行星齿轮减速箱运动仿真分析
26页10000字数+说明书+任务书+外文翻译+7张CAD图纸【详情如下】
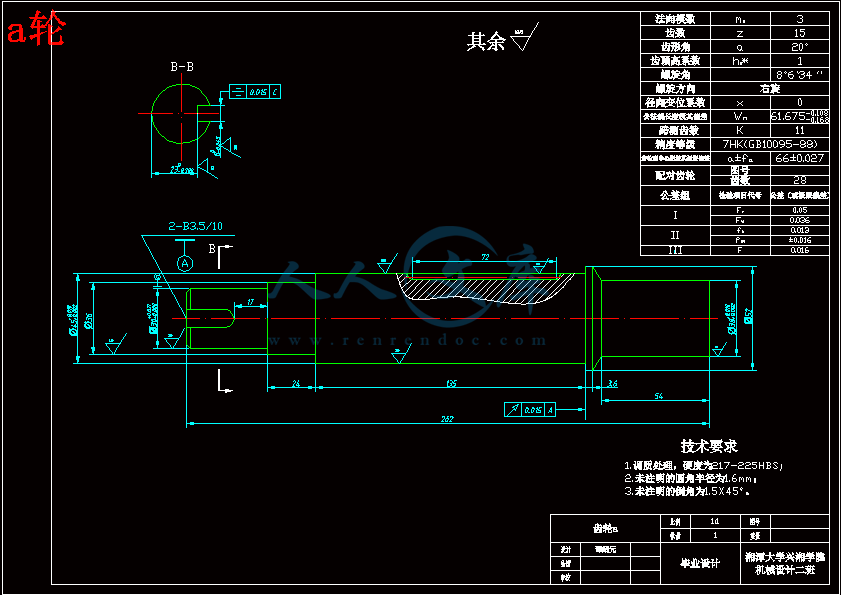
a轮.dwg
e轮.dwg
任务书.doc
前端盖.dwg
后端盖.dwg
外文翻译--轴和齿轮.doc
目录.docx
箱体1.dwg
行星齿轮减速箱运动仿真分析说明书.doc
装配图.dwg
论文封面.doc
评阅表.doc
转臂.dwg
鉴定意见.doc






目录
1 绪论
1.1行星减速器发展状况……………………………………………………………1
1.2选题分析与设计内容……………………………………………………………3
2行星齿轮减速器装置设计
2.1基本参数要求与选择………………………………………………………………5
3行星齿轮设计计算
3.1行星齿轮传动类型和传动简图的选择……………………………………………6
3.2配齿计算……………………………………………………………………………6
3.3初步计算齿轮的主要参数…………………………………………………………7
3.4啮合参数计算………………………………………………………………………7
3.5几何尺寸计算………………………………………………………………………10
3.6装配条件计算………………………………………………………………………13
3.7传动效率计算………………………………………………………………………13
3.8机构设计……………………………………………………………………………14
3.9行星齿轮强度验算…………………………………………………………………17
4 总结………………………………………………………………………………… 25
第一章 绪论
1.1行星减速器发展状况
由于国家采取了积极稳健的财政货币政策,固定资产投资力度加大,特别是基础建设的投资,使冶金、电力、水泥、建筑、建材、能源等加快了发展,因此,对减速机的需求也逐步扩大。随着国家对机械制造业的重视,重大装备国产化进程的加快以及城市化改造进程的加快,减速机行业仍将保持快速发展态势,尤其是齿轮减速机的增长将会大幅度提高,这与进口设备大多配套采用齿轮减速机有关。因此,业内专家希望企业抓紧开发制造齿轮减速机,尤其是大、中、小功率硬齿面减速机,以满足市场的需求。
国内外动力齿轮传动正沿着小型化、高速化、标准化、小振动、低噪声的方向发展。行星齿轮传动的发展和少齿差零齿差内齿轮副的应用,是当代齿轮的一大特征,是齿轮传动小型化的一个典型的标志。行星传动把传统的定轴传动改为动轴传动,采用了功率分流并合理应用内啮合及均载装置,具有重量轻,体积小,承载高等优点,因此,行星传动技术的应用日渐广泛。
20世纪末的20多年,世界齿轮技术有了很大的发展,铲平发展的总趋势是小型化,高速化,低噪声,高可靠度。技术发展中最引人注目的是应吃面技术,功率分支技术和模块化设计技术。
硬面齿轮技术到20世纪80年代在国外日趋成熟。采用优质合金钢锻件神探淬火磨齿的硬齿面齿轮,精度不低于IS01328-1975的6级,综合承载能力为中硬齿面调质齿轮的4倍,为软齿面齿轮的5-6倍。一个中等规格的硬齿面齿轮减速器的重量仅为软吃面齿轮减速器的1/3左右
功率分支技术主要指行星及大功率齿轮箱的功率双份及多分支装置,如中心传动的水泥磨主减速器,其核心技术是均载。
模块化设计技术队通用和标准减速器旨在追求高性能和满足用户多样化大覆盖面需求的同时,尽量减少零部件及毛坯的品种规格,以便于组织生产,使零部件产生形成批量,降低成本,取得规模效益。
其他技术的发展还表现在理论研究(如强度计算,修形技术,现代设计方法的应用,新齿形,新结构的应用等)更完善,更接近实际;普通采用各种优质合金钢锻件;材料和热处理质量控制水平的提高;结构设计更合理;加工精度普遍提高到ISO的4-6级;轴承质量和寿命的提高;润滑油质量的提高;加工装备和检测手段的提高等方面。
这些技术的应用和日趋成熟,使齿轮产品的性能价格比大大提高,产品越来越完美。如非常粗略地估计一下,输出100N m转矩的齿轮装置,如果在1950年时重10kg,到80年代就可做到仅为1kg。
20世纪70年代至90年代初,我国的高速齿轮技术经历了测绘仿制,技术引进到独立设计制造3个阶段。现在我国的设计制造能力基本可满足国内生产需要,设计制造的最高参数:最大功率44MW,最高线速度168m/s,最高转速67000r/min。
我国的低速重载齿轮技术,特别是硬齿面齿轮技术也经历了测绘仿制等阶段,从无到有逐步发展起来。除了摸索掌握制造技术外,在20世纪80年代末至90年代初步推广硬齿面技术过程中,我们还做了解决“断轴”,“选用”等一系列有意义的工作。在20世纪70-80年代一直认为是国内重齿轮两大难题的“水泥磨减速器”和“轧钢机械减速器”可以说已完全解决。
20世界80年代至90年代初,我国相继制定了一批减速器标准,如ZBJ19004—88《圆柱齿轮减速器》,ZBJ19026—90《运输机械用减速器》和YB/T050—93《冶金设备用YNK齿轮减速器》等几个硬齿面减速器标准,我国有自己只是产权的标准,如YB/T079—95《三环减速器》。按这些标准生产的许多产品的主要技术指标均可达到或接近国外同类产品的水平,其中YNK减速器较完整地吸取了德国FLENDER公司同类产品的特点,并结合国情做了血多改进与创新。
世界上一些工业发达国家,如日本,德国,英国,美国和俄罗斯等,对行星齿轮传动的应用,生产和研究都十分重视,在结构优化,传动性能,传动效率,转矩和速度等方面均处于领先地位,并出现一些新型的行星齿轮传动技术,如封闭行星齿轮传动,行星齿轮变速传动和微型行星齿轮传动等早已在现代化的机械传动设备中获得了成功的应用。
行星齿轮传动与普通定州齿轮传动相比较,具有质量小,体积小,传动比大,承载能力大以及传动平稳和传动效率高等优点,这些已经被我过越来越多的机械工程技术人员所了解和重视。由于在各种类型的行星齿轮传动种均有效地利用了功率分流性和输入,输出地同轴性以及合理的采用了内啮合,才使得其具有了上述的许多独特的优点。行星齿轮传动不仅适用于高速,大功率而且可用于低速,大转矩的机械传动装置上。它可以用作减速,增速和变速传动,运动的合成和分解,以及其特殊的应用中:这些功用对于现代机械传动发展有着重要意义。因此,行星齿轮传动在起重运输,工程机械,冶金矿山,石油化工,建筑机械,轻工纺织,医疗器械,仪器仪表,汽车,船舶,兵和航空航天等工业部门获得了广泛的应用。
本设计以本设计基于Solid Works便于交互及强大的二维、三维绘图功能。先确定总体思路、设计总体布局,然后设置零部件,最后完成一个完整的设计。利用Solid Works模块实现装配中零部件的装配、运动学仿真等功能。
行星齿轮减速器的体积、重量及其承载能力主要取决于传动参数的选择,设计问题一般是在给定传动比和输入转矩的情况下,确定各轮的齿数,模数和齿宽等参数。其中优化设计采用Solid Works自带的模块,模拟真实环境中的工作状况进行运动仿真,对元件进行运动分析。
减速器作为独立的驱动元部件,由于应用范围极广,其产品必须按系列化进行设计,以便于制造和满足不同行业的选用要求。针对其输人功率和传动比的不同组合,可获得相应的减速器系列。在以往的人工设计过程中,在图纸上尽管能实现同一机座不同规格的部分系列表示,但其图形受到极大限制。采用Solid Works工具来实现这一过程,不仅能完善上述工作,,方便设计操作,而且使系列产品的技术数据库,图形库的建立、查询成为可能,使设计速度加快。在设计过程中,我利用互联网对本课题的各设计步骤与任务进行了详细了解。采用计算机辅助设计的技术,利用Solid Works参数化建模。
在设计计算方面:分析行星齿轮机构传动方案;并通过计算分析,确定行星轮系齿轮的齿数、模数和轴、行星架的各项参数,校核齿轮的接触和弯曲强度;完成内外啮合齿轮、轴、行星架的设计计算;在整机设计开发背景下,结合运动参数完成建模。
在工程仿真分析方面:本论文利用三维软件Solid Works对行星轮减速器进行三维建模,并完成与整机的装配。2.1基本参数要求与选择
行星齿轮传动的类型很多,其分类方法也不少。在库氏的分类方法中,行星齿轮传动的基本代号为:Z——中心轮,X——转臂,V——输出轴(现说明:在库氏原著作中,K—中心轮,H—转臂)。根据其基本构件的配置情况,可将行星齿轮传动分为2Z-X、3Z和Z-X-V三种基本传动类型;其他的结构型式的行星齿轮传动大都是它们的演化型式或组合型式。
设计行星齿轮减速器,已知该行星传动的输入功率P1=22KW,输入转速n1=1500r/min,传动比ip=134,允许的传动比偏差△ip=0.01,短期间断的工作方式,每天工作16h,要求使用寿命8年;且要求该行星齿轮传动结构紧凑、外廓尺寸较小和传动功率较高。
参考文献
[1] 璞良贵,纪名刚主编.机械设计.第八版.北京:高等教育出版社,2005
[2] 王昆主编.机械设计课程设计.武汉:华中理工大学出版社,1922
[3] 卢颂峰、王大康主编.机械设计课程设计.北京:北京工业大学出版社,1993
[4] 吴宗泽、罗圣国主编.机械设计课程设计手册.北京:高等教育出版社,1992
[5] 孙桓,陈作模主编.机械原理.第六版.北京:高等教育出版社,2002
[6] 成大先主编.机械设计手册.北京:化学工业出版社,2004
[7] 饶振纲编著.行星齿轮传动设计.北京:化学工业出版社,2003
[8] 饶振纲.行星齿轮变速箱的设计与研究.传动设计,1999,(2)
[9] 中华人民共和国国家标准.GB/T272-93.滚动轴承的代号.北京:中国标准出版社
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号