电吹风外壳模具设计
吹风机外壳的注塑模设计
电吹风外壳注塑模的设计【含全套CAD图纸】【优秀】【word+11张CAD图纸全套】【注射塑料模具类】【毕业设计】
【带任务书+开题报告+选题审批表+中期检查表+实习报告+外文翻译】【51页@正文23500字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】.bat
2.3注射成型外文文献翻译.doc
中期检查.doc
中期检查表.doc
任务书.doc
凸模.dwg
凹模.dwg
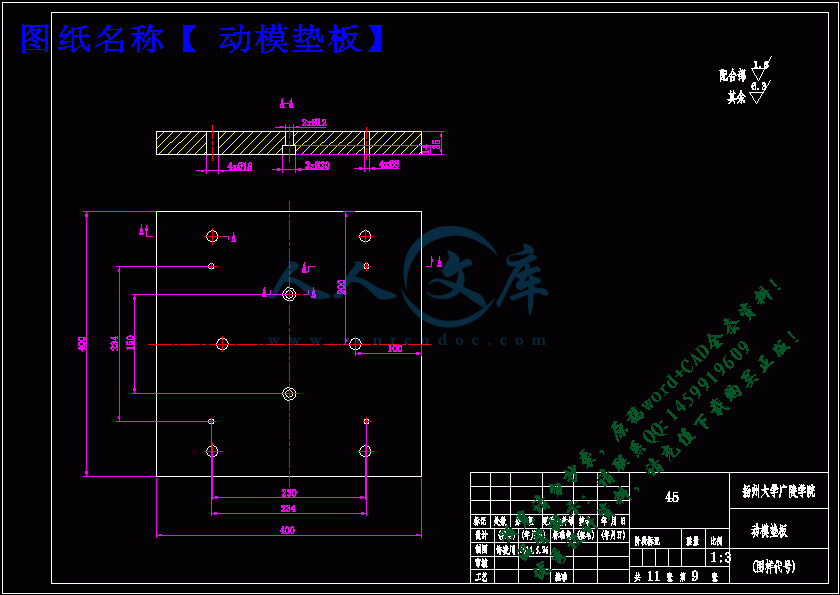
动模垫板.dwg
动模座板.dwg
动模板.dwg
定模座板.dwg
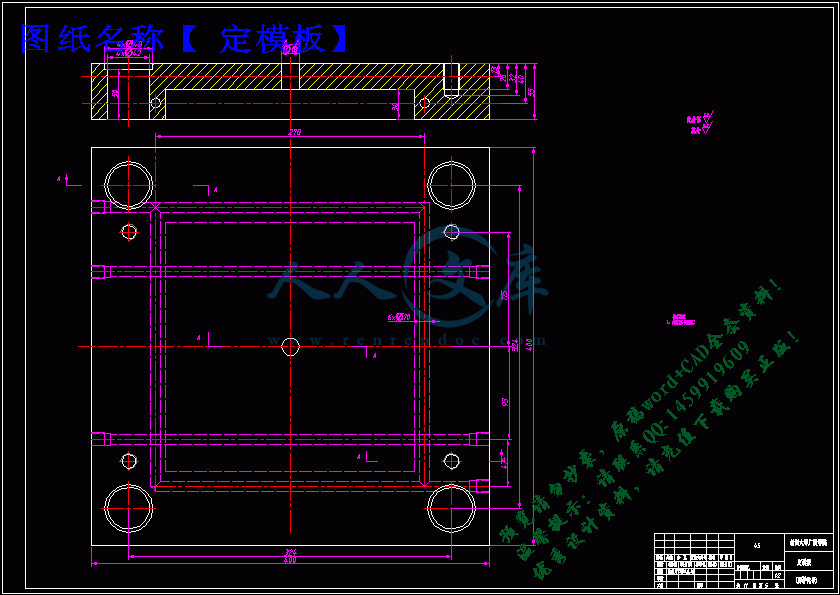
定模板.dwg
实习报告.doc
开题报告.doc
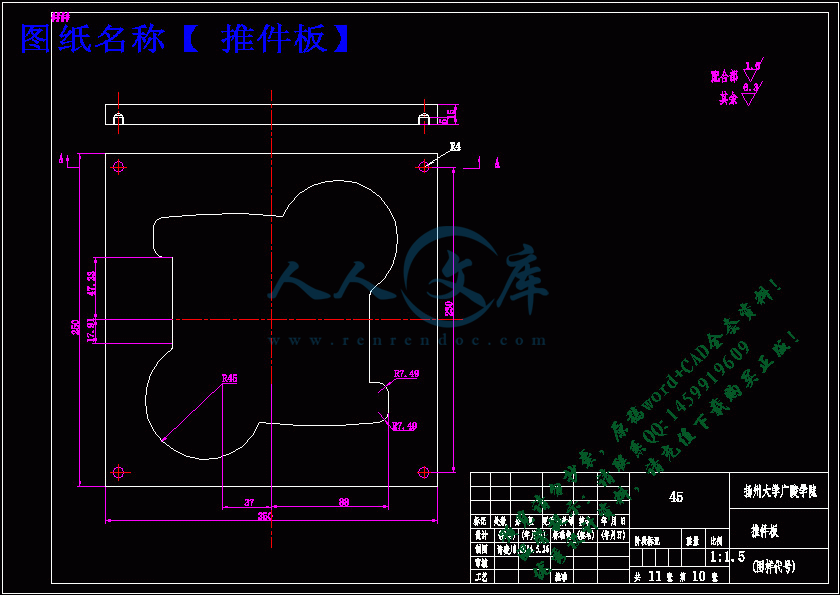
推件板.dwg
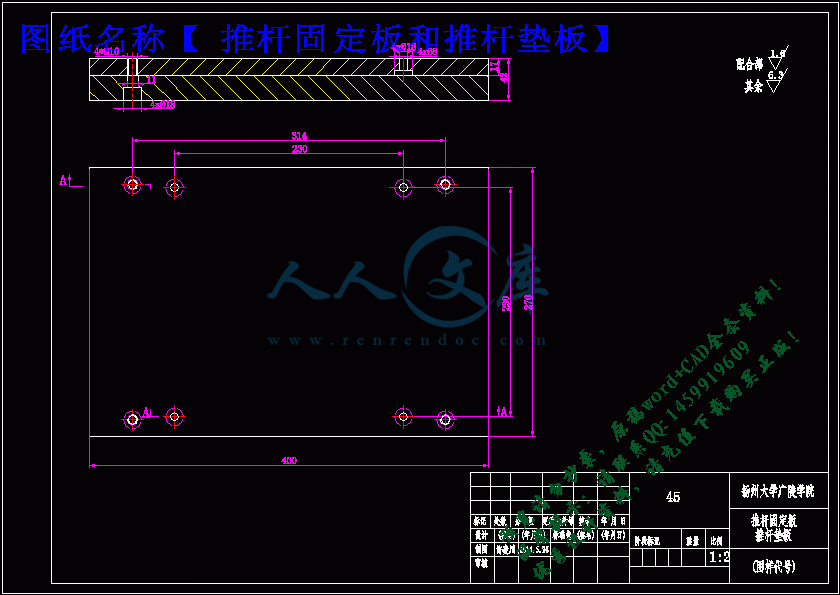
推杆固定板和推杆垫板.dwg
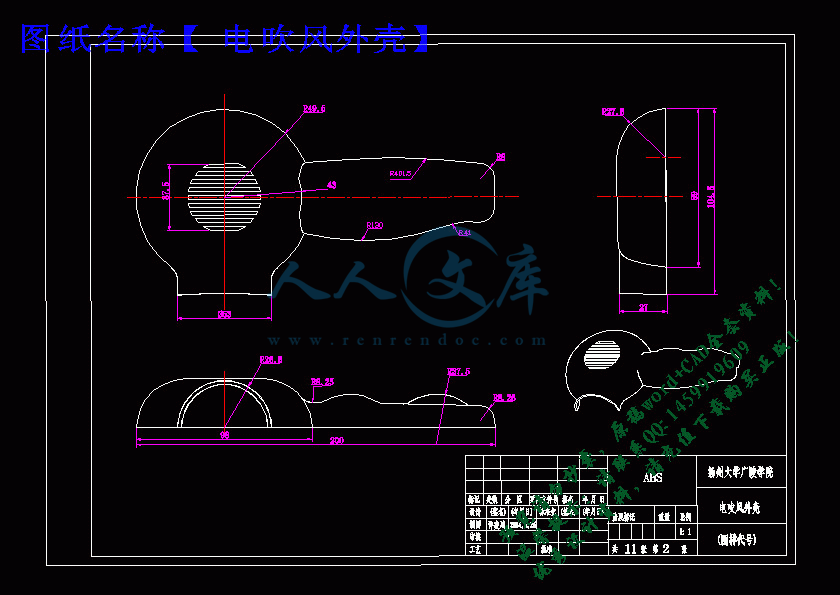
电吹风外壳.dwg
电吹风外壳模具设计正文.doc
装配图.dwg
选题审题表.doc
任务书
1、本毕业设计(论文)课题应达到的目的:
① 掌握塑料模具的相关知识
② 了解注塑模具的设计方法
③ 阅读大量模具设计相关文献,能独立翻译外语资料
④ 初步学会CAD绘图和Pro/e等软件的三维造型
⑤ 结合查找的资料与自己的设计,能撰写设计说明书
2、本毕业设计(论文)课题任务的内容和要求(包括原始数据、技术要求、工作要求等):
1)本课题应完成的主要内容有:
①收集阅读大量资料,完成文献翻译和文献综述;
②电吹风面壳三维造型;
③由三维模型设计出上下模;
④完成模架的设计;
⑤设计模具整体结构;
⑥生成上下模及部分模架构件的工程图。
2)本课题应完成的主要要求有:
①设计的模具及注塑件的质量寿命达到要求;
②模具及其组成系统结构合理,经济性好;
③模具装配方便,零件结构合理,加工可行;
④出图数量跟质量达到要求;
毕业设计(论文)任务书
3、对本毕业设计(论文)课题成果的要求(包括毕业设计论文、
图表、实物样品等):
1.开题报告:包括任务书,文献综述,实习报告与外文翻译跟中期检查表等。
2.出图:①电吹风外壳三维造型;②由三维模型设计出上下模;
③设计模具整体结构;④生成上下模及部分模架构件的工程图;
3. 注射模设计说明书
4、主要参考文献:
1、何满才 Pro/ENGINEER模具设计与Mastercam数控加工 人民邮电出版社
2、单泉、陈砚、阚虎等 Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire3.0中文版模具设计专家指导教程
机械工业出版社
3、凯德. 精通Pro/Engineer中文野火版模具设计[M]. 北京:中国青年出版社.2007.
4、张磊、谢龙汉 Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire4.0 模具设计视频精讲 人民邮电出版社
5、胡仁喜、康士廷 Pro/Engineer Wildfire5.0中文版模具设计从入门到精通 机械工业出版社
6 张鲁阳.《以工程思维为主线组织教学内容.再谈模具专业材料学课程改革》
[J].机械工业高教研究 2001.7
7 陈志刚.《塑料模具设计》[M].北京 机械工业出版社 2002.
8 吴兆祥.《模具材料及表面处理》[M].北京 机械工业出版社 2003.
9 屈华昌.塑料成型工艺与模具设计.北京机械工业出版社.2003.
10 李德群.唐志玉.《中国模具设计大典》.江西科学技术出版社.2003.1.
11 塑料模设计手册编写组.《塑料模设计手册》.北京机械工业出版社.1982.12.3.
12 姜勇.《AutoCAD2006基础培训教程》.人民邮电出版社.2006.3.
13 伍先明等编著.《塑料模具设计指导》[M].国防工业出版社,2006.
14 邹强主编.《塑料模具设计参考资料汇编》[M].清华大学出版社, 2005.
15 邹玉堂编著.《Pro/ENGINEER实用教程》[M].机械工业出版社,2005.
16 杨占尧 自柳主编.《塑料模具典型结构设计实例》.化工公业出版社,2008
17 申开智主编.《塑料成型模具(第二版)》 中国轻工业出版社 2009
18 丁 浩主编.《 塑料加工基础》 上海科技出版社 1998
毕业设计(论文)任务书
5、本毕业设计(论文)课题工作进度计划
起止日期工 作 内 容
第1~3周了解相关知识、完成实习调研,作开题报告
第4、5周完成模具结构设计,包括凸凹模具、模架的三维造型
第6、7周完成相关的零件图、装配图。中期检查
第8~10周撰写毕业设计说明书
第11、12周完善相关资料、答辩
摘 要
模具现在已经成为工业发展的基础,而塑料模占模具总量的比例达到35%~40%,塑料成型模具的应用在各类模具的应用中占有领先地位。注射成型是塑料成型的一种重要方法,它主要适用于热塑性塑料的成型,可以一次成型形状复杂的精密塑件。本课题就是电吹风外壳作为设计模型,将注射模具的相关知识作为依据,阐述塑料注射模具的设计过程。
通过对电吹风外壳成型工艺的分析,本人设计了一副一模两腔的塑料模具。模具中决定塑件几何形状和尺寸的零部件称为成型零件,包括上模板、上模芯、下模板、下模芯、下模镶件等的设计与加工工艺过程。设计成型零部件时,应根据塑料的特性、塑件的结构和使用要求,确定型腔的总体布局,选择分型面,确定脱模方式,设计浇注系统、排溢系统。然后进行成型零部件的结构设计,计算成型零部件的工作尺寸,对关键的成型零部件进行强度和刚度校核。然后运用Pro/E软件完成电吹风外壳模具的整体设计;最后应用Pro/E中的塑料顾问模块(Plastic Advisor),对塑料制品进行注射仿真分析。
关键词:注射成型;电吹风外壳;一模两腔;Pro/E。
Abstract
The?design?of?the?Cd-rom?shell?injection?mould?Abstract?Mould?has?become?the?foundation?for?industrial?development?,and?plastic?moulds?account?for?the??Proportion?of?the?total?35%~40%,plastic?mould?used?in?the?application?of?various?types?of?mould?occupies?a?leading?position?.Injection molding is an important method of plastic molding. It mainly suits thermoplastic molding which can be used to shape a precision plastic part in one time. My topic is to explain the design process of the plastic injection mold on the basis of the injection mold-related knowledge, taking the hair dryer enclosure as a design model.
Through analysis of the hair dryer shell molding process, I designed a double-cavity plastic mould. Those parts that deciding the geometrical shape and dimensions of the plastic mold are known as molded parts, including the design and machining process of the upper plate, the upper mold core, the lower plate, the lower mold core, and the inserting of lower mold.While designing molding components, based on the characteristics of plastic, plastic parts of the structure and use requirements, the overall layout of the cavity, the joint face, the stripping methods, design of gating system, exhaust system should be determined. Then structure of molded parts are designed, the working size of the molded parts is calculated, the key molded parts are checked for strength and rigidity. Then use Pro / E software to complete the overall design hair dryer shell mold; and finally the plastic module consultant (Plastic Advisor) in Pro / E is applied for plastic injection simulation analysis.
Key word: Injection molding; hair dryer shell; double-cavity mold; Pro / E.
目 录
摘要
Abstract
第一章 绪论
1.1塑料模具业的现状1
1.2常见的塑料成型模具1
1.3注射模具的发展趋势2
第二章 塑料成型工艺
2.1塑料制品的结构和工艺性能设计3
2.2注塑成型工艺过程5
2.3注塑成型设备6
第三章 电吹风外壳注射模设计
3.1注射模具分类及典型结构 13
3.2电吹风外壳模具的结构设计 16
3.3注射模具与注射机的关系 26
第四章 电吹风外壳模具三维设计
4.1Pro/e模具设计过程简介32
4.2EMX模架设计34
第五章 电吹风外壳注射仿真分析
5.1 Plastic Advisor的简介38
5.2塑料顾问模块的进入38
5.3 分析功能应用 39
5.4 分析结果 41
第六章 小结43
致 谢44
参考文献45
第一章 绪论
1.1塑料模具业的现状
随着工业发展水平的不断提高,工业产品更新的速度越来越快,对模具的要求也越来越高。改革开放以来,模具工业的发展有了较大发展,但无论数量和质量都仍满足不了市场的需要,目前满足率只能达到百分之七十左右,造成产需矛盾突出的原因,异世专业化、标准化程度低,除了少数标准件外购外,大部分工作量都需要模具厂去完成,因此造成模具制造周期长,不能适应市场的要求。二是设计和工艺技术落后,如模具CAD/CAM技术采用不普遍,加工设备数控化程度低,亦造成模具生产效率不高周期长。总之,是拖了机电,轻工业的后退,因此对模具设计的研究的目的和意义在于能够更好的认识模具工业在国民经济中的重要性。因为利用模具成型零件的方法,是一种少切削乃至无切削打的多工序重合的生产方法,采用模具成型的工艺替代传统工艺,可以大大提高成产率、保证零件质量、节约材料、降低生产成本,从而提高经济效益。因此,德国把模具称为“金属加工中的帝王”,把模具工业称为“关键工业”,美国把模具称为“美国工业的基石”,把模具工业视为“不可估量的工业”,在罗马尼亚则更为直接:“模具就是黄金”。可见模具工业在国民经济中重要地位。我国对模具工业的发展也十分重视,早在1989年3月颁布的《关于当前国家产业政策要点的决定》中,就把模具技术的发展作为机械行业的首要任务。人们对产品要求其独具个性,特别是一些生活用品,不仅要求它要实用,还要求它外观漂亮,美丽的外观以及产品的环保性吸引着每个人的眼球。
目前,吹风机的样式越来越多,外观也越来越复杂。因而模具的要求也越来越高,设备也更先进,制造工艺也比以前要更有难度。在这样的市场中要有立足之地,对我们设计人员是一个相当大的考验,设计人员必须多掌握几种软件。设计出来的东西要有创新才行,这样才不会被淘汰。
1.2常见的塑料成型模具
按照成型方法的不同,可以划分出对应不同工艺要求的塑料加工模??具类型,主要有注射成型模具、挤出成型模具、吸塑成型模具、高发泡聚苯乙烯成型模具等。下面具体介绍的是本课题采用的塑料注射模具。
1.2.1塑料注射模具?
它主要是热塑性塑料件产品生产中应用最为普遍的一种成型模具,塑料注射成型模具对应的加工设备是塑料注射模具对应的加工设备是塑料注射成型机,塑料首先在注射机底加热料筒内受热熔融,然后在注射机的螺杆或柱塞推动下,经注射机喷嘴和模具的浇注系统进入?模具型腔,塑料冷却硬化成型,脱模得到制品。其结构通常由成型部件、浇注系统、导向部件、推出机构、调温系统、排气系统、支撑部件等部分组成。制造材料通常采用塑料模具钢模块,常用的材质主要为碳素结构钢、碳素工具钢、合金工具钢,高速钢等。注射成型加工方式通常只适用于热塑料品的制品生产,用注射成型工艺生产的塑料制品十分广泛,从生活日用品到各类复杂的机械,电器、交通工具零件等都是用注射模具成型的,它是塑料制品生产中应用最广的一种加工方法。?
1.3注射模具的发展趋势
近年来,模具增长十分迅速,高效率、自动化、大型、微型、精密、高寿命的模具在整个模具产量中所占的比重越来越大。从模具设计和制造角度来看,模具的发展趋势可分为以下几个方面:?加深理论研究?在模具设计中,对工艺原理的研究越来越深入,模具设计已经有经验设计阶段逐渐向理论技术设计各方面发展,使得产品的产量和质量都得到很大的提高。高效率、自动化?大量采用各种高效率、自动化的模具结构。高速自动化的成型机械配合以先进的模具,对提高产品质量,提高生产率,降低成本起了很大的作用。?大型、超小型及高精度?由于产品应用的扩大,于是出现了各种大型、精密和高寿命的成型模具,为了满足这些要求,研制了各种高强度、高硬度、高耐磨性能且易加工、热处理变形小、导热性优异的制模材料。?革新模具制造工艺?在模具制造工艺上,为缩短模具的制造周期,减少钳工的工作量,在模具加工工艺上作了很大的改进,特别是异形型腔的加工,采用了各种先进的机床,这不仅大大提高了机械加工的比重,而且提高了加工精度。?标准化?开展标准化工作,不仅大大提高了生产模具的效率,而且改善了质量,降低了成本。
第二章 塑料成型工艺
塑料成型是将塑料原材料转变为所需形状和性能的塑件的一门工程技术。在设计模具时不仅要了解塑料制作的技术要求和注射成型的工艺过程,还必须了解注射机的技术规范,以保证设计的模具与使用的注射机相适应。
其中,塑料注塑成型,又称注射成型,是目前塑料加工中最普遍采用的方法之一,除用于热塑性塑料成型外,近年来,也用于部分热固性塑料的成型加工。注塑成型生产效率高、易于实现机械化和自动化、并能制造外形复杂、尺寸精确的塑料制品,大约60%~70%的塑料制件用此方法生产。
2.1塑料制品的结构和工艺性能设计
2.1.1塑件结构形状
制品的整体外形尺寸与塑料的流动性有关。在注射成型与传递成型中,当塑料流动性能差时(如玻璃纤维或石棉纤维增强塑料)以及制品壁厚较薄时,其整体外形尺寸不能设计过大。此外,整体外形尺寸受到成型设备的制约。
2.1.2塑件材料选择
结合电吹风外壳壁薄的特点,本课题选流动性较好的材料:丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯共聚物(ABS)。ABS的密度和收缩率见表2-1。
2.1.3物料性能
1.综合性能较好,冲击强度较高,化学稳定性,电性能良好.
2.与372有机玻璃的熔接性良好,制成双色塑件,且可表面镀铬,喷漆处理。
3.有高抗冲、高耐热、阻燃、增强、透明等级别,柔韧性好。
4.适于制作一般机械零件,减磨耐磨零件,传动零件和电讯零件。
2.1.4成型性能
无定形料,流动性中等,吸湿大,必须充分干燥,表面要求光泽的塑件须长时间预热干燥80-90度,3小时。宜取高料温,高模温,但料温过高易分解。对精度较高的塑件,模温宜取50-60度,对高光泽.耐热塑件,模温宜取60-80度。冷却速度快,模具宜加热,应选用耐磨钢。
2.1.5塑料制件的结构工艺性
要想获得合格的塑料制件,除合理选用塑件的原材料外,还必须考虑塑件的结构工艺性。塑件的结构工艺性与模具设计有直接关系,只有塑件结构设计满足成型
工艺要求,才能设计出合理的模具结构,以防止成型时产生气泡、缩孔、凹陷及开裂等缺陷,达到提高生产率和降低成本的目的。塑件结构工艺性设计的主要内容包括:尺寸和精度、表面粗糙度、塑件形状、壁厚、脱模斜度、加强筋、支承面、圆角、孔、螺纹、齿轮、嵌件、文字、符号及标记等。
下面重点介绍一下脱模斜度,壁厚,制品的精度和粗糙度等四个方面
1、脱模斜度
查表2-2可知ABS型腔的脱模斜度为,型芯的脱模斜度为。
2、壁厚
塑料制品的壁厚对制品质量有至关重要的影响。壁厚过后,不但用料多,成本高还容易产生气泡、缩化、凹陷等缺陷,而且冷却时间长生产效率低(对热塑性塑料制品而言)。壁厚过薄,成型困难,流动阻力大,尤其是大型制品和形状复杂制品。
制品最小壁厚的确定原则:(1)脱模时受顶出零件的推力不变形;(2)能承受装配时紧固力。壁厚因制品大小和塑料品种的不同而异。热塑性塑料制品的最小壁厚可达到0.25mm,但一般在(0.6~0.9)mm之间。常用壁厚为(2~4)mm。
本课题电吹风外壳的壁厚为2.25mm。
3、制品的精度
影响制品精度的因素较多。首先是模具的制造精度和模具的磨损量,其次是成型工艺条件的变化所引起的塑料收缩率的波动。另外,成型后的实效率变化和模具结构形式对尺寸精度也有一定的影响。因此,对塑料制品的精度要求不能过高,应在保证使用性能的情况下,尽可能选用低精度等级。
本课题采用一般精度MT3,对应公差为0.55mm。
参考文献
[1]模具设计与制造技术教育丛书编委会编.模具结构设计. 机械工业出版社. 2006 年7月
[2]周斌兴. 冲压模具设计与制造实训教程. 国防工业出版社. 2006 年4月
[3]何满才. Pro/ENGINEER模具设计与Mastercam数控加工. 北京:人民邮电出版社,2005.
[4]谭雪松、姜胜、陈霖. Mastercam数控加工实战训练. 北京:人民邮电出版社,2005.
[5]单泉、陈砚、阚虎等. Pro/ENGINEER Wildfire3.0中文版模具设计专家指导教程. 北京:机械工业出版社,2006.
[6]凯德. 精通Pro/ENGINEER中文野火版模具设计. 北京:中国青年出版社,2007.
[7]赵俊武、谭刚、汤浩. Mastercam模具设计实例教程. 北京:清华大学出版社,2008.
[8]宋满仓、黄银国、赵丹阳. 注塑模具设计与制造实践. 北京:机械工业出版社,2003.
[9]张荣清. 模具设计与制造. 北京:高等教育出版社,2008.
[10]凃序斌、朱三武、李奇. 塑料成型与模具设计. 北京:北京理工大学出版社,2009.
[11]曹丽平、赵祝和. 塑料模具设计步骤与实例精解. 北京:机械工业出版社,2010.
[12]陈少克. 塑料注射模具设计及其CAD技术. 北京:中国电力出版社,2010.
[13]许发樾. 模具标准化与原型机构设计. 北京:机械工业出版社,2009.
[14]刘朝福. 注塑模具设计师速查手册. 北京:化学工业出版社,2010.
[15]王永平. 注塑模具设计经验点评. 北京:机械工业出版社,2005.
[16]邹继强. 塑料模具设计参考资料汇编. 清华大学出版社,2005.
[17]王华山. 塑料注塑技术与实例. 北京:化学工业出版社,2006.
[18]齐晓杰. 塑料成型工艺与模具设计. 北京:机械工业出版社,2005.








 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号