立式过滤沉降离心机(总体设计及外壳部件设计)【11张CAD图纸和毕业论文】【机械专业答辩通过】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:(预览前20页/共24页)
编号:349355
类型:共享资源
大小:5.39MB
格式:RAR
上传时间:2014-10-30
上传人:好资料QQ****51605
认证信息
个人认证
孙**(实名认证)
江苏
IP属地:江苏
45
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
立式
过滤
沉降
离心机
总体
整体
设计
外壳
部件
cad
图纸
毕业论文
机械
专业
答辩
通过
- 资源描述:
-
【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
[全部文件] 那张截图中的文件为本资料所有内容,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
目 录
1前言 1
2国内外研究现状及发展动态 2
3 立式过滤沉降离心机的总体设计 4
4具体设计说明 5
4.1转鼓的设计计算 5
4.2离心机驱动功率的计算。 10
4.3电机的选择 13
4.4带轮的设计计算 13
4.4卸料口的设计 15
4.5电机的固定机架调节机构的设计 16
4.6 柱脚部件减震机构的设计 16
5 结 论 17
参 考 文 献 18
致 谢 19
附 录 20
1前言
离心机自1926年问世以来,已被广泛用于工业、农业、国防、生物医学工程、动植物研究及医疗卫生等各个领域。离心机能有效地分离、纯化所需样品,因而深受人们的重视。
本课题为立式过滤沉降离心机(总体设计及外壳部件设计),课题为两人,本人主要负责总体设计。本课题来源于盐城市制药厂,现今市场上用于固液分离的沉降离心机工作时,由于滤渣在转鼓内的移动是籍其内的一套与转鼓同轴线的差动机构而实现的,故其结构复杂,制造成本高;其被分离出来的滤液流出转鼓前都经过出料端的滤网再行过滤,由于滤网容易被堵塞,致使脱液过程中必须定时清理或更换滤网,造成运行操作成本上升和产品质量不稳定。本设计旨在消除这一弊端,将转鼓改成内外两层,让滤渣籍其自身所受的离心力而流向出渣端(被分离出来的滤液则沿着与离心力相反的方向流经滤网,实现了滤液和滤渣各行其道,彻底分开),从而可将其差动机构取消,也克服了滤网被堵塞的现象。本设计旨在提供一种解决上述缺点和弊端的新机型---立式过滤沉降离心机。
此设计的立式过滤沉降离心机的结构比较简单,采用一台电机作为动力源,采用V带传动。在设计中使离心机满足下列要求。
a、离心机为立式机构,转鼓由内外不同锥度的圆锥组成,其外圆锥为无孔的沉降圆锥,内圆锥为安装了过滤网的过滤圆锥;该两圆锥之轴线均呈立式安置;
b、该立式过滤沉降离心机能使滤料在转鼓内进行固,液沉降分离的同时,对被分离出来的滤液再次进行过滤分离,从而提高分离效果;
c、本机工作时滤料由离心机上部料斗的进料口进入转鼓内圆锥,同时经由转鼓底座的径向均布的通道进入转鼓外圆锥的小端;电机起动运转;滤料在高速旋转的转鼓内外圆锥的夹层内同时进行沉降和过滤分离,被分离的滤液和滤渣分别经离心机的出液口和出渣口被引出机外;整个操作过程是在全速、连续运转下自动进行;
d、进料口直径不小于50mm;生产率为每小时排出渣3立方米;
e、该离心机的转鼓内圆锥能延其轴线作稍小轴向移动,以调整其大端与转鼓外圆锥之间隙以适应不同滤料之需;
f、本机工作可靠,运行平稳,产品质量稳定,操作维护简单;
g、本机结构紧凑,其进料口、出液口和出渣口便于连接到自动生产线上。
2 国内外研究现状及发展动态
当今市场上的沉降式离心机已广泛用于石油、化工、冶金、煤炭、医药、轻工、食品等工业部门和污水处理工程,其中以螺旋卸料沉降式离心机应用最为广泛. 螺旋卸料沉降式离心机是高速运转,连续进料、分离分级、螺旋推进器卸料的离心机,螺旋卸料沉降式离心机分立式螺旋卸料沉降式离心机和卧式螺旋卸料沉降式离心机。它利用离心沉降法来分离悬浮液,能连续操作、处理量大、无滤布和滤网、单位产量的耗电量较少、适应性强、维修方便、能长期运转。
最初的卧式螺旋卸料离心机是由两对开式齿轮传动获得转鼓与螺旋之间的差转速,以输送沉渣并被应用于淀粉工业上。真正现代的有实用价值的第一台螺旋离心机首次使用了二级行星齿轮差速器。卧螺离心机出现后,由于具有突出的优点而得到了迅速的发展。在各种国际展览会上,各种各样的螺旋离心机,是所展示出的离心机中最吸引人的机型,可见各国对螺旋离心机的重视。
螺旋卸料沉降式离心机是国际上五十年代发明的机械,七十年代,我国开始引进。国产化一些机型成为原化工部七五科技攻关项目。八十年代我国就开始测绘,己测绘美国SHAPLESS公司、法国GUINARD公司等国外著名公司生产的多种规格的离心机,并进行仿制,国家当时在全国组织6个生产厂家进行仿制生产。现国内己能生产的螺旋卸料沉降式离心机有WL200、WIJ350、WL450、WL600、LW800、LW350、LW400、LW50O、LW620等。
随着化学工业的飞速发展,各化工生产厂家对高精度、高质量设备的需求量不断增加。当前各种类型的离心机品种繁多,各具特色,并且都向提高技术参数、系列化、机电一体化方向发展。螺旋卸料沉降离心机由于能够连续出料,生产能力大,对物料的适应性强,结构紧凑,占地面积少等特点,因此应用越来越广泛。目前其发展速度很快,但从总的趋势看:
a、为了提高单机生产能力,采取加大转鼓直径,增加长径比的方法,如GUINARD公司的D型螺旋卸料沉降式离心机,转鼓直径最大的为1500mm,长径比为4.7,我国目前生产的螺旋卸料沉降离心机的直径最大为1000mm,长径比还不到 2。
b、为了分离固相颗粒比较细,粘度大的悬浮液,采取提高转速度方法,如阿法拉法公司生产的4500型离心机,转鼓直径310mm,转速达7600r/min,这样高的转速,目前我国还不能达到。
c、目前国外离心机正向着机电一体化方向发展,己实现在离心机上对分离物料的自动检测与调节,机械性能自动保护,振动的随机检测和自动报警,过载保护分离反馈等。我国目前己开始注意机电一体化的研究与应用,但在离心机方面也只是刚刚起步。
d、适应不同物料及工况的需要,目前国内外离心机制造厂又推出来许多不同型号的防爆型离心机,用于易燃易爆场合的物料分离。
近来由于石油化学工业的迅猛发展,以及污水治理的需要,使卧螺沉降式离心机得到了进一步的发展。例如在合成塑料(聚氯乙烯、聚丙烯)及合成纤维(聚对苯二甲酸乙二脂)生产分离设备中,卧螺沉降式离心机是关键设备之一,在聚乙烯醇的生产中也要使用螺旋离心机;在污泥脱水中使用了高分子絮凝剂,是螺旋离心机的固相回收率大大提高,因而它成为污水治理的有效分离设备。在连续离心机中,卧螺沉降式离心机是对物料适应性较好、应用范围较广的一种离心机.
通过对市场上的卧螺沉降式离心机研究发现现今市场上用于固液分离的沉降离心机工作时,由于滤渣在转鼓内的移动是籍其内的一套与转鼓同轴线的差动机构而实现的,故其结构复杂,制造成本高;其被分离出来的滤液流出转鼓前都经过出料端的滤网再行过滤,由于滤网容易被堵塞,致使脱液过程中必须定时清理或更换滤网,造成运行操作成本上升和产品质量不稳定。本设计旨在消除这一弊端,将转鼓改成内外两层,让滤渣籍其自身所受的离心力而流向出渣端(被分离出来的滤液则沿着与离心力相反的方向流经滤网,实现了滤液和滤渣各行其道,彻底分开),从而可将其差动机构取消,也克服了滤网被堵塞的现象。
为解决上述弊端,为克服现行沉降式离心机的缺点,本设计旨在提供一种解决上述缺点和弊端的新机型—立式过滤沉降离心机。
3 立式过滤沉降离心机的总体设计
由于此次设计的立式过滤沉降离心机重在内部结构的设计,因此总的设计路径应是从内部结构开始进行设计,再根据设计完成的各机构,结合结构和设计要求,进行其它外部零部件的设计。
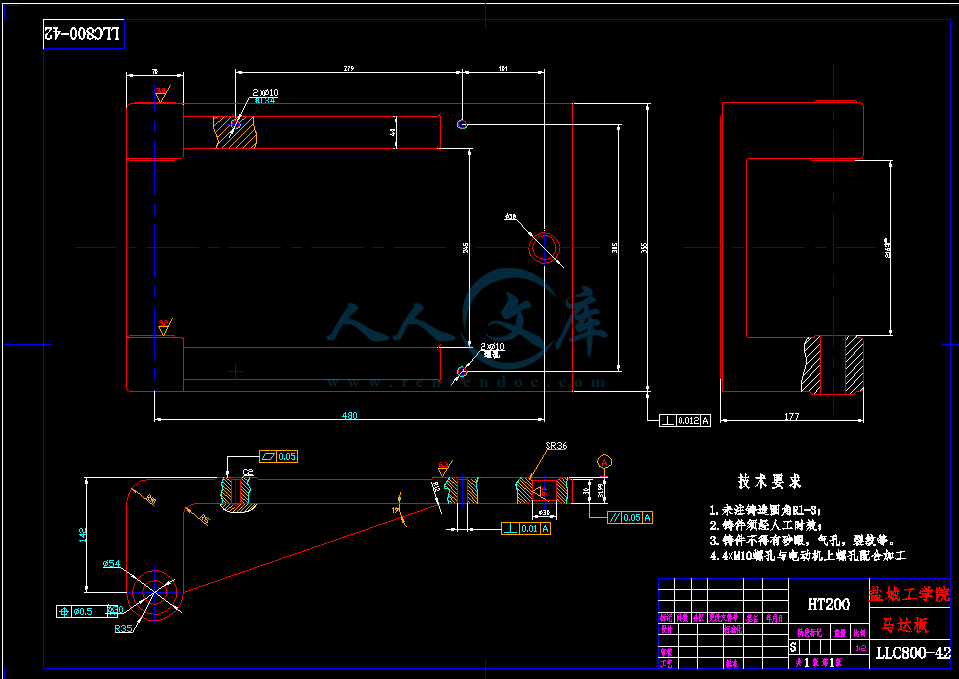
该离心机为立式机构,转鼓由内外不同锥度的圆锥组成,其外圆锥为无孔的沉降圆锥,内圆锥为安装了过滤网的过滤圆锥;该两圆锥之轴线均呈立式安置;该立式过滤沉降离心机能使滤料在转鼓内进行固,液沉降分离的同时,对被分离出来的滤液再次进行过滤分离,从而提高分离效果;本机工作时滤料由离心机上部料斗的进料口进入转鼓内圆锥,同时经由转鼓底座的径向均布的通道进入转鼓外圆锥的小端;电机起动运转;滤料在高速旋转的转鼓内外圆锥的夹层内同时进行沉降和过滤分离,被分离的滤液和滤渣分别经离心机的出液口和出渣口被引出机外;整个操作过程是在全速、连续运转下自动进行;进料口直径不小于50mm;生产率为每小时排出渣3立方米;该离心机的转鼓内圆锥能延其轴线作稍小轴向移动,以调整其大端与转鼓外圆锥之间隙以适应不同滤料之需;本机工作可靠,运行平稳,产品质量稳定,操作维护简单,具体结构如图3-1所示。









- 内容简介:
-
外文翻译专 业 机械设计制造及其自动化 学 生 姓 名 顾 建 刚 班 级 B机制034 学 号 0310110102 指 导 教 师 刘 仲 威 用于吸力式基础离心机模拟的动力加载设备 王淑云1, 张建红2 , 鲁晓兵1 , 矫宾田1(1. 中国科学院力学研究所 ,北京 100080 ; 2. 清华大学水利系 ,北京 100084)顾建刚 译摘要: 吸力式桶形基础广泛地应用于海洋油气开发的海洋平台。在冬季 ,渤海冰排会对平台产生强烈的冲击 ,引起振动。本文介绍了一套用于土工离心机实验的动力加载设备 ,并介绍了该套设备在模拟吸力式桶形基础在受到等效动冰载作用下的响应的实验研究情况及实验结果。结果表明 ,当载荷幅值超过一个临界值时 ,地基上部会发生软化甚至液化。超孔隙水压从土体上部到下部 ,从桶形基础壁面到远处逐渐减小。在动载荷作用下 ,桶形基础和临近土体会发生大的沉降。桶形基础尺寸越小 ,动载荷响应越大。关键词: 吸力式桶形基础 ; 动力加载设备; 冰致振动; 离心机模拟1.绪论近几年来,吸力式桶形基础已经经常被应用到海上工程上。首次利用吸力式桶形基础是有吸引力的,因为它安装使用和维护方法简便。例如,只通过水泵抽水在一到三个小时内就能把一个9米宽10米高的吸力式桶形基础安装好。第二个优点是他可以提供能量巨大的提升吸力。尽管对吸力式桶形基础的安装和静态承载能力都进行了一系列的研究试验,但是其动力性载荷的的作用下的状况我们还不得而知。由于在动力性载荷方面实验数据的匮乏而导致了我们我们对其一系列的试验计划已加深这方面的认识.。在花费巨大的人力和物力在不同环境下对其原型机进行承载能力的测试发现起实用性是有限的。小规模实验的参数很容易被改变。但是问题是依靠标准装载的小数量土壤的压力测量不能正确反映不同的设计。如果在岩土离心机中进行这些实验这些限制是可以克服的。在离心机中泥土所受的压力和在原型中所受的压力是一样的。例如:在100g(100倍地球引力)下,一个直径9米高9米的基础所提供的吸力可以用直径0.09米高0.09米的基础来模拟。原型和模型的缩放比例是100:1。在中国的渤海冰振装置的动力载荷的装载是被控制的。通过对平台和参数的控制这种类型的水平负载的动力载荷可以向土层传递,例如土层的厚实度和参数的变化。结果桶形基础的承载能力将会减小。因此,阐明桶形基础在这种类型下的装载的动力行为为实际的设计提供方法和参数是重要的也是必要的。在这篇文章中,我们首先引进了一套动力装载装置用来模拟横向动力载荷。随后吸力式桶行基础的冰致循环实验得出了一系列数据,研究主要集中在对装载振幅效应,斗的大小和结构重量的研究上。插图:激励式电磁动力驱动装置动力驱动装置主要如图的激励式电磁的组成.这种激励式的装置由永久磁铁圆柱形银制线圈,2个铜制弹簧片、测压元件和一根钢棒通过线圈连接起来.该设计主要有两个主要的技术挑战。(1)圆柱线圈要悬浮在永久磁铁上,悬浮空间必须要很小以免损磁,但是在正交引力的作用。下圆柱线圈会发生横向运动,在这狭小空间里线圈的变形会被锁定。为了避免种情况一根轴和两个铜制弹簧片被安装而使线圈直线运动而不被锁.这种技术还没有完全被有效的论证。(2)线圈的重量在装载方向上的变形应尽量最小化。银线圈所形成的圆柱线圈用来提高性能和限制重量在0.5kg以内。装置的总重量为14kg,因此0.5kg的线圈重量不会对150kg的保险装置产生影响。线圈在刚性杆上的周期来回运动所形成的周期载荷形成了桶的模型。图2是控制系统的负载装置装载功能是将电脑信号反馈给伺服放大器。激励式电磁的装载输出不断的被测压装置监测并反馈给示波器。孔隙压力传感器的输出信号(PPT)和线性变量变压器(LVDT)通过离心机滑动环并修改数据。这个装置在80g的离心加速度下以不同的振幅和频率进行着的横向循环力。所以,模型的装载频率和原型的换算系数是1:80,模型的振幅频率和原型的换算系数是1:6400。模型离心机100N的最大周期负荷和64HZ的频率代表了原型640KN最大周期负荷和0.8HZ的工作频率。表1表明了离心机的技术规格。80N所需要的电力在图3种表示。2离心机系统结构组成图4 显示了离心机和模型的结构组成。铝制箱体长宽高是600mm350m350mm,在箱体内部周围围上了210mm的厚沙,在它的底部垫上了20mm的粗沙以用来隔热。有20mm的水在沙子的表面。执行机构由二个紧固在法兰上面的钢粱支持。图4显示了两根梁决定了相对于箱体的那一边它在传动机构的后面。一台微型摄像机装在模型中的法兰上用来监视模型的运动。模型桶是一个外径为60mm内径为56mm高为72mm的钢桶。平台的静负载通过在轴表面裱好的沙囊来模拟。桶的运动情况被2台低压试验装置监控,当离心机模型在80g的力下测试,它的动作和直径4.8米的原型机的动作是根本上相符的。3. 实验的准备实验在清华大学50g-tons离心机上进行,其最大离心加速度为200g,其有效载荷为250kg每200g离心加速度。实验材料是重力为2.69颗粒直径为0.14mm的细沙,渗透性为5 10-3mm/s。三个钢制模型桶被用在实验中,内部深度(不包括顶面盖帽厚度)分别为48mm、72mm、90mm,其内部直径都为60mm,壁厚和盖厚都为2mm。一个外径10mm内径8mm高度100mm的管子被焊接在桶盖的中心。保证球能够上下移动的光滑凹槽使其适应与管道连接的桶的沉降,钢杆的一端与球连接另一端与电磁驱动装置连接,因此当桶静止时杆无法牵引。一个线性变量变压器()位于管子的上部用来测量它的垂直位移,另一个线性变量变压器()位于管子和钢杆同一水平线上用来测量其水平位移。其余两个低压试验装置位于沙子表面用来测量不同位置的沙子的沉降状况。十个产于Druck Co的PPTs被埋在桶中沙子中(图5所示)。为了保证实验的重复性,制造中将210mm厚的沙层模型分成5层,并用手轻轻将其压缩。通过干燥剂控制此过程,水深超过沙表面1cm。干沙样品准备好了以后,通过容器底部孔慢慢地把水渗透到沙层里。20mm厚的粗砂层堆积在容器底部保证水均匀的上升并且防止水发热。当水位低于沙的表面,就使用真空机持续38小时抽吸沙子里的气体,以保证饱和度。在实验中采用了两种方案。第一个方案:一排PPT倾向于沙层深度激励面并且远离桶边缘2mm,上层的低于沙层表面20mm,从上到下其他的都是以20MM间隔一个一个排开。双排的倾向于沙层的反面。一排离桶壁2mm,另一排52mm。第二种方案:在承载方向对边上双排PPT都是离壁边缘2mm。一排PPT低于沙的表面倾向水平偏转方向20mm,除了桶外被处理的PPT,一排PPT注入低于上部20mm的桶内,另一排注入底部(图5)。在离心机离制造冰并使它影响平台是困难的,因此一个相对于人造冰动力源在试验中被用。由于动力人造冰负载引起的平台精确频率在中国渤海湾是0.81.2Hz。因此试验频率为0.8Hz。开始时负载位置时水箱顶上8cm处。这个重点位置会随着确定的发展改变一些。不同重要的钢撑架是位于尖钢管的顶部为了代替结构重量的影响。 图4 模型的设计 图5 两种类型的疲劳压力传感器4实验结果4.1试验的重要性为了保证重复性一些试验被重复2次或更多次。在图6中,在这种环境下的重复结果:负载振幅是60N,频率为0.8HZ,水箱内径为60mm内部高度为72mm。没有一个钢塞位于钢管的顶部。因此过程上少于80g和至少40分钟。过程前后的干密度为1520g/mm和1600g/mm3。固定结束后浮动元件的密度为= 971g/ mm3和定位点为8mm(如果没有特别提出数据都在这篇论文的例子中)说明了固定过程有一个好的重复性(图6a)。 图6 重复的试验结果重复性的孔压力沿沙子基础深度在图6中显示。说明了重复性是好的虽然总共进行了40个离心机的试验,一些结果在分析时被丢掉,作为离心机演示的相关问题发生包括PPTs不工作。4.2 动态 这儿显示的结果是在如下条件下的:载荷幅值为60N,频率为64Hz,与一个384KN和0.8Hz的样机负载相应。水箱模型直径60mm,高为72mm。图7显示的时励磁的过量孔隙水压。显示过量的孔隙压力被P5、P7、P8记录下。最大的过量孔隙水压um比例,在土上垂直有效压力约为1.0。在表2中显示液化可能出现在1.5m深度处。当离心机停止,优良土壤颗粒在水箱地表面被观察。尽管P1位于表面附近,它展示了尖锐的变异,说明快速耗散过量孔隙水压。 - 图7a通过P5和P7记录显示过度疲劳压力,两种传感器安装在距桶的5mm的侧面,它的记录时既然相反的。P5um/vat的比率是0.94,非常接近1.0,但是它位于离桶很远的地方所以其峰值来的较慢。然后P5急剧发生变化并减少到一个很低的值,随着土壤深度的增加2个PPTs的值ur逐渐减少。图7b表示桶的过度疲劳压力的产生,实际产生的是疲劳压力代替了吸力,这表明水平负载引线导致了泥土内部的压缩。 图7 模型1过度疲劳水压模型桶周围的土壤的削落取决于过度疲劳水压。80cm(原型高度)乘余结果被观察当装载振幅为3. 84 105N如图8所示。在驱动过程中,61 %的沉降在一个小时内完成,似乎伴生在泥土的最大限度的疲劳水压中,连续的震动使泥沙逐渐增稠。所以当过度疲劳水压趋于稳定时80 %的已经完成在5个小时里。模型桶连接到动力上,显示出,当桶远离动力时沉降速度变慢,在离桶20米(原型)远时沉降时不明显的,当离桶8米时是离20米时沉降的一半,这也许是不同种类的桶引起的。原型的沉降残余是37cm,如图8所示。模型2 的95 %在三小时内沉降完。5 讨论和总结一个器件动态加载装置主要已应用电磁器的装置,在这个装置中,一个水平的循环的振幅和频率是在80g的离心加速度上产生。离心测试已经被用于研究一个在水平循环加载下一个持续26.7小时的样机的抽吸水箱的行为.试验结论说明过量孔的水后会在水箱周围沉淀物中产生,最大的过量孔水压大概的垂直有效土重量.例如:um/比率为0.94-0.96.液化性能在1.5米的深处产生.和孔的水压会随着深度减少,尽管土壤在长时间刺激下变弱,重大决止也随着产生.正如我们知道的,石砾层的干扰力将随着负载振幅的增加而变大.因此,过量孔的水压力和安排快速增加.在第一层,孔隙水很难排尽,因此孔隙压力增大,土砾层的强度降低,而且会随着孔隙压力的增长而液化,尽管如此,过载孔隙压力的散布将随着孔隙压力倾斜度的增长而逐渐产生,因此,土砾层的排布和孔压力的减少 图8 桶基的沉降事实证明,小型号水箱有较小的惯性瞬间和结构重量,也就是说在相同的振幅下小型号水箱比大型号水箱有较小的能量损耗,小型号水箱有较小的水箱接触面.因此,较小型号比较大型号水箱的土砾层承受更大的负载。参考文献1 Clukey E C , Morrison M J , Garnier J , et al. The response of suction caissons in normally consolidated clays to cyclic TL P loading conditionsC. Proc Offshore Tech Conf , Houston , O TC 7796 , 1995 :909918.2 Allersma H G B , Plenevaux F J A , Wintgens J F P C M E. Simulation of suction pile installation in sand in a geocentrifugeC. 7th Int. Offshore and polar engrg. Conf. ISOPE97 , 1997 , 1 :761765.3 Allersma H G B , Kierstein A A , Maes D. Centrifuge modeling on suction piles under cyclic and long term vertical loadingC. Proc Offshore Tech Conf , Seattle , 2000 :334341.4 Senpere D , Auvergne G A. Suction anchor piles2a proven alternative to driving or drilling C. Proc Offshore Tech Conf , Houston , O TC4206 , 1982 :483493.5 Aas P M , Andersen K H. Skirted foundation for offshore structureC. In : 9th Offshore South East Asia Conf. ,Singapore : World Trade Center Singapore , 1992 : 17.6 Dyme W , Houlsby G T. Drained behavior of suction caisson on very dense sand C. Proc Offshore Tech Conf ,Houston , O TC10994 , 1998 : 765782.7 Tjelta T L , Hermstad J , Andenaes E. The skirt piled gullfaks c platform installation C . Proc Offshore Tech Conf , Houston , O TC6473 , 1990 :453462.8 Bye A , Erbrich C , Earl K , et al. Geotechnical design of bucket foundation C . Proc Offshore Tech Conf ,Houston , O TC7793 , 1995 : 869883.9 Ding H Y , Qi L , Du X Z. Estimating soil liquefaction in ice2induced vibration of bucket foundationJ . J Cold Reg.Eng , 003 , 17 (2) : 6067.10 Lu Xiaobing , Zheng Zhemin , Zhang Jinlai. Progress in the study on the bucket foundation of offshore platform J . Advances in Mechanics (in Chinese) ,2003 , 33 (1) : 2740.7 毕业设计开题论证报告专 业 机械设计制造及其自动化 学生姓名 顾 建 刚 班 级 B机制034 学 号 0310110102 指导教师 刘 仲 威 完成日期 2007年4月15日 课题名称:立式过滤沉降离心机(总体设计及外壳部件设计)一、课题来源、课题研究的主要内容及国内外现状综述1. 课题来源:课题来源于对沉降式离心机市场的调研结果。2. 课题研究的主要内容:现今市场上用于固液分离的沉降离心机工作时,由于滤渣在转鼓内的移动是籍其内的一套与转鼓同轴线的差动机构而实现的,故其结构复杂,制造成本高;其被分离出来的滤液流出转鼓前都经过出料端的滤网再行过滤,由于滤网容易被堵塞,致使脱液过程中必须定时清理或更换滤网,造成运行操作成本上升和产品质量不稳定。本设计旨在消除这一弊端,将转鼓改成内外两层,让滤渣籍其自身所受的离心力而流向出渣端(被分离出来的滤液则沿着与离心力相反的方向流经滤网,实现了滤液和滤渣各行其道,彻底分开),从而可将其差动机构取消,也克服了滤网被堵塞的现象。为解决上述弊端,为克服现行沉降式离心机的缺点,本设计旨在提供一种解决上述缺点和弊端的新机型-立式过滤沉降离心机。3国内外现状: 当今市场上的沉降式离心机已广泛用于石油、化工、冶金、煤炭、医药、轻工、食品等工业部门和污水处理工程,其中以螺旋卸料沉降式离心机应用最为广泛螺旋卸料沉降式离心机是高速运转,连续进料、分离分级、螺旋推进器卸料的离心机,螺旋卸料沉降式离心机分立式螺旋卸料沉降式离心机和卧式螺旋卸料沉降式离心机。它利用离心沉降法来分离悬浮液,能连续操作、处理量大、无滤布和滤网、单位产量的耗电量较少、适应性强、维修方便、能长期运转。最初的卧式螺旋卸料离心机是由两对开式齿轮传动获得转鼓与螺旋之间的差转速,以输送沉渣并被应用于淀粉工业上。真正现代的有实用价值的第一台螺旋离心机首次使用了二级行星齿轮差速器。卧螺离心机出现后,由于具有突出的优点而得到了迅速的发展。在各种国际展览会上,各种各样的螺旋离心机,是所展示出的离心机中最吸引人的机型,可见各国对螺旋离心机的重视。螺旋卸料沉降式离心机是国际上五十年代发明的机械,七十年代,我国开始引进。国产化一些机型成为原化工部七五科技攻关项目。八十年代我国就开始测绘,己测绘美国SHAPLESS公司、法国GUINARD公司等国外著名公司生产的多种规格的离心机,并进行仿制,国家当时在全国组织6个生产厂家进行仿制生产。现国内己能生产的螺旋卸料沉降式离心机有WL200、WIJ350、WL450、WL600、LW800、LW350、LW400、LW50O、LW620等。随着化学工业的飞速发展,各化工生产厂家对高精度、高质量设备的需求量不断增加。当前各种类型的离心机品种繁多,各具特色,并且都向提高技术参数、系列化、机电一体化方向发展。螺旋卸料沉降离心机由于能够连续出料,生产能力大,对物料的适应性强,结构紧凑,占地面积少等特点,因此应用越来越广泛。目前其发展速度很快,但从总的趋势看:l、为了提高单机生产能力,采取加大转鼓直径,增加长径比的方法,如GUINARD公司的D型螺旋卸料沉降式离心机,转鼓直径最大的为1500mm,长径比为4.7,我国目前生产的螺旋卸料沉降离心机的直径最大为1000,长径比还不到2。2、为了分离固相颗粒比较细,粘度大的悬浮液,采取提高转速度方法,如阿法拉法公司生产的4500离心机,转鼓直径310,转速达7600/min,这样高的转速,目前我国还不能达到。3、目前国外离心机正向着机电一体化方向发展,己实现在离心机上对分离物料的自动检测与调节,机械性能自动保护,振动的随机检测和自动报警,过载保护分离反馈等。我国目前己开始注意机电一体化的研究与应用,但在离心机方面也只是刚刚起步。4、适应不同物料及工况的需要,目前国内外离心机制造厂又推出来许多不同型号的防爆型离心机,用于易燃易爆场合的物料分离。近来由于石油化学工业的迅猛发展,以及污水治理的需要,使卧螺沉降式离心机得到了进一步的发展。例如在合成塑料(聚氯乙烯、聚丙烯)及合成纤维(聚对苯二甲酸乙二脂)生产分离设备中,卧螺沉降式离心机是关键设备之一,在聚乙烯醇的生产中也要使用螺旋离心机;在污泥脱水中使用了高分子絮凝剂,是螺旋离心机的固相回收率大大提高,因而它成为污水治理的有效分离设备。在连续离心机中,卧螺沉降式离心机是对物料适应性较好、应用范围较广的一种离心机通过对市场上的卧螺沉降式离心机研究发现现今市场上用于固液分离的沉降离心机工作时,由于滤渣在转鼓内的移动是籍其内的一套与转鼓同轴线的差动机构而实现的,故其结构复杂,制造成本高;其被分离出来的滤液流出转鼓前都经过出料端的滤网再行过滤,由于滤网容易被堵塞,致使脱液过程中必须定时清理或更换滤网,造成运行操作成本上升和产品质量不稳定。本设计旨在消除这一弊端,将转鼓改成内外两层,让滤渣籍其自身所受的离心力而流向出渣端(被分离出来的滤液则沿着与离心力相反的方向流经滤网,实现了滤液和滤渣各行其道,彻底分开),从而可将其差动机构取消,也克服了滤网被堵塞的现象。为解决上述弊端,为克服现行沉降式离心机的缺点,本设计旨在提供一种解决上述缺点和弊端的新机型-立式过滤沉降离心机。二、本课题拟解决的问题在对立式过滤沉降离心机总体设计的过程中,主要有以下一些问题需要解决1、离心机为立式机构,转鼓由内外不同锥度的圆锥组成,其外圆锥为无孔的沉降圆锥,内圆锥为安装了过滤网的过滤圆锥;该两圆锥之轴线均呈立式安置;2、该立式过滤沉降离心机能使滤料在转鼓内进行固,液沉降分离的同时,对被分离出来的滤液再次进行过滤分离,从而提高分离效果;3、本机工作时滤料由离心机上部料斗的进料口进入转鼓内圆锥,同时经由转鼓底座的径向均布的通道进入转鼓外圆锥的小端;电机起动运转;滤料在高速旋转的转鼓内外圆锥的夹层内同时进行沉降和过滤分离-被分离的滤液和滤渣分别经离心机的出液口和出渣口被引出机外;整个操作过程是在全速、连续运转下自动进行;4、进料口直径不小于50mm;生产率为每小时排出渣3立方米;5、该离心机的转鼓内圆锥能延其轴线作稍小轴向移动,以调整其大端与转鼓外圆锥之间隙以适应不同滤料之需;6、本机工作可靠,运行平稳,产品质量稳定,操作维护简单;7、本机结构紧凑,其进料口、出液口和出渣口便于连接到自动生产线上;8、用AUTOCAD编制二维工程图。三、解决方案及预期效果首先认真调查收集关于过滤沉降离心机方面的详细资料,对过滤沉降离心机装置总体结构进行分析、理解,通过所学的机械设计制造知识对工厂所见得离心机进行仔细的观察分析和研究,对该装置的总体机构有个清晰的认识,认识理解其各部分的相关性和独立性。其次着重对本课题(总体设计及外壳部件)进行仔细认真的分析研究,结合参考资料等对其进行分析计算,并对各零部件进行设计与强度校核,绘出机构的原始草图。再次主要通过以上准备的各主要资料,运用AUTOCAD等相关软件编制出课题所需要的二维或三维图。四、课题进度安排3月19日4月1日毕业实习阶段。毕业实习,查阅资料,到多个公司实践,撰写实习报告。4月2日4月15日开题阶段。提出总体设计方案及草图,填写开题报告。4月16日5月23日 设计初稿阶段。完成总体设计图、部件图、零件图。5月24日6月7日 中期工作阶段。完善设计图纸,编写毕业设计说明书,中期检查。6月8日6月10日毕业设计预答辩。6月11日6月18日毕业设计整改。图纸修改、设计说明书修改、定稿,材料复查。6月19日6月21日毕业设计材料评阅。6月22日6月24日毕业答辩。6月25日6月28日材料整理装袋。五、指导教师意见 签名 年 月日六、专业系意见 签名 年 月日七、学院意见 签名 年 月日4 毕业设计任务书课题:立式过滤沉降离心机(总体设计及外壳部件设计)专 业 机械设计制造及其自动化 学 生 姓 名 顾 建 刚 班 级 B机制034 学 号 0310110102 指 导 教 师 刘 仲 威 专 业 系 主 任 王 琪 发 放 日 期 2007年3月16日 一、 设计内容本课题来源于对沉降式离心机市场的调研结果。 现今市场上用于固液分离的沉降离心机工作时,由于滤渣在转鼓内的移动是籍其内的一套与转鼓同轴线的差动机构而实现的,故其结构复杂,制造成本高;其被分离出来的滤液流出转鼓前都经过出料端的滤网再行过滤,由于滤网容易被堵塞,致使脱液过程中必须定时清理或更换滤网,造成运行操作成本上升和产品质量不稳定。本设计旨在消除这一弊端,将转鼓改为内外两层,让滤渣籍其自身所受的离心力而流向出渣端(被分离出来的滤液则沿着与离心力相反的方向流经滤网,实现了滤液和滤渣各行其道,彻底分开),从而可将其差动机构取消,也克服滤网被堵塞的现象。为解决上述弊端,为克服现行沉降式离心机的缺点,本设计旨在提供一种能解决上述缺点和弊端的新型机种立式过滤沉降离心机。二、设计依据1工厂现行生产的沉降式离心机有关产品样本;2机型为立式结构,转鼓为圆锥型,其轴线呈立式安置; 3转鼓:其外圆锥大端内直径为800mm;转鼓高度为520600mm,转鼓长径比(L/D)为0.60.75;4转鼓转速:2000r/min;5分离因数为Fr1788;6电机功率:小于22kw。三、设计要求1离心机为立式结构,转鼓由内外不同锥度的圆锥组成,其外圆锥为无孔的沉降圆锥,内圆锥为安装了过滤网的过滤圆锥;该两圆锥之轴线均呈同轴立式安置;2该立式过滤沉降离心机能使滤料在转鼓内进行固、液沉降分离的同时,对被分离出来的滤液再次进行过滤分离,从而提高分离效果;3本机工作时滤料由离心机上部料斗的进料口进入转鼓内圆锥,同时经由转鼓底座的径向均布的通道进入转鼓外圆锥的小端;电机起动运转;滤料在高速旋转的转鼓内外圆锥的夹层内同时进行沉降和过滤分离被分离的滤液和滤渣分别经离心机的出液口和出渣口被引出机外;整个操作过程是在全速、连续运转下自动进行;4 进料口直径不小于50mm;生产率为每小时排出渣3M3;5该离心机的转鼓内圆锥能沿其轴线作稍小轴向移动,以调整其大端与转鼓外圆锥之间隙以适应不同滤料之需;6本机工作可靠,运行平稳,产品质量稳定,操作维护简单;7本机结构紧凑,其进料口、出液口和出渣口便于连接到生产自动线上。四、毕业设计物化成果的具体内容及要求1、设计成果要求: 按教务处毕业设计(论文)格式规范统一编排、打印,字数不少于1万字。 1)毕业设计说明书 1 份2)总装图 1 张3)柱脚、外壳部件图 各1张4)零件图 不少于7张2、外文资料翻译(英译中)要求1)外文翻译材料中文字不少于3000字。2)内容必须与毕业论文课题相关;3)所选外文资料应是近10年的文章,并标明文章出处。五、 毕业设计(论文)进度计划起讫日期工作内容备 注3月17日3月18日布置任务 3月19日4月1日调查研究,毕业实习4月2日4月15日方案论证,总体设计4月16日4月30日技术设计(部件设计)5月8日5月23日工作设计(零件设计)5月24日6月7日撰写毕业设计说明书6月8日6月10日毕业设计预答辩6月11日6月18日修改资料6月19日6月21日评阅材料6月22日6月24日毕业答辩6月25日6月28日材料整理装袋六、 主要参考文献:1徐 灏. 机械设计手册M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1991.2机械工程手册,电机工程手册编辑委员会. 机械工程手册M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1995.3徐 灏. 新编机械设计师手册M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1995.4胡家秀. 机械零件设计实用手册M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1999.5李益民. 机械制造工艺设计手册M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1995.6全国化工设备设计技术中心站机泵委员会. 工业离心机选用手册M. 北京:化学工业出版社,1999.7余国宗. 化工机器M. 天津:天津大学出版社,1987.8孙启才,金鼎五. 离心机原理结构与设计计算M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1987.9B.N索柯罗夫,汪泰临,孙启才,陈文梅. 离心分离理论及设备M. 北京:机械工业出版社,1986.10东北重型机械学院. 机床夹具设计手册(第二版)M.上海:上海科技出版社,1988.11刘文剑. 夹具工程师手册M. 哈尔滨:黑龙江科技出版社,1987.12杨黎明. 机床夹具设计手册M. 北京:国防工业出版社,1996.七、其他 学生必须按照毕业设计进度计划表明的时间,分期按时完成,并且保证各期工作的工作质量,以确保毕业设计任务的完成。八、专业系审查意见系主任: 年 月 日九、机械工程学院意见院长: 年 月 日6 毕 业 设 计 说 明 书立式过滤沉降离心机(总体设计及外壳部件设计)专 业 机械设计制造及其自动化 学生姓名 顾建刚 班 级 B机制034 学 号 0310110102 指导教师 刘仲威 完成日期 2007年6月13日 第21卷 第4期2006年8月实 验 力 学JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MECHANICSVol. 21No. 4Aug. 2006文章编号:100124888(2006)0420439208A Dynamic Loading Device for SuctionFoundations in Centrifuge Modeling3WANG Shu2yun1, ZHANGJian2hong2, LU Xiao2bing331, J IAO Bin2tian1(1. Institute of Mechanics , China Academy of Science , Beijing 100080 , China ;2. Department of Hydraulic Engineering , Tsinghua University , Beijing 100084 , China)Abstract : Suction bucket foundations are widely used in the offshore platform for theexploitation of the offshore petroleum and natural gas resources. During winter seasons , icesheets formed in Bohai Bay will impose strong impact and result in strong vibration on theplatform.This paper describes a dynamic loading device developed on the geotechnicalcentrifuge and its application in modeling suction bucket foundation under the equivalent ice2induced vibration loadings. Some experimental results are presented. It is shown that when theloading amplitude is over a critical value , the sand at the upper part around the bucket softensor even liquefies. The excess pore pressure decreases from the upper part to the lower part ofthe sand foundation in vertical direction while decreases from near to far away from thebuckets side wall in the horizontal direction. Large settlements of the bucket and the sandaround the bucket occur under the horizontal dynamic loading. The dynamic responses of thebucket with smaller size are heavier.Key words : suctionbucketfoundation ;dynamic loadingdevice ;ice2inducedvibration ;centrifuge modeling0IntroductionIn recent years , suction bucket foundations have been applied increasingly often in offshoreengineering (Clukey et al1, 1995 ; Allersma et al2 ,3, 1997 , 2000) . The first advantage of suctionbucket foundations are attractive because of the convenient method of installation and repeatedly use.For an example , a suction bucket foundation with a diameter of 9m and a height of 10m can beinstalled in 13 hours , by using only a pump.The second advantage is that it may mobilize asignificant amount of passive suction during uplift. Despite several studies on the installation andstatic bearing capacity have been carried out , the detail responses of suction bucket foundations underdynamic loadings have remained unknown (Senpere et al4, 1982 ; Aas et al5, 1992 ; Dyme et al6,1998) . The dynamic loading condition is significant when suction buckets are used as the foundation ofa platform. Wave loading and ice2induced dynamic loading cause the foundation to be subjected tocyclic loadings ( Tjelta et al7, 1990 ; Bye et al8, 1995) . The lack of experiences under these loading333收稿日期: 2005208224 ;修订日期: 2006207210基金项目: This program is supported by the fund of Chinese Ocean Oil Co. and Chinese Academy of Sciences KJCX22SW2L03201 (40025103) and National Natural Science Fund(No. 10202024)通讯作者:鲁晓兵(1968 - ) ,男,博士,现在中科院力学所从事岩土力学研究。E2mail : xblu imech. conditions led to a proposal for a test program intended to gain a deeper understanding.Theconsiderable expense and time consuming nature of prototype tests mean that the investigation of thebearing capacity of real scale devices under different circumstances is of limited practicality. It is mucheasier to change parameters in small scale tests. But problems arise concerning the stress2dependentbehavior of soil that the measured loadings are so low that measurements are not sufficiently accurateto visualize differences in design.These restrictions can be overcome if performing the tests in ageotechnical centrifuge. In a centrifuge the soil stresses over a similar depth are the same as in theprototype situation. For an example , at 100g (100 times the Earths gravity) , a suction foundationwith a diameter 9m and a height of 9m may be simulated with a foundation with a diameter of 0. 09mand a height of 0. 09m. The scaling factor of the prototype to the model is 1001.The ice2induced dynamic loading is the controlling loading in Bohai Bay in China.This type ofhorizontal dynamic loading is translated to the soil layer by platform and causes the parameters , e. g.strength and modulus of the soil layer , to degrade. As a result , the bearing capacity of bucketfoundations decreases.Therefore , it is important and necessary to clarify the dynamic behavior ofbucket foundations under this type of loadings in order to provide practical design method andparameters (Ding et al9, 2003 ; Lu et al10, 2003) .In this paper , we first introduced a set of dynamic loading devices designed for simulating thehorizontal dynamic loadings.Then some experimental results of the ice2induced cyclic behavior ofsuction bucket foundations are presented. The effects of the loading amplitude , the size of the bucketand the structural weight are mainly investigated.Fig. 1The electro2magnetic actuator1Dynamic loading deviceThe dynamic loading device is composed primarily of an electro2magnetic actuator as shown inFig. 1.This actuator consists of a permanent magnet , a cylindrical silver coil , two copper disksprings , a load cell and a steel rod connected to the coil.There are two main technical challengesassociated with the design of the actuator.(1)The cylindrical coil is suspended in a prefabricatedspace in the permanent magnet.The space is very tiny in order to avoid magnetic loss.However ,since this cylindrical coilmoves horizontally , it is orthogonal to the gravitational force , thedeformation of the coil under this gravity may lock it in this tiny space. In order to avoid this situationa linear bearing and two disk springs are installed to make the coil move linearly without being locked.This technique has been demonstrated to be very effective.(2)The weight of the coil should beminimized to increase its deformation in the direction of loading. Silver wire is used to form thecylindrical coil so as to enhance the performance and limit the weight within 0. 5 kg. The total weight044 实 验 力 学 (2006年)第21卷 of the device is 14 kg. Consequently , the vibration of the 0. 5 kg coil would not impose significantimpact on the strong box whose weight is 150 kg.The coil moves back and forth to apply cyclicloading on the model bucket through a rigid rod.Fig. 2 is the controlling system for the loading device.The loading function is fed from acomputer signal generator into a servo amplifier. The latter in turn generates the necessary electricalsignals to control the intensity of electric current in the actuator. The output from the actuator in theform of loading is continuously monitored by the loading cell and fed back through a charged amplifierto the oscillograph.Outputsignal from pore pressure transducer( PPT)and linear variabledisplacement transformers (LVDT) were passed across the centrifuge slip2ring and converted to digitaldata.With this device , different amplitudes and the frequencies ofhorizontal cyclic forces arereproduced at centrifugal acceleration of 80 g. Therefore , the scaling factor of the load frequency ofthe prototype to the model is 180 , and the scaling factor of the load amplitude of the prototype tothe model is 64001. In the centrifuge , the peak cyclic loading of 100 N and 64 Hz represents aprototype loading of 640 KN and 0. 8 Hz. Table 1 shows the technical specifications of this actuator.The force2electricity relation at 80 g is shown in Fig. 3.Tab. 1Technical specification of the electromagnetic actuatorDiameter (mm)Length (mm) Weight (kg)Frequency range (Hz)Peak cyclic load (N)1802601411201002Centrifuge system configurationFig. 4 shows the configuration of the centrifuge and the model. The internal area of the aluminumstrong box measures 600 mm350 mm and height is 350 mm. The thickness of the silty sand is 210mm , underlain by 20 mm coarse sand which is to prevent the piping during penetration of water.There is 20 mm high water above the soil surface.The actuator is supported by two steel beamsfastened on the flange. Two rods fix the back of the actuator against the side of the strong box asshown in Fig. 4. A miniature TV camera was attached to the flange of the model container to monitorthe motion of the model bucket. The model bucket is a steel cylinder which has an external diameterof 60 mm , an internal diameter of 56 mm , and a height of 72 mm. The dead weight of the platformwas simulated by a ballast mounted on the top of the shaft.The movement of the bucket wasmonitored by two LVDTs.When the centrifuge model is tested under 80 g , its behavior wouldprimarily correspond to that of a prototype footing with a diameter of 4. 8 m.144第4期 WANG Shu2yun et al :A Dynamic Loading Device for Suction Foundations in Centrifuge ModelingFig. 4The layout of the model3Preparation of the experimentsThe experiments are performed in the 50g2tons centrifugeinTsinghuaUniversity.The maximum of the centrifuges accelerationis 200g.The payload is 250kg under 200g.The experimental material is fine sand whosespecial gravity is 2. 69 and the average grainsdiameter is 0. 14mm. The permeability is 510- 3mm/ s.Three model buckets made bysteel areused in experiments.The innerdepths (do not include the top cap thickness)are 48mm , 72mm and 90mm , respectively ,theinnerdiametersareall60mm ,thethicknesses of the wall and the top cap areboth 2mm. A fine pipe with an outer diameterof 10mm , an inner diameter of 8mm and aheight of 100mm is welded at the center of thetop cap. A sliding groove permitting a ballmoving up and down to adapt the settlementof thebucket is connected with the pipeclosely. One end of a steel pole is jointed witha ball , the other end of the pole is connectedwith the electromagnetic vibration actuator. Thus the pole cannot be dragged when the bucket settles.One LVDT is located at the top of the fine pipe to measure the vertical displacement. One LVDT islocated at the fine pipe at the same level as that of the steel pole to measure the horizontaldisplacement. The other two LVDTs are located on the sand surface to measure the settlements of thesand surface at different positions. Ten PPTs made in Druck Co. ( English) , are buried in the sandaround and in the bucket (Fig. 5) . The PPTs are not fixed but suspended in the sand.In order to guarantee the repeatability , 210mm thick model sand layer is divided into five layers tocreate and be compacted gently by hand striking. This course is controlled by dry density. The waterdepth over the sand surface is 1cm.After the dry sand sample has been prepared , the sand layer is saturated by penetrating waterinto from the bottom of the tank through a vulva. A 20mm thick coarse sand layer is deposited at thebottom of the tank to guarantee the water rise uniformly and preventing the piping. When the waterlevel is over the sand surface , a vacuum pump is used to pump the gas in the sand for 38 hours toincrease the saturation.Two types of PPT layout are adopted in the tests. The first type : one row PPTs are disposed inthe sand along depth at the actuator side and 2mm away from the buckets side wall. The upper one is20mm below the sand surface. The others have a 20mm distance one by one from the upper to thelowest. Two rows are disposed in the sand at the opposite side. One row is 2mm away from thebuckets wall and the other row is 52mm away from the buckets wall. The second type : two rows areboth 2mm away from the buckets side wall on the opposite side in the loading direction. A row ofPPTs are disposed in the horizontal direction 20mm below the sand surface.Except for the PPTs244 实 验 力 学 (2006年)第21卷 disposed outside of the bucket , one PPT is put in the bucket 20 mm below the top and one is put atthe bottom of the bucket (Fig. 5) .It is difficult to make real ice in a centrifuge and drive it to interact with platform , thus anequivalent ice2induced dynamic loading is adopted in the experiments. The measured frequency of theplatform caused by the dynamic ice2induced loading is 0. 81. 2Hz in Bohai bay , China. Accordingly ,the frequency in experiments is adopted as 0. 8Hz.The loading position is 8cm over the top of thebucket at the beginning.This relative position will change a little with the development of thesettlement. Steel blocks with different weights are located at the top of the fine steel pipe to simulatethe effects of the structural weight.Fig. 5Two types of the pore pressure translators4Experimental results4. 1The repeatability of the experimentsIn order to guarantee the repeatability , some experiments are repeated three or more times. InFig. 6 , the repeated results under the condition : the loading amplitude is 60N , the frequency is 0. 8Hz. The bucket is with an inner diameter of 60mm and an inner height of 72mm , there is not a steelblock placed at the top of the fine steel pipe , are shown. The consolidation course is under 80g andlasts for 40 minutes. The dry densities before and after consolidation are 1520g/ mm3and 1600g/ mm3,respectively. The buoyant unit density is = 971g/ mm3 and the settlement is 8mm after consolidationfinished. (If there is no indication , the data are all in the model in the this paper. ) It is shown thatthe consolidation course has good repeatability (Fig. 6(a) .Fig. 6The repeatability of the experiments resultsThe repeatability of the pore pressure along the depth of the sand foundation is shown in Fig. 6(b) . It is shown that the repeatability is good also.344第4期 WANG Shu2yun et al :A Dynamic Loading Device for Suction Foundations in Centrifuge ModelingAlthough a total of 40 experiments were performed in the centrifuge , some of the results werediscarded during the analysis as centrifuge performance related problems occurred including PPTsbeing not work.4. 2The dynamic responsesThe results presented here is in the following conditions: The cyclic loading amplitude is 60 Nand frequency is 64 Hz , which corresponds to a prototype load of 384 kN and 0. 8 Hz.The modelbucket has a diameter of 60 mm and a height of 72 mm. Fig. 7 shows the excess pore water pressureduring excitation (prototype scale , PPT is placed as Model 1 in Fig. 5) . It is shown that the excesspore pressure recorded by P5 , P7 and P8. The ratio of the maximum excess pore water pressureum,over the vertical effective stress in the soil is approximately to be 1. 0 at P1 , as shown in Table 2.Liquefaction potential may exist within a depth of 1. 5 m (in prototype) . Also when centrifuge wasstopped , fine soil particles were observed at the surface of the ground on the edge of the bucket. SinceP1 is located near the surface , it also presents sharp variation , indicating fast dissipation of excesspore water pressure. Both the maximum and residual excess pore pressure profiles ,umandur,decrease with the soil depth.Fig. 7a shows that the excess pore pressure recorded by P5 and P7. These two transducers wereinstalled at 5 mm distance to the opposite side of the bucket , they present distinct peaks. The ratio ofum/vat P5 is 0. 94 , being very close to 1. 0. However , since it is located comparatively far fromthe bucket , the peak comes up slowly. P5 also experiences sharp variation and then decreases to alower value. The two PPTs have their residual valuesurdecrease with the soil depth.Fig. 7b shows that the excess pore pressure generated inside the model bucket.Positive porepressure instead of suction is generated , indicating that this horizontal loading leads to shearcompression of the inside soil.Fig. 7Excess pore water pressure in Model 1The soil surrounding the model bucket is weakened due to the excess pore water pressure. 80 cm(prototype scale) residual settlement was observed when the loading amplitude is 3. 84105N , asshown in Fig. 8. During the excitation , 61 % settlement happened within one hour , which seemsassociated with the occurrence of the maximum pore water pressure in the soil. Successive shakingmakes the silt densification. Therefore 80 % settlement was completed within 5 hours when the porewater pressures tend to be stable. Since the model bucket is connected to the actuator. It is shownthat the settlements decrease from the bucket to far away. The settlement at 20m (in prototype) awayfrom the buckets side wall is not obvious , while the settlement 8m away is nearly half of that at thetop of the bucket.This may be caused by the heterogeneous settlement.The prototype residual444 实 验 力 学 (2006年)第21卷 settlement of the bucket is 37 cm , as shown in Fig. 8. 95 % settlement of Model 2 happened withinthree hours.Fig. 8Settlement of the bucket foundation5Discussions and conclusionsA dynamic loading device composed primarily of an electromagnetic actuator has been developed.With this device , the amplitude and the frequency of a horizontal cyclic force is reproduced atcentrifugal acceleration of 80 g.Centrifuge tests have been carried out to investigate the behavior of a suction bucket underhorizontal cyclic loading for a duration of prototype 26. 7 hours. The experimental results indicate thatexcess pore water pressures were generated in the silt surrounding the bucket. The maximum excesspore water pressure is approximately equal to the vertical effective soil stress , e. g.um/ vratio is0. 940. 96. Liquefaction potential exists within a depth of 1. 5 m. The residual pore water pressuredecreases with the depth. Since the soil is weakened during long time excitation , grea
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号