齿轮箱壳体多孔钻专用机床设计【含CAD图纸、说明书】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:22905979
类型:共享资源
大小:1.41MB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2019-11-04
上传人:机****料
认证信息
个人认证
高**(实名认证)
河南
IP属地:河南
50
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
含CAD图纸、说明书
齿轮箱
壳体
多孔
专用
机床
设计
CAD
图纸
说明书
- 资源描述:
-
【温馨提示】压缩包内含CAD图有下方大图片预览,下拉即可直观呈现眼前查看、尽收眼底纵观。打包内容里dwg后缀的文件为CAD图,可编辑,无水印,高清图,压缩包内文档可直接点开预览,需要原稿请自助充值下载,所见才能所得,请见压缩包内的文件及下方预览,请细心查看有疑问可以咨询QQ:11970985或197216396
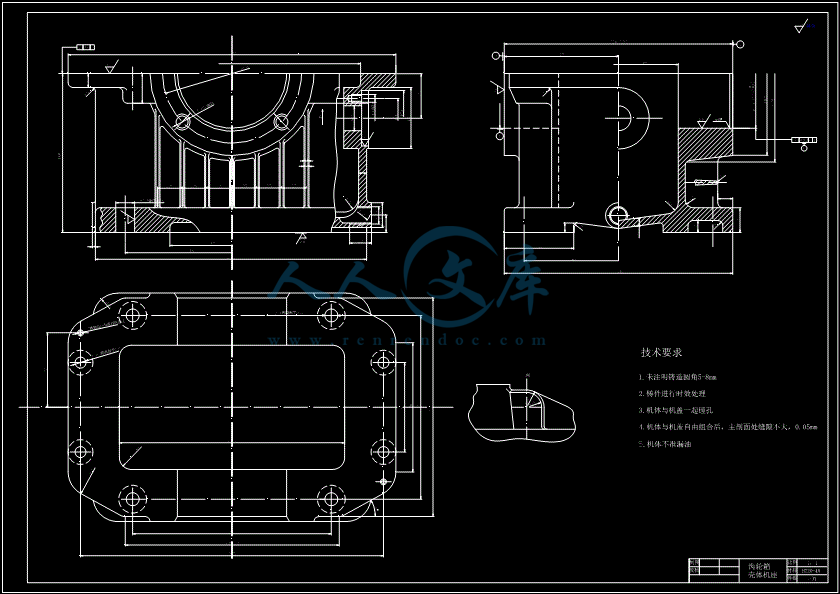
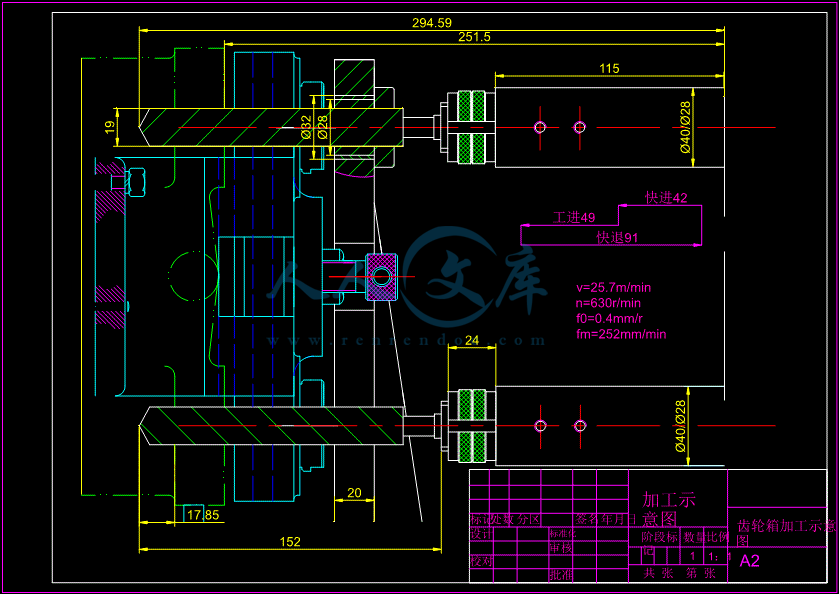
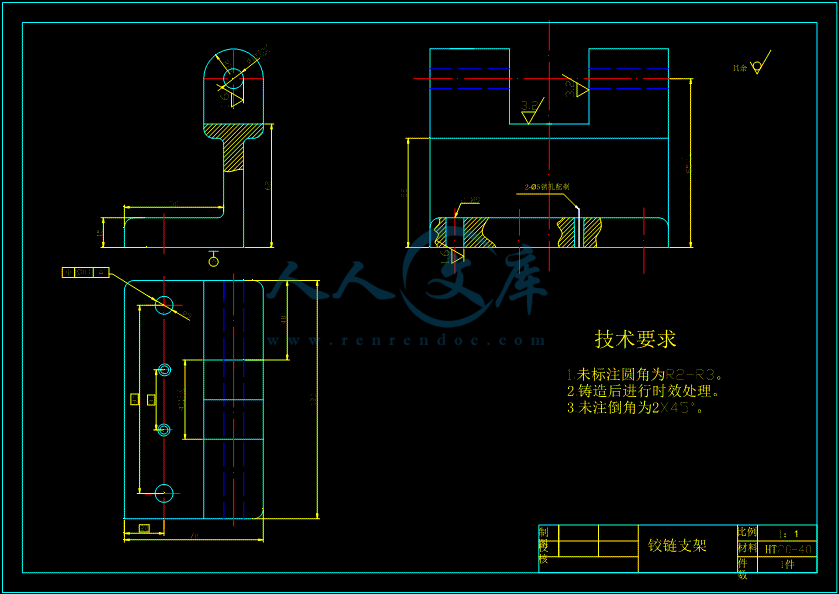
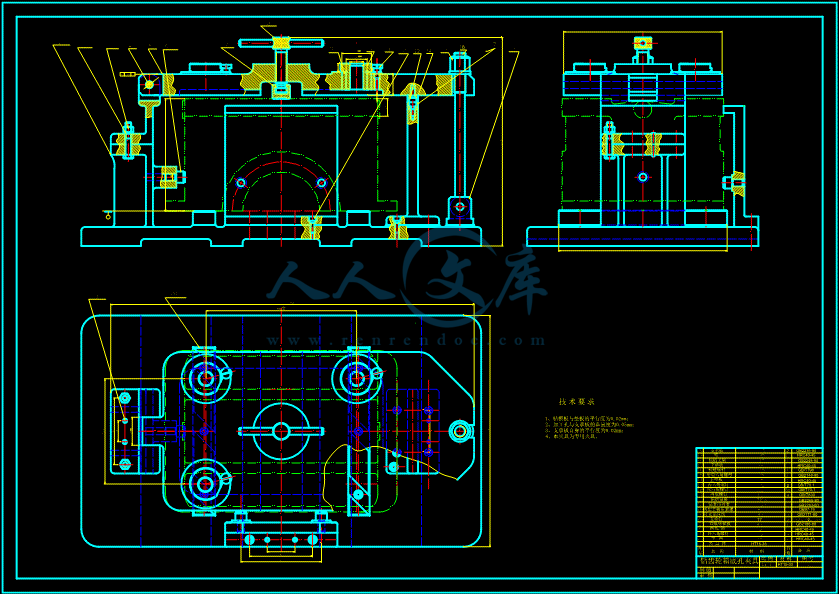
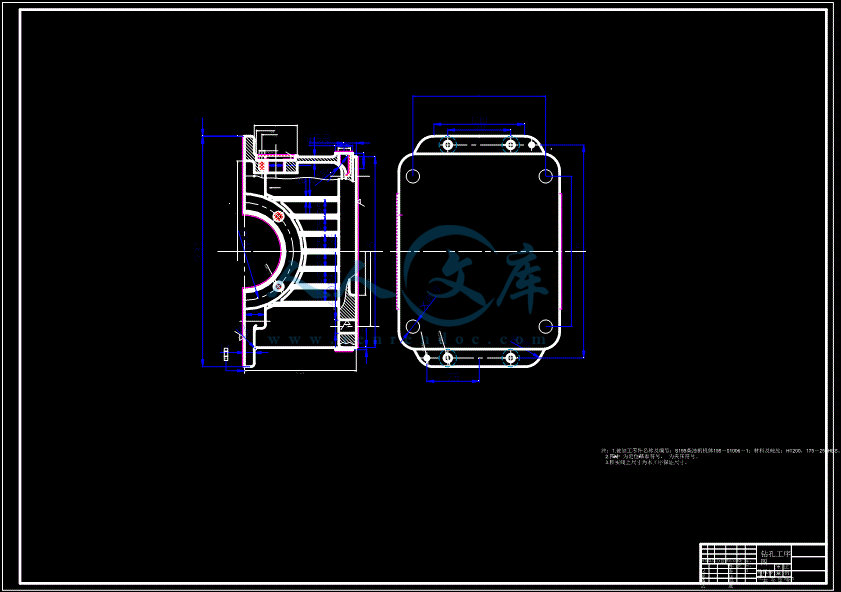
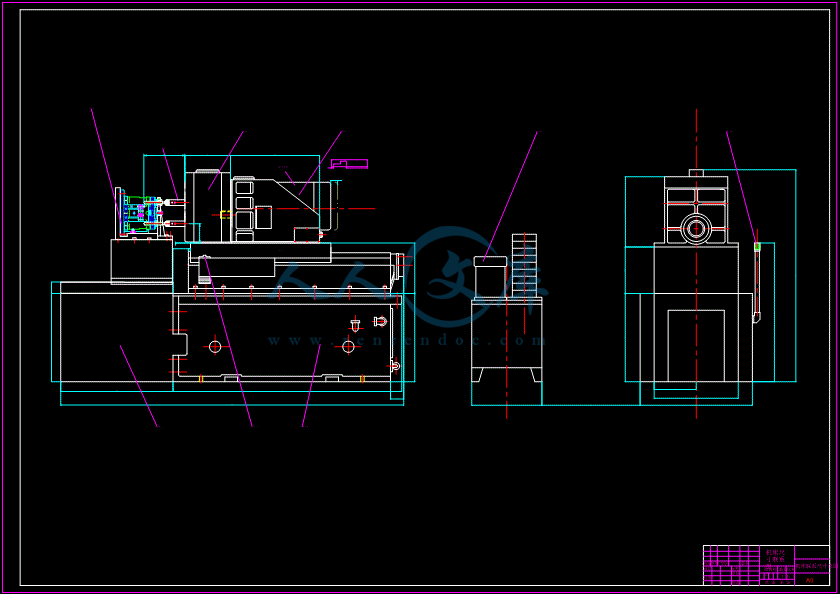
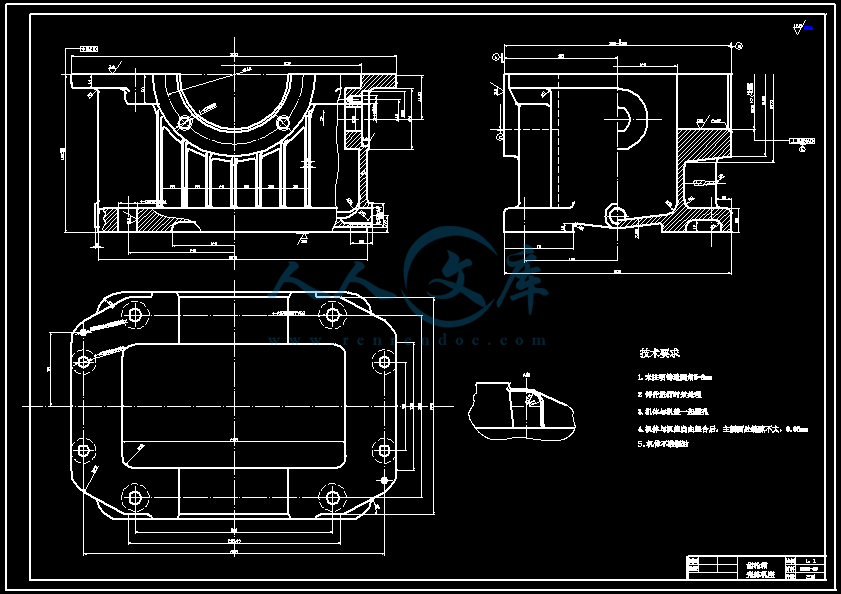



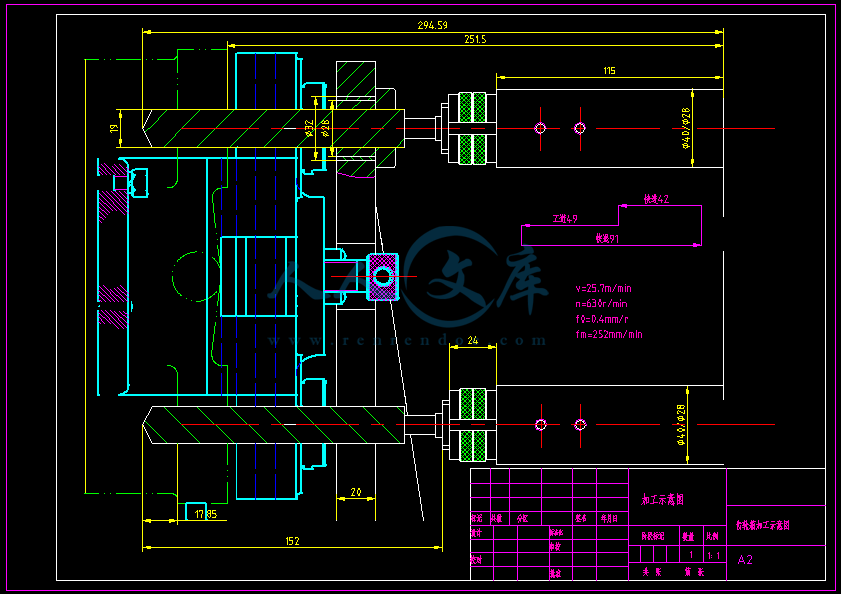
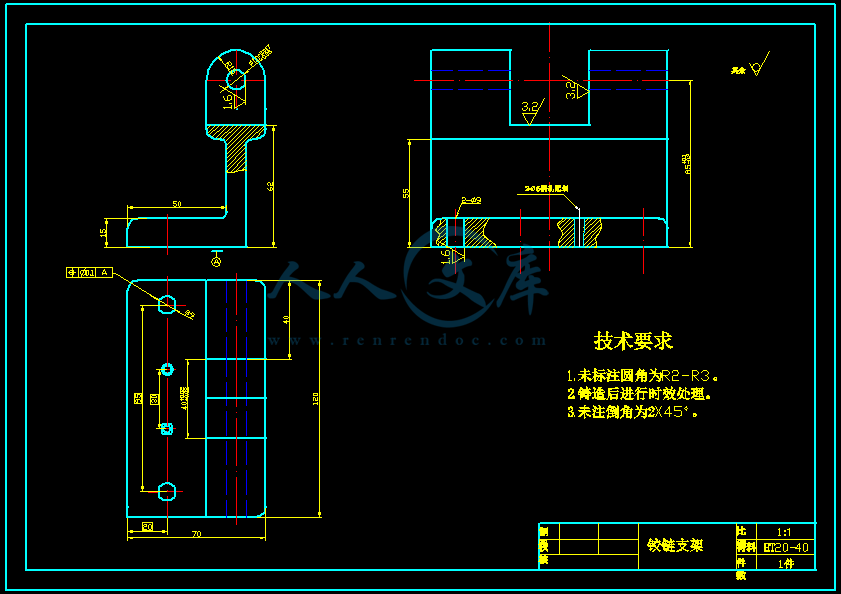















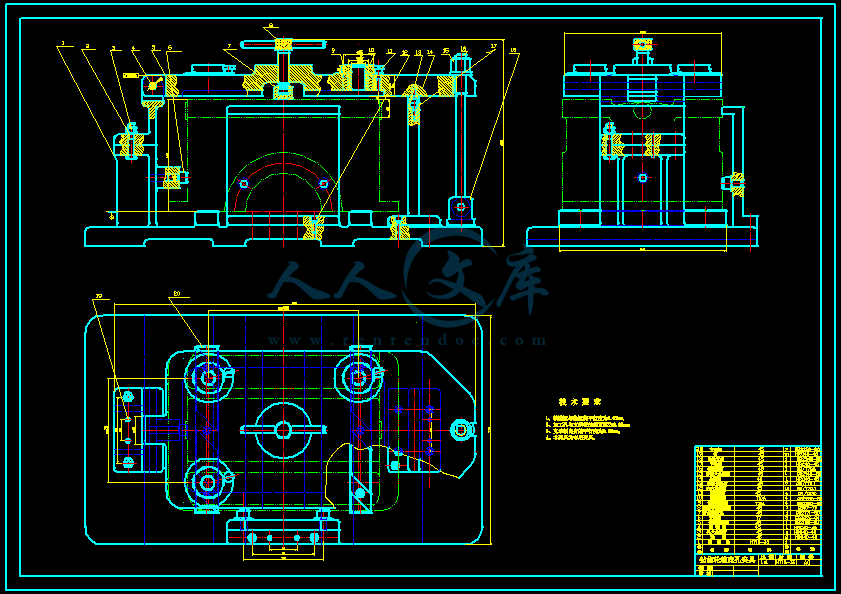
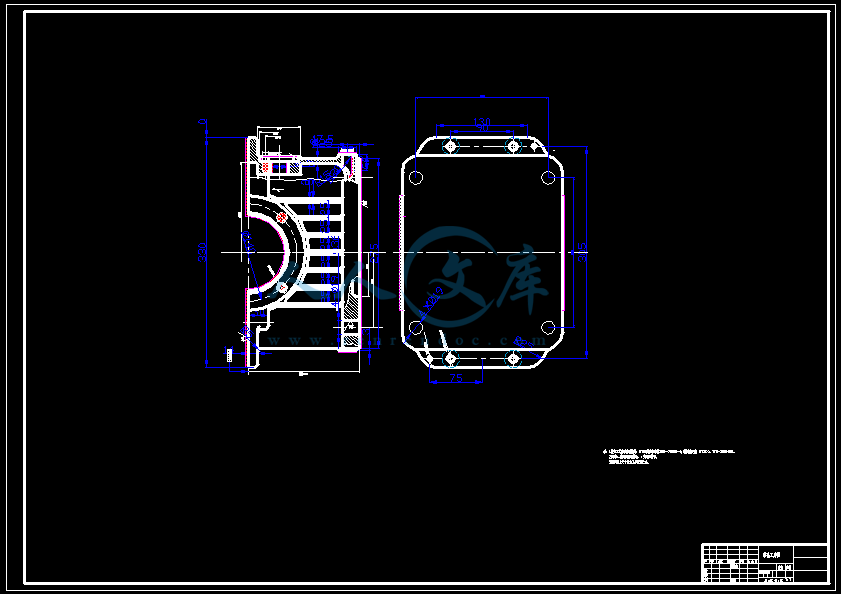
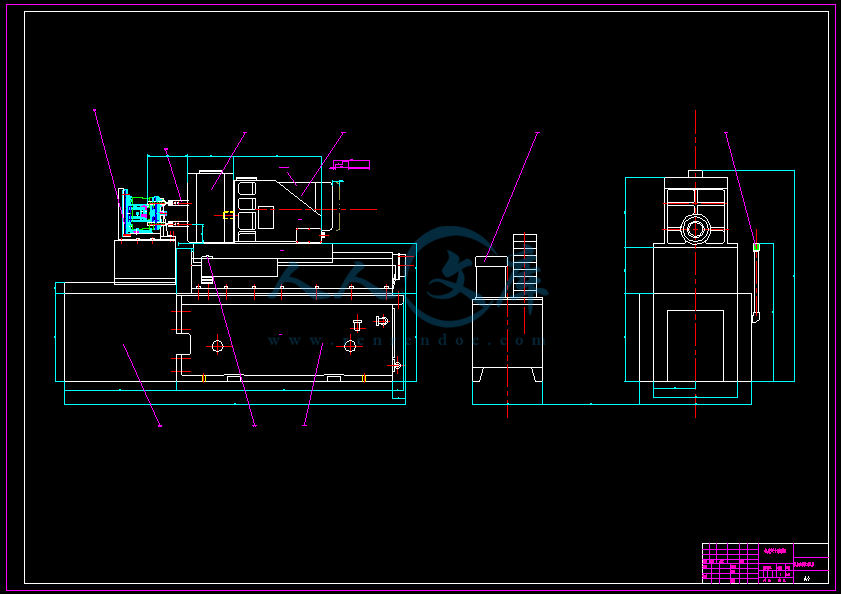
- 内容简介:
-
任 务 书任务书填写要求1毕业设计(论文)任务书由指导教师根据各课题的具体情况填写,经学生所在专业的负责人审查、系(院)领导签字后生效。此任务书应在毕业设计(论文)开始前一周内填好并发给学生。2任务书内容必须用黑墨水笔工整书写,不得涂改或潦草书写;或者按教务处统一设计的电子文档标准格式(可从教务处网页上下载)打印,要求正文小4号宋体,1.5倍行距,禁止打印在其它纸上剪贴。3任务书内填写的内容,必须和学生毕业设计(论文)完成的情况相一致,若有变更,应当经过所在专业及系(院)主管领导审批后方可重新填写。4任务书内有关“学院”、“专业”等名称的填写,应写中文全称,不能写数字代码。学生的“学号”要写全号,不能只写最后2位或1位数字。 5任务书内“主要参考文献”的填写,应按照金陵科技学院本科毕业设计(论文)撰写规范的要求书写。6有关年月日等日期的填写,应当按照国标GB/T 740894数据元和交换格式、信息交换、日期和时间表示法规定的要求,一律用阿拉伯数字书写。如“2002年4月2日”或“2002-04-02”。毕 业 设 计(论 文)任 务 书1本毕业设计(论文)课题应达到的目的: 本设计课题旨在解决箱体类零件在大批量生产中的生产技术问题,是符合机械专业特点的设计课题,该课题完成的过程,将比较全面地覆盖机械类本科专业在校期间所学的技术基础知识和专业知识,培养学生综合运用所学基础理论、专业知识和各项技能进行设计、分析和解决工程实际问题的能力,是对学生综合素质与工程实践能力的全面检验。 2本毕业设计(论文)课题任务的内容和要求(包括原始数据、技术要求、工作要求等): 本课题要求学生完成壳体零件工艺规程的编制,并设计多孔钻削组合机床。具体内容及要求如下:(1)查阅文献资料15篇以上,翻译外文资料3000字,撰写文献综述和开题报告;(2)零件结构分析,画零件图(A3图纸);(3)编制零件工艺流程简卡;(4)机床总体设计,绘制三图一卡及主要零件图(A0图纸);(5)必要的设计计算与分析;(6)文档整理、撰写毕业设计说明书及使用说明书。有关技术要求如下:(1)生产纲领:年产5万件;生产方式:单班制,半自动操作;生产线各工序节拍一致。(2)具体尺寸及技术要求见零件图 毕 业 设 计(论 文)任 务 书3对本毕业设计(论文)课题成果的要求包括图表、实物等硬件要求: 开题报告一份专业文献中英文翻译一份机床联系尺寸图A0一张生产率计算卡一张加工示意图一张零件图若干设计计算说明书一份。以上均需电子稿与打印稿 4主要参考文献: 1机床夹具设计手册(第二版)M.北京:机械工业出版社,2000-82机械工艺人员手册M.北京:机械工业出版社,1986-83成大仙.机械设计手册(第四版 第4卷).北京:化学工业出版社2002-14沈鸿.机械工程手册(第5卷)M.北京:机械工业出版社,1982-35刘震北.液压元件制造工艺学M.哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,1992-126大连机床研究所.组合机床设计M.北京:机械工业出版社,1966-17杨培元,朱福元.液压系统设计简明手册M.北京:机械工业出版社,1999.128徐灏.机械设计手册(第二版 第3卷)M.北京:机械工业出版社,2000-6,9吴宗泽.机械设计课程设计手册(第二版)M.北京:高等教育出版社,199910王先逵.机械制造工艺学M.北京:机械工业出版社,2004-511周冀平,林岗,等.机械制造自动化技术M.北京:机械工业出版社, 2007.12顾冠群,万得钧.机电一体化设计手册M.南京:江苏科技出版社,1996.13冯辛安主编.机械制造装备设计M.北京:机械工业出版社,2006.14陈发任主编.现代组合机床的发展趋势M.重庆:重庆大学出版社,1993.15韦彦成.组合机床设备改装M.北京:国防工业出版社,1995.16谢家瀛.组合机床设计简明手册M.北京:机械工业出版社,1994. 毕 业 设 计(论 文)任 务 书5本毕业设计(论文)课题工作进度计划:20xx.12.16-20xx.1.10 领任务书、开题20xx.2.25- 毕业实习调研,完成开题报告、中英文翻译、论文大纲20xx.3.19-20xx.4.25 提交论文草稿,4月中旬中期检查20xx.4.26-20xx.5.6 提交论文定稿20xx.5.6-20xx.5.13 准备答辩20xx.5.13-20xx.5.26 答辩,成绩评定,修改完成最终稿 所在专业审查意见:通过负责人: 20xx 年 12 月25 日 毕 业 设 计(论 文)外 文 参 考 资 料 及 译 文译文题目:Failure Analysis,Dimensional Determination And Analysis,Applications Of Cams 故障的分析、尺寸的决定以及凸轮的分析和应用 学生姓名: 轩 学号: 专业: 所在学院: 指导教师: 职称: 年 01月 20日说明:要求学生结合毕业设计(论文)课题参阅一篇以上的外文资料,并翻译至少一万印刷符(或译出3千汉字)以上的译文。译文原则上要求打印(如手写,一律用400字方格稿纸书写),连同学校提供的统一封面及英文原文装订,于毕业设计(论文)工作开始后2周内完成,作为成绩考核的一部分。Failure Analysis,Dimensional Determination And Analysis,Applications Of CamsINTRODUCTIONIt is absolutely essential that a design engineer know how and why parts fail so that reliable machines that require minimum maintenance can be designedSometimes a failure can be serious,such as when a tire blows out on an automobile traveling at high speedOn the other hand,a failure may be no more than a nuisanceAn example is the loosening of the radiator hose in an automobile cooling systemThe consequence of this latter failure is usually the loss of some radiator coolant,a condition that is readily detected and correctedThe type of load a part absorbs is just as significant as the magnitudeGenerally speaking,dynamic loads with direction reversals cause greater difficulty than static loads,and therefore,fatigue strength must be consideredAnother concern is whether the material is ductile or brittleFor example,brittle materials are considered to be unacceptable where fatigue is involvedMany people mistakingly interpret the word failure to mean the actual breakage of a partHowever,a design engineer must consider a broader understanding of what appreciable deformation occursA ductile material,however will deform a large amount prior to ruptureExcessive deformation,without fracture,may cause a machine to fail because the deformed part interferes with a moving second partTherefore,a part fails(even if it has not physically broken)whenever it no longer fulfills its required functionSometimes failure may be due to abnormal friction or vibration between two mating partsFailure also may be due to a phenomenon called creep,which is the plastic flow of a material under load at elevated temperaturesIn addition,the actual shape of a part may be responsible for failureFor example,stress concentrations due to sudden changes in contour must be taken into accountEvaluation of stress considerations is especially important when there are dynamic loads with direction reversals and the material is not very ductileIn general,the design engineer must consider all possible modes of failure,which include the followingStressDeformationWearCorrosionVibrationEnvironmental damageLoosening of fastening devicesThe part sizes and shapes selected also must take into account many dimensional factors that produce external load effects,such as geometric discontinuities,residual stresses due to forming of desired contours,and the application of interference fit jointsCams are among the most versatile mechanisms availableA cam is a simple two-member deviceThe input member is the cam itself,while the output member is called the followerThrough the use of cams,a simple input motion can be modified into almost any conceivable output motion that is desiredSome of the common applications of cams areCamshaft and distributor shaft of automotive engineProduction machine toolsAutomatic record playersPrinting machinesAutomatic washing machinesAutomatic dishwashersThe contour of high-speed cams (cam speed in excess of 1000 rpm) must be determined mathematicallyHowever,the vast majority of cams operate at low speeds(less than 500 rpm) or medium-speed cams can be determined graphically using a large-scale layoutIn general,the greater the cam speed and output load,the greater must be the precision with which the cam contour is machinedDESIGN PROPERTIES OF MATERIALSThe following design properties of materials are defined as they relate to the tensile testFigure 2.7Static StrengthThe strength of a part is the maximum stress that the part can sustain without losing its ability to perform its required functionThus the static strength may be considered to be approximately equal to the proportional limit,since no plastic deformation takes place and no damage theoretically is done to the materialStiffnessStiffness is the deformation-resisting property of a materialThe slope of the modulus line and,hence,the modulus of elasticity are measures of the stiffness of a materialResilienceResilience is the property of a material that permits it to absorb energy without permanent deformationThe amount of energy absorbed is represented by the area underneath the stress-strain diagram within the elastic regionToughnessResilience and toughness are similar propertiesHowever,toughness is the ability to absorb energy without ruptureThus toughness is represented by the total area underneath the stress-strain diagram, as depicted in Figure 28bObviously,the toughness and resilience of brittle materials are very low and are approximately equalBrittlenessA brittle material is one that ruptures before any appreciable plastic deformation takes placeBrittle materials are generally considered undesirable for machine components because they are unable to yield locally at locations of high stress because of geometric stress raisers such as shoulders,holes,notches,or keywaysDuctilityA ductility material exhibits a large amount of plastic deformation prior to ruptureDuctility is measured by the percent of area and percent elongation of a part loaded to ruptureA 5%elongation at rupture is considered to be the dividing line between ductile and brittle materialsMalleabilityMalleability is essentially a measure of the compressive ductility of a material and,as such,is an important characteristic of metals that are to be rolled into sheetsFigure 2.8HardnessThe hardness of a material is its ability to resist indentation or scratchingGenerally speaking,the harder a material,the more brittle it is and,hence,the less resilientAlso,the ultimate strength of a material is roughly proportional to its hardnessMachinabilityMachinability is a measure of the relative ease with which a material can be machinedIn general,the harder the material,the more difficult it is to machineCOMPRESSION AND SHEAR STATIC STRENGTHIn addition to the tensile tests,there are other types of static load testing that provide valuable informationCompression TestingMost ductile materials have approximately the same properties in compression as in tensionThe ultimate strength,however,can not be evaluated for compressionAs a ductile specimen flows plastically in compression,the material bulges out,but there is no physical rupture as is the case in tensionTherefore,a ductile material fails in compression as a result of deformation,not stressTemperature can affect the mechanical properties of metalsIncreases in temperature may cause a metal to expand and creep and may reduce its yield strength and its modulus of elasticityIf most metals are not allowed to expand or contract with a change in temperature,then stresses are set up that may be added to the stresses from the loadThis phenomenon is useful in assembling parts by means of interference fitsA hub or ring has an inside diameter slightly smaller than the mating shaft or postThe hub is then heated so that it expands enough to slip over the shaftWhen it cools,it exerts a pressure on the shaft resulting in a strong frictional force that prevents loosening故障的分析、尺寸的决定以及凸轮的分析和应用前言介绍:作为一名设计工程师有必要知道零件如何发生和为什么会发生故障,以便通过进行最低限度的维修以保证机器的可靠性。有时一次零件的故障或者失效可能是很严重的一件事情,比如,当一辆汽车正在高速行驶的时候,突然汽车的轮胎发生爆炸等。另一方面,一个零件发生故障也可能只是一件微不足道的小事,只是给你造成了一点小麻烦。一个例子是在一个汽车冷却系统里的暖气装置软管的松动。后者发生的这次故障造成的结果通常只不过是一些暖气装置里冷却剂的损失,是一种很容易被发现并且被改正的情况。能够被零件进行吸收的载荷是相当重要的。一般说来,与静载重相比较,有两个相反方向的动载荷将会引起更大的问题,因此,疲劳强度必须被考虑。另一个关键是材料是可延展性的还是脆性的。例如,脆的材料被认为在存在疲劳的地方是不能够被使用的。很多人错误的把一个零件发生故障或者失效理解成这样就意味着一个零件遭到了实际的物理破损。无论如何,一名设计工程师必须从一个更广泛的范围来考虑和理解变形是究竟如何发生的。一种具有延展性的材料,在破裂之前必将发生很大程度的变形。发生了过度的变形,但并没有产生裂缝,也可能会引起一台机器出毛病,因为发生畸变的零件会干扰下一个零件的移动。因此,每当它不能够再履行它要求达到的性能的时候,一个零件就都算是被毁坏了(即使它的表面没有被损毁)。有时故障可能是由于两个两个相互搭配的零件之间的不正常的磨擦或者异常的振动引起的。故障也可能是由一种叫蠕变的现象引起的,这种现象是指金属在高温下时一种材料的塑性流动。此外,一个零件的实际形状可能会引起故障的发生。例如,应力的集中可能就是由于轮廓的突然变化引起的,这一点也需要被考虑到。当有用两个相反方向的动载荷,材料不具有很好的可延展性时,对应力考虑的评估就特别重要。一般说来,设计工程师必须考虑故障可能发生的全部方式,包括如下一些方面:压力变形磨损腐蚀振动环境破坏固定设备松动在选择零件的大小与形状的时候,也必须考虑到一些可能会产生外部负载影响的空间因素,例如几何学间断性,为了达到要求的外形轮廓及使用相关的连接件,也会产生相应的残余应力。凸轮是被应用的最广泛的机械结构之一。凸轮是一种仅仅有两个组件构成的设备。主动件本身就是凸轮,而输出件被称为从动件。通过使用凸轮,一个简单的输入动作可以被修改成几乎可以想像得到的任何输出运动。常见的一些关于凸轮应用的例子有:凸轮轴和汽车发动机工程的装配专用机床自动电唱机印刷机自动的洗衣机自动的洗碗机高速凸轮(凸轮超过1000 rpm的速度)的轮廓必须从数学意义上来定义。无论如何,大多数凸轮以低速(少于500 rpm)运行而中速的凸轮可以通过一个大比例的图形表示出来。一般说来,凸轮的速度和输出负载越大,凸轮的轮廓在被床上被加工时就一定要更加精密。材料的设计属性当他们与抗拉的试验有关时,材料的下列设计特性被定义如下。静强度:一个零件的强度是指零件在不会失去它被要求的能力的前提下能够承受的最大应力。因此静强度可以被认为是大约等于比例极限,从理论上来说,我们可以认为在这种情况下,材料没有发生塑性变形和物理破坏。刚度:刚度是指材料抵抗变形的一种属性。这条斜的模数线以及弹性模数是一种衡量材料的刚度的一种方法。弹性:弹性是指零件能够吸收能量但并没有发生永久变形的一种材料的属性。吸收的能量的多少可以通过下面弹性区域内的应力图表来描述出来。韧性:韧性和弹性是两种相似的特性。无论如何,韧性是一种可以吸收能量并且不会发生破裂的能力。因此可以通过应力图里面的总面积来描述韧性,就像用图2.8 b 描绘的那样。显而易见,脆性材料的韧性和弹性非常低,并且大约相等。脆性:一种脆性的材料就是指在任何可以被看出来的塑性变形之前就发生破裂的材料。脆性的材料一般被认为不适合用来做机床的零部件,因为当遇到由轴肩,孔,槽,或者键槽等几何应力集中源引起的高的应力时,脆性材料是无法来产生局部屈服的现象以适应高的应力环境的。延展性:一种延展性材料会在破裂之前表现出很大程度上的塑性变形现象。延展性是通过可延展的零件在发生破裂前后的面积和长度的百分比来测量的。一个在发生破裂的零件,其伸长量如果为5%,则认为该伸长量就是可延展性和脆性材料分界线。可锻性:可锻性从根本上来说是指材料的一种在承受挤压或压缩是可以发生塑性变形的能力,同时,它也是一种在金属被滚压成钢板时所需金属的重要性能。硬度:一种材料的硬度是指它抵抗挤压或者拉伸它的能力。一般说来,材料越硬,它的脆性也越大,因此,弹性越小。同样,一种材料的极限强度粗略与它的硬度成正比。机械加工性能(或切削性):机械加工性能是指材料的一种容易被加工的性能。通常,材料越硬,越难以加工。压应力和剪应力除抗拉的试验之外,还有其它一些可以提供有用信息的静载荷的实验类型。压缩测试:大多数可延展材料大约有相同特性,当它们处于受压状态的紧张状态时。极限强度,无论如何,不能够被用于评价压力状态。当一件具有可延展性的样品受压发生塑性变形时,材料的其它部分会凸出来,但是在这种紧张的状态下,材料通常不会发生物理上的破裂。因此,一种可延展的材料通常是由于变形受压而损坏的,并不是压力的原因。剪应力测试:轴,螺钉,铆钉和焊接件被用这样一种方式定位以致于生产了剪应力。一张抗拉试验的试验图纸就可以说明问题。当压力大到可以使材料发生永久变形或发生破坏时,这时的压力就被定义为极限剪切强度。极限剪切强度,无论如何,不等于处于紧张状态的极限强度。例如,以钢的材料为例,最后的剪切强度是处于紧张状态大约极限强度的75%。当在机器零部件里遇到剪应力时,这个差别就一定要考虑到了。动力载荷不会在各种不同的形式的力之间不停发生变化的作用力被叫作静载荷或者稳定载荷。此外,我们通常也把很少发生变化的作用力叫作静载荷。在拉伸实验中,被分次、逐渐的加载的作用力也被叫作静载荷。冲击载荷:这类载荷是由于冲击作用产生的。一个例子就是一台升降机坠落到位于通道底部的一套弹簧装置上,这套装置产生的力会比升降机本身的重量大上好几倍。当汽车的一个轮胎碰撞到道路上的一个突起或者路上的一个洞时,相同的冲击荷载的类型也会在汽车的减震器弹簧上发生。 温度对屈服强度和弹性模数的影响一般说来,当在说明一种拥有特殊的属性的材料时,如弹性模数和屈服强度,表示这些性能在室温环境下就可以存在。在低的或者较高的温度下,材料的特性可能会有很大的不同。例如,很多金属在低温时会变得更脆。此外,当温度升高时,材料的弹性模数和屈服强度都会变差。图2.23 显示了低碳钢的屈服强度在从室温升高到1000oC过程中被降低了大约70%。当温度升高时,图2.24显示了低碳钢在弹性模数E方面的削减。正如从图上可以看见的那样,弹性模数在从室温升高到1000oC过程中大约降低了30%。从这张图表中,我们也能看到在室温下承受了一定载荷而不会发生变形的零件却可能在高温时承受相同载荷时发生永久变形。蠕变: 一种塑性变形的现象由于温度效应的影响,金属中产生了一种被称为蠕变的现象,一个承受了一定的载荷的零件的塑性变形是按照一个时间函数来逐渐增加的。蠕变现象在室温的条件下也是存在的,但它发生的过程是如此之慢,以致于很少变得像在预期寿命中温度被升高到300oC或更多时那样显著,逐渐增加的塑性变形可能在一段短的时期内变得很明显。材料的抗蠕变强度是指材料抵抗蠕变的属性,并且抗蠕变强度的数据可以通过处理长期的蠕变试验(模拟实际零件的操作条件)来获得。在试验的过程中,给定的材料在规定的温度下的塑性应变被被进行了实时监控。由于蠕变是一种塑性变形现象,发生了蠕变的零件的尺寸可能就会被永久的改变。因此,如果一个零件是在很强的强度下运转的话,那么设计工程师必须精确地预言将在机器的使用寿命期间可能发生的蠕变的次数。否则,与此伴随的或者相关的问题就可能发生。在高温下,当螺栓被用来紧固零件时,蠕变就可能变成一个必须解决的问题。处在压力状态下的螺钉,蠕变是按照一个时间函数来发生的。因为变形是塑性的,夹紧力的损失将可能导致螺纹连接件的意外松动。像这种特殊的现象,通常被称为松弛,我们可以通过进行适当的蠕变强度时测试来确定是不是发生了蠕变。总结机器设计者必须理解进行抗拉的静止强度的测试目的。这种试验可以确定被在设计方程式过程中使用的许多金属的机械特性。像弹性模数,比例极限,屈服强度,弹性,以及延展性等等可以根据抗拉试验来决定它们的特性。温度能影响金属的机械特性。温度的增加可能会引起金属的热胀和蠕变,并且还可能降低它的屈服强度和它的弹性模数。如果大多数金属不被允许在温度发生变化时发生膨胀或者收缩,那么压力就会被当做载荷来看待。这现象在依靠干涉配合来进行零件装配时是有益的。一个毂或者孔的内径比与它相配的轴或者圆柱的直径小一点。先将毂加热后,由于热胀冷缩,此时可以轻松的将轴插入其中。当它冷却以后,同样由于热胀冷缩,它的内孔直径会变小,从而对插入其中的轴产生了很大的摩擦力,有效的防止了轴的松动。TheAggregateMachine-toolTheAggregateMachine-toolisbasedontheworkpieceneeds,basedonalargenumberofcommoncomponents,combinedwithasemi-automaticorautomaticmachinewithasmallnumberofdedicatedspecialcomponentsandprocessaccordingtotheworkpieceshapeanddesignofspecialpartsandfixtures,composed.Combinationmachineisgenerallyacombinationofthebase,slide,fixture,powerboxes,multi-axle,tools,etc.From.Combinationmachinehasthefollowingadvantages:(1)ismainlyusedforprismpartsandothermiscellaneouspiecesofperforatedsurfaceprocessing.(2)highproductivity.Becausetheprocessofconcentration,canbemulti-faceted,multi-site,multi-axis,multi-toolsimultaneousmachining.(3)precisionandstability.Becausetheprocessisfixed,thechoiceofamaturegenericparts,precisionfixturesandautomaticworkingcycletoensureconsistentprocessingaccuracy.(4)thedevelopmentcycleisshort,easytodesign,manufactureandmaintenance,andlowcost.BecauseGM,serialization,highdegreeofstandardization,commonpartscanbepre-manufacturedormassorganizationsoutsourcing.(5)ahighdegreeofautomation,lowlaborintensity.(6)flexibleconfiguration.Becausethestructureisacross-piece,combination.Inaccordancewiththeworkpieceorprocessrequirements,withplentyofcommonpartsandafewspecialcomponentsconsistingofvarioustypesofflexiblecombinationofmachinetoolsandautomaticlines;toolstofacilitatemodification:theproductorprocesschanges,thegeneralalsocommoncomponentscanbereused.Combinationofbox-typedrillinggenerallyusedforprocessingorspecialshapeparts.Duringmachining,theworkpieceisgenerallynotrotate,therotationalmotionofthetoolrelativetotheworkpieceandtoolfeedmovementtoachievedrilling,reaming,countersinking,reaming,boringandotherprocessing.Somecombinationofturningheadclamptheworkpieceusingthemachinetomaketherotation,thetoolforthefeedmotion,butalsoonsomeoftherotatingparts(suchastheflywheel,theautomobileaxleshaft,etc.)ofcylindricalandfaceprocessing.Generallyuseacombinationofmulti-axismachinetools,multi-tool,multi-process,multi-facetedormulti-stationmachiningmethodssimultaneously,productivityincreasedmanytimesmorethangenerictools.Sincethecommoncomponentshavebeenstandardizedandserialized,socanbeflexiblyconfiguredaccordingtoneed,youcanshortenthedesignandmanufacturingcycle.Multi-axlecombinationisthecorecomponentsofgeneralmachinetools.Itisthechoiceofgenericparts,isdesignedaccordingtospecialrequirements,incombinationmachinedesignprocess,isonecomponentofalargerworkload.Itisbasedonthenumberandlocationofthemachiningprocessdiagramandschematicdesigncombinationmachineworkpiecedeterminedbythehole,cuttingtheamountofpowertransmissioncomponentsandthedesignofeachspindlespindletypemovement.Multi-axlepowerfromacommonpowerbox,togetherwiththepowerboxinstalledonthefeedslide,tobecompletedbydrilling,reamingandothermachiningprocesses.Thepartstobeprocessedaccordingtothesizeofmulti-axleboxcombinationmachinetooldesign,basedonanoriginaldrawingmulti-axlediagram,determinetherangeofdesigndata,theabovedesign,implementation,completionofatwo-sided24-holemachining,achievebetterthedesignrequirements.InordertoadapttothedevelopmentofCNCmachinetoolsincombination,appearedcomposedofCNCmachinetoolsCNCmachiningmodules.Modularistheresultofacombinationofmachinetoolnumericalcontrolmachinetoolcombinationbrings,butalsothebasisofacombinationofCNCmachinetools,CNCmachiningenrichedtheuniversalmodularcombinationofcomponentsofthemachine,itwillcauseafundamentalpieceformachinetooltypechanges.Overthepastdecade,thecombinationofmachinetoolsandautomaticlinehasmadegreatstridesinefficiency,productivity,flexibilityandtheuseofconcurrentengineeringtodevelopamorerational,moresavingsprograms.Withthedevelopmentofdigitaltechnology,electronictechnology,thecombinationofmachinemechanicalstructureandcontrolsystemhasundergonegreatchanges.Withacombinationofthefollowingdevelopmenttools:1NC.CombinationofCNCmachinetoolsemerge,notonlychangedinthepastbytherelaycircuitconsistingofacombinationofmachinetoolcontrolsystems,butalsomakeheadorevenacombinationofthemechanicalstructureofthemachinecomponentsofgeneralcriteriahugechangeoccurred.2modular.NCmodulargreatlyenrichedthecommoncombinationofcomponentsofthemachine,itwillcauseafundamentalchangeoccurredformachinetoolparts,accordingtotheprinciplesofmodulardesign,basedonthefunctionalanalysisdivisionofthecombinationofmulti-axleboxforeachmachinelevelmodules.3speed.Asthehigh-speedprocessingcanreducethesurfaceroughnessandcuttingforcecomponents,reducingthecuttingtemperature,improveproductivity,sothespeedofthemachineisjustbeginningresearch,especiallythemainmovementofCNCmachinetoolsandfeedvelocityhasreachedaveryhighspeed.Conformtothetrendofhigh-speedmachinetools,machinetoolsspeedwillbehigher.4,precision.BecausetheCNCmachinetoachieve,somoreandmorehig
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号