真空抬包设计大速比倾包系统设计
31页 12000字数+说明书+外文翻译+7张CAD图纸【详情如下】
上箱体1 A1.dwg
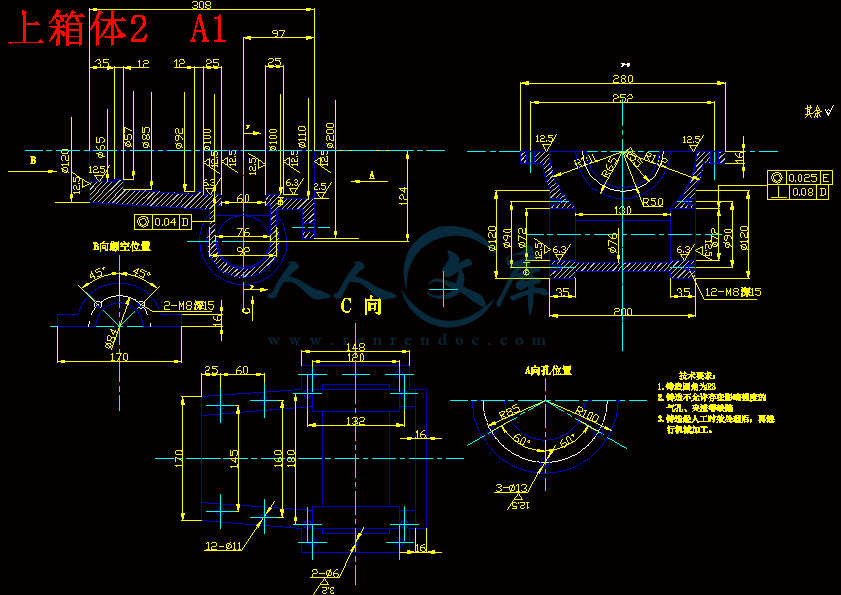
上箱体2 A1.dwg
下箱体2 A1.dwg
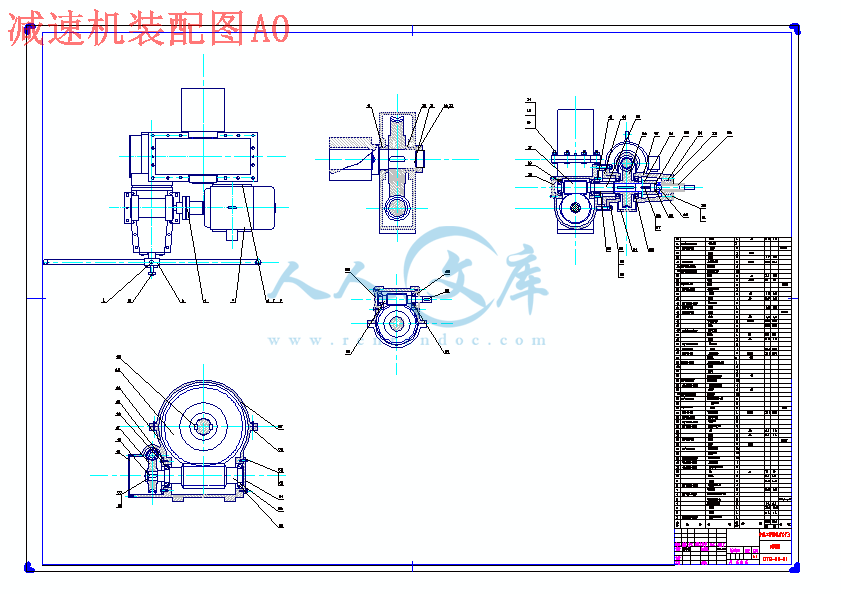
减速机装配图A0.dwg
外文翻译--数控机床.doc
摘要.doc
真空抬包装配图A0.dwg
真空抬包设计大速比倾包系统设计说明书.doc
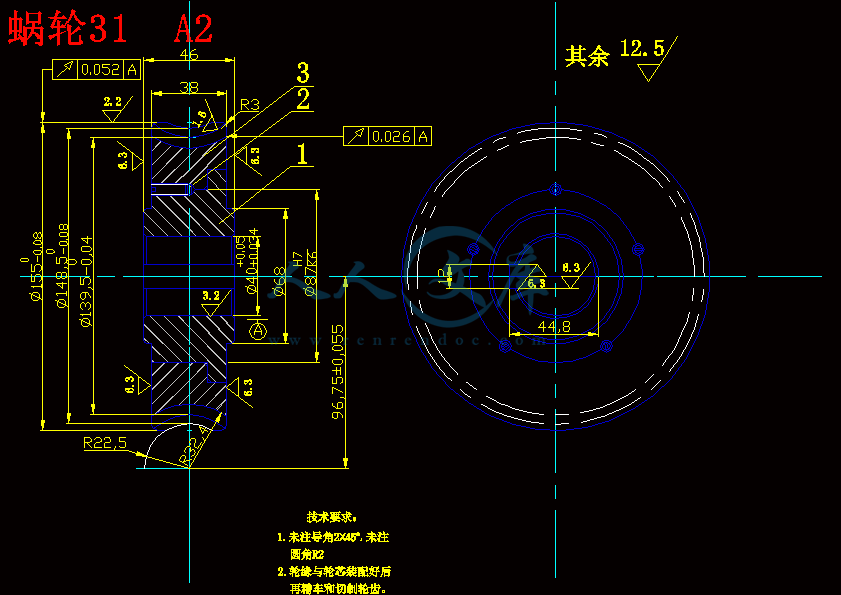
蜗轮31 A2.dwg
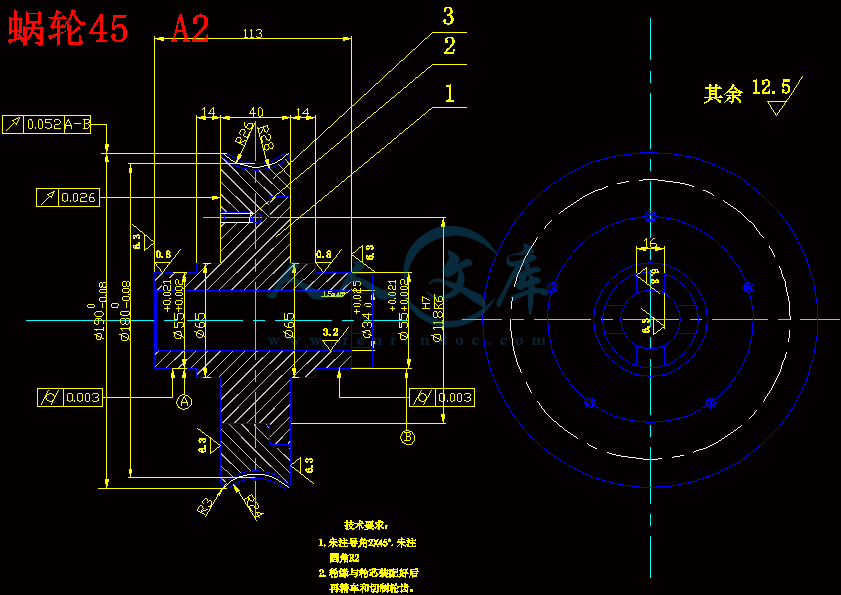
蜗轮45 A2.dwg


摘 要
真空抬包是电解铝冶炼过程中的一个重要设备,其主要功能是将电解槽中的电解铝液吸出并倒运至混合炉,是转运铝水的重要设备。真空抬包能够将电解槽中的电解铝液吸出并倒运到混合炉后浇铸成铝锭。该设备维护费用低、安全性高、工人劳动强度低等特点,一次可吸取几个电解槽内的铝液并直接送至混合炉,无需中途转浇包倒运,铝液热量损失小。该抬包采用正压喷射吸铝,改变了传统的负压直接吸铝,消除了负压吸铝对真空系统的危害,由于其可与电解槽共用一个气源,可省去整套真空系统,减少岗位配置,降低设备维护、检修费用,节约运行中的电费开支。
真空抬包采用茶壶式浇包的结构形式,铝液从包底浇出,熔渣被挡在包内,撇渣效果好。减速机是抬包的倾转机构,采用3级蜗轮蜗杆减速机。由于抬包容积的增大,自重及盛铝量均增大,抬包的倾转力矩增大,手动倾转费力、效率低而且不安全,该减速机在结构形式设计为手动与电动均可,正常操作为电动,手动为检修和突发事故时用,手动与电动的切换采用爪式离合器,切换迅速方便,安全可靠。该减速机电动为三级蜗轮蜗杆减速,手动为两级蜗轮蜗杆减速,减速比大。
关键词:真空抬包、减速机、蜗轮、蜗杆
Abstract
Vacuum Ladle electrolytic aluminum smelting process is important for the equipment, Its main function is to the electrolytic aluminum electrolytic cell fluid aspirated and unlucky to mixed stoves, aluminum water transit is important equipment. Ladle vacuum can be electrolyzer the smelter was sucked out of the mix and unlucky after casting furnace into ingots. The equipment maintenance costs low, safe, low labor intensity characteristics, Several lessons can be a cell of molten aluminum and directly sent mixed furnace without the halfway turn Ladle unlucky. Al small liquid heat loss. Ladle the use of suction pressure spray of aluminum, changed the traditional vacuum suction direct aluminum, Elimination of aluminum suction vacuum system for the harm, because of their shared cell with a gas source. package can be saved vacuum system to reduce the allocation of posts, reducing equipment maintenance, repair costs, saving operation of the electricity bill.
Ladle using vacuum-pouring teapot packet structure, aluminum liquid poured from the underwrite that was blocking the slag ladle, skims good effect. Reducer is Ladle dip turn, used three worm-drive. Ladle volume due to the increase of self-respect and all aluminum volume increased, ladle the tilting torque increases, manual dumping switch effort, inefficient and unsafe, the slowdown in aircraft structure design of the manual and electric may, the normal operation of electric, Manual for Maintenance and use of emergency, manual and electrical switch using a claw-type clutch, switching speedy and convenient, safe and reliable. The electric drive for three worm-slow manual for the two worm-deceleration than decelerating.
Keywords : vacuum ladle, reduction gears, worm gears, Worm
目 录
前言……………………………………………………………………………………1
1 项目分析……………………………………………………………………………3
1.1 真空抬包系统现有情况………………………………………………………3
1.2 本次设计改进所要解决的问题………………………………………………3
2 真空抬包总体设计方案……………………………………………………………5
3 大速比倾包系统设计………………………………………………………………6
3.1 倾转力矩的分析………………………………………………………………6
3.1.1 空包包体的倾转力矩 …………………………………………………6
3.1.2 余留铝液的倾转力矩 …………………………………………………7
3.1.3 摩擦力矩 ………………………………………………………………9
3.1.4 结论分析 ………………………………………………………………9
3.2 减速机构的分析………………………………………………………………9
3.2.1 蜗轮蜗杆减速机介绍 …………………………………………………9
3.2.2 传动比的分配…………………………………………………………11
3.2.3 电动机的选择…………………………………………………………11
3.2.4 蜗轮蜗杆设计…………………………………………………………11
4 真空抬包工艺参数 ………………………………………………………………21
5 主要部分的设计计算与校核 ……………………………………………………22
5.1 吊钩处………………………………………………………………………22
5.2 吊臂处………………………………………………………………………22
5.3 吊臂与包体连接处…………………………………………………………23
6 经济性分析 ………………………………………………………………………24
总结 …………………………………………………………………………………25
致谢 …………………………………………………………………………………27
参考文献 ……………………………………………………………………………28
前 言
众所周知,铝资源是铝业乃至国家铝工业的生存之基本和发展之本。是中国铝业如何实现铝矿资源持续稳定供应,是中围铝工业在市场竞争中求得生存并实现可持续发展必须要解决的重大课题。我国氧化铝工业的产量山l999年的146.1万吨增至2004年的700万吨,午均增幅为27.08%。但是,随着国内新建氧化铝企业生产能力的不断释放,市场竞争同趋激烈。自中国加入世界贸易组织后,逐渐实现了贸易白由化,进口氧化铝随着关税的逐步降低,配额等数量限制措施的消除都导致我国氧化铝企业受到国外氧化铝企业的冲击。随着氧化铝生产能力的提高,铝土矿一氧化铝一电解铝产业链中的瓶颈逐渐向铝土矿转移。在氧化铝的产量规模方面,我国一直遵循稳步提高的原则。但近几年来,我国氧化铝的增长速度明显加快。2000~2004年,氧化铝产量从432万吨增长到700万吨,年均增幅为12.3%,但是仍然难以满足铝业的要求,因此,从2001年开始,我围氧化铝进口量每年都以100万吨的速度递增。2004年我国共进口587万吨氧化铝,达到当年同内氧化销产茸的83%,是当年国内氧化铝需求的45%,比2000年我国进口氧化铝188万吨增张399万吨,累计增加2l3%。但是随着我国氧化铝产量的逐渐提高,氧化铝进口增幅正在下降。2006年前5 个月我国氧化铝产量98.8万 吨,同比增长49.33%,其中非中铝公司,产量为98.8万吨,同比增长67.8%。同期 氧化铝进口量278万吨,同比下降8.52%,特别自3月份
以来,连续3个月出现口氧化铝负增长。与此同时,中国氧化铝的出口量在不断增加。有报告显示,中围将在2008年成为氧化铝的纯出口国。
真空抬包是电解铝冶炼过程中的一个重要设备,主要功能是将铝电解槽中的电解铝液吸出并倒运至混合炉,本抬包适用于铝铸造行业,既可直接采用负压吸铝,也可通过喷射器利用压缩空气抽真空吸铝,抬包减速机为手动、电动两种操作均可,并可采用爪式离合器进行切换,抬包包衬采用重质浇注料整体浇注,强度高,使用寿命长。包体上焊接固定有喷嘴、吸铝管和出铝口,吊装总成连接机架,机架上装有传动机构,包盖上锁紧装置采用肘节式压紧,包盖侧板与连接板一端铰接,连接板另一端与肘节式把手铰接,肘节式把手前端与T型导杆横边一端固定连接,导杆横边另一端与侧板铰接,导杆坚边装有螺栓,包盖上与螺栓对应处固定有凸台。真空抬包系统,结构简单,性能好,容积大,大大提高生产率,降低成本,非常适用于电解铝生产线。
本次毕业设计对中原铝业河南分公司机械制造分公司的真空抬包系统,在原有的基础之上及厂里工程技术人员和老师的指导下进行改进和优化设计,得到现在的设计成果。以降低产品成本,最大的发挥原有产品的效能,提高产品的竞争力,提高经济效益,以适应竞争日益激烈的市场,为企业创造效益。也使我们的设计水平得到提高,提高了动手及创造的能力,是理论与实践的结合,使大家明确设自己设计目的和设计原则,为日后的工作打下一个良好的基础。
1.项目分析
1.1真空抬包系统现有情况:
真空抬包是电解铝冶炼过程中的一个重要设备,其主要功能是将电解槽中的电解铝液吸出并倒运至混合炉,是转运铝水的重要设备。真空抬包能够将电解槽中的电解铝液吸出并倒运到混合炉后浇铸成铝锭。该设备维护费用低、安全性高、工人劳动强度低等特点,一次可吸取几个电解槽内的铝液并直接送至混合炉,无需中途转浇包倒运,铝液热量损失小。该抬包采用正压喷射吸铝,改变了传统的负压直接吸铝,消除了负压吸铝对真空系统的危害,由于其可与电解槽共用一个气源,可省去整套真空系统,减少岗位配置,降低设备维护、检修费用,节约运行中的电费开支。
中国铝业河南分公司电解厂原电解槽为60kA自焙槽,年产铝量为3万吨,采用容重为2吨的真空抬包来吸铝,并配合5吨的敞口包来倒运即可满足生产的需要。随着电解技改扩建项目的完成,电解槽变为85kA预焙槽,电解厂年产铝量为5万吨,为解决铝液抽吸运转效率低下、铝液热量损失大的问题,需要研发容重为 4~6 吨无需中转浇包倒运的真空抬包。随着国内一些大型预焙电解槽的研发成功,电流已陆续提高至160kA.200kA.280kA.320kA,电解槽产铝量大增,小型吸铝真空抬包已不能满足生产的需要。
1.2 本次设计改进所要解决的问题:
吸铝真空抬包在外形上一般为普通倾注式锥桶形真空抬包,在结构上可分为包体、人孔、吊架、吸铝管、减速机及真空管等几部分,减速机可以手动操作。真空抬包主要用于电解铝厂,工作时直接采用负压吸铝,需要单独配置一套真空系统,由于吸入空气温度较高,真空泵一般采用水环真空泵,设备配置价高。抬包的清渣、检修及砌包衬均通过人孔进行,极为不便。为提高使用效率,使用时往往需要大型敞口浇包配合使用,这样会带来铝液热量的损失。而需解决这些问题所采用的方法是:
包盖与包体的密封及防变形措施。对于大型吸铝真空抬包,包体直径较大,包盖与包体法兰采用凸凹止口密封,密封件为石棉盘根。由于包盖与包体受热不均以及包体在起吊时的受力不均,容易导致包盖与包体法兰止口错位,从而引起密封不严。对于这个问题,一方面要加强包体与包盖强度,包体与包盖均需加筋,采用厚法兰。另一方面要采用合理的密封方式,可将包盖法兰嵌入至包体法兰内,形成双重止口密封,一旦小止口密封失效,可启用大止口密封。
包衬及吸铝管使用寿命。对于小型吸铝真空抬包,由于其直径小、高度低,采用耐火砖砌包衬,其强度足可满足其使用寿命,对于大型吸铝真空抬包,由于其容积大,包衬必需采用浇注料整体浇注,其强度才可满足使用寿命。吸铝管属耗损件,为提高其使用寿命,可采用耐温900℃以上的耐热铁铸造,并需进行热处理,耐热铁材质中Si含量不可过高,以防止和电解槽中的氟化盐发生化学反应,影响吸铝管使用寿命。
转轴位置的确定及倾转力矩的计算。对于大型吸铝真空抬包,由于采用电动操作,从操作安全的观点出发,转轴位置应高于空包和满包的重心。抬包倾转力矩M 包括空抬包包体所引起的转矩M1,以及在浇注过程中由于铝液不断倾出,余留在抬包内的铝液所引起的转矩M2,此外还有转轴与其轴颈的摩擦力矩M3,三者均为转角θ的函数。 M=M1+M2+M3
2.真空抬包总体设计基本方案
1.外形为圆柱状,方便制作、节省材料,与同体积锥桶形真空抬包相比,散热面积小,有利于保温。虽然锥桶形抬包比圆柱状抬包更有利于清理熔渣及残余铝液,但对于大容积抬包清除残渣已较为方便。
2.采用茶壶式浇包的结构形式,铝液从包底浇出,熔渣被挡在包内,撇渣效果好。抬包带包盖,包盖与包体采用活节螺栓连接,固定方便。包盖与包底封头采用平底封头。抬包大修、清渣、砌包衬均可开盖进行,十分方便。考虑到抬包的少量清渣、日常检修以及解决抬包在使用间歇中自身散热的问题,在包盖上设立了人孔。
3.包嘴盖设计成快开的结构形式,包嘴盖与包口管铰接,并采用搭扣来控制包嘴盖的开启与关闭,使用安全方便。
4.采用喷射器利用压缩空气抽真空吸铝。考虑到电解槽工作时,打壳下料、母线提升等工序均采用压缩空气工作,因此可与电解槽共用一个气源,减少设备配置。
5.喷射器由工作喷嘴、负压室、扩压管、接收室、消声器等组成,压缩空气通过收缩的喷嘴后,在负压室内形成一束高速射流,吸卷负压室内的空气一起进入扩压管,在扩压管内减速扩压后进入接收室,最后在接收内消音后排出至大气。
6.减速机是抬包的倾转机构,由于抬包容积的增大,自重及盛铝量均增大,抬包的倾转力矩增大,手动倾转费力、效率低而且不安全,该减速机在结构形式设计为手动与电动均可,正常操作为电动,手动为检修和突发事故时用,手动与电动的切换采用爪式离合器,切换迅速方便,安全可靠。该减速机电动为三级蜗轮蜗杆减速,手动为两级蜗轮蜗杆减速,减速比大。
参考文献
1.濮良贵,纪名刚.机械设计。北京[M]:高等教育出版社,2001.
2.刘鸿文,材料力学[M]。北京:人民教育出版社,1985。
3.韩向东,机械工程力学[M]。北京:机械工业出版社,2002。
4.联合编写组,机械设计手册(上中下)[S]。北京:机械工业出版社,1988。
5.联合编写组,机械设计手册(1-5卷)[S],。北京。机械工业出版社,1998。
6.朱龙根,黄雨华。机械设计系统[M]。北京:机械工业出版社,1992。
7.徐灏等,新编机械设计师手册[M]。北京:机械设计出版社,1995。
8. 王连明,机械设计课程设计。哈尔滨;哈尔滨工业大学出版社 2004。
9. 郁明山,现代机械传动手册[S]。北京:机械工业出版社,1994.5
10.Homer D.Eckhardc,Kinematic Design of Machines and Mechanisms[M],Beijing:McGrao-Hill
companies.Inc&China Machine Press,2002.
11..Rober L. Mott, machine Element in Mechanical Design[M],Beijing:Pearson
Education&China Machine Press,2004.
12.Richard.C.Dorf, ModenControlSystem[M], NEWYORK Addison-Wesley Puhlishing Company.Inc,1992
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号