通风盖板模具设计及装配过程的动画设计
38页 15000字数+说明书+任务书+PROE三维图+动画仿真+11张CAD图纸【详情如下】
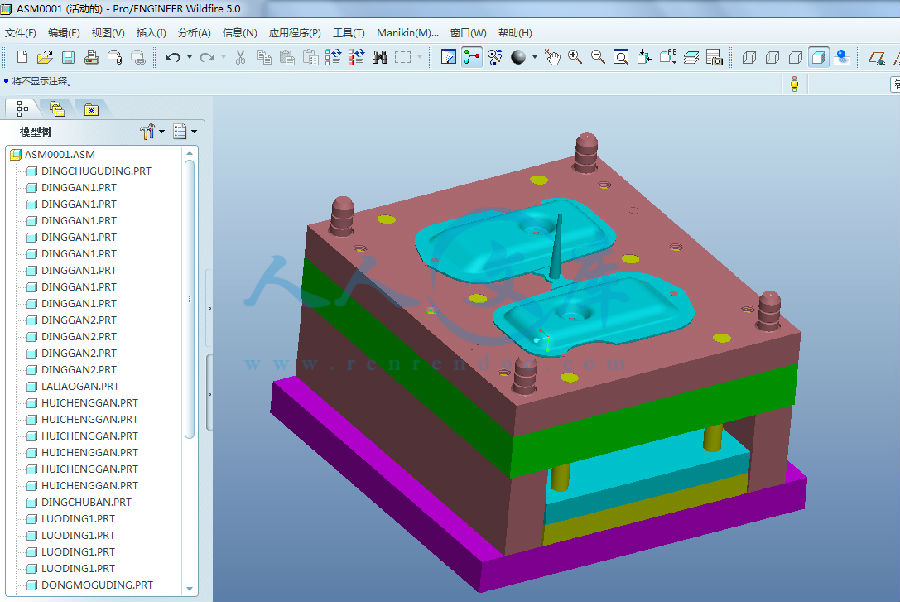
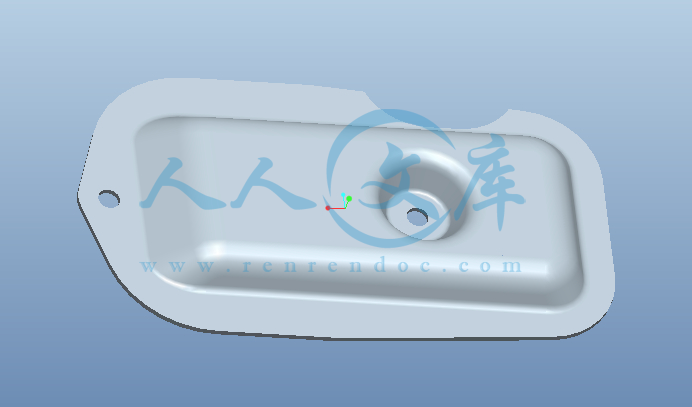
PROE三维图+动画仿真
任务书.doc
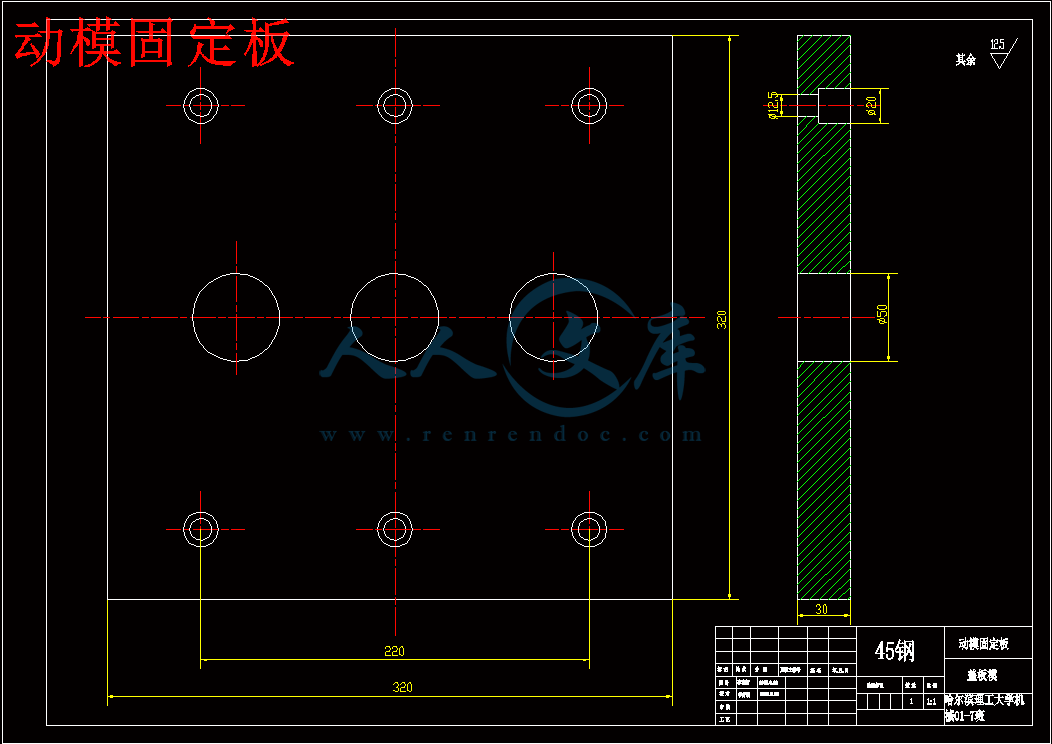
动模固定板.dwg
动模板.dwg
动模板型芯.dwg
垫板.dwg
外文翻译--注塑模的温度调节系统.doc
定模固定板.dwg
定模板.dwg
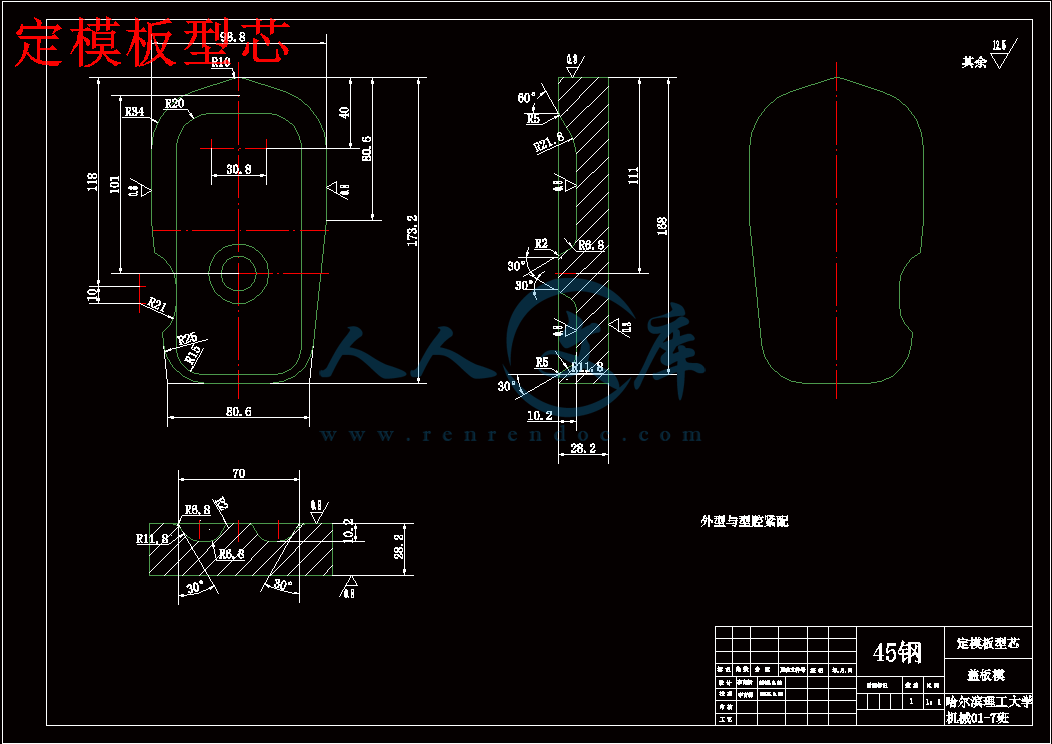
定模板型芯.dwg
支柱.dwg
装配图.dwg
通风盖板模具设计及装配过程的动画设计论文.doc
顶出固定板.dwg
顶出板.dwg
通风盖板模具设计及装配过程的动画设计
摘要
目前塑料在实现“以塑代钢”方面起着不可忽视的作用,它正以其物美价廉的特征渗透到国民经济的各个领域。工程塑料制品的速度增长率为每年10%,然而在工程塑料中70%—80%以上的制品是采用注塑成型加工。如今塑料制品广泛应用于广泛应用于电子、机械、汽车、航天、家电、玩具等各个行业。因此也使注塑模具的设计与制造带来了繁荣的景象。在模具设计中,Pro/E软件以它强大的实体建模功能和结构分析功能扮演着不可或缺的角色。
本文简要概述了CAD技术在国内外的发展状况,介绍了CAD在模具工业中的使用和发展情况,介绍了在我国研究和发展模具CAD技术的必要性和迫切性, 介绍了Pro/E软件的一些模块及其功能,介绍模具与注射机的关系等,并图文并茂介绍了利用Pro/E软件进行模具设计的整个过程。涵盖主题包括:模具型腔设计,浇注系统设计,脱模机构设计,温度调节系统设计, 开模模拟等知识面。
在英文翻译中,我将对国内资料没有详细介绍的温度调节系统作了介绍。
关键词 :塑料;模具;CAD技术;Pro/E
The Design of the Ventilates Lap Mold and the Animation of the Assembly Process
Abstract
At present the plastic is playing the noticeable role in realizing "by plastic instead of steel" aspect. It is famous as its excellent in Quality and reason able in price characteristic and infiltrate to each domain of national economy. Engineering plastics go up by the ratio of 10% each year, however 70% - 80% above product isuses in the engineering plastics casts takes shape the processing. Now the plastic product widely applies in the domain of the electron, the machinery, the automobile, astronautics, the electrical appliances, the toy and so on. Therefore the design and the manufacture about the mold has broad foreground In mold design, Pro/E software is playing the indispensable role in its formidableentity modelling function and the structure analysis function.
This article has briefly outlined the development condition of the CAD technology in the domestic and foreign , introduced the use and development situation of the CAD in the mold industry ,introduced the necessity and urgency that develop and study mold CAD technology in our country, introduced some modules and its the function of the Pro/E software , introduced the relationship of the mold and the injection machine and introduced the entire processuses which realize the mold designs using the Pro/ E software abundantly and elegantly. The design subject includes: the design of mold cavity, the design of pours system, the design of drawing of patterns organization, the control system design about temperature, simulation of opening mold and so on.
In English translation, I have made the introduction to temperature control system that the domestic material not detailed introduction.
Keywords :plastic; Injection Mold; CAD technology; Pro/E
不要删除行尾的分节符,此行不会被打印
目录
摘要I
AbstractII
第1章 绪论1
1.1 课题背景1
1.2 塑料注射模具CAD综述1
1.3 塑料注射模具CAD的特点2
1.4 计算机在塑料注射模具设计与制造中的应用2
1.5 现代模具技术发展3
1.6 新一代模具设计软件技术4
1.7 Pro/ENGINEER软件介绍4
第2章 注塑零件的设计6
2.1 材料特性6
2.1.1 使用性能6
2.1.2 成型性能6
2.2 塑料制品结构设计6
第3章 模具设计8
3.1 塑料的成型工艺特性8
3.2 注射机的选择9
3.3 模具材料的选择11
3.4 模具加工工艺12
3.5 注射模具设计13
3.5.1 成型零件结构设计14
3.5.2 浇注系统设计23
3.5.3 导向机构的设计25
3.5.4 排气系统设计26
3.5.5 脱模机构设计27
3.5.6 温度调节系统设计30
结论32
致谢33
参考文献34
附录35
课题背景
塑料注射模具CAD综述
产品的制造工艺过程都必须先进行设计,设计工作是新产品研制的第一步。设计工作的水平直接关系到新产品质量性能、研制周期和技术经济效益。手工设计,设计人员必须查阅大量的技术资料和设计手册,根据本单位和有关企业的技术资料,通过理论计算和实验分析,把设计思想用图纸和说明书表达出来后,再与有关工程人员讨论、修改。在整个设计过程中.设计人员花费了大量的时间在绘图和查阅资料上,造成智力和时间的浪费,这远远不能适应当今生产的发展。随着计算机的发展,为了提高设计效率和质量,CAD应运而生了。
CAD是二十世纪下半叶最重要的技术成果之一,其应用水平往往体现一个国家(地区)的科学技术水平,现已广泛应用在各个行业和部门。模具行业是应用计算机辅助设计最多,并同时也是最能体现CAD优越性的部门之一。
随着科学技术的发展,模具行业在国民经济中的地位日益提高、重要性日趋明显。传统的模具设计与制造方法己不能适应工业产品的迅速更新换代和提高质量的要求。因此,国外工业发达的国家对模具CAD和模具CAM技术的开发非常重视。早在二十世纪六十年代,国外一些飞机制造公司就开始了CAD和CAM的研究工作。
工业发达国家较大的模具生产厂家在模具CAD/CAM上进行了较大投资,正大力开发研究这一技术。如法国的FOS模具公司己购买了大型CAD/CAM系统,日本、美国、德国等国家也己开发CAD/CAM系统,并广泛应用于模具制造。
我国模具CAD/CAM的开发开始于二十世纪七十年代末。虽然起步较晚,但发展迅速。到目前为止,先后经过国家有关部门鉴定的有精冲模、普通冲裁模、辊锻模、锤模和塑料注射模等,但这些系统大多数仍处于研究开发阶段,被推广生产使用并形成商品化的不多。近几年来华中理工大学、上海交通大学、合肥工业大学、北京航空航天大学等高等院校对模具CAD进行了卓有成效的研究。其中华中理工大学研究开发的HSC2.0注射模CAD/CAM/CAE系统,己受到川门的重视。它是在Auto CAD软件的基础上,采用Auto CAD提供的ADS开发平台用C语言编写的。它除了具有Auto CAD本身的功能外,还具有模具结构设计子系统、结构及工艺参数计算校核子系统、塑料注射流动、保压与冷却模拟子系统、数控线切割编程子系统、建库工具和设计进程管理等模块。所有程序均能在Auto CAD的环境中集成运行。
塑料注射模具CAD的特点
塑料注射模具设计的特点主要是:
1.外部约束多
即根据制品及生产厂家的要求,对成型制品的材料性能、成型工艺条件、模具结构、使用设备等都要进行充分的考虑。但主要的还是要考虑塑料制品的形状结构、尺寸大小以及由此带来的模具结构问题。如成型零件的结构、顶出方式、排气形式、冷却回路的布置等。
2.模具结构复杂且灵活
注射模具包括浇注系统、成型零部件、脱模系统、导向系统、冷却系统、排气系统等组成。每一系统都有各自的结构形式,且结构形式由于加工制造方法、加工设备等的不同又有所区别,因此在设计中没有固定的准则,不同的设计人员对同一制品可能有多种结构设计,灵活性很大。
因此,针对上述特点反映到模具CAD系统的开发方面,要求系统具有功能丰富、流程复杂、交互性强、用户界面友好等特点。
塑料注射模具CAD技术主要从两个方面对模具设计人员提供强有力的帮助:一是模具结构CAD;二是模具CAE。
模具结构CAD包括模具总体结构方案设计和零部件设计,数控仿真和数控程序的生成,模具装配模拟,零件图和装配图的生成与绘制等方面。
计算机在塑料注射模具设计与制造中的应用
塑料注射模具的设计与制造是一个十分复杂的过程。它包括产品的概念设计、模具总体方案设计、模具结构设计、模具零件制造加工、模具装配以及制品生产等多个环节,在模具设计阶段还要进行有关部件的分析模拟与校核。传统的模具设计与制造方法难以全面考虑这些所有的环节。现在,计算机己应用于上述的各个环节。借助于计算机这一强有力的工具和CAD这一先进技术,可以把这些环节有机地结合起来。下面主要论述模具总体方案设计和分析模拟过程中计算机CAD的应用。
1.模具总体方案设计阶段
该阶段主要是根据塑料制品的要求,考虑成型型腔的数量、镶件的材料、浇注系统、冷却系统、脱模系统以及侧向分型系统的结构形式,选择模架类型、规格以及对注射设备的要求等。模具总体方案设计属概念设计范畴,对整个设计过程和设计结果具有决定性影响。但是,其经验性强,需要考虑多方面的因素和要求。因此,对设计人员的要求高.此外,由于模具结构的复杂性,总体方案的设计往往要经过反复修改,是一个逐步寻优的过程。
模具总体方案设计CAD系统,为模具设计人员表达设计构思和反复修改设计方案提供了有效的手段,从而提高了设计结果的合理性和设计效率。人们对模具结构CAD的柔性技术进行了研究,提出了有关装配模型、虚零件和符号零件等不同方案,并开发出一些注射模具总体方案设计的CAD系统。
现在,KBS技术(基于知识的系统,Knowledge-Based System)在模具总体方案设计方面的应用,己成为一个重要的研究课题。这种技术应用知识库中的设计知识,从塑料产品应用需求、所用塑料的特性和工艺特征出发,经过逐步推理得出模具结构的各部分方案,从而得到总体设计方案。模具结构总体方案确定后,通过数控加工模块生成模具零件的数控加工程序,实现了设计CAI〕与制造CAM两个过程的连接,从而加快了模具设计与制造的周期。
2.分析模拟
对于精密、大型的塑料注射模具,其成型过程是一个复杂的过程。在以往的模具设计中,设计人员的经验起着十分重要的作用。但也经常会进行反复的试模和修模,以不断修整模具的不合理部分。但这样会造成制造周期的延长和模具本身质量的下降。
现代模具技术发展?
模具设计是一个多环节的复杂过程,从初始化到最后的装配检测,实质上是将产品的设计信息在生产环节间进行不间断传送与处理并反馈的过程,正确的模具设计方法应该是并行工程的方法,是实现模具CAD等各个模具间信息的提取、交换和处理的集成化,必须建立模具集成化的产品信息模型。采用基于特征变量化设计,工程数据库管理系统等技术已成为目前研究的热门。
运用计算机辅助设计技术进行实物零件到实物的整个复杂过程称为反演化工程,采用反演化技术,可迅速将事物CAD模型化,再利用已有的模具CAD系统进行模具设计,具有速度快等优点,同时它使模具设计的流程由传统的开环结构向闭环结构转变:制件----模具设计----模具设计----制件同原件进行比较调整,从而建立模具质量保证体系。利用和集成各种计算机技术,网络为通讯手段,协调企业的各种行为以获得好的经济效益为目标来设计产品,模具作为一种特殊的行业无疑要向计算机化方向发展,这是未来模具设计总的发展趋势。
新一代模具设计软件技术
新一代模具软件是建立在模具设计实践中归纳总结出来的大量知识上。具有智能化意义 。在智能化软件的支持下,CAD不在是对传统设计与计算方法的模仿,而是在先进设计理论的指导下,充分运用本领域专家的丰富知识和成功经验,其设计结果必然具有合理性和先进性 。
新一代模具软件以立体的思想,直观的感觉来设计模具结构,所以生成的三维结构信息能方便地用于模具可制造性评价和数控加工,在三维参数化特征造型、成型过程模拟、数据加工过程仿真以及信息流的组织与管理方面已达到相当完善的程度并具有较高的集成化水平。
新一代软件已能具有面向装配的功能,因为模具的功能还有通过装配结果才能体现出来,而新一代模具软件可为模具设计人员提供多种途径来建立模具的装配模型。采用南向装配的设计方法后,模具装配不在是几个零件的简单拼装,起数据结构既能描述模具的功能,又可定义模具零部件间相互关系的装配特征,实现零部件的关联,因而能有效地保证模具的质量,目前,车内模具企业中已有相当多的厂家引进了较高档次的CAD/CAM/CAE系统,诸多软件在中车模具工业中应用。
Pro/ENGINEER软件介绍
随着模具技术的发展,涌现出了很多设计和制造模具的优秀的软件。有:CADAM软件包(Computer-graphics Augmented Design and Manufacturing,计算机图形增强设计与制造)、CATIA软件包(Computer-Graphics Aided Three-Dimensional Interactive Applications,计算机辅助三维图形交互应用软件包)、Autodesk公司的AutoCAD系统、EDS公司的Unigraphics系统、PTC公司的Pro/ENGINEER系统。这些软件的出现,使模具的设计和制造过程变的更为方便和快捷。本设计采用的软件是Pro/ENGINEER。
Pro/ENGINEER自1988年问世以来,10年间已成为全世界及中国地区最普及的3D、 CAD/CAM系统。Pro/ENGINEER在今日俨然成为世界3D CAD/CAM系统的标准软件,广泛应用于电子、机械、模具、工业设计、汽机车、自行车、航天、家电、玩具等各行业。Pro/ENGINEER可谓是个全方位的3D产品开发软件,集合了零件设计、产品组合、模具开发、NC加工、钣金件设计、铸造件设计、造型设计、逆向工程、自动测量、机构仿真、应力分析、产品数据库管理等功能于一体。
Pro/ENGINEER是一套由设计至生产的机械自动化软件,是新一代的产品造型系统,是一个参数化、基于特征的实体造型系统,并且具有单一数据库功能。
1.参数化设计和特征功能
Pro/ENGINEER是采用参数化设计的、基于特征的实体模型化系统,工程设计人员采用具有智能特性的基于特征的功能去生成模型,如腔、壳、倒角及圆角,您可以随意勾画草图,轻易改变模型。这一功能特性给工程设计者提供了在设计上从未有过的简易和灵活。
2. 单一数据库
Pro/ENGINEER是建立在统一基层上的数据库上,不象一些传统的CAD/CAM系统建立在多个数据库上。所谓单一数据库,就是工程中的资料全部来自一个库,使得每一个独立用户在为一件产品造型而工作,不管他是哪一个部门的。换言之,在整个设计过程的任何一处发生改动,亦可以前后反应在整个设计过程的相关环节上。例如,一旦工程详图有改变,NC(数控)工具路径也会自动更新;组装工程图如有任何变动,也完全同样反应在整个三维模型上。这种独特的数据结构与工程设计的完整的结合,使得一件产品的设计结合起来。这一优点,使得设计更优化,成品质量更高,产品能更好地推向市场,价格也更便宜。
Pro/ENGINEER具有包括Pro/DESIGN、Pro/MECHANICAL、Pro/MOLDESIGN等27个模块,本设计使用的主要是Pro/DESIGN、Pro/MOLDESIGN模块。Pro/MOLDESIGN模块用于设计模具部件和模板组装,它包括如下功能:
(1) 采用参照设计模型的方法,自动生成模具型腔几何体。
(2) 对单一、多面类似或者多面不同的型腔,采用 Pro/ENGINEER的组装命令及花样组来定出型腔。
(3) 对复杂的多面/注模,提供 Slider/CAMMED移动功能。
(4) 用不同的缩减补偿方式,修改造型几何体。
(5) 在模拟过程,采用干扰核查的方法支定度及模似模具开口及 Molding Ejection Sequence.
(6) 备有 AC Technology的 C—Flow/EZ分析软件,提供空腔冲填及 AIR TRAPPING模拟、 Front、ram速度、weld线及流体速度(Flow)。
(7) 直接取得 Pertinent模具设计工程的信息,包括冲填器皿及型腔表面积等信息。
(8) 可生成模具的特定功能,包括浇口(Sprue)、浇道(Runner)、浇槽(Gates)、冷凝线(cooling line)及分离线。
(9)标准化的模具组装及元件。
参考文献
1. 申树义 高济 .塑料模具设计. 机械工业出版社. 2003年;
2.塑料模具技术手册编委会编. 塑料模具技术手册. 机械工业出版社.1997年;
3.陈万林等 .实用塑料注射模设计与制造. 机械工业出版社.2000年;
4.詹友刚.Pro/ENGINEER中文野火版教程——通用模块.清华大学出版社. 2004. 年;
5.陆宁编.实用注塑模具设. 中国轻工业出版社. 1997年;
6.许发越 .模具标准应用手册. 机械工业出版社 .1994年;
7.郭芝俊,邱宣怀.机械设计.高等教育出版社.1990年;
8.林清安.Pro/ENGINEER零件设计基础篇(上、下) .北京大学出版社,1999年;
9.林清安.Pro/ENGINEER零件组合.北京大学出版社 .2000年;
10.郭芝俊,邱宣怀.机械设计.高等教育出版社 .1990年;
11.冯炳尧 韩太荣 殷振海 蒋文森. 模具设计与制造简明手册 .上海科学技术出版社 .1992年;
12.Alan pugh “Injection mould design and manufacture” IFS(Publication)Ltd.HK 1986;
13.R.Paul “Plastics process technology” The MIT Press 1981。





 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号