矿井提升机总体结构设计
82页 20000字数+说明书+中期报告+开题报告+外文翻译+7张CAD图纸
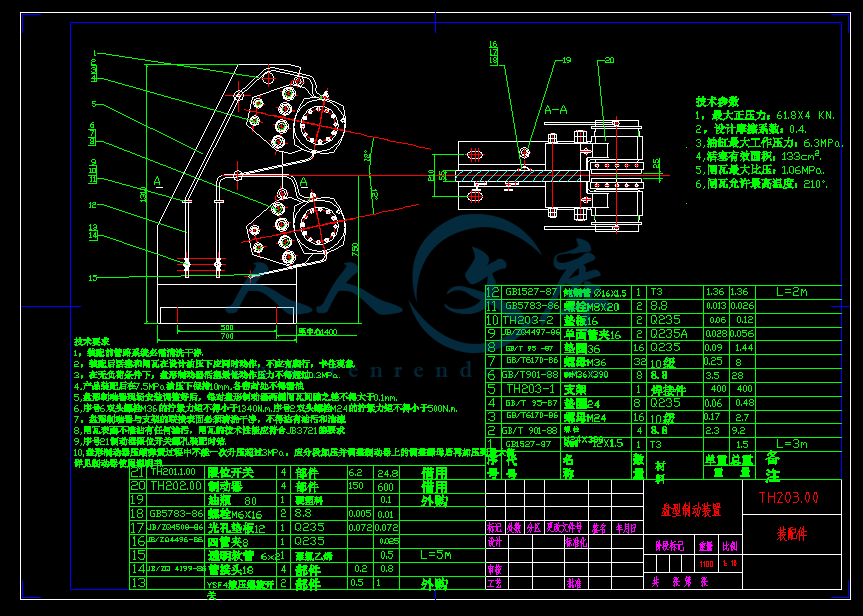
TH203制动装置A2.dwg
中期报告.doc
减速器中间轴大齿轮A2.dwg
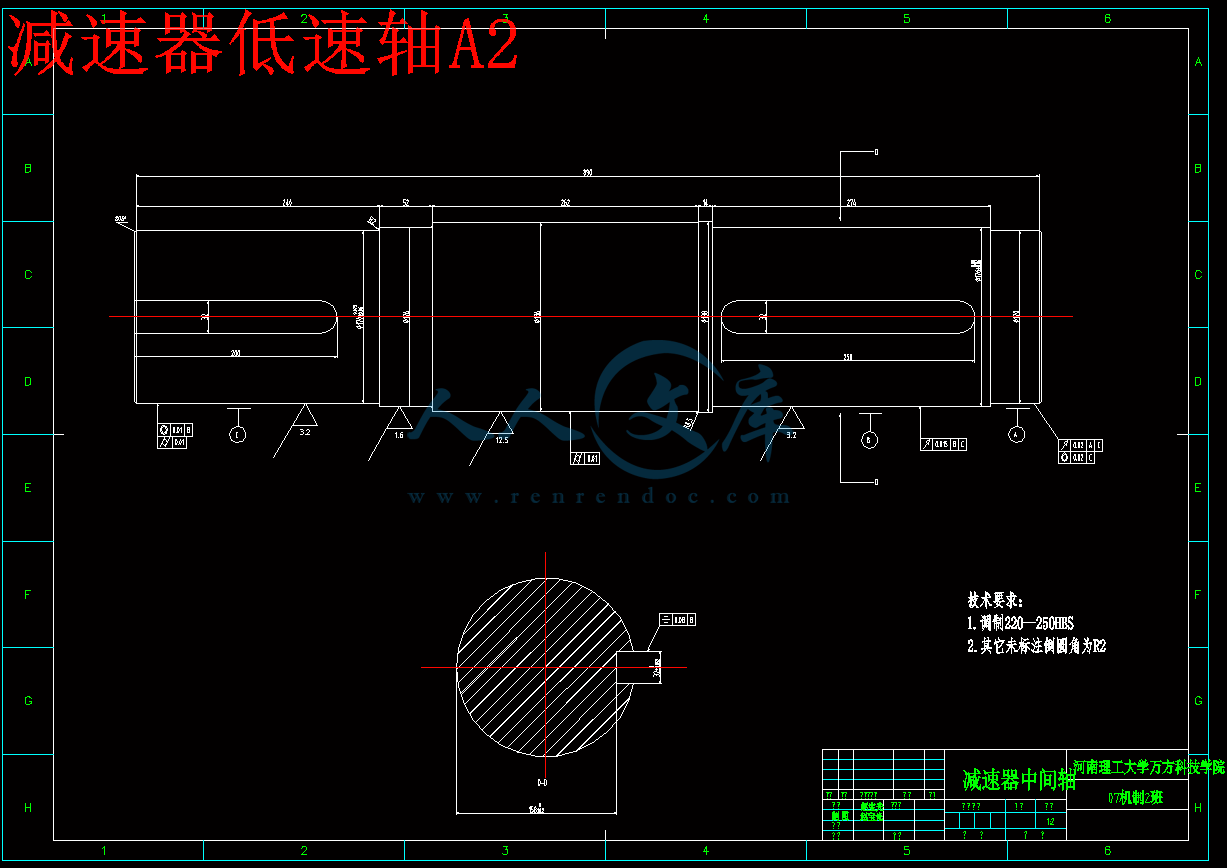
减速器低速轴A2.dwg
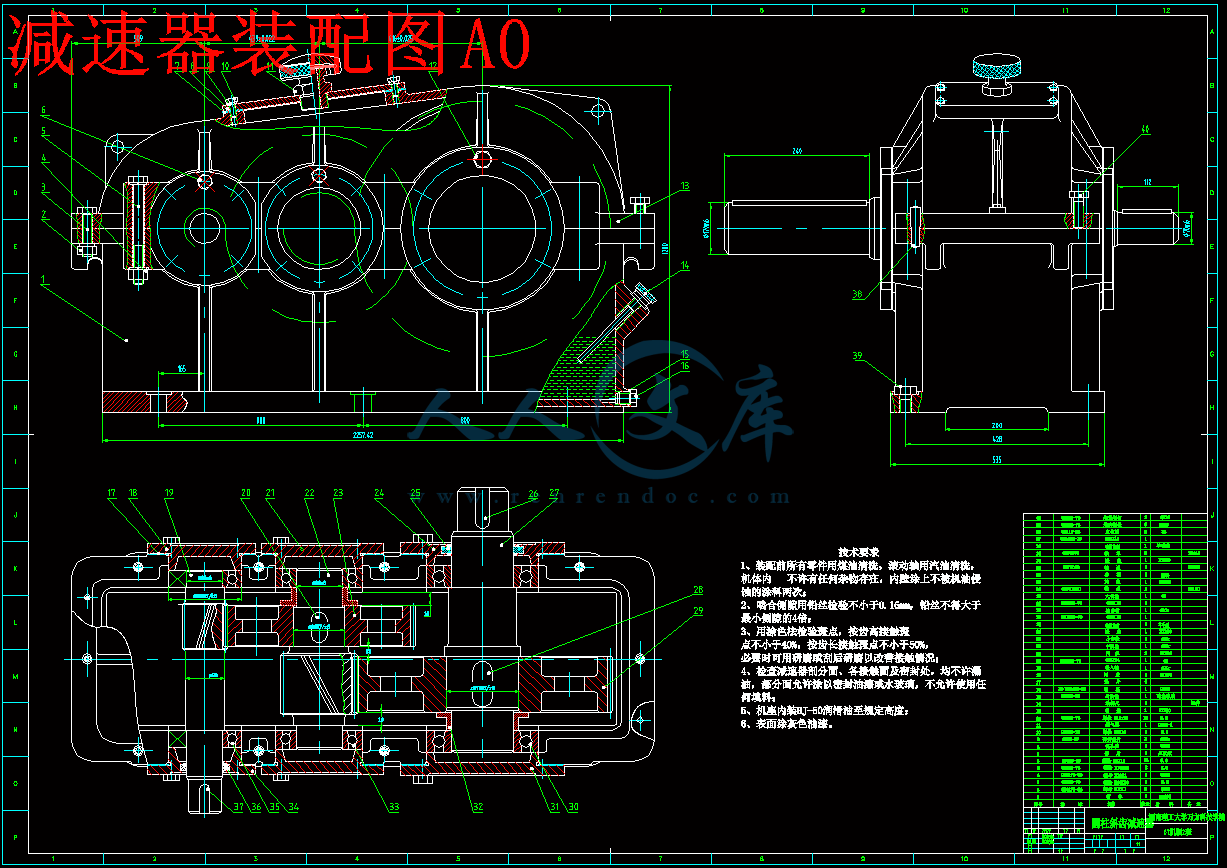
减速器装配图A0.dwg
制动盘A2.dwg
外文翻译--车床.docx
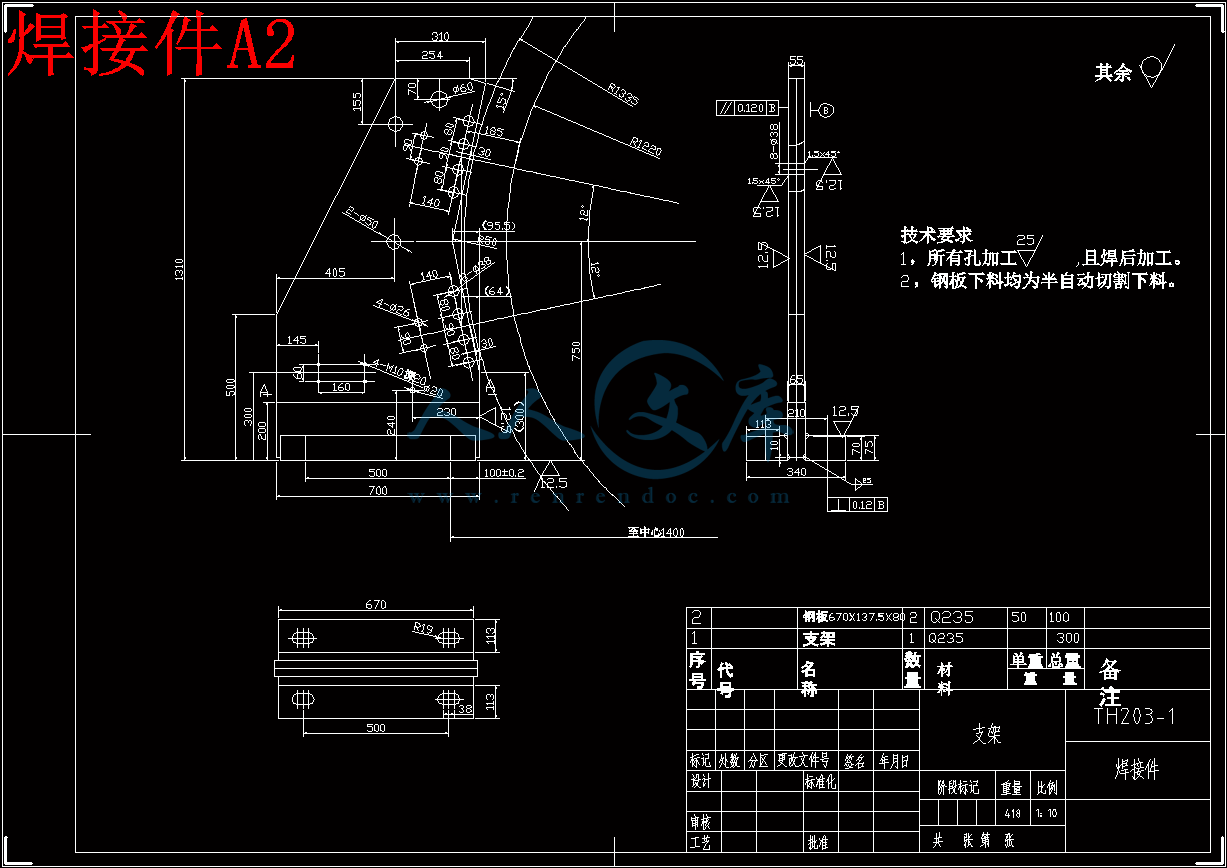
焊接件A2.dwg
矿井提升机总体结构设计开题报告.doc
矿井提升机总体结构设计论文.docx
矿井提升机总装图A0.dwg
1摘要.docx
目 录
前 言4
1、绪论5
1.1 矿井提升机的任务及其地位5
1.2 矿井提升机的发展历程6
1.2.1 缠绕式提升机的发展状况6
1.2.2 各个系列提升机的主要特点6
1.3 矿井提升机的类型和工作原理8
1.3.1 矿井提升机的类型及其组成部分的特点8
1.3.2 矿井提升机的工作原理10
2提升机的选型和计算18
2.1.1 罐笼选择18
2.1.2 钢丝绳设计及选择18
2.1.3提升机的选用19
2.2 提升机的运动学计算20
2.2.1 选择加减速度20
2.2.2 速度各参数的计算20
2.3 提升动力学计算21
2.3.1 预选电动机21
2.3.2 提升系统的变位质量21
2.3.3 力图的计算22
3 提升机减速器的设计25
3.1 减速器的作用25
3.2 减速器的国内外现状25
3.3 减速器的总体设计26
3.3.1 拟定传动方案26
3.3.2 电机选型27
3.3.3传动装置的总传动比及其分配27
3.3.4 计算传动装置的运动和动力参数28
3.4 齿轮设计29
3.4.1 高速级齿轮设计29
3.4.2 低速级齿轮设计37
3.5 轴的设计44
3.5.1减速器高速轴1的设计44
3.5.2 中间轴2的设计49
3.5.3 低速级轴3的设计51
4提升机制动装置的结构设计54
4.1 矿井提升机制动装置的功用及类型54
4.1.1 制动装置的功用54
4.1.2 制动装置的类型54
4.1.3 制动系统的要求55
4.2 制动装置的有关规定和要求55
4.3 制动器的主要类型56
4.3.1 块闸制动器56
4.3.2 综合式制动器59
4.3.3 盘式制动器60
4.4 液压盘式制动器的结构和工作原理61
4.4.1 液压盘式制动器的结构61
4.4.2 液压盘式制动器的工作原理62
4.5盘式制动器的设计计算63
4.5.1 盘式制动器工作时所需制动力63
4.5.2 每副闸应有的制动力矩66
4.6 盘式制动器的调整和维护66
4.6.1 闸瓦间隙的调整66
4.6.2 蝶形弹簧的检查67
4.7 提升机液压工作站的设计67
4.7.1 液压站的功用67
4.7.2 对交流拖动提升机液压站的工作要求68
4.7.3 液压站的组成部分68
4.7.4 液压站类型及其结构原理69
4.7.5 制动力的调节72
4.7.6 液压站的维护及注意事项76
总 结78
致 谢79
参考文献80
附录81
摘 要
目前我国许多煤矿矿井已经转向中、深部开采,矿井提升设备作为煤矿的关键设备,在矿井机械化生产中占有重要地位。制动器是提升机(提升绞车)的重要组成部分之一,直接关系着提升机设备的安全运行。多绳摩擦提升机具有体积小、质量轻、安全可靠、提升能力强等优点,适用于较深的矿井提升。本文针对JK型提升机,对其制动系统进行设计。在对提升机的制动器选型过程中,因盘式制动器是近年来应用较多的一种新型制动器,它以其独特的优点及良好的安全性能被广大用户认可,特别是在结合了液压系统和PLC 控制之后,液压系统和PLC 超强的控制性能为盘式制动器的应用提供了巨大的工作平台。制动盘的制动力,靠油缸内充入油液而推动活塞来压缩盘式弹簧来实现。
液压盘式制动器作为最新一种制动器,具有许多优点,所以它在现代多种类型提升机中获得广泛的应用。它具有制动力大、工作灵活性稳定、敏感度高等特点,对生产安全具有重要意义。
关键词:提升机;单绳摩擦;制动器;设计;液压传动。
Abstract
Currently many of our coal mine has turned to deep mining. Mine coal upgrading equipment as the key equipment holds an important position in mechanized production of the mine. The brakes are one of the important components of a direct bearing on hoistthe safe operation of equipment. Multi-rope friction hoist with small size, light weight, safe, reliable, and strong ability to upgrade apply to the deeper mine hoist. In this paper, the braking system for JK type hoist have been designed. In the hoist brake selection process, because in recent years disc brake is used in the new brakes It's unique strengths and good safety performance recognized by the majority of use。Especially in the light of the hydraulic control system and the PLC, Hydraulic System and PLC super performance of the disc brake provide tremendous platform for the work. Brake disc braking force and rely on the fuel tank filled with oil that drives the piston to compress spring to achieve Disc.
Hydraulic disc brakes as the latest development of a brake, which has many advantages. Therefore it in a modern aircraft types to upgrade gain wider application. It is the braking force, flexibility stability, high sensitivity; on production safety is of great significance.
Keywords: Hoist; Multi-rope friction; Brake; Design; Hydraulic drive.
2.1.1 罐笼选择
根据矿车类型按表选择单层罐笼(YJGS-1.8-1)其技术规格为:
装载矿车一辆,最大载重2.2吨、自重2吨、乘人数10人、断面尺寸1800X1150
矿石一次提升重量:
废石一次提升重量:
一次提升矿车总重:
2.1.2 钢丝绳设计及选择
选择钢丝绳时,应根据使用条件和钢丝绳的特点来考虑。我国单绳缠绕式提升机多为右螺旋缠绕,故应选右捻绳,目的是防止钢丝绳松捻。
1) 最大悬垂长度:
我国是个能源大国,也是矿山机电设备制造和使用大国。从20世纪50年代仿造第一台矿井提升机以来,至今已设计制造、使用了近600多台。随着社会需求和现代技术的高速发展,矿山工业企业亟待生产设备及设施的机械化、电气化、现代化。而矿山工业的提升机是咽喉设备,产品不断更新换代,老产品运行年深日久,原本落后的结构问题暴露突出,故障增多,严重影响矿山的安全运转,抑制了矿山工业的高速发展,给国民经济带来了不良的影响。
随着国内矿井生产量的日新月异的提高,对提高提升机的安全性、可靠性、生产效率以及整机自动化运行水平, 降低操作者及维护人员的劳动强度、处理设备事故的速度与对策等,成了迫切要求。
本次设计是关于2JK-2.0/20单绳缠绕式矿井提升机的设计,在本次设计中将大学四年所学习的材料力学,理论力学,机械制造,机械设计,机械制图等知识进行了一次综合的运用。本次设计不仅是对大学所学知识的总结和巩固而且为以后进入社会参见工作积累了一定的经验,本次设计是个难得的学习机会。
在毕业设计过程中,通过上网查资料,图书馆借书,我逐步认识了矿井提升机的工作原理和基本构造,为我能够圆满完成设计任务奠定了良好的基础。另外我要特别感谢这次毕业设计的指导老师,刘建慧老师不仅给我提供了矿井提升机的相关资料而且给了我不少有用的建议,给我带来莫大的帮助。由于本人理论水平有限,实践经验较少,本次设计就难免有错误和考虑不足之处,敬请各位老师以及阅读者提出宝贵的意见和建议。
1、绪论
1.1 矿井提升机的任务及其地位
煤炭是我国的主要能源,又是重要的化工原料。煤炭被誉为黑色金子,工业的食粮,它是十八世纪以来人类世界使用的的主要能源之一。虽然它的重要位置已被石油所代替,但在今后相当长的一段时间内,由于石油的日渐枯竭,必然走向衰败,而煤炭因为储量巨大,加之科学技术的飞速发展,煤炭气化等新技术日趋成熟,并得到广泛应用,煤炭必将成为人类生活中的无法代替的能源之一。我国既是煤炭生产大国又是消费大国,而根据我国的国情,在我国一次性能源结构中,煤炭所占的比重一直是70%以上,在今后相当长的时期内,煤炭仍然是我国的主要能源,故煤炭对我国的重要性不言而喻。随着我国经济的不断改革开放,煤炭工业必将高速持续地向前发展。
矿井提升是煤炭生产过程中必不可少的重要生产环节。从井下采煤工作面采出的煤炭,只有通过矿井提升设备运到地面,才能加以利用。可以说,矿井提升是矿井生产的“咽喉”,其设备在工作中一旦发生故障,将直接影响生产,甚至造成人身伤亡。此外,矿井提升系统的耗电量很大,一般占矿井生产总耗电量的50%-70%。因此,合理选择维护使用这些设备,使之安全可靠、经济高效地运转,对保证矿井安全高效的生产,对提高煤炭企业的经济效益.都具有重要的现实意义。由于矿井提升设备是在并下巷道内和井简内工作,空间受到限制,故要求它们结构紧凑,外部尺寸尽量小;又因工作地经常变化,因而要求其中的许多设备应便于移置;因为井下有瓦斯、煤尘、淋水、潮湿等特殊工作条件,还要求设备应防爆、耐腐蚀等。此外,矿井提升设备是一大型的综合机械—电气设备,其成本和耗电量比较高,所以,在新矿井的设计和老矿井的改建设计中,确定合理的提升系统时,必须经过多方面的技术经济比较,结合矿井的具体条件,在保证提升设备在选型和运转两个方面都合理的前提下,要求提升设备具有良好的经济性。
1.2 矿井提升机的发展历程
1.2.1 缠绕式提升机的发展状况
缠绕式提升机的发展是为适应我国矿山建设的需要,国产提升机大致可分为仿苏、改进及自行设计等三个阶段。1953~1958年期间生产仿苏产品BM系列提升机;KJ系列提升机是1958~1966年期间生产的仿苏改进产品;JKA系列是在KJ型基础上的改进产品;XKT系列提升机是1971年7月开始生产的自行设计产品,后又改为XKT-B系列,是已成批生产的新型矿井提升机。时至今日,中信公司生产的产品最齐全,JK/E,JKM,JTP,2JTP,JT等等。
1.2.2 各个系列提升机的主要特点
A. KJ型矿井提升机
1.)主轴装置采用铸铁法兰盘;
2.)调绳装置为手动蜗轮蜗杆式;
3.)制动器为角移式;
4.)液压传动装置为手动杠杆控制的三通阀和电磁铁控制的四通阀;
5.)深度指示器为机械牌坊式;
6.)减速器为渐开线人字齿轮减速器。
B.JK(A)型矿井提升机
1.)调绳装置为电动蜗轮蜗杆式;
2.)制动器为综合式,改善了闸瓦的磨损情况;
3.)液压传动装置为手动控制的低压电液调节阀和电磁铁控制的安全三通阀,操纵省力,易于实现自动化和半自动化控制;
4.)减速器采用圆弧人字形齿轮减速器;提高了承载能力并减轻了重量。
C. XKT型矿井提升机
1)滚筒为焊接结构,重量轻;
2.)采用液压齿轮式快速调绳装置,调绳省力省时;
3.)采用圆盘制动系统(包括圆盘式制动器和液压站两部分),此种系列具有以下的优点:
(1)安全性较高;
(2)制动力矩可调性好;
(3)惯性小、动作快、灵敏性强;
(4)结构紧凑、外形尺寸小、重量轻;
(5)通用性好;
(6)安装、使用及维护比较简单;
4.)采用圆弧齿轮减速器,提高了承载能力,减轻了重量;
5.)采用了圆盘深度指示器。
XKT系列矿井提升机与KJ和JK(A)系列比较,有以下的优点:
1)提升能力平均提高25%,重量平均减轻25%,
2)采用了一些新技术、新结构,如:盘式制动器、液压站、快速调绳装置、微拖动装置等
3)通用化程度高。
D. GKT系列矿井提升机
采用JSZ-2×500型双力线中心驱动减速器,结构紧凑,传动平稳,噪音小。并采用双列向心滚动轴承,传动效率高,在实际工作中厂家建议传动效率取0.85~0.9;
滚筒为整体焊接结构(2m提升机可根据用户要求,供应分割的焊接滚筒和制动盘),采用滚动轴承支座。双滚筒提升机的主轴装置,具有液压操纵的、在结构上作了改进的齿轮离合器,调绳操作时间仅司机一人即可完成,节省了时间和人力;
配有自整角机传动的圆盘深度指示器(2m提升机若用户要求时,可以改供给牌坊式深度指示器);
制动器为综合式的液压开启的盘式制动器;
采用集中控制的操纵台。
1.3 矿井提升机的类型和工作原理
1.3.1 矿井提升机的类型及其组成部分的特点
提升机是矿井提升设备的主要组成部分,目前我国生产及使用的矿井提升机,按其滚筒的构造特点可分为三大类,即单绳缠绕式、多绳摩擦式及内装式提升机。
单绳缠绕式提升机在我国矿井提升中占有很大的比重,目前在竖井、斜井、浅井、中小型矿井大量使用。其工作原理是把钢丝绳的一线固定缠绕在提升机的滚筒上,另一端绕过井架上的天轮悬挂提升容器,利用滚筒转动方向的不同,将钢丝绳缠上或放松,完成提升或下放重物的任务。多绳摩擦式提升机其特点是靠钢丝绳与摩擦轮之间的摩擦力传动,这种提升机由于具有安全可靠、体积小、质量小,适用于深井提升等优点,在我国矿井提升中也已得到较广泛的应用。
内装式提升机是世界上近年来研制成功的一种全新的新型提升机,从提升机的工作原理来看,它亦属于摩擦提升范畴,但它实现了“内装”。所谓内装,就是格拖动电机直接装在摩擦轮内部,使电机转子与摩擦轮成为一体。内装式提升机摩擦轮的外观与一般的摩擦式提升机毫无区别,但它却把由电动机、减速器和摩擦轮组成的常规式,发展成为省去减速器,而使摩擦轮相当于电动机的转子,主轴相当于电动机定子的高度,结构新颖的提升机。同时为了使内部电动机冷却,主轴可以做成空心轴作为冷却风道,这样减少了设备结构重量又减少了提升系统的转动惯量。世界上第1台内装式提升机于1988年在德国豪斯阿登矿投入运行,我国的开滦矿业集团东欢坨煤矿也于1992年从德国引进了1台内装式提升机,迄今设备运行良好。
内装式提升机是提升机的机械与电气高度一体的完美结合,由于它体积小.重量轻、基础设施简单、设备造价低、运行费用低,与传统的提升机相比,其各项技术、经济指标都显示出了很高的优越性,引起了国际提升界极大的关注。内装式提升机的问世,是提升机领域里的一个新的里程碑,它不但对提升机制造业产生巨大影响,还对矿井提升机的使用、维修也将引起变革,迫使人们用全新的概念去评价提升机性能的优劣。内装式提升机的研制,在我国尚属空白,应给予足够重视,以促进国内提升机的发展,赶超世界先进水平。 单绳缠绕式提升机的工作原地如图1-2所示,简单地说,就是用一根较粗的钢丝线在卷筒上缠上和缠下来实现容器的提升和下放运动。提升机安装在地面提升机房里,钢丝绳一端固定在卷筒上,另一端绕过天轮后悬挂提升容器。图1-2所承为单绳缠绕式单卷筒提升机,卷筒上固定两根钢丝绳,并应使每根钢丝绳在卷简上的缠绕方向相反。这样,当电动机经过减速器带动卷简旋转时,两根钢丝绳便经过天轮在卷筒上缠上和缠下,从而使提升容器在井筒里上下运动。不难看出,单绳缠绕式提升机的一个根本特点和缺点是钢丝绳在卷筒上不断的缠上和缠下,这就要求卷简必须具备一定的缠绕表面积,以便能容纳下根据井深或提升高度所确定的钢丝绳悬垂长度。单纯缠绕式提升机的规格性能、应用范围及机械结构等,都是由这一特点来确定的。
单绳缠绕式双卷筒提升机具有两个卷简,每个卷筒上固定一根钢丝绳,并应使钢丝绳在两卷筒上的缠绕方向相反,其工作原理和特点与单卷筒提升机完全相同。多绳摩擦式提升机的工作原理与单纯缠绕式提升机不同,钢丝绳不是固定和缠绕在主导轮上,而是搭放在主导轮的摩擦衬垫上,如图1-3所示,提升容器悬挂在钢丝绳的两端,在容器的底部还悬挂有平衡尾绳。提升机工作时,拉紧的钢丝绳必须以一定的正压力紧压在摩擦衬垫上。当主导轮由电动机通过减速器带动向某一个方向转动时,在钢丝绳和摩擦衬垫之间使发生根大的摩擦力,使钢丝绳在这种摩擦力的作用下,跟随主导轮一起运动,从而实现容器的提升和下放。不难看出,多绳摩擦式提升机的一个根本特点和优点是钢丝绳不在主导轮上缠绕,而是搭放在主导轮的摩擦衬垫上,靠摩擦力进行工作。同样,多绳摩擦式提升机的规格性能、应用范围和机械结构等,都是由这—特点来确定的。多绳摩擦式提升机特别适应于深井和大产量的提升工作。多绳摩擦式提升机与单绳缠绕式提升机比较,在规格性能、应用范围、机械结构和经济效果等方面都优越得多,就深井和大产量来说,是竖井提升的发展方向。但是,根据我国目前浅井多、斜并多的特点,单绳缠绕式提升机仍然是目前制造和使用的重点。对于部分深井和大产量的矿井,则应该合理的选用多绳摩擦式提升机,而不宜选用大型的单绳缠绕式提升机。
参考文献
[1]濮良贵、纪名刚主编。《机械设计》第7版。 高等教育出版社出版 2001.6
[2]孙恒、陈作模、葛文杰主编。《机械原理》第七版。高等教育出版社出版 2005.12
[3]洪晓华、陈军主编。《矿井运输提升》中国矿业大学出版社2005.1
[4]陈维健、齐秀丽、肖林京、张开如主编。《矿山运输与提升设施》中国矿业大学出版社2007.2
[5]王文斌主编。《减速器和变速器》机械工业出版社2007.2
[6] 任济生、唐道武、马克新主编。《机械设计、机械设计基础课程设计》中国矿业大学出版社2008.1
[7]潘英 著. 《矿山提升机械设计》.中国矿业大学出版社出版 2001.1
[8]李仪钰 主编. 《矿山提升运输机械》(高等学校教学用书) . 冶金工业出版社出版 1989.5第1版



 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号