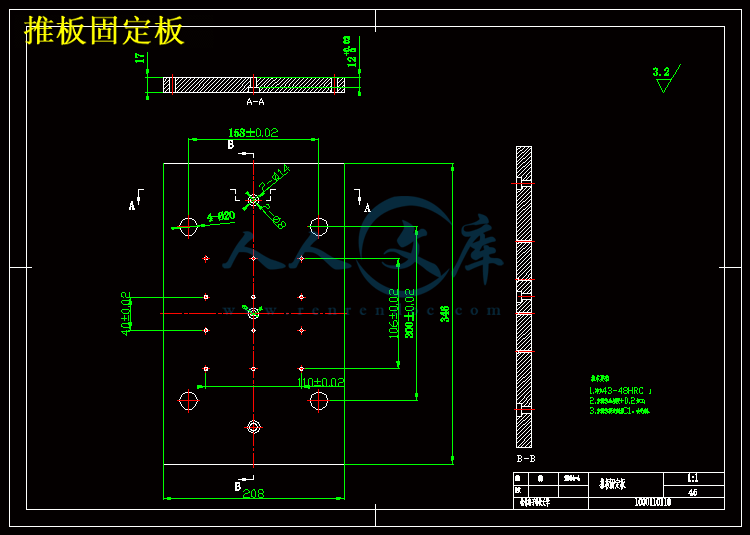
第十二章 推出脱模机构设计 29
12.1 推出机构的选用原则 29
12.2 推杆的形式 29
12.3 推杆材料 30
12.4 推杆的复位 30
12.5 推出力的计算 30
12.6 型腔壁厚和底板厚度计算 31
12.6.1侧壁厚度计算 32
12.6.2矩形型腔底板厚度计算 32
第十三章 结构零部件设计 33
13.1 合模导向机构的设计 33
13.1.1设计导柱需要注意的事项 33
13.2 导向机构的设计 33
13.3 定位圈的设计 34
13.4 侧向分型与抽芯机构的设计 34
13.5 斜导柱的设计 36
13.6 滑块的设计 37
13.7 楔紧块的设计 37
第十四章 模架的选择 38
14.1模架厚度H和注射机的闭合距离L 38
14.2所需行程之间的尺寸关系 38
第十五章 排气系统的设计 40
第十六章 成型零件加工工艺规程 41
谢辞 42
参考文献 43
附录 44
引言
随着我国制造业的迅速发展,一些新兴产业业取得了长足的进步。模具是工业生产的基础工艺装备,在机械、电子、汽车、航空以及通信等领域有着广泛的应用。随着人民生活水平的不断提高,日常生活中使用的物品越来越多地用到了模具。目前,模具生产水平的高低已经成为衡量一个国家制造水平高低的重要标志。
当前,计算机技术和网络技术取得了突破性的成就,CAD/CAM技术、数控加工技术以及快速成型技术为模具技术的发展提供了强大的技术支持。同时,以高分子塑料为主的模具材料不断被开放出来,这些材料种类繁多,性能优良,价格低廉,这更为模具产业的发展提供了有力的帮助。
本设计主要是为让读者们能够清楚地了解到塑料注射模的设计过程,能够对模具设计过程中所使用的各种基本工具,例如Pro/ENGINEER,Moldflow Plastics Insight等等,具有一个基本的了解。从零件的尺寸确定,模具设计,模架设计,到最后的注塑仿真,向读者们展示手机塑料模具的整个设计过程。
随着Pro/ENGINEER的不断完善,借助于Pro/ENGINEER设计软件,我们可以比较轻松地完成一些复杂的设计工作,同时也可以全面地提高设计效率和设计质量。






 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号