具有空间运动能力的产品输送机械手的机械结构设计
36页 17000字数+说明书+开题报告+任务书+答辩PPT+文献翻译+11张CAD图纸
中期检查表.doc
传动轴.dwg
传动轴底部端盖.dwg
具有空间运动能力的产品输送机械手的机械结构设计开题报告.doc
具有空间运动能力的产品输送机械手的机械结构设计答辩PPT.ppt
具有空间运动能力的产品输送机械手的机械结构设计论文.doc
导向套.dwg
导向杆前支架.dwg
底座.dwg
底座上端盖.dwg
底座转盘.dwg
支承端盖.dwg
文献翻译--工业机器人.doc
机械手手爪.dwg
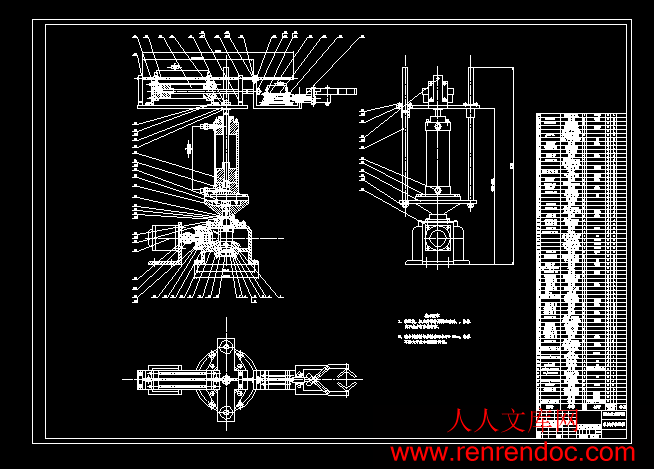
机械手装配图.dwg
齿轮轴.dwg
工业机器人
摘要
在当今大规模制造业中,企业为提高生产效率,保障产品质量,普遍重视生产过程的自动化程度,工业机器人作为自动化生产线上的重要成员,逐渐被企业所认同并采用。工业机器人的技术水平和应用程度在一定程度上反映了一个国家工业自动化的水平,目前,工业机器人主要承担着焊接、喷涂、搬运以及堆垛等重复性并且劳动强度极大的工作,工作方式一般采取示教再现的方式。
本文将设计一台三自由度的工业机器人,用于给输送产品。首先,本文将设计机器人的机械手爪、手臂、腰部和基座的设计,然后选择合适的传动方式、驱动方式,搭建机器人的结构平台;在此基础上,本文将设计该机器人的驱动控制系统,包括驱动方式和电机的选择、反馈方式和反馈元件的选择、端子板电路的设计以及控制软件的设计,重点加强控制软件的可靠性和机器人运行过程的安全性,最终实现的目标包括:关节的伺服控制和制动问题、实时监测机器人的各个关节的运动情况、机器人的示教编程和在线修改程序、设置参考点和回参考点。
关键词:机器人,示教编程,伺服,制动
目录
1 绪论…………………………………………………………………(1)
1.1工业机器人简介………………………………………………………… (1)
1.2工业机器人的发展……………………………………………………… (3)
1.3课题的提出、意义及主要任务………………………………………… (4)
2 工业机器人的总体设计……………………………………………(5)
2.1工业机器人的组成及各部分关系概述………………………………… (5)
2.1.1执行系统………………………………………………………… (5)
2.1.2驱动系统………………………………………………………… (5)
2.1.3控制系统………………………………………………………… (6)
2.1.4检测系统………………………………………………………… (6)
2.2工业机器人的设计分析………………………………………………… (6)
2.2.1设计要求………………………………………………………… (6)
2.2.2工业机器人主要技术参数……………………………………… (7)
2.3 机器人的运动概述………………………………………………………(7)
2.3.1工业机器人的运动自由度……………………………………… (8)
2.3.2 机器人的工作空间和机械结构类型……………………………(8)
2.3.3 机器人的运动过程分析 ……………………………………… (9)
2.4原理方案的拟定………………………………………………………… (9)
2.4.1原理方案的选择………………………………………………… (9)
2.4.2原理方案的确定…………………………………………………(10)
3 工业机器人机械子系统的设计………………………………… (11)
3.1机械手手爪的设计………………………………………………………(11)
3.1.1设计时要注意的问题……………………………………………(11)
3.1.2总体结构设计……………………………………………………(11)
3.1.3气缸的选择和夹紧力的校验……………………………………(12)
3.1.4弹性爪的强度校验………………………………………………(13)
3.2手臂机构的设计…………………………………………………………(14)
3.2.1手臂的设计要求…………………………………………………(14)
3.2.2手臂机械结构设计………………………………………………(14)
3.2.3伸缩气缸的选择…………………………………………………(15)
3.2.4活塞杆的强度校核………………………………………………(15)
3.3腰部和基座设计…………………………………………………………(17)
3.3.1结构设计…………………………………………………………(17)
3.3.2升降气缸的选择…………………………………………………(18)
3.3.3步进电机的选择 ……………………………………………… (18)
3.3.4连轴器的选择……………………………………………………(21)
3.3.5 轴承的选取………………………………………………………(22)
3.3.6齿轮的选择………………………………………………………(24)
4 工业机器人气动系统的设计…………………………………… (25)
4.1气动系统的概述…………………………………………………………(25)
4.2气动系统的分析与设计…………………………………………………(25)
5 工业机器人运行时应采取的安全措施………………………… (27)
5.1安全要求…………………………………………………………………(27)
5.2实施方法…………………………………………………………………(28)
总结………………………………………………………………… (28)
致谢………………………………………………………………… (29)
参考文献…………………………………………………………… (30)
1.3课题的提出、意义及主要任务
机械手是在自动化生产过程中使用的一种具有抓取和移动工件功能的自动化装置,它是在机械化、自动化生产过程中发展起来的一种新型装置。近年来,随着电子技术特别是电子计算机的广泛应用,机器人的研制和生产已成为高技术领域内迅速发展起来的一门新兴技术,它更加促进了机械手的发展,使得机械手能更好地实现与机械化和自动化的有机结合。机械手能代替人类完成危险、重复枯燥的工作,减轻人类劳动强度,提高劳动生产力。机械手越来越广泛的得到了应用,在机械行业中它可用于零部件组装 ,加工工件的搬运、装卸,特别是在自动化数控机床、组合机床上使用更普遍。目前,机械手已发展成为柔性制造系统FMS和柔性制造单元FMC中一个重要组成部分。把机床设备和机械手共同构成一个柔性加工系统或柔性制造单元,它适应于中、小批量生产,可以节省庞大的工件输送装置,结构紧凑,而且适应性很强。当工件变更时,柔性生产系统很容易改变,有利于企业不断更新适销对路的品种,提高产品质量,更好地适应市场竞争的需要。而目前我国的工业机器人技术及其工程应用的水平和国外比还有一定的距离,应用规模和产业化水平低,机械手的研究和开发直接影响到我国自动化生产水平的提高,从经济上、技术上考虑都是十分必要的。因此,进行机械手的研究设计是非常有意义的。
在机械加工过程或者自动化社设备中,常常要求有自动输送和产品装卸功能的机械手来实现辅助作业。本次设计拟定题目为在机械产品加工过程中,能够完成生产线上预定零部件的夹取、输送及其到达预定目的地后放置等动作的自动化机械手系统设计。要求能够设计出满足工业生产要求的典型一体化系统。
此题目重在培养学生在给定任务下的创造性和创造性思维的能力,在预定时间内解决与专业相关的实际问题的的能力,同时培养学生的时间能力和动手能力。
课题中所要设计的主要任务有四点:机械手的原理方案设计、机械手的结构方案设计、机械手的转臂功能的设计、机械手抓取和释放预定产品功能的设计。
2.2.2工业机器人主要技术参数
(1)用途:用于小型零件搬运。
(2)设计技术参数:
a)抓重 5公斤(夹持式手部)
b)3个自由度数(手臂二个自由度, 手腕一个自由度)
c)座标型式
圆柱座标 这种运动形式是通过一个转动,两个移动,共三个自由度组成的运动系统(代号RPP),工作空间图形为圆柱形。它与直角坐标型比较,在相同的工作条件下,机体占体积小,而运动范围大。
d)最大工作半径 920mm(720+200)
e)手臂最大中心高 1200mm
f)手臂运动参数(手臂二个自由度,用一个移动服,一个回转副)
伸缩行程200mm
伸缩速度300mm/s
升降行程200mm
升降速度300mm/s
回转范围00 -2400
回转速度900/s
g)手腕运动参数(手腕一个自由度, 一个回转副)
回转范围 00--1800
回转速度1800/s
h)手指夹持范围
片料:面积不大于0.02㎡(准备设计成正方形)
i)定位精度
士0. 5mm
j)缓冲方式
液压缓冲器
要执行的详细的动作为:(1)定位 (2)抓取(3)提升(4)顺时针转90°(5)前进 6)下降 (7)松开 (8)提升 (9)后退 (10)逆时针转90°(11)下降,完成一个工作循环。
2.3.机器人的运动概述
工业机器人的运动,可从工业机器人的自由度,工作空间和机械结构类型等三方面来讨论。
工业机器人机构的简图
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号