2YAH1548型圆振动筛设计【含8张CAD图纸、说明书】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:15969417
类型:共享资源
大小:1.16MB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2019-03-10
上传人:机****料
认证信息
个人认证
高**(实名认证)
河南
IP属地:河南
30
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
含8张CAD图纸、说明书
2YAH1548型圆振动筛设计
2YAH1548型圆振动筛设计说
2YAH1548型圆振动筛设计含CAD图纸
含CAD图纸
圆振动筛设计
型圆振动筛设计
- 资源描述:
-
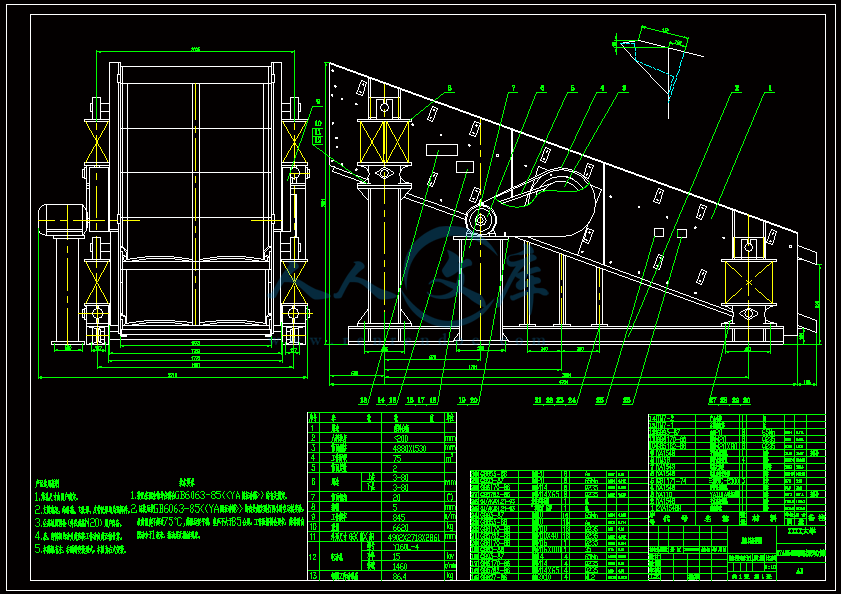




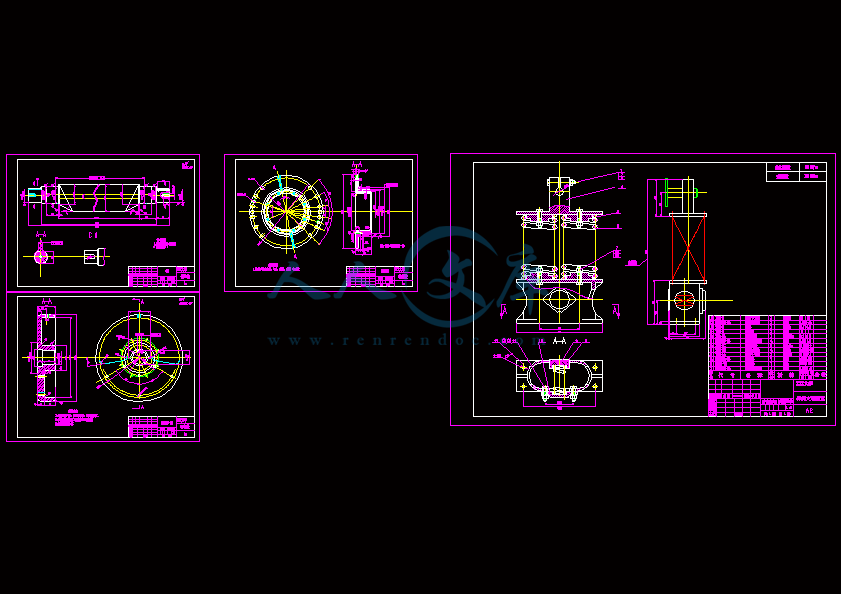



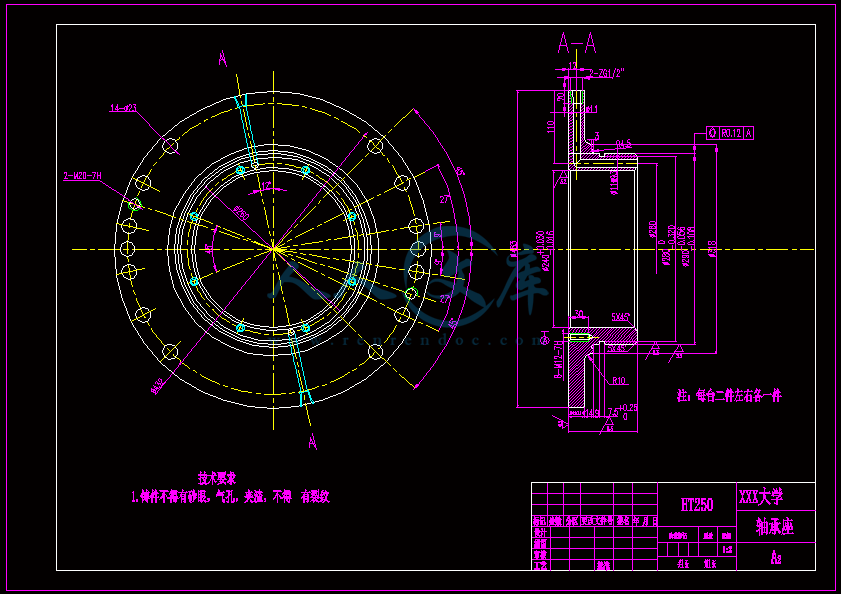





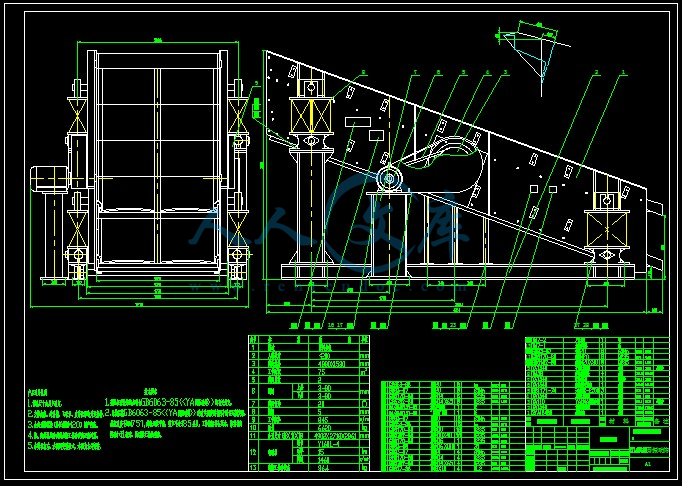


- 内容简介:
-
振动筛的选择振动筛的选择原则:选择振动筛的原则是所选择的振动筛要节省空间、重量并且驱动的功率要小,因为筛选表面可以驱动并且发生振动。同时还要保证旋转或脉动运动振幅要小,但振动筛的振动频率在通常情况下是要超过三千次每分钟的。选择合适的振动显示屏:要确定显示屏供应商知道所有有关方面的使用细节。离心力或组合频率振动(速度)以及振幅(投掷)等因素都可能影响到任何振动筛的正常工作。此外,需要有一个正确的组合坡度和方向的轮换机制,这对于显示屏来说是至关重要的。通常情况下,振动筛需要大开放、大振幅的显示屏。如果投入太少的话,则这些材料可能出现木屐或楔形开口等情况。增加投入以后,需要知道如何防止堵塞因为堵塞是不必要的,而且会增加日常轴承的磨损以及和降低筛选的效率。单位时间内材料上升速率曲线都要通过整个屏幕,因此该处材料以较快的速率通过较薄的车床的同时需要用较高的效率来进行筛选。当材料速度过快导致材料丝带被击穿并当材料到达屏幕布料开口处时出现最大倾斜角。此时大量的优质材料通过屏幕的速度过快,从而导致效益不佳。 当一个现有的屏幕画面出现故障时,如果该屏幕的结构还适合于新的应用,这时应及时进行检查并询问供应商,看看是否有需要修改的地方。操作者还可以通过供应商提供的下列资料得到良好的振动筛: 通过最高每小时吨数进行筛选,包括任何循环负荷或任何突然增加的进给速度。通过一个完整的粒度分析或对材料进行筛分分析,如果条件允许的话,最好使用估计分析法。材料的种类和每立方米重量失效的概率。各个筛板的预期断裂的情况。通过表面材料所携带的水分进行筛选,如果是潮湿的需要将水份晒干或添加一定数量的材料。特殊的操作要求或条件,例如温度、磨损情况、腐蚀情况或具有其他物理特性的材料、效率或产品的要求,确定筛选表面或安装问题,因为这将直接影响到屏幕尺寸的选择以及屏幕实际使用的能力。一般的类型:振动筛可分为两大类:一类为机械振动型振动筛,另一类为电力振动型振动筛。 前者是根据振动是如何产生的可被细分入类由偏心轮产生;由失衡的重量产生;由凸轮或防撞器产生;它们也可以按照倾斜和横向进行细分。 尺寸:振动的屏幕通常被制造成宽为从12英尺到10英尺,长为从2 1 / 2英尺到28英尺。在通常情况下,干式筛选显示屏的长度应该是宽度的2.5 倍。对于湿式筛选来说,更宽和更短的屏幕是最好的选择。为防止屏幕提前而导致被压碎,操作斜率应保持在12度至18度左右,并有多达11种开口情况。异常投掷为开头从5英尺到11英尺通常是1/2英尺;开头为3英尺到5英尺,大约3 / 8英尺和较小的开口1/4英尺。筛选表面是由一辆重型铸造服务台、钢穿孔或无打滑焊接钢筋之间的空隙、筛网等部分组成的。机械振动筛的屏幕由一个长方形框架、已打孔的钢或丝织物组成。它通常倾斜和暂停在悬浮松散杆或电缆上。这些屏幕现在主要用于有特殊任务的时侯,此时应让位给振动筛的屏幕。电热屏幕-电热布屏幕面板提供了较佳的保护功能并且具有粉尘少等优点。现代或更新筛选作业,现在处理粘土、石灰石、钾、盐、磷和各种的吸湿材料,当配备暖帘时,报告的粉尘损失最低。 控制因素在这方面的改善是使用电热幕小灵通平台。任何振动筛的屏幕以良好的开幕(小于1 / 2英寸),可配备低电压使用年龄高的焙电阻来抵抗热化。 电热化的原则是基于这样的事实:小直径线材丝网布(尤其是不锈钢) 作为导体,但是能够抵抗高焙电流。当强有力的变压器和特别地被设计的母线接上屏 幕面板被推至6000安培电流进入电路时,这种抵抗导致导线的热化目前是安全防震,因为电压较低,从大约从1 / 2伏特至16伏特。因此工人们可以在没有殊防范措施的情况下在电热屏幕附近安全的工作。热屏幕能有效地防止材料的水分累积和堵塞。根据材料本身的特征和被处理的吨位,屏幕导线能够被被保留在100 度到130 华氏度。这个温度并不足够高导致减弱导线布料或屏幕的结构,也不足够除去材料中的水分。 加热导线使其保持干燥,否则会打破束缚在潮湿的材料中对冷, 潮湿的金属的表面张力。这一差动或温暖、干燥筛线对寒冷、潮湿的材料可以通过控制设定,而变得更加经济合理。每个热屏幕筛网的前端被保护,以避免堵塞。无法猜测多少尺寸的颗粒将被提供。无论是什么天气,一个统一的、品质不变的、满足苛刻的规格每天都有通过。(高湿度造成未加热的屏幕的问题)。操作热的显示屏不会有太多的麻烦,多灰尘的材料以前是在被堵塞的屏幕上通过减少筛网来过滤的。当电热化结束后可以使用传统的清洁方法清理屏幕,如果使用粗洗或电刷洗等方法,屏幕布料产品的使用寿命将会大大的提高。小型发焰装置在一定的区域内产生大量的热量,他所产生的连锁反映就是增加了磨损以及断裂。但是,据说屏幕电热化保持清洁和开放很少被采用而且最多能使用8次。暖底甲板的物料堆积和应变,可以导致滤网被打破。对于电热屏幕来说最经济的操作是需要有一个变压器装置来为屏幕布料(最大面积412英尺)。两台变压器是用在更长的甲板。任何甲板(顶部中心或底部),都可以用来加热。处理屏幕表面是很难获取的地方,使用电热化是最可取的方法。对于普通的屏幕来说,更换热的显示屏时并不需要过多的开插销。在指定的显示屏里通过加热网提供一个一致的微粒,首先要考虑的事情是量出每平方英尺导线布料所要求的重量,以便设来定适当的阻力。大多数计算都是基于方形洞口的基础上进行的。开槽开孔被识别是在量出每平方英尺的重量和找到任何屏幕布料制造商的产品目录之前,通过前端精确的宽度,导线的直径和每平方英尺一定数量导线的重量来实现的。被确定能用的每平方英尺屏幕布料的重量,下一步是清楚的选出所需要的开头的大小,制造无加工余量尺寸大小减少到以前的情况时,材料贴到电线上。加热导线将一直保持清晰的开放,使得画面清晰无黑屏。 通过导线编目,仅仅通过重量选择一个筛网(重量可以少称量)使用的方法是通过前端特征来决定的。这通常是一个更有效率的方法,因为这样屏幕上的钢丝直径将变得更小,而且开放范围的百分比将会变得更大。例如,在一个1/8英尺的未加热的显示屏上,它的前端能够被清楚的显示出来,(但是屏幕经常黑屏),其导线直径为0.63及开放范围的百分比为为44%。布料重量为1.43磅/英尺。一个被加热的312英尺的显示屏,重量不得超过1.1磅/英尺。两个方案通过比较发现,布料以1/8英尺前端被清楚的显示出来的显示屏上:导线直径为0.054,重量1.09磅/英尺,开放范围的百分比为48.8%;一个加热312英尺的显示屏上:线直径为0.047,重0.85磅/英尺,开放范围的百分比为52.8%。 在负荷的状态下可以解决碳钢导线直径不足的问题。在这种情况下,对于好的热化来说,不锈钢导线直径以更大的承载能力来抵抗外部的载荷。更轻的导线并有更多开阔地带能够产生更高的吨位,而且热的筛网能够保持百分之百处于打开的状态。两块屏幕布料被连系成一个系列,也许是网格尺寸大小不同或者是前端的清晰度不同。只要它们满足每平方英尺的重量相同而且不超过该规定的重量,尤其是屏幕的尺寸。 对于振动筛的热屏幕来说,通过控制从而大大节省污染是可能的。同时材料中的水分根据数据显示增加了5至8个百分点。这些水分是在破碎粉磨作业的期间或之后产生的,通过灰尘在材料中的持续运动以及通过以上所述的热屏幕来降低的。温暖的导线的处理量在5 %到百8 %之间。供热设备和喷雾设备的成本据说是低于袋子塔和沉淀器的成本。Screening Vibrating screensPrinciples -Vibrating screens save space and weight and operate on little power because the screening surface may be actuated by vibrating, gyrating or pulsating movement of small amplitude, but at frequencies that normally exceed 3,000/min. Selection of Proper Vibration Sereen -Be sure the screen supplier knows all details of the application. The centrifugal force factor, or combination of frequency of vibration (speed) and amplitude (throw), may affect performance of any vibrating screen. Also, a correct combination of slope and direction of mechanism rotation is vital for inclined screens. Usually, the larger the opening, the greater the amplitude needed for a screen. If the throw is too small, the material may clog or wedge in the openings. Increasing the throw beyond what is required to prevent blinding or plugging does not necessarily increase the life of the bearings and reduce screening efficiency. Increased rate of travel permits more tonnage to be passed over the screen per unit of time. For a given tonnage, a faster rate of travel results in a thinner bed of material and high screening efficiency. Maximum slope is reached when the material travels too fast for the fines to penetrate the ribbon of material and reach the apertures in the screen cloth. At this point an excessive amount of fine material passes over the screen with the oversize, resulting in poor efficiency. When an existing screen is to be used for an application other than that for which it was originally intended, check with the Supplier to see if any of the operating characteristics need modification and if the the screen is structurally suitable for the new application. The operator can get the correct vibrating screen by providing the supplier with the following information: Maximum tons per hour to be screened, including any circulating load or any surges in the feed rate. A complete size consist or sieve analysis of the material or, if available, an estimated analysis. Type of material and weight per cubic foot in broken state. Separations desired on each deck. Surface moisture carried by the material if screening is to be dry or amount of water with feed if wet. Special operating requirements or conditions such as temperature, abrasiveness, corrosiveness or other physical characteristics of the feed, efficiency or product requirements which determine selection of screening surface, or installation problems which affect screen size selection or capacity. General Types -Vibrating screens may be divided into two main classes: mechanically-vibrated and electrially-vibrated. The former can be subdivided into classes based on how the vibration is produced-by eccentrics; by unbalanced weight; by cams or bumpers. They can also be subdivided as inclined and horizontal. Sizes -Vibrating screens are made in standard sizes of from 12 in. to 10 ft wide and from 2 1/2 ft to 28 ft long. Common practice dictates that the length of the screen should be 2.5 times the width for dry screening. For wet screening, wider and shorter screen is best. Screens for scalping ahead of primary crushers, operate at a slope of from 12 degrees to 18 degrees and have openings as large as 11-in. square. The eccentric throw for openings from 5 to 11 in. is usually 1/2 in.; for openings from 3 to 5 in. about 3/8 in.; and for smaller openings 1/4 in. The screening surface consists of a heavy cast desk, perforated steel with or without skid bars welded between the holes, rod deck, etc. The mechanical shaking screen comprises a rectangular frame, with perforated steel or wire cloth screening medium. It is usually inclined and suspended on loose rods or cables. These screens now are used mainly for special tasks of coarse screening, having given way to vibrating screens.Electrically-Heated Screens -Electrically heated screen cloth decks have afforded better screening and less dust. Modern or updated screening operations, now handling clays, limestone, potash, salts, phosphates and various hydroscopic materials, report minimum dust loss when equipped with heated screens. The controlling factor in this improvement is the electrically-heated screen doth deck. Any vibratory screen with fine opening (less than 1/2 in.) can be equipped with low volt-age-high amperage resistance heating. The principle of electric heating is based on the fact that small diameter wire of screen cloth (especially stainless steel) serves as a conductor, but offers resistance to a high-amperage current. This resistance causes heating of the wire when powerful transformer and specially designed bus bars connected to screen doth decks push up to 6,000 amps current into a circuit. The current is safe and shock-proof because voltage is low, ranging from approximately 1 1/2 to 16 volts. Workers can do their jobs around electrically-heated screens without special precautions. Heated screens are effective in preventing moisture content of material from causing buildup and blinding. The screen wire is kept at 100 degrees to 130 degrees F depending on character and tonnage of the material processed. This temperature is not high enough to weaken the wire cloth or screen structure, nor does it suffice to drive off moisture held in material. The warm wire stays dry, breaking the surface tension that otherwise would bind damp material to cold, damp metal. This differential or warm, dry screen wire versus cold, damp material can be maintained economically through transformer control settings. With every opening in the heated screen mesh protected against blinding, there is no guesswork about what size particle will be delivered. A uniform, unvarying quality to meet tough specifications comes through day after day, no matter what the weather. (High humidity makes trouble with unheated screens.) Plants operating heated screens will have no trouble with excessive amounts of fine, dusty material that formerly sifted through reduced meshes on clogged screens. Service life of screen cloth is greatly increased when electric heating ends the punishment of old-fashioned cleaning methods, such as rough pounding or brushing. Blowtorch flames put too much heat in one spot and bouncing chains added to wear and tear. But, screens kept clean and open with electric heating reportedly are seldom mistreated and last up to eight times as long. Heated decks end the threat of pile ups and strains that can break the mesh. Economical operation of electric heating for screens requires one transformer for installations of up to three panels of screen cloth (maximum area 4- x 12-ft). Two transformers are used on longer decks. Any deck (top, center or bottom) can be heated. Electric heating is most desirable of all where a screen surface is hard to get at. Changing heated screens does not involve more unbolting than needed for ordinary screens. In specifying screens to deliver a uniform particle through heated mesh, the first thing to consider is weight per square foot of the wire cloth needed to set up appropriate resistance. Most calculations are based on square openings. Slotted openings must be identified as to width of clear opening, diameter of wire and number of wires per inch before weight per square foot can be found in any screen cloth manufacturers catalog. Having determined the usable weight per square foot of screen cloth, the next step is to select the size of clear opening needed, making no allowance for reduction in this size as formerly was the case when material stuck to the wires. Heated wires will maintain the clear opening at all times, making it possible to screen finer without blinding. From a wire catalog, select a mesh weighing no more per square foot (can weigh less) than determined using the method above with the clear opening characteristics desired. This often turns out to be a more efficient screen because the wire diameter will be smaller and the percentage of the open area will be greater. For example, where a 1/8-in. clear opening was desired (but often blinded) on unheated screens, the wire diameter was 0.63 and the open area was 44 percent. The cloth weighed 1.43 lb/ft. 2. For a heated 3- x 12-ft screen,
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号