摘要
目前国内使用的破碎机类型很多,主要有鄂式破碎机、锤式破碎机、圆锥破碎机、反击式破碎机和辊式破碎机。复摆式颚式破碎机与简摆式相比较,其优点是:质量较轻,构件较少,结构更紧凑,破碎腔内充满程度较好,所装物料块受到均匀破碎,加以动颚下端强制性推出成品卸料,故生产率较高,比同规格的简摆颚式破碎机的生产率高出20-30%;物料块在动颚下部有较大的上下翻滚运动,容易呈立方体的形状卸出,减少了像简摆式产品中那样的片状成分,产品质量较好。
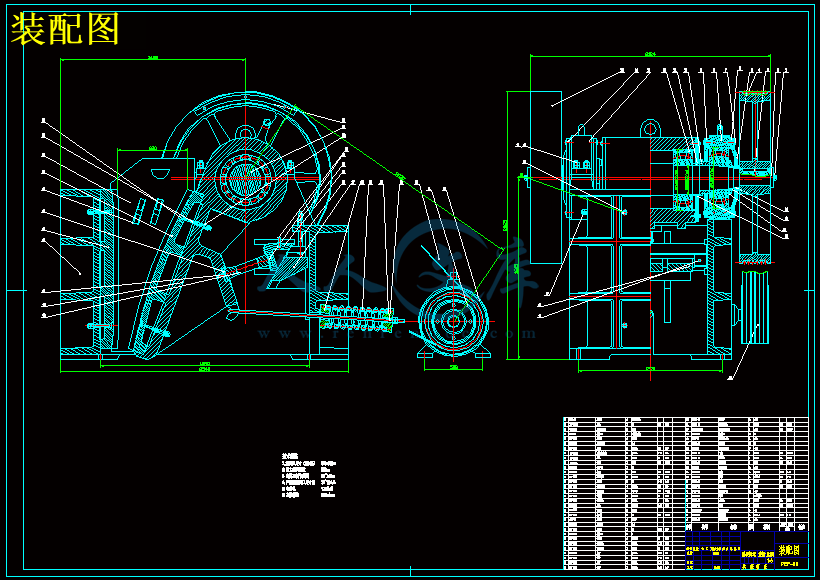
本设计需求参数为进料口尺寸:620×900mm;最大进料粒度:340mm;处理能力:4~10m³/h;偏心轴转速:275r/min;排料口调整范围:40~100mm;电动机功率:30KW。设计分析了破碎机的发展现状和研究颚式破碎机的意义及复摆颚式破碎机机构尺寸对破碎性能的影响,计算确定了PE400×600的机构参数,设计内容主要包括复摆颚式破碎机的动颚、偏心轴、皮带轮、动颚齿板、定颚齿板、机架等一些重要部件;另外,对颚式破碎机的工作原理及特点和主要部件的作用作了介绍,包括保险装置、调整装置、机架结构、润滑装置等;同时对机器的参数(主轴转速、生产能力、破碎力、功率等)作了计算。此外,对破碎的意义、破碎工艺和破碎比的计算,颚式破碎机的主要部件的安装、操作及维修作了简单介绍。
关键词:复摆颚式破碎机 带传动 飞轮 磨损
ABSTRACT
Currently ,the type of the crusher is multitudinous in domestic, mainly including jaw crusher, hammer crusher, cone crusher, impact breaker and roll crusher. Compared with fine impact crusher ,SBM(swinging jaw break machine)´s advantage is: quality is lighter, less compact structure component, broken lumen filled with degree is good, with materials by uniform broken, to block bottom mandatory move jaw is unloading, launch finished higher, than with specifications productivity of fine impact crusher 20-30% higher than the productivity; Material blocks in the lower have bigger jaws move up and down movement, a cube tumbling to the shape of, reducing the discharged as Jane tilting products that flake composition, product quality is better.
This design is done for:the feeding port size is 400 x 600mm; Maximum feeding granularity is 340mm; Production efficiency is 4-10m ³/ h; Eccentric shaft speed is 275r/min; Discharging mouth adjustment range 40mm to 100mm; Motor power is30 KW. This design analysis of the current development of the crushier,the meanings of researching the crusher,how the dimensions of jaw crusher effect on the performance of the broken, calculate and determine the PE400 x 600 structure parameters, the design content mainly includes swing jaw, eccentric shaft, pulley, seing jaw gear plate, and settled jaw gear plate and frame and some other important components; In addition, jaw crusher principle and characteristics and main component function is introduced, including insurance device, adjusting devices and frame structure, lubrication device, etc.; Also on the machine parameters (spindle speed, production capacity, crushing strength, power) calculate as well. In addition, the significance of broken, crushing process and calculation of crushing ratio, jaw crusher main component installation, operation and maintenance are introduced.
KEY WORDS:Jaw crusher Belt drive Flywheel Wear
目录
第1章 绪论··················································································1
1.1引言·························································································1
1.2复摆颚式破碎机的特点 ··································································3
1.3国内外颚式破碎机的发展及现状·························································5
第2章 总体设计············································································8
2.1复摆鄂式破碎机的基本结构····························································· 8
2.2复摆鄂式破碎机的工作原理·····························································10
第3章 主要参数的确定··································································12
3.1已知参数··················································································12
3.2部分结构参数的确定·····································································12
3.3动鄂的摆动次数···········································································14
3.4电动机的选择·············································································15
3.5四连杆机构各杆长度的确定·····························································16
3.6最大破碎力················································································17
3.7各部件受力分析···········································································17
第4章 传动装置的设计··································································20
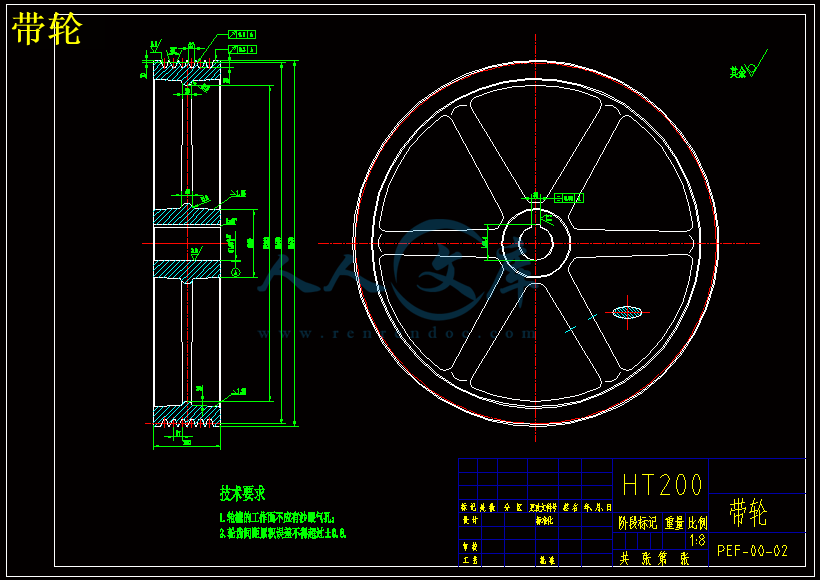
4.1带轮的设计················································································20
4.2偏心轴的设计·············································································25
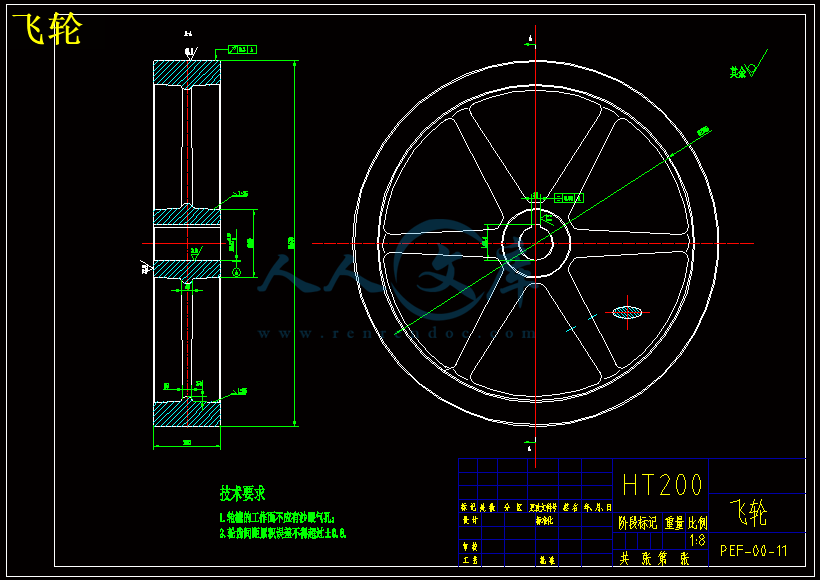
4.3飞轮的设计················································································27
4.4轴承的选择与校核········································································29
4.5轴承座的设计·············································································31
4.6配重的选择················································································32
4.7外形尺寸的设计···········································································33
第5章 各基本构件的设计······························································35
5.1动鄂的设计···············································································35
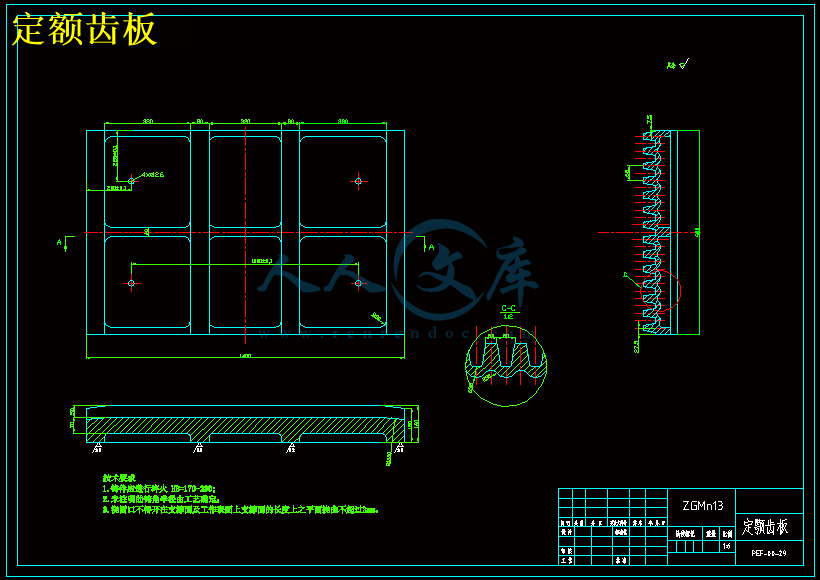
5.2齿板的设计················································································38
5.3推力板的设计·············································································40
5.4调整装置的设计···········································································41
5.5破碎腔型的形状···········································································43
5.6机架的设计···············································································44
第6章 复摆鄂式破碎机的安装························································47
6.1破碎机的安装·············································································47
6.2机架的安装···············································································47
6.3偏心轴和机架的安装·····································································48
6.4肘板的安装···············································································48
6.5动鄂的安装···············································································49
6.6齿板的安装···············································································49
第7章 颚式破碎机的磨损······························································50
7.1齿板的磨损分析··········································································50
7.2颚板磨损机制·············································································51
7.3颚板材质的选择··········································································52
第8章 破碎机出口扬尘的解决和噪声防治·········································54
8.1破碎机出口扬尘的解决··································································54
8.2破碎机的噪声危害及防治途径···························································55
第9章 颚式破碎机的使用·····························································56
9.1颚式破碎机的操作········································································56
9.2颚式破碎机的维护与保养·······························································57
总结···························································································59
鸣谢···························································································60参考文献·····················································································61
第1章 绪论
1.1 引言
凡是外力将大颗粒物料变成小颗粒物料的过程称为破碎,破碎所使用的机械为破碎机。物料碎磨得目的是:增加物料的比表面积;制备混凝土骨料与人造沙;使矿石中有用成分解离;为原料的下一步加工作准备或便于使用。
物料的破碎是许多行业(如冶金、矿山、建材、化工、陶瓷、筑路等)产品生产中不可缺少的工艺过程。由于物料的物理性质和结构差异很大,为适应各种物料的要求,破碎机的品种也是五花八门的。就金属矿选矿而言, 破碎是选矿厂的首道工序,为了分离有用矿物,不但分为粗碎、中碎、细碎, 而且还要磨矿。因为磨矿是选矿厂的耗能大户(约占全厂耗电的50%),为了节能和提高生产效率,所以提出了“多碎少磨”的技术原则。这使破碎机向细碎、粉碎和高效节能方向发展。另外随着工业自动化的发展,破碎机也向自动化方向迈进(如国外产品已实现机电液一体化、连续检测,并自动调节给料速率、排矿口尺寸及破碎力等)。随着开采规模的扩大, 破碎机也在向大型化发展,如粗碎旋回破碎机的处理能力已达6000t/h。至于新原理和新方式的破碎(如电、热破碎) 尚在研究试验中,暂时还不能用于生产。对粗碎而言,目前还没有研制出更新的设备以取代传统的颚式破碎机和旋回式破碎机主要是利用现代技术,予以改进、完善和提高耐磨性,达到节能、高效、长寿的目的。细碎方面新机型更多些。总的来看,值得提出的有:颚式破碎机、圆锥破碎机、冲击式破碎机和辊压机。








 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号