摘 要
本文介绍了采煤机的发展历史、组成及工作原理,在分析煤炭工业及煤炭工业的行业背景的基础上,展望了采煤机的发展趋势,并针对采煤机的发展现状,进行了 MG200/487 型采煤机的截割部设计。
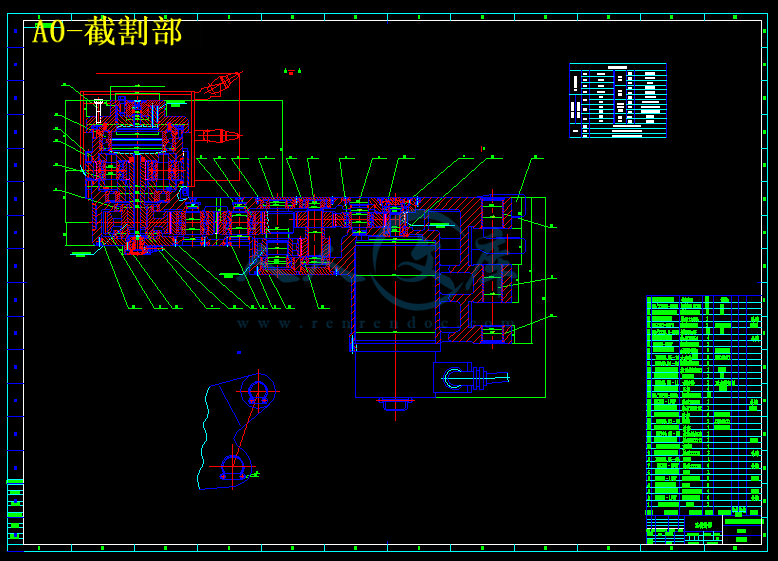
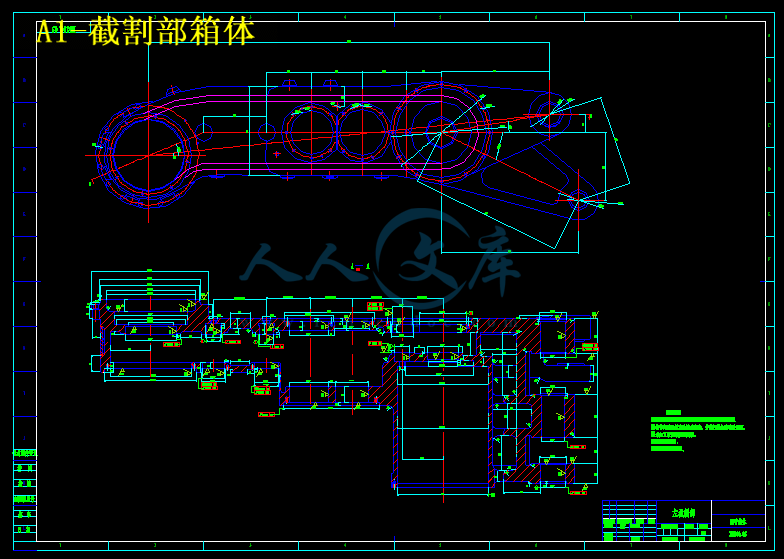
本文首先确定了设计方案和选择了基本部件并开展了传动系统的可靠性分析,MG200/487型采煤机截割部主要是由一个减速箱和四级齿轮传动组成,截割部电机放在摇臂内横向布置,电动机输出的动力经由三级直齿圆拄齿轮和行星轮系的传动,最后驱动滚筒旋转。并对所设计的齿轮和花键进行了公差分析,同时介绍了截割部的安装、维护和故障处理。本采煤机截割部具有较高的可靠性和安全维修性。
关键词:滚筒式采煤机; 截割部; 行星齿轮传动
ABSTRACT
This paper presents the development history, the composition and the principle of shearers in brief. On the foundation of analyzing the trade background of coal industry and mining equipment, look ahead the development of shearers, and according to the present development situation of shearers, we carried out the design of MG200/487-WD Shearer’s cutting unit.
This design firstly fixed on design scheme and selected basic components, and besides, developed the reliability analysis of transmission system. The design of MG200/487-WD Shearer’s cutting unit. It is made up of a gearbox and moderate breeze gear wheel transmission that the MG200/487-WD type mining machine cuts the cutting department, Cut the electrical machinery of cutting department and put to fix up horizontally in the rocker arm, The power that the motor outputs leans on a round of transmission of department of gear wheel and planet round via the tertiary straight tooth, Urge the cylinder to rotate finally. And gears and involute splines’ tolerances of geometrical quantity were analyzed. At the same time, introduced the installation, maintenance and fault disposal of this cutting unit. The cutting unit of MG200/487-WD Shearer has reliability and installation maintainability.
Keywords: shearer; the cutting unit; planetary gear drive
目 录
1 概述 1
1.1引言 1
1.2我国采煤机30多年的发展进程 1
1.2.1 20世纪70年代是我国综合机械化采煤起步阶段 1
1.2.2 20世纪80年代是我国采煤机发展的兴旺时期 2
1.2.3 20世纪90年代至今是我国电牵引采煤机发展的时代 3
1.2.4 国际上电牵引采煤机的技术发展状况 4
1.3 国内电牵引采煤机的发展状况 6
1.4 结构特征与工作原理 7
1.4.1 摇臂 7
1.4.2 截割电动机 8
1.4.3 牵引部 9
2 总体方案的确定 12
2.1主要技术参数如下: 12
2.2传动方案的确定 14
2.2.1 传动比的确定 14
2.2.2传动比的分配 14
3传动系统的设计 15
3.1各级传动转速、功率、转矩的确定 16
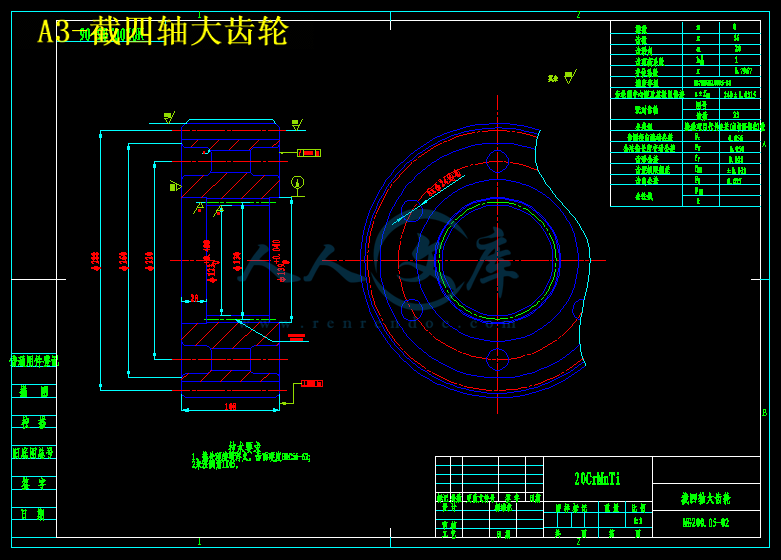
3.2齿轮设计及强度效核 17
3.3截割部行星机构的设计计算 24
3.3.1齿轮材料热处理工艺及制造工艺的选定 25
3.3.2确定各主要参数 25
3.3.3几何尺寸计算 28
3.3.4.啮合要素验算 30
3.3.5齿轮强度验算 31
3.4 轴的设计及强度效核 42
3.4.1选择轴的材料 42
3.4.2轴径的初步估算 42
3.4.3求作用在齿轮上的力 42
3.4.4轴的强度效核: 43
3.4.5安全系数效核计算 46
3.5 轴承的寿命校核 48
3.5.1对截Ⅲ轴的轴承22219c和Nj419进行寿命计算 48
3.5.2行星轮轴承寿命的计算 49
3.6 花键的强度校核 50
3.6.1截Ⅳ轴花键校核 50
3.6.2行星轮系花键校核 50
4 采煤机的使用和维护 50
4.1润滑及注油 51
4.2地面检查与试运转 51
4.2.1试运转前的检查: 51
4.2.2试运转时检查: 51
4.3下井及井下组装 52
4.4采煤机的井下操作 52
4.4.1操作前的检查: 52
4.4.2试运转中注意事项: 52
4.5机器的维护与检修 53
4.6采煤机轴承的维护及漏油的防治 54
4.7 硬齿面齿轮的疲劳失效及对策 56
4.8煤矿机械传动齿轮失效的改进途径 59
4.8.1设计 59
4.8.2 选材 60
4.8.3 加工工艺 60
4.8.4 热处理 61
4.8.5 表面强化处理 61
4.8.6 正确安装运行 61
4.8.7 润滑 62
5总结 63
参考文献 64
英文原文 65
中文译文 72
致 谢 77
1 概述
1.1引言
采煤机械的装备水平是煤矿技术水平的重要标志之一。采煤机械的选用取决于煤层的赋存条件、采煤方法和采煤工艺,而采煤机械的技术发展又促进了采煤方法和采煤工艺的更新。
采煤方法按采煤工艺可分为长壁式采煤法和房柱式采煤法两大类。我们广泛使用长壁式采煤法。
长壁式采煤法所使用的机械设备按机械化程度分为爆破采煤机械、普通机械化采煤机械和综合机械化采煤机械三类。
炮采工作面的机电设备较少,主要靠人力完成各项工序。破煤工序有直接打眼放炮和先掏槽后打眼放炮两种,装煤工序主要依靠人工攉煤,运煤工序依靠工作面刮板输送机来完成。
普通机械化采煤机工作面用采煤机或刨煤机和工作面刮板输送机实现破煤、装煤和运煤工序的机械化,用单体支护设备实现人工控制顶板。
综合机械化采煤工作面将各种相对独立的机电设备合理的组合在一起,在工艺过程中协调工作,使采煤工作面的破、装、运、支全部工序实现机械化。
1.2我国采煤机30多年的发展进程
1.2.1 20世纪70年代是我国综合机械化采煤起步阶段
20世纪70年代初期,煤炭科学研究总院上海分院集中主要科技骨干,研制出综采面配套的MD-150型双滚筒采煤机,另一方面改进普采配套的DY100型、DY150型单滚筒采煤机;70年代中后期,制造出MLS3-170型双滚筒采煤机。20世纪70年代我国采煤机的发展有以下特点:
1.装机功率小
例如,MLS3-170型双滚筒采煤机,装机功率170KW;KD-150型双滚筒采煤机,装机功率150KW;DY-100和DY-150型单滚筒采煤机,装机功率100KW和150KW。
2.有链牵引,输出牵引力小
此时期的采煤机牵引方式都是圆环链轮与牵引链轮啮合传动,传递牵引力小,牵引力在200KN以下。
3.牵引速度低
由于受液压元部件可靠性的限制,设计的牵引力功率较小,牵引速度一般不超过6m /min 。
4.自开切口差
由于双滚筒采煤机摇臂短,又都是有链牵引,很难割透两端头,且容易留下三角煤,故需要人工清理,单滚筒采煤机更是如此.
5.工作可靠性较差
我国基础工业比较薄弱,元部件质量较差,反映在采煤机的寿命普遍较低,特别是液压元部件的损坏比较严重。




 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号