连接座零件的加工工艺规程及夹具设计
连接座机械的加工工艺规程及6×Ф7孔加工专用夹具设计
车床连接座的机械加工工艺编制及夹具设计
连接座钻床专用夹具设计
车床连接座的加工工艺规程夹具设计
连接座的工艺规程及钻6×Ф7孔夹具设计
连接座的工艺规程及夹具设计
连接座的夹具设计
连接座工艺规程及钻6×Ф7孔工艺装备设计
连接座工艺规程及钻3×Ф7孔工艺装备设计
车床连接座的加工工艺规程及钻3XФ7孔夹具设计【优秀】【工艺装备夹具类】【带UG三维零件】【5张CAD图纸】【LJZ02】【毕业设计】
【word文档包含:开题报告、外文翻译工艺过程、工序卡片,43页@正文14200字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609 】.bat
hanming.prt
lingjiantu.igs
外文翻译.doc
夹具体.dwg
夹具总装.dwg
工序卡.doc
工序卡片.dwg
开题报告.doc
摘要.doc
说明书.doc
连接座.dwg
连接座毛坯.dwg
摘要
在生产过程中,使生产对象(原材料,毛坯,零件或总成等)的质和量的状态发生直接变化的过程叫工艺过程,如毛坯制造,机械加工,热处理,装配等都称之为工艺过程。在制定工艺过程中,要确定各工序的安装工位和该工序需要的工步,加工该工序的机车及机床的进给量,切削深度,主轴转速和切削速度,该工序的夹具,刀具及量具,还有走刀次数和走刀长度,最后计算该工序的基本时间,辅助时间和工作地服务时间。
关键词: 工序,工艺,工步,加工余量,定位方案,夹紧力
ABSTRACT
Enable producing the target in process of production (raw materials, the blank , state of quality and quantity on part become always ) take place direct course of change ask craft course, if the blank is made, machining, heat treatment , assemble etc. and call it the craft course. In the course of making the craft , is it confirm every erector location and worker step that process need this of process to want, the locomotive of processing , this process , and the entering the giving amount of the lathe, cut depth , the rotational speed of the main shaft and speed of cutting, the jig of this process, the cutter and measuring tool, a one hundred sheets of number of times still leaves and a one hundred sheets of length leaves, calculate basic time of this process , auxiliary time and service time of place of working finally.
Keywords: The process, worker one, worker's step , the surplus of processing, orient the scheme , clamp strength目录
绪论3
第一章 零件的分析5
1.1零件的形状5
1.2零件的工艺分析7
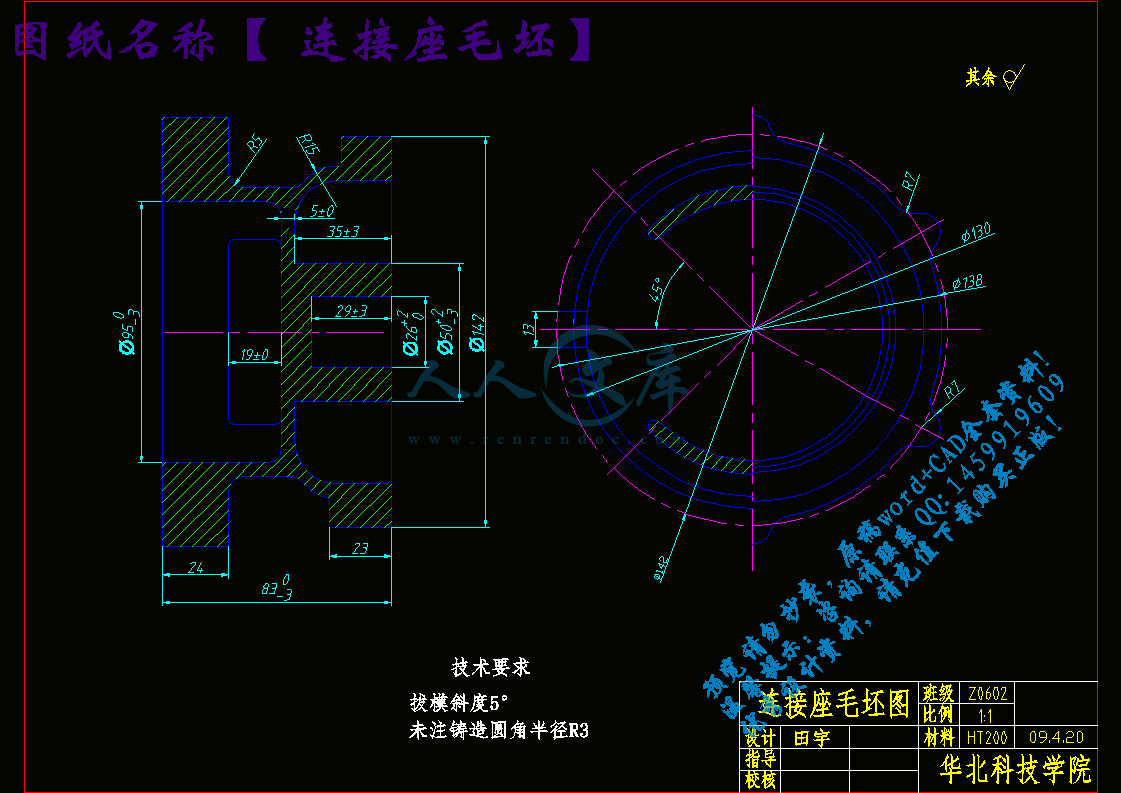
第二章 毛坯设计9
2.1毛坯的选择9
2.2毛坯尺寸和公差10
2.2.1确定毛坯尺寸10
2.2.2确定毛坯尺寸公差10
2.3设计毛坯图11
第三章 机械加工工艺过程设计13
3.1定位基准的选择13
3.1.1精基准的选择13
3.1.2粗基准的选择14
3.2表面加工方法的选择14
3.2.1加工经济精度14
3.2.2选择表面加工方法应考虑的因素17
3.3加工阶段的划分17
3.4工序顺序的安排19
3.4.1工序顺序安排的原则19
3.4.3辅助工序的安排20
3.5制定加工工艺路线21
3.5.1拟定比较两种工艺路线21
3.5.2拟定工艺过程24
第四章 工序设计26
4.1选择机床,根据不同的工序选择机床26
4.1.1车床用CA614026
4.2工艺装备的选择27
4.2.1刀具的选择27
4..2.2夹具的选择28
4.2.3量具的选择28
4.3确定机械加工余量28
4.3.1确定加工余量的方法28
4.3.2影响加工余量的因素29
4.3.3确定加工余量29
4.4工序尺寸及公差的确定30
4.4切削用量的选择31
第五章 基本时间的确定33
5.1时间定额的定义33
5.2时间定额的组成33
5.3工时定额的计算34
第六章 夹具设计35
6.1 定位基准的选择35
6.2压紧元件的选择35
6.3切削力及夹紧力的计算35
6.4误差分析与计算37
6.5夹具设计及操作的简要说明38
结论39
参考文献40
致谢41
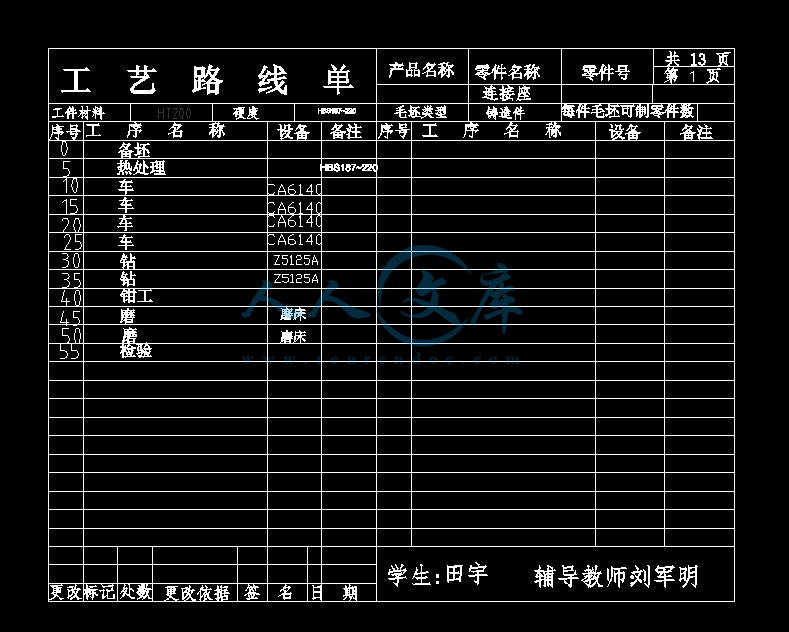
附:连接座机械加工工艺过程卡、工序卡
绪论
进入21世纪,随着科学技本的迅猛发展,传统的制造技术已进入现代制造技术的新阶段。机械制造工艺学则是现代制造技术的主要基础近年来随着经济的飞速发展,无论是国防建设,还是汽车、轮船、交通等都对机械产品的需求越来越大,因此,极大的推动了机械制造业的发展。然而机械制造业的发展离不开加工机械——机床。为了满足生产的需要,对机床的种类、性能业都有了很高的要求。同时,为了使机械产品由原材料在机床上经过加工变为机械成品这就需要相应的机床夹具及合理的机械加工工艺。先进的机床夹具和合理的制造工艺是制造业降低成本提高生产效率的关键。因此,设计高效能的机床夹具和制定经济合理的工艺方案对提高制造企业的竞争力有着很大的帮助。所以,我们有必要研究他,而且应该仔细研究他。
机电一体化专业毕业设计所设计的内容比较多,他集专业课、基础课知识于一体,是在学习完机械制造工艺学(含机床夹具)、机械设计基础、机械制图、计算机绘图、工程力学等全部专业课的基础上进行的,是对我们所有课程的一次综合性的复习,业师理论联系实际的练习,为今后走上工作岗位打下台阶,因此我们必须以严谨、认真务实的态度对待这次设计,把设计做好。
机械工业是为国民经济提供装备和为人民生活提供耐用消费品的产业。机械工业的技术水平和规模是衡量一个国家科技水平和经济实力的重要标志。经过建国40多年的发展,机械工业已成为我国工业中产品门类比较齐全,具有相当规模和一定技术基础的支柱产业之一。为了达到产品的要求,必须研究和控制机械产品的制造过程,研究和解决工艺技术问题的方法和措施。
机械制造工艺学的研究范畴是零件的机械加工和装配的工艺过程。很长时间以来机械加工工艺最广泛采用的方法是切削加工和磨削加工。随着科学技术的发展,出现了很多硬度极高的难加工材料,这些材料很难用传统的切削或磨削的方法来加工;另一方面,科学技术的发展对机械产品的精度提出了越来越高的要求,于是各种精密加工方法应运而生,而且其加工的精度等级还在不断的提高。
刀具材料的革新和新刀具材料的开发,优良的机床静态、动态特性和高转速,使告诉切削和高速磨削成为可能,从而缩短了机动切削时间,充分发挥了传统加工方法的技术潜力,使劳动生产率得到显著提高。
制造过程的自动化发展是机械制造业中最新技术进步的又一个重要方面。随着数控加工的应用和推广,计算机辅助设计(CAD)和计算机辅助制造(CAM)逐步进入实用阶段,尤其是柔性制造系统(FMS)的出现,不仅大大提高了生产效率,降低了生产成本,同时也可靠的保证了产品的质量和从根本上改善了劳动条件。目前,世界各国正致力于计算机集成制造系统(CIMS)的研究和开发。这种计算机集成制造系统是由一个多级计算机控制的全盘自动化系统。它通过一套软件将设计、制造和管理综合为一个整体。它是工厂各个环节自动化的有机地集成是工厂自动化的发展方向。
第一章 零件的分析
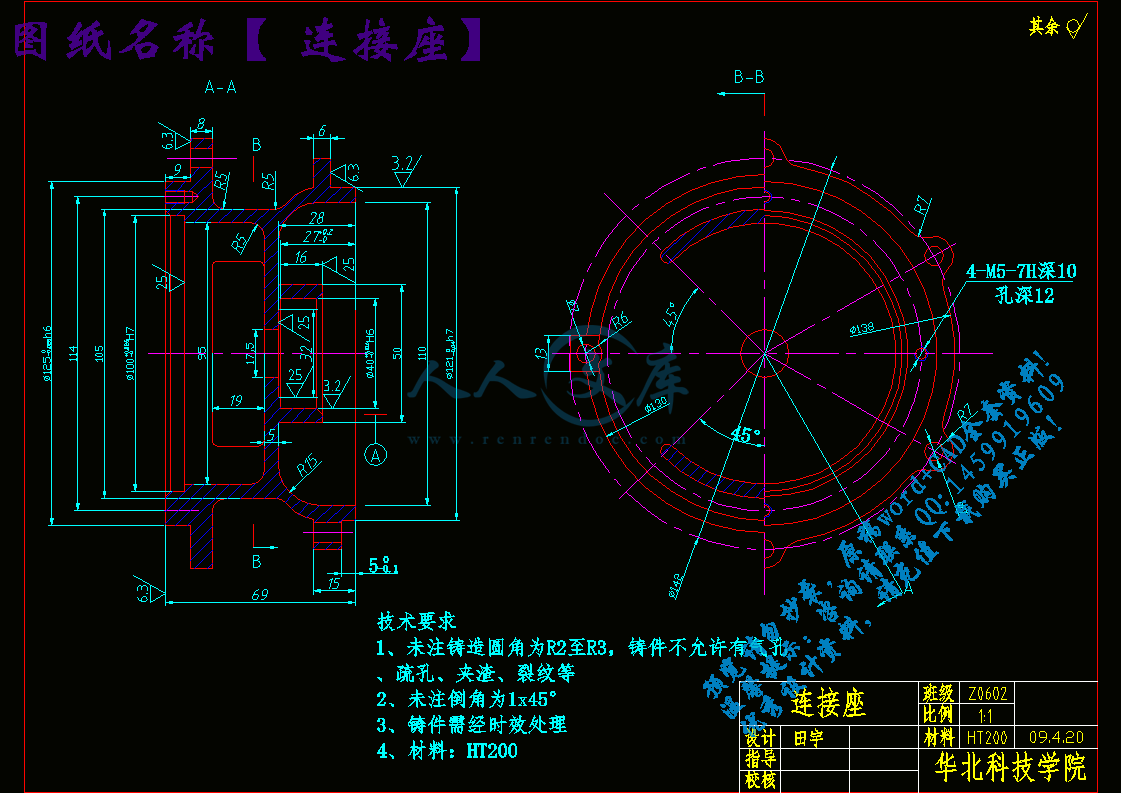
1.1零件的形状
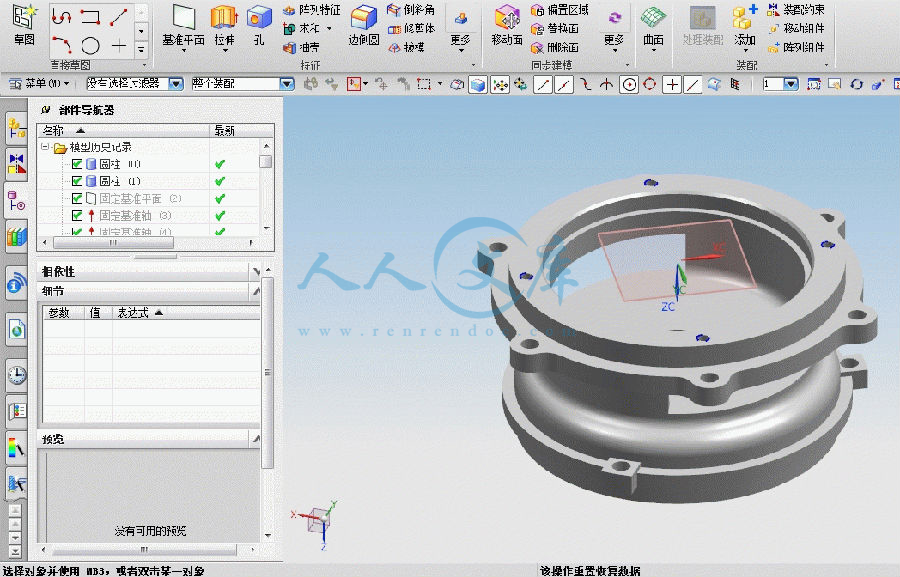
零件的实际形状如上图所示,?从零件图上看,该零件是典型的零件,结构比较简单。具体尺寸,公差如下图所示。
1.2零件的工艺分析
由零件图可知,其材料为HT200,该材料为灰铸铁,具有较高强度,耐磨性,耐热性及减振性,适用于承受较大应力和要求耐磨零件。
连接座共有两组加工表面,他们之间有一定的位置要求。现分述如下:
(1).左端的加工表面:
? ? 这一组加工表面包括:左端面,Φ1250-0.025外圆,Φ100内圆,倒角,钻通孔Φ7,钻孔并攻丝。这一部份只有端面有6.3的粗糙度要求,Φ100的内圆孔有25的粗糙度要求。其要求并不高,粗车后半精车就可以达到精度要求。而钻工没有精度要求,因此一道工序就可以达到要求,并不需要扩孔、铰孔等工序。
参考文献
[1] 纪名刚,濮良贵. 机械设计. 第七版. 北京:高等教育出版社,2003
[2] 熊良山,严晓光,张福润. 机械制造技术基础. 武汉:华中科技大学出版社, 2007
[3] 刘光启,赵海霞. 机械制造制图手册. 北京:化学工业出版社,2005
[4] 杨家军. 机械原理. 武汉:华中科技大学出版社, 2005
[5] 常明,童秉枢. 画法几何及机械制图. 第三版. 武汉:华中科技大学出版社,
2004
[6] 孙训方,方孝淑,关来泰. 材料力学. 第四版 北京:高等教育出版社,2005
[7] 周风云,毛志远. 工程材料及应用. 第二版. 武汉:华中科技大学出版社,
2002
[8] 沈其文,傅水跟. 材料成型工艺基础. 第三版. 武汉:华中科技大学出版社,
2003
[9] 杨叔子. 机械加工工艺师手册. 北京:机械工业出版社,2004
[10] 李益民. 机械制造工艺简明手册. 北京:机械工业出版社,2003
[11] 艾兴,肖诗纲. 切削用量简明手册. 北京:机械工业出版社,1994
[12] 叶玉驹. 机械制图手册. 北京:机械工业出版社,2002
[13] 孙丽媛. 机械制造工艺及专用夹具设计指导. 北京:冶金工业出版社,2005
[14] 王光斗,王春福. 机床夹具设计手册. 第三版. 上海:上海科学技术出版社,2000
[15] 陈宏钧,马素敏. 金属切屑速查速算手册. 第二版. 北京:机械工业出版社,2003





 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号