电池内部金属精密连接件级进模具设计【优秀含CAD图+说明书+文献翻译】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:18315429
类型:共享资源
大小:2.67MB
格式:RAR
上传时间:2019-04-28
上传人:hon****an
认证信息
个人认证
丁**(实名认证)
江苏
IP属地:江苏
12
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
优秀含CAD图+说明书+文献翻译
级进模具设计【优秀含
CAD图纸+
模具设计【优秀含
级进模具设计【优秀含CAD图纸
连接件模具设计【优秀含CAD图纸
设计【优秀含CAD图纸】图纸
- 资源描述:
-





- 内容简介:
-
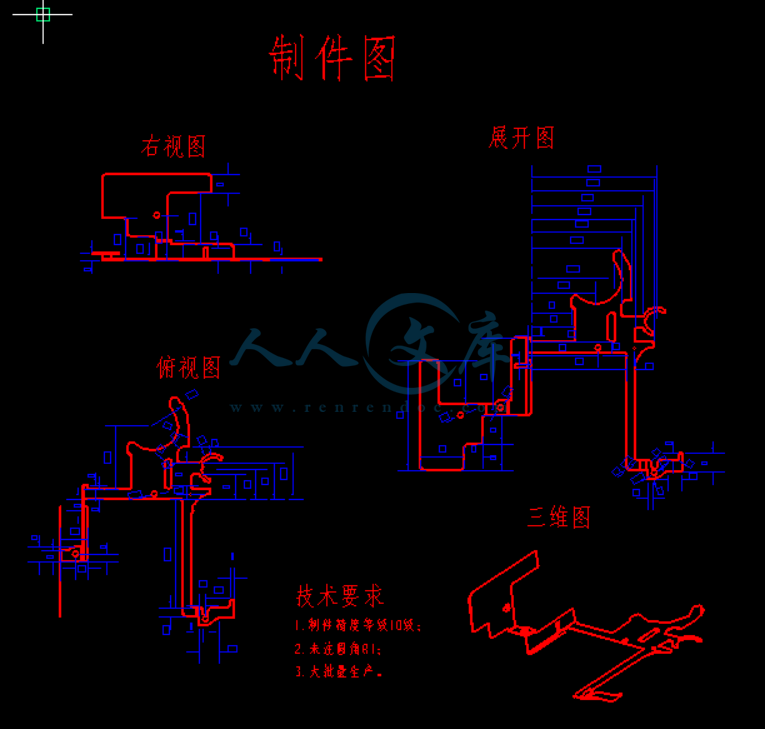
中期检查表课题名称电池内部金属精密连接件级进模具设计指导教师检查情况总结:已经按照学校安排完成毕业实习、撰写了实习报告、开题报告、外文翻译等工作。同时完成了设计前必要原始资料的查阅和制件的测绘任务;工艺方案已经确定,正在进行相应的工艺计算;目前正按照计划绘制装配草图。可以按照计划完成毕业设计任务。 指导教师签字: 年 月 日学院检查小组检查结果: 检查小组负责人签字: 年 月 日注:毕业设计(论文)完成后此表装入毕业设计(论文)档案袋。设计任务书一、 题目名称:电池内部金属精密连接件级进模具设计二、 设计(论文)内容及要求:设计内容: 1、根据毕业设计题目,查阅国内外相关文献,完成开题报告; 2、制件测绘,零件图绘制以及尺寸标注;材料08钢,大批量生产;精度:IT10 3、根据制件结构、形状、材料、批量等因素分析结构工艺性,确定工艺方案; 4、结构设计及工艺计算,并绘制装配图;确定方案,选择相关设备; 5、完成非标准件的设计与零件图绘制,以及标准件的选取;设计部分3D图。 6、填写零件制造工艺卡,其中包括材料的选择与热处理工艺的制定; 7、完成设计说明书; 8、翻译一篇相关内容的外文资料。 设计要求: 1、设计图纸折合为A0号图纸不少于三张,其中,手工绘制A0号图纸一张; 2、按照学校规定的格式和内容编写出说明书,字数不少于两万字;参考文献15篇以上,其中,外文文献不少于3篇; 3、翻译与毕业设计相关的外文文献,译文字数不少于五千汉字; 4、完成毕业实习报告一份,字数在两千五百字以上; 5、填写零件制造工艺卡。1 外文资料翻译 机械科学与技术杂志21(2007)1452 - 1455 微型零件微冲压成型和组装级进模微型零件微冲压成型和组装级进模 杨明 1,真果建一2,伊藤伊托3 1日本东京都大学系统设计学院 2日本东京都大学科学与工程研究生院 3日本东京塞其公司 (手稿收到 5月31日,2007;修改后 8 月 30 日,2007;接受 9月 30日,2007) 摘要摘要 一个微冲压成形过程和装配技术被开发并应用于金属零件制造和控制元件 上。 此研究主要基于高能量的光束,如离子和短脉冲激光技术,此技术开发了制 造在微观尺度和纳米尺度的表面精加工模具的特点。 另外,在模具的表面上的类 金刚石涂层是为了提高耐磨性和减少摩擦开发的。 例如采用金属板生产一个直径 为 0.2 mm的微型齿轮。此外,部分单位有三个组成部分制造的精密级进模使用 的是微印刷机系统。 该结果表明,微金属成型在低成本和大批量上可能是制造一 种新的技术的微器件,如微机电系统,生物芯片。 关键词关键词:微冲压成形,自动装配,级进模,微型金属装置 1.介绍 在近十年MEMS(微机械电子系统)和生物芯片引起了社会的关注。这些种 微型装置主要由硅或玻璃制作,并采用微机械加工技术,这通常成本很高。 制造 技术用于提供所述MEMS稳定地在更低的成本是一个重要问题。 由于微机械加工 技术是基于光刻,该进程基于2维或2.5 维的特点, 微机电系统只能限制于特 定的结构与脆弱材料。 与此相反,金属具有的性质,如延展性,导电性,这样的 MEMS 基于金属成形制成能有更多的在结构上具有较高的强度和韧性的自由的材 料。 另一方面,由于小型化的技术设备结构件1,2产生的问题 ,金属在亚毫米 或微米尺度形成对于音频或视频信息也变得非常重要。 作者一直关注于一种新型微金属成形技术,其中微型零件或部件制造成形 和用于在级进模自动装配过程 3 。 几种金属板被供入模,通过进料器和在几 个步骤中同时形成,然后在级进模中组装在一起。 我们还推出了高能光束对微芯 片的具有几个特征的制造,微米级和使用DLC(类金刚石碳喜欢)涂布技术的 表面上形成膜模具用于提高耐磨性4。在这项研究中,我们尝试开发几种模具 的冲压和深拉延,并利于级进模冲压成形,以产生一些微型金属零件及部件。 2 外文资料翻译 2.微冲压成形的 MEMS 的制造 压制成形对于金属在压制机器上加工复杂零件是最显著加工成形工艺之一。 大多数声像使用的零件(AY)和信息技术(IT)设备都由冲压成形制造出来。 近 年来这类功能的这些部件逐渐变小。此外,MEMS和生物芯片包括多部件的构造 的一个系统或一个单元具有复杂的结构。在未来几年,部分结构/单位的特点制 造采用冲压成型的子毫米可能会显得很重要。 具有亚毫米特点的形成部分的难题 是: - 用于制造新方法开发和评价子毫米级模具的特征, - 研究表面处理模具保护模具免受磨损和破损, - 对细晶粒金属材料的发展与评价, - 处理微型部件和微型组件。 在这项研究中,我们提出一个微加工系统,通过使用冲压成形设备,以多 步骤方式来形成微型部件,然后,把这些部件在一个级进模中组装成一个单元。 如下图所示。我展示了微型制造系统的概念。几种材料由给料机分别供应进级进 模,并经过几个步骤在级进模里同时制成,然后,这些材料在同一个级进模中 组装在一起。最后,一个单元部分在压制的形势下被制造出来。为了建立微加工 系统,每个准确性的对齐的维度的模具的元素是具有挑战性的。 具体问题如下所 示: 图.1 原理构造形成和级进模的进程装配 3 外文资料翻译 - 用于建立新的制造方法和评价尺寸小于20微米的模具, - 当尺寸和编配小于1微米时持续出现的问题, - 从无润滑剂的过程实现无磨损无退化处理保护模具表面, - 在装配工艺之前去除比几微米大的毛刺, - 在这些过程中减少小型化和数字化冲压机在竖直和水平位置产生的错误。 大小为几十微米的微型模具的加工方法和带有装配系统的压制过程的设计 将分别在第三章和第四章中讨论。 3.微型模具制造 3.1通过组合加工和高能量光束加工微型模具 高能量的光束,包括短波长激光束和离子束被引入到微加工具有微米级特 点的模具中。 短波长激光和离子束等广泛应用于半导体生产过程中,有分别去除 以微米和纳米级特征材料的能力,而一般的传统加工成形流程具有小到亚毫米 顺序的特点。 在这里,我们提出加工的组合和利用高能光束流程制造微型模具的 方式通过激光处理来加工模具的大致轮廓,然后,通过离子束来完成加工以形 状更小的为特征的纳米级或亚微米级表面3。 图.2照片显示的是用组合制作齿轮的方式来展示微型模具冲压微型零件的 方法。 微型齿轮的直径为 200 微米,模数为 20。 由冲床加工后圆形,如直径为20 微米的微齿轮是由短脉冲激光功能与是微电放电过程组合制造的。 此外,施加离 子照射在消除侧壁上的痕迹和微裂纹上有领先优势。 表面形状和光洁度的制造的 详细情况均在我们以前的工作3,4出现过。 似乎冲压的表面粗糙度在照射后 进行了改进。 对于微型模具来说,由于增加了应力集中,表面粗糙度和机械性能 的改善在保护模具免受磨损至关重要。 4 外文资料翻译 图.2 对微型齿轮形冲离子束照射表面处理(800 V,1.65毫安,1 小时,入射角45 度) 3.2 使用离子膜DLC对模具进行表面涂层 研究者们还在金属模具上涂敷DLC膜以减少摩擦并保护模具免受磨损4。 在微观尺度上的金属形成的情况下,模具承担的较大的次应力或主应力,较宏 观尺度来看,这使得DLC涂层变得更容易被损坏而且模具变得更加容易被磨损 或破坏。研究者通过使用纳米压痕试验,根据不同浓度DLC涂层的应力/应变来 评价其机械性能和粘合性能,通过使用微弯曲实验来确定摩擦性能依赖于尺寸 4 。该结果表明,该DLC膜在特定条件下被涂覆可以承受的平均应力高达10 千兆而且无脱层或破损;使用具有较大的硬度和弹性模量的DLC膜显示更强的耐 磨属性,但更容易剥离,相反,用更小的硬度和弹性模量的DLC膜显示更强的 与基体粘合强度,但容易磨损。 从磨损试验结果可看出,具有梯度性能的DLC膜 通过不同条件下组合在耐磨和较低的摩擦下可能是有效的。 在这项研究中,两层 DLC 膜涂布在基板上,摩擦特性受到好评。图.3 示表示出了具有梯度性能DLC膜 所产生的结果。它似乎没有被观察到显著损坏在超过50000 次,半径为600微米 的模具成形后。结果表明,具有梯度性能DLC膜是对实际生产是实用的。 图.3 观察多层 DLC 膜摩擦后试验;拍摄 5,000 后用于基板上的DLC 膜半径为 100 微米 (左)和拍摄 50,000 后用于基板上的 DLC 膜半径为 600微米(右) 5 外文资料翻译 型号:S-23台式伺服压力机, 最大压力:23KN,最大速度:500spm, 最大行程:15mm, 滑动调整行程:15mm, 装模高度:100mm, 外形尺寸:W340 x D330 x H545 图.4 微型台式机伺服压力机及其规范 4.单个和单元部件的冲压成形 4.1微型冲床的开发 一种为微冲压成型和组装开发的桌面大小的的小型冲压机,如图.4。图.4为 该机器的照片和列出了其工艺规格。该压机是由一个精确可控的伺服电机驱动。 因此能够提供同时在三个方向中的材料冲压过程。 4.2 微单件的制造 通过使用微加工系统采用两个步骤过程来制造带有中央孔的微型齿轮。 在这 种情况下,对应模具的每个过程步骤的元素和材料的送进和定位在每个步骤中 都将是非常重要的。图.5显示出了齿轮的照片和其说明书。同心圆齿轮已被成功 制作而且误差为3微米左右。在这种情况下,处理率为60 次每分钟。 6 外文资料翻译 图.5 微型齿轮和冲压成形模具的照片图像 4.3 单体部分的制造 使用微冲压成形系统对一个单体部分进行制作。 一个单位体部分有三个元件 被设计成与图6中所示的试样。 两个可移动部件和一块基板在相同的级进模冲压 成形和装配在一起。 可动部件接合通过定位销固定在底板上并可以围绕定位销旋 转。该工艺包括冲压,弯曲,压印,穿孔等相关工艺。用于冲压功能元件的形状 的 5 个过程的步骤,分别地,冲压和成型底板的10 个步骤,此外,并在这种情 况下进行组装再加入4个步骤。图 7显示出通过该方法制造出的产品。该结果表 明,该单体部分是通过使用一个压制成型的级进模制作成功的。 其中一个制造微 功能器件的最重要的问题是操纵和组装部件,如微机电系统,生物芯片等等。 对 使用微冲压成形生产微功能器件,该自动操作和组装在级进模中显示出非常高 的潜力。 图.6 压制成型模具和单体部分的设计图 7 外文资料翻译 在级进模中一个微冲压成形和自动装配过程的开发和适用于制作微单体和 单位的部分。 高能束被引入到制作以微米级为特征的微型模具中,类金刚石膜涂 层涂于模具表面上用于提高其耐磨性。 一些种模具是通过使用开发制作技术被制 作出来并应用到压制成形微金属部分。冲压加工被用于加工制作一个微型齿轮。 此外,通过使用冲压成形和自动装配工艺能加工出含有不受约束组件的单体部 件。 鸣谢鸣谢 研究者们将感谢日本经济部,贸易部和工业部支持这项工作。 参考文献参考文献(略) I Y. Saotome, Application of glassy metal to micromachine, J Material Sci. and Eng. 39(4) (2002)141-145 2 Y. Saotome, Technology for micro parts and dieprocess in nano scale, J Tooling Eng. 43(13) (2003)84-89. 3 M. Yang, S. Nakano, K. Manabe, K. Morikawa, K.Ito, H. Saito, K.Fuchigami and Yokoi, Fabricationof MEMS Using Micro Metal Forming Process, Proc.ICNFT. 135-140 (2004). 4 K. Fujimoto, M. Yang, M. Hotta, H. Koyama, S.Nakano, K. Morikawa and J. Caimey, Fabricationof Dies in micro-scale for micro sheet metalforming, Journal of Material Processing Technology.177 (1-3) (2006) 639-643. Journalof Mechanical Scienceand Technology Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology 21 (2007) 1452-1455 Micro press forming and assemblingofmicro parts in a progressive die Ming Yang:“, Ken-ichi Manabe/ and Kuniyoshi Ito3 IGraduate School0/system design, TokyoMetropolitan Univ.,Japan, 2GraduateSchoolofScience and Engineering, TokyoMetropolitan Univ.,Japan, 3SekiCorporation, Tokyo,Japan (Manuscript Received May 31, 2007; Revised August 30, 2007; Accepted September 30, 2007) Abstract Amicro press formingand in-processassembly technology were developedand applied to fabricationof metal parts and units. Technologiesbased on high-energybeams, such as ion and short pulse laser were developed for fabrication of featuresof dies in micro scale and finishingsurface in nano scale.Inaddition,DLC coatingon surfaceofthe die was developed in order to improve wear-resistance and reduce friction. A micro gear with diameterof0.2 mm was producedusing sheet metals.Furthermore,a unit part with threecomponentswasfabricatedina preciseprogressive die using the micro press system.The resultsshow that the micro metal forming couldbe a new technology for fabrication of microdevices, suchas MEMS, bio-chipsinlow cost and with largequantities. Keywords:Micro press forming; Automatic assembly; Progressive die; Micro metallic device 1.Introduction MEMS (Micro Mechanical Electro system) and Biochips attract attention in this decade. These kinds ofmicro devices are mainly madeofsilicon or glass, and fabricated by using micro machining technique, which usually costsveryhigh. Fabrication tech- nology for providing the MEMS stably in lower cost is an important issue. Since the micro machining technique is based on photolithography that pro- cesses features in 2 dimensions or 2.5 dimensions, MEMScanonly have restricted structures with fra- gile materials. On the contrary, metals have the pro- pertiesofductility, conductivity so thatMEMS fabricated based on metal forming could have more freedom in structure with high strength and ductile materials. On the other hand, metal forming in sub- Corresponding author.Tel.:+81425858440, Fax.:+81425858440 E-mail address. yangtgtmu.ac.jp millimeter or micrometer scales also becomes a very important issue for the audio-video or information technological devices due to miniaturizationofthe structure parts 1,2. The authors have been working on a novel micro metal forming technology in which micro parts or units are fabricated by micro press formingand automatic assembly processes in a progressive die 3. Several kinds of sheet metals are supplied into the die by feeders and formed simultaneously in several steps and then, assembled together to a unit in the pro- gressive die. We also introduced high-energy beams for the fabrication of micro die with featureofseveral micrometers and using DLC (Diamond Liked Car- bon) coating technique to form film on the surfaceof the die for improving the wear-resistance 4. Inthis study, we attempt to develop several kinds ofdie for punching and deep drawing, and utilize to press forming in a progressive die to produce some M.Yang et al. / JournalofMechanical Science and Technology21(2007) 1452-14551453 micro metallic parts and units. 2.Micropress forming for fabrication of mems Press forming is oneofmost significant metal forming process for fabricationofcomplicated parts in a press machine. Mostofparts used in Audio- Video (AY) and Information Technological (IT) de- vices are fabricated by the press forming. The feature ofthese parts became smaller and smaller these years. Furthermore, MEMS and Biochips consist of multi- parts constructing a system or a unit with complicated structure. Fabrication of parts/units with featureof sub-millimeters using press forming could be impor- tant in next few years. The issues for forming parts with sub-millimeters features are: - Developmentofnew method for fabrication and evaluationofdie with featureofsub-millimeters, - Surface treatment of die for protection from wear and breakage, - Development and evaluation of metallic ma- terials with fme grains, - Handling and assemblyofmicro parts. Inthis study. we proposed a micro fabrication system by using press forming to form micro parts in multi-steps and then, to assemble parts into a unit in a progressive die. Fig. I shows conceptionofthe micro fabrication system. Several kinds of materials su- pplied into the progressive die by feeders,respectively, and formed simultaneously in the progressive die in several steps and then, assembled together in the same die. As the result, a unit part could beformedas an output of the press forming. In order to establish the micro fabricationsystem, accuracyofeach elementofdies in dimensions andofalignment is challengeable.The issues are shown as follows: Fig. I. Schematic configurationofpress forming and in-pro- cess assembly in a progressive die. - Establishing new methods for fabrication and evaluationofdie features smaller than 20 um, - Keeping errors in dimension and allocationofthe elements smaller than 1urn, - Treatmentofdie surface for protection from wearing and degradation and for processes without lubricant, - Removingburrslargerthanseveral micron before assembly process, - Miniaturization and digitizationofpress machine for reducing errors in vertical and horizontal positions during the processes. Methodologies on fabricationofmicro die in size ofseveral ten micrometers and design of the press forming process with the assembly system will be discussed in chapter 3 and 4, respectively. 3. Fabrication of micro dies 3.1 Fabricationofmicro die by combining machin- ing and high energy beams High-energybeamsincludingshort-wavelength laser beam and ion beam was introduced to the fabricationofmicro die with featureofseveral micrometers. The short-wavelength Laser and ion beams, which are widely applied in semiconductor process, have ability of removing materials with the features of several micro- and nano-meters, respec- tively, while the conventional machining generally processes shape with features as small as sub-milli- meter order. Here, we proposed a combinationofthe machining and high energy beam processes for fabrication of micro die in such manner to process profileofthe die roughly by the machining and the smaller features by laser process and then, the shape with sub-micrometer or finish surface in nano-order by ion beam 3. Fig. 2 shows photoofa micro die for punching micro parts with gear shape fabricated by using the combination. The micro gear has a diameter of pitch circleof200urn and a moduleof20.After machining the circle shapeofpunch, the micro gear with the feature of about 20 urn was fabricated by combi- nationofshort pulse laser and micro electrical discharge processes. Furthermore, the ion irradiation was applied to remove the traces on the sidewall and micro cracks on the leading edge. The detail con- ditions for the fabricationofthe shape and finishof the surface were appeared in our previous works 3, 1454M. Yang et al. IJournalofMechanical Science and Technology21(2007) 1452-1455 ,- l.4ulti-tayeredOLefilm ;roplayer.Dl C(-1.0kV)Higl1hardness and Etasnc Modulus Inter layer - OLCC -3.0kVlowresidual stress .LowModulus CLC (l.OkIl) CLC (-J.OkIl) Sl.bf, ttoiraWCICO Thol4 Olq-J,()II,V):OLC(l.(Ilo:V). 1: 1 4. Press forming for single and unitparts 4.1 Developmentofminiaturepress machine A miniature press machine with desktop size was developed for press forming and assembly of micro parts. Fig. 4 shows a photo of the machine and its specifications. The press is actuated by a servomotor and controllable precisely.Itis possible to supply materials simultaneouslyinthree directions during process. 4.2FabricationofMicro singleparts 1-, iType: S-23 desk-top servo press machine IMax. Force 23kN, Max. speed 500spm, !Max Stroke: 15mm, ISlide Adjustment 15mm, Die height: 100mm iDimensions: W340 x D330 x H545I _J Fig. 4. miniature desktop servo-press machine and its speci- fication. A two-steps punching process was carried out for fabrication of a micro gear with a central hole by Fig. 3. Observation for Multi-Layered DLC film after tribolo- gical test; after 5,000 shots for DLC film on substrate with radius of I00 urn (left) and after 50,000 shots for DLC film on substrate with radiusof600 urn (right). o o . 4.Itseemed that the surface roughness of punch was improved after the irradiation. For micro-die, improvementofsurface roughness and mechanical properties is important for protection from wear and breakage due to increase in stress concentration. Fig. 2. Surface treatment for micro gear shaped punch by ion beam irradiation (800 V, 1.65rnA,Ihr,incident angle 45 degree). 3.2 Die surface coating usingionDLCfilm The authors also coated a DLC film on the die for reductionoffriction and protection from wear 4. Inthe case of metal forming in micro scale, the die bears larger stress on the shoulders or the leading edges than that in macro scale so that the DLC coating becomes easier to be damaged and the die becomes easier to be worn or broken. The authors evaluated the mechanical and adhesive properties of DLC coating due to the concentrationofstress/strain by using a nano-indentation test, and tribological property depended on size by using a micro-bending test 4. The results show that the DLC film coated with certain conditions could bear average stress as high as 10GPa without delaminationor breakage; the DLC film with larger hardness and elastic modulus show stronger wear-proof property but easier to delaminate; on the contrary, the DLC film with smaller hardness and elastic modulus show stronger adhesion strength with substrate but easier to wear. From the results of the wearing test, a DLC film with gradient properties by combining different coating conditions could be effective on both wear-proof and lower friction.Inthis study, a two-layered DLC film was coated on the substrate and the tribological property of the film was evaluated. Fig. 3 shows that the results for DLC film with gradient properties.It seemed that the significant damage was not observed after more than 50000 times for the die with radius of 600 urn. The results show that the DLC film with gradientpropertiesispractical for real production. M. Yang et al. / JournalofMechanical Science and Technology 21(2007) 1452-14551455 Dllmsions Ditor: Teo Botloll 001. n.iclO.ISa 40.1 O.la SEllIlla;:. fabricated by using the press forming in a progressive die. Oneofmost important issues for fabricationof micro functional devices such as MEMS, Biochip and so on, is manipulation and assemblyofthe parts. The automatic manipulation and assembly in the pro- gressivediemanifestsveryhigher potentialfor productionofmicrofunctionaldevicesby using micro press forming. 5. Conclusions Fig. 5. Photo image of a micro gear and the dies for the press forming. Fig. 6. Design imageofpress-forming dies and unit part. using the micro fabrication system. In this case, align- mentofelementsofthe die for each process step, and feeding and positioningofmaterial at each step will be very important. Fig. 5 shows the photoofthe gear and the specification. The gear was successfully fabri- cated and the en-or in concentric circles was about 3 11m.In this case, the process rate was 60 spm. 4.3 Fabricationofunitpart Fabricationofa unit part was carried out using the micro press forming system. A unit part with three components was designed as a sample shown in Fig. 6. Two movable components and a base plate are press-formed and assembled together in the sam
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号