摘要
柔性制造系统(FMS)是一种形式的柔性自动化,把若干个机床联系在一起的一个材料处理系统,该系统的所有方面的控制都有一个中央电脑完成。这一系统减少了安装或转换时间和便利的生产小数目的产品。 转移的重点是从大规模生产的少数产品转化为车间作业的环境中定制订单产品。The shift in emphasis is from mass production of a few products to a job-shop environment in which customized orders are manufactured. Automation allows for better quality and scheduling, rapid changes in product lines, and lower inventories and costs .自动化设计具备更好的质量和调度能力,使生产线可以快速变化,降低了库存和成本。
柔性制造系统具有灵活性的特点,他们的装置控制器和中央控制计算机可以复制出新的零件或改造旧零件。 They can also often make a number of different types of parts at the same time.他们也可以在同一时间内作出多项不同类型的零件。 然而,这种灵活性是有局限性的,以车轴为例, However, this flexibility is limited to a certain family of parts, for example, axles.A general goal for designers is to increase flexibility, and advanced flexible manufacturing systems are more flexible than the earlier ones.总体目标是增加灵活性,因此柔性制造系统相较于从前的制造系统更具有灵活性。
总体来说,柔性制造系统具备以下优势:更大的劳动生产率:只需要具有专门的教育和技能的较少的工人。更大的机械效率:产品的生产需要较少的及其楼面面积和空间。质量的提高:由于上线测试,使之能即时反馈信息和调整制造过程。增加了系统的可靠性:智能化,自诊断控制,为确定硬件问题减少了时间。减少了部分库存:柔性制造系统的一个主要特点就是柔性制造能力,在经济上容纳不同的一批大小、甚至下降至运行一个单一的部分。改进调度能力:容许这些快速反应的变化,在产品设计和生产调度,有能力,以符合刚刚在时间调度,并减少前置作业时间。 适应性的CAD\CAM行动:数码规格开发的电脑辅助设计/电脑辅助制造系统可以作为投入的过程。
作为一个柔性制造系统,必须具备的关键要素有:计算机控制,自动化材料处理能力,工具处理能力。柔性制造整合了自动化制造的概念:计算机数值控制个别机床,分布式数字控制的制造系统,自动化物料处理系统,成组技术。当这些自动化流程,机器和观念聚集在一个集成的系统,就是所谓的柔性制造系统。在柔性制造系统中,人类和计算机发挥主要作用。
关键字:柔性制造系统;灵活性;柔性制造能力;计算机控制
1.
Abstract
A flexible manufacturing system (FMS) is a form of flexible automation in which several machine tools are linked together by a material-handling system, and all aspects of the system are controlled by a central computer.
Flexible manufacturing systems are flexible in the sense that their device controllers and central control computer can be reprogrammed to make new parts or old parts in new ways. They can also often make a number of different types of parts at the same time. However, this flexibility is limited to a certain family of parts, for example, axles. A general goal for designers is to increase flexibility, and advanced flexible manufacturing systems are more flexible than the earlier ones.This system reduces setup or changeover times and facilitates the production of differentiated products in small numbers. The shift in emphasis is from mass production of a few products to a job-shop environment in which customized orders are manufactured. Automation allows for better quality and scheduling, rapid changes in product lines, and lower inventories and costs.
Greater labor productivity. Fewer workers requiring specialized education and skills. Greater machine efficiency. Fewer machines, less floor space and less space for operator movement. Improved quality. Less waste because on-line gauging allows immediate feedback and adjustment of the manufacturing process. Increased system reliability. Intelligent, self-diagnosing controls decrease the time required to identify and correct hardware problems. Reduced parts inventories. A key feature of flexible manufacturing is its ability to economically accommodate different batch sizes - even down to a run of a single part. Improved scheduling capabilities. These allow rapid response to changes in product design and production scheduling, the ability to conform to just-in-time scheduling, and reduced lead times. Adaptability to CAD/CAM operations. The digital specifications developed by Computer Aided Design/Computer Aided Manufacturing systems can serve as inputs to the process.
The key elements necessary for a manufacturing system to qualify as an FMS are as follows:Computer controlautomated materials handling capabilityTool handling capabilityFlexible manufacturing integrates several automated manufacturing concepts:Computer numerical control (CNC) of individual machine toolsDistributed numerical control (DNC) of manufacturing systemsautomated materials handling systemsGroup technology (families of parts).When these automated processes, machines, and concepts are brought together in one integrated system, an FMS is the result. Humans and computers play major roles in an FMS.
Keywords: flexible manufacturing system, flexible, flexible manufacturing ability, Computer controlautomated materials
目录
摘要 (中文)……………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅰ
(英文)……………………………………………………………………………………………..Ⅱ
第一章 概述.........................................................................................................1
1.1 柔性制造系统以及起重机…………………………………………………………………....1
1.2 研究内容…………………………………………………………………………………………5
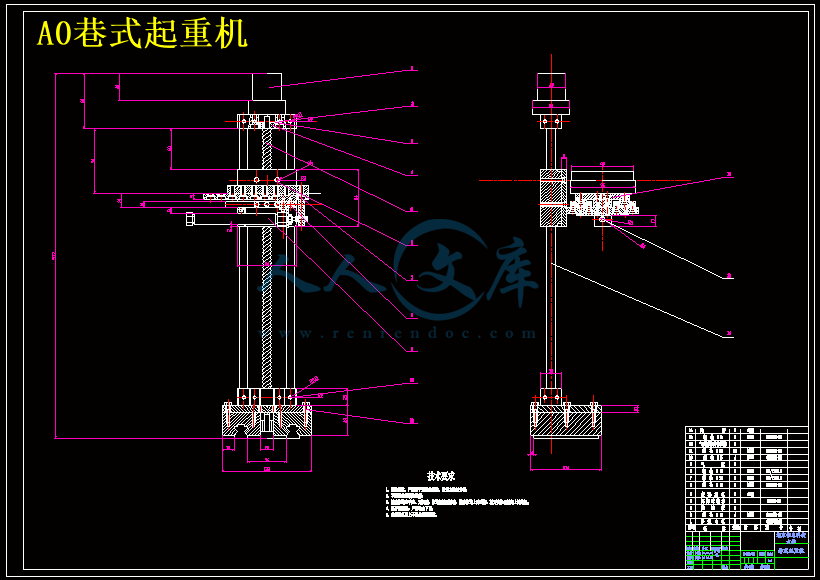
第二章 巷式起重机的结构设计.........................................................................8
2.1 步进电机的选择............................................................................................8
2.2 气动机构的选择...........................................................................................14
2.3 主轴轴承的配置...........................................................................................20
第三章 导轨的结构设计.....................................................................................24
3.1 导轨的作用和设计要求.................................................................................24
3.2 导轨设计的主要内容.....................................................................................24
3.3 导轨的结构设计............................................................................................24
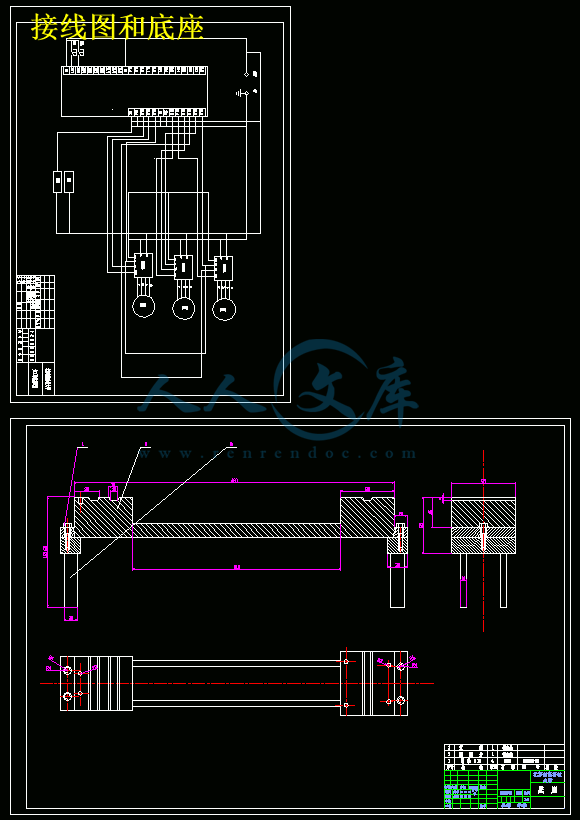
第四章 PLC编程以及电路图............................................................................36
结束语....................................................................................................................39
参考文献................................................................................................................39
第一章 概述
本次毕业设计的题目为小型模具柔性制造系统——立体仓库及巷式起重机的设计。立体仓库及巷式起重机是这个小型模具柔性制造系统的一部分,首先要了解柔性制造系统,理解它的工作原理,进而详细研究巷式起重机的结构,组成,工作原理。
1.1柔性制造系统以及起重机
1.1.1柔性制造系统简介
随着社会进步和和生活水平的提高,市场更加需要具有特色、符合客户要求样式和功能千差万别的个性化产品。激烈的市场竞争迫使传统的大规模的生产方式发生改变,要求对传统的零部件生产工艺加以改进。传统的制造系统不能满足市场对多品种小批量产品的需求,因此生产制造系统的柔性对系统的生存越来越重要。随着批量生产时代正逐渐被适应市场动态变化的生产所替换,一个制造自动化系统的生存能力和竞争能力在很大成都上取决于它是否能在很短的开发周期内,生产出较低成本、较高质量的不同品种产品的能力。柔性已占有相当重要的位置。“柔性”是相对于“刚性”而言的,传统的“刚性”自动化生产线旨在实现单一品种的大批量生产,其优点是神产率高,由于设备是固定的,所以设备利用率也很高,单件产品的成本低,但价格相当昂贵,且只能加工一个或几个相类似的零件。如果想要获得其他品种的产品,则必须对其结构进行大调整,重新配置系统内各要素,其工作量和经费投入与构造一个新的生产线往往不相上下,刚性的大批量制造自动化生产线只适合生产少数几个品种的产品,难以应付多品种中小批量的生产。柔性制造系统是由统一的信息控制系统、物料储运系统和一组数字控制加工设备组成,能适应加工对象变换的自动化机械制造系统FMS。
FMS目前尚无统一的定义,一般认为柔性制造技术是一种能迅速相应调整生产品种的制造技术;柔性制造系统是由若干台数控设备、物料运储装置和计算机控制系统组成的,并能根据制造任务和生产品种变化而迅速进行调整的自动化制造系统。一般定义可以用以下三个方面来概括:(1)FMS是一个计算机控制的生产系统;(2)系统采用半独立的NC机床;(3)这些机床通过物料输送系统连成一体。FMS的结构如图1所示。
FMS从20世纪60年代诞生至今已有40多年的历史,它从探索阶段走向实用化和商品化阶段,并在80年代辉煌一时,成为机械制造业技术进步的重要标志,美、英、德、日等许多先进国家的企业争相创造出自己的FMS,其中不乏成功的例子。1994年初,世界各国已投人运行的FMS约有3000多个,其中日本拥有2100多个,占世界首位。在现已运行的FMS中,50%FMS由美国制造商提供,另外50%由日本和德国厂商提供。著名的FMS生产厂家有:法那克、日立精机、丰田公机、新泻铁工、山崎(日本),公机、新泻铁工、山崎(日本),Ingersoll milling,Sundstung,Bendaw,Kearaey& Trecker,cincinnati Milacron(美国),Werner & Kolb,Burkhandt&Weber,Huller Hille,Scharman(德国)等。我国第一套FMS于1986年10月在北京机床研究所投入运行,用于加工伺服电机的零件。许多科研院所和大学都开展FMS的研究和开发,成功设计制造了许多FMS案例。





 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号