四轮驱动汽车变速器设计
东风悦达起亚2.0L手动档四驱狮跑车汽车变速器设计
狮跑车汽车手动变速器设计
东风悦达起亚2.0L手动档变速器的设计
四轮驱动汽车变速器设计
手动档变速器的设计
四轮驱动狮跑车汽车变速器设计
东风悦达起亚2.0L手动档四轮驱动狮跑车汽车变速器设计【优秀汽车变速器设计+13张CAD图纸】
【带任务书+开题报告+审题表+指导记录+外文翻译+73页@正文27150字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609 】.bat
01.题目审定表.doc
02.任务书.doc
03.开题报告.doc
04.指导记录.doc
一档从动齿轮.dwg
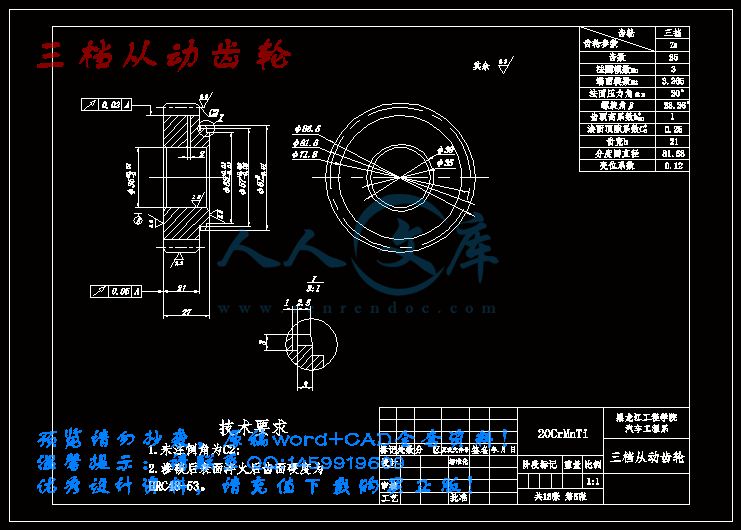
三档从动齿轮.dwg
中期检查表.doc
中间轴.dwg
二档从动齿轮.dwg
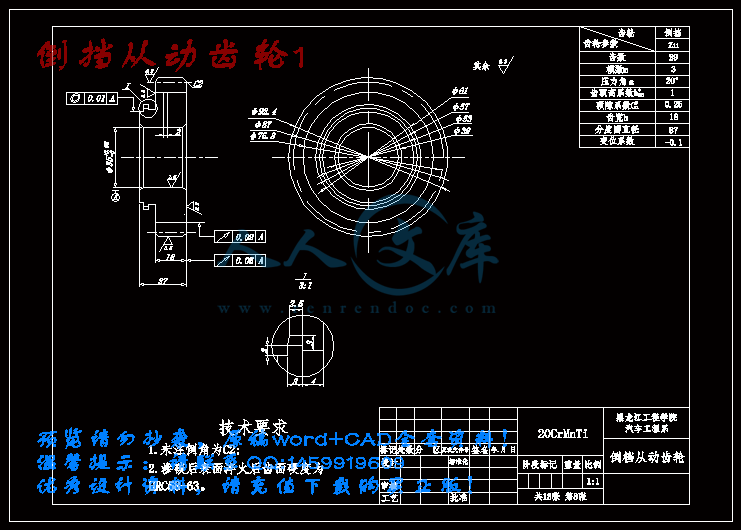
倒挡从动齿轮1.dwg
倒挡从动齿轮2.dwg
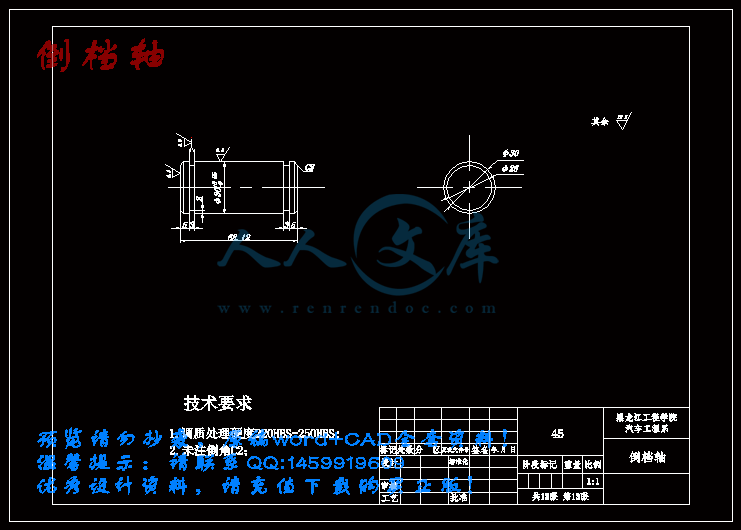
倒档轴.dwg
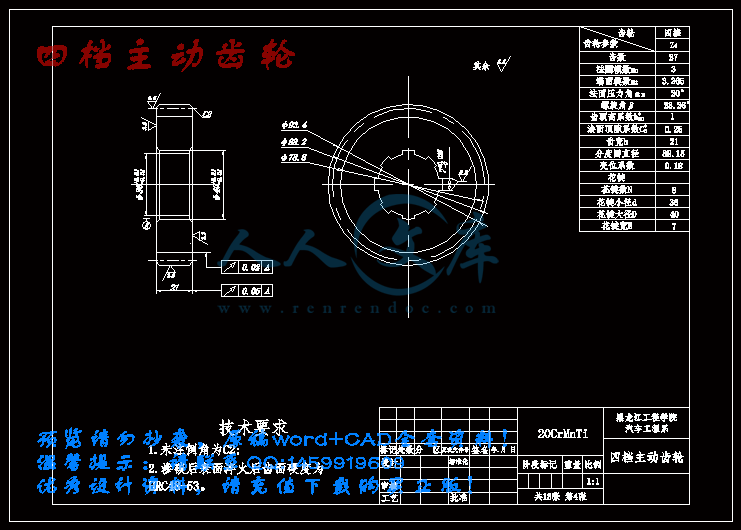
四档主动齿轮.dwg
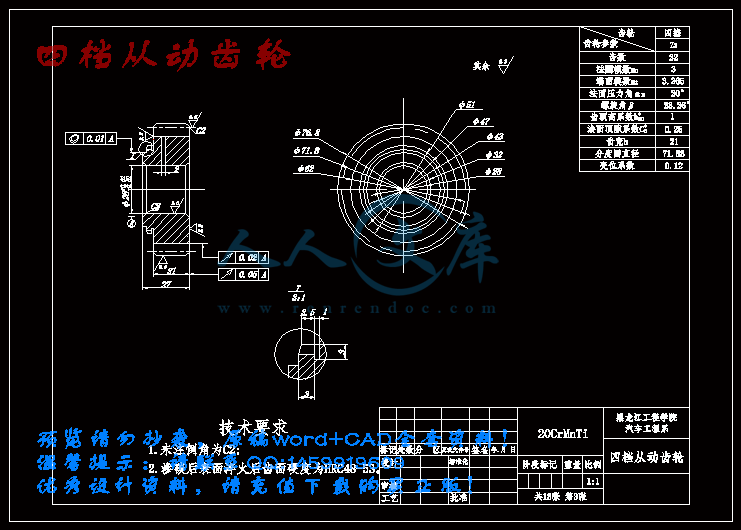
四档从动齿轮.dwg
图纸及正文备份.rar
封皮.doc
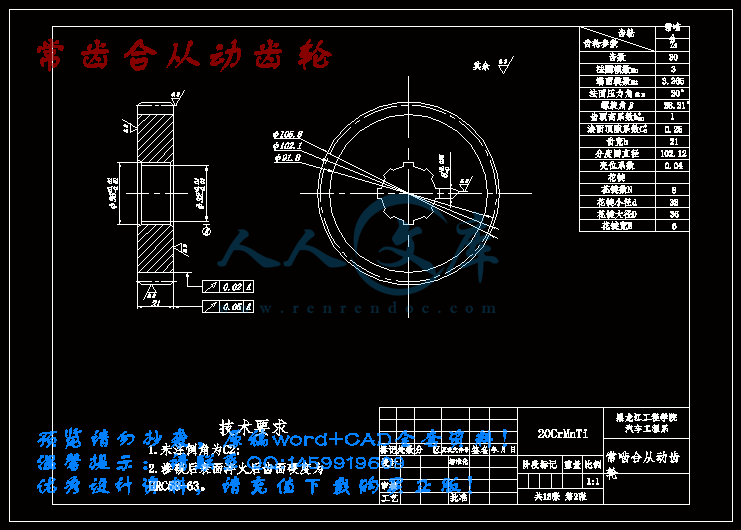
常齿合从动齿轮.dwg
开题报告.doc
成绩评定表.doc
指导教师评分表.doc
推荐表.doc
正文.doc
第一轴.dwg
答辩评分表.doc
装配图剖.dwg
评阅人评分表.doc
说明书封面.docx
输出轴.dwg
任务书
题目名称四轮驱动汽车变速器设计
一、设计(论文)目的、意义
学习和研究四轮驱动汽车变速器设计,进行主要部件(齿轮、轴等部件)设计,必要时可采用逆向方法。设计应满足院本科生毕业设计规范的要求并达到及格水平以上。
二、设计(论文)内容、技术要求(研究方法)
1、设计的主要内容
(1)掌握汽车变速器结构及工作原理,绘出结构原理简图。(2)确定主要零部件(齿轮、轴等)主要设计参数,并对关键部位进行校核。(3)确定零部件结构尺寸。 (4) 使用AutoCAD完成工程图纸。利用Pro-E建立体图。(5)编写设计说明书。
2、技术要求(研究方法)
(1)通过文献资料收集,熟悉汽车变速器设计和CAD的有关理论知识,国内外汽车设计方法和汽车计算机辅助设计的发展状况。实地到汽车厂等部门实习调查,了解变速器设计方法。
(2)编写课题研究大纲和开题报告。
(3)以狮跑四轮驱动汽车变速器设计为例,方案合理可行;确定主要零部件(齿轮、轴等)主要设计参数,并对关键部位进行校核。确定零部件结构尺寸。
(4)按进度要求独立完成毕业设计,服从指导教师安排;完成的毕业设计格式规范;方案选择合理,具有可行性、经济性、适用性,设计思路清晰,符合实际,图纸正确符合制图标准,内容完整。设计和汽车计算机辅助设计的发展状况。
三、设计(论文)完成后应提交的成果
折合CAD A0图纸1张,A3图纸12张;
Pro-E A4图纸14张;
设计说明书1.5万字以上。
四、设计(论文)进度安排
(1)调研、资料收集,完成开题报告 第1-2周(3月2日~3月13日)
(2)变速器方案确定 第3-4周(3月16日~3月27日)
(3)参数选择与设计计算 第5-6周(3月30日~4月10日)
(4)完成设计说明书,完成图纸绘制 第7~13周(4月13日~5月29日)
(5)交稿 第14周(6月1日~6月5日)
(6)设计审核、修改 第15、16周(6月8日~6月19日)
(7)毕业设计答辩准备及答辩 第17周(6月22日~6月26日)
五、主要参考资料
[1] 安相璧.汽车试验工程[M].北京:国防工业出版社,2006
[2] 周鹤良,王天顺.加速电动自行车产业化.中国机电工业,2001(5)
[3]王望予.汽车设计.第3版.北京:机械工业出版社,2000
[4]《汽车工程手册》编辑委员会.汽车工程手册.设计篇.北京:人民交通出版社,2001
[5]《汽车工程手册》编辑委员会.汽车工程手册.制造篇.北京:人民交通出版社,2001
[6]余志生.汽车理论.第3 版.北京:机械工业出版社,2000
[7]张洪欣.汽车底盘设计.北京:机械工业出版社,1998
摘 要
汽车作为人类的代步工具,在生活中起着越来越重要的作用。变速器是传动系中的主要部件。它用来改变发动机传到驱动轮上的转矩和转速。目的是在各种工作状况下,使汽车获得不同的牵引力和速度。从而使汽车拥有良好的动力性和燃油经济性。本次设计以东风悦达起亚2.0L手动档四驱狮跑车汽车的一些整车参数和发动机参数为设计依据,进行手动档变速器的设计。设计的主要内容包括变速器传动机构布置方案的确定,变速器主要参数如挡数、传动比范围、中心距、各挡传动比、齿轮参数、各挡齿轮齿数的选择,齿轮、轴的设计校核,同步器、操纵机构及箱体的设计。在设计的过程中,本文根据轿车变速器的设计要求和车辆动力传动系统自身的特点,参考多篇文献资料,以及变速器设计图册,设计出中间轴式变速器。
关键词:变速器;齿轮;轴;设计;计算机辅助设计
ABSTRACT
Automobile as a means of transport of human life plays an increasingly important role. Transmission is the main power train components. It is used to change the engine's torque spread and wheel speed. Aim is to work in a variety of conditions,different vehicle traction and speed,so that the car has good power and fuel economy。The transmission is designed based on engine parameters and vehicle parameters of Dongfeng Yuedaqiya 2.0L Shipao automobile in this text. The main design contents include the layout program of transmission drive-mechanism, the selection of main transmission parameters such as shifts, the range of gear ratio, center-spacing, each gear ratio, gear parameters and the numble of each gear, the design and verification of gears and shafts, the design of synchronizer, manipulation-framework and gearbox. Bases on the design requirement and the characteristic of power transmission system, consulting a great deal of literatures and transmission design drafts, a kind of three-shafted transmission is designed.
Key words: Transmission;Gear;Shaft;Design;Computer Aided Design
目 录
摘要………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅰ
Abstract ………………………………………………………………………………Ⅱ
第1章 绪论………………………………………………………………………………1
1.1 课题研究的现状………………………………………………………………1
1.2 课题研究的目的和意义………………………………………………………2
1.3 设计完成的主要内容…………………………………………………………3
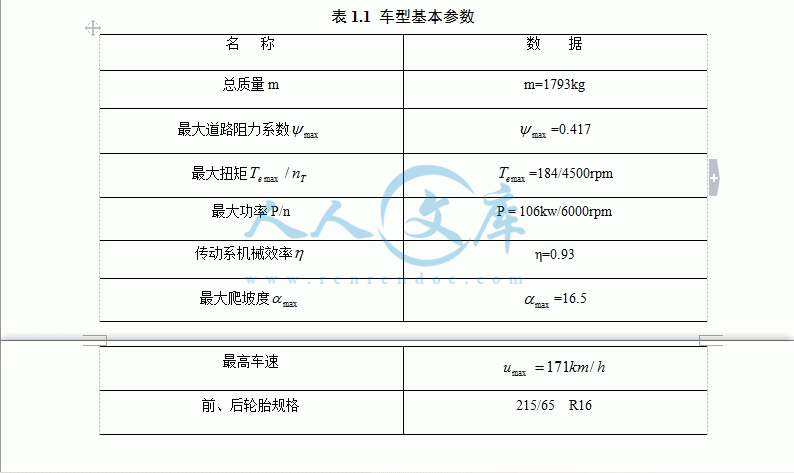
1.4 车型基本参数…………………………………………………………………3
第2章 变速器传动机构布置方案…………………………………………………5
2.1 传动机构布置方案分析………………………………………………………5
2.1.1两轴式和中间轴式变速器………………………………………………5
2.1.2倒档的形式和布置方案…………………………………………………5
2.2 零、部件布置方案分析…………………………………………………………7
2.2.1齿轮形式…………………………………………………………………7
2.2.2换档的结构形式…………………………………………………………7
2.2.3变速器轴承………………………………………………………………7
2.3本章小结…………………………………………………………………………8
第 3 章 变速器主要参数的选择及设计计算……………………………………9
3.1变速器的档位数,传动比和中心距的确定……………………………………9
3.1.1档数………………………………………………………………………9
3.1.2传动比范围………………………………………………………………9
3.1.3确定最低档传动比………………………………………………………9
3.1.4初步确定其他各档传动比……………………………………………11
3.1.5初选中心矩……………………………………………………………11
3.2齿轮参数的确定………………………………………………………………12
3.2.1齿轮的模数……………………………………………………………12
3.2.2压力角………………………………………………………………13
3.2.3螺旋角………………………………………………………………14
3.2.4齿宽……………………………………………………………………14
3.2.5 齿轮的变位系数的选择原则…………………………………………15
3.2.6齿顶高系数……………………………………………………………16
3.2.7 各档传动比及其齿轮齿数的确定……………………………………16
3.2.8变速器齿轮的几何尺寸计算…………………………………………21
3.3本章小结………………………………………………………………………29
第4章 变速器主要结构元件的设计与计算……………………………………30
4.1 齿轮损坏的原因及形式………………………………………………………30
4.2 轮齿强度计算…………………………………………………………………31
4.2.1轮齿弯曲强度计算……………………………………………………31
4.2.2轮齿接触应力计算……………………………………………………35
4.3 变速器齿轮材料的选择及热处理……………………………………………39
4.4轴的设计计算…………………………………………………………………40
4.4.1初选轴的直径…………………………………………………………40
4.4.2轴的刚度验算…………………………………………………………41
4.4.3 轴的强度计算…………………………………………………………48
4.5本章小结………………………………………………………………………53
第5章 同步器的选择…………………………………………………………………54
5.1 惯性式同步器…………………………………………………………………54
5.1.1 锁环式同步器的结构…………………………………………………54
5.1.2锁环式同步器的工作原理……………………………………………55
5.1.3锁环式同步器主要尺寸的确定………………………………………55
5.2主要参数的确定………………………………………………………………56
5.2.1摩擦因数f ……………………………………………………………56
5.2.2同步环主要尺寸的确定………………………………………………57
5.2.3锁止角………………………………………………………………58
5.2.4同步时间………………………………………………………………58
5.2.5转动惯量的计算………………………………………………………58
5.3本章小结………………………………………………………………………59
第6章 变速器操纵机构的选择和箱体设计原则………………………………60
6.1变速器操纵机构的选择………………………………………………………60
6.2变速器箱体设计原则…………………………………………………………60
6.3本章小结………………………………………………………………………61
第7章 变速器齿轮和轴的建模……………………………………………………62
7.1齿轮建模………………………………………………………………………62
7.2轴的建模………………………………………………………………………64
7.3本章小结………………………………………………………………………65
结论………………………………………………………………………………………66
参考文献…………………………………………………………………………………67
致谢………………………………………………………………………………………68
附录………………………………………………………………………………………69
附录A 英语科技文献……………………………………………………………69
附录B 文献翻译…………………………………………………………………73
第1章 绪 论
1.1课题研究的现状
汽车变速器是汽车的重要部件之一,用来改变发动机传到驱动轮上的转矩和转速,目的是在原地起步、爬坡、转弯、加速等各种行使工况下,使汽车获得不同的牵引力和速度,同时使发动机在最有利的工况范围内工作。变速器设有空档,可在起动发动机、汽车滑行或停车时使发动机的动力停止向驱动轮传输。变速器设有倒档,使汽车获得倒退行使能力。
汽车变速器技术的发展历史:
手动变速器(MT:Manual Transmisson)主要采用了齿轮传动的降速原理。变速器内有多组传动比不同的齿轮副,而汽车行驶时的换挡工作,也就是通过操纵机构使变速器内不同的齿轮副工作。
自动变速器(AT:Automatic Transmisson)是由液力变矩器,行星齿轮和液压操纵系统组成,通过液力变矩器和齿轮组合的方式来达到变速变矩。
AMT是在传统干式离合器和手动齿轮变速器的基础上改造而成,主要改变了手动换挡操纵部分。即在MT总体结构不变的情况下改用电子控制来实现自动换挡。
无级变速器(CVT:Continuously Variable Transmission),又称为连续变速式机械变速器。金属带式无级变速器主要包括主动轮组,从动轮组,金属带和液压泵等基本部件。主要靠主动轮,从动轮和传动带来实现速比的无级变化,传动带一般用橡胶带,金属带和金属链等。
无限变速式机械无级变速器(IVT:Infinitely Variable Transmisson)采用的是一种摩擦板式变速原理。IVT的核心部分由输入传动盘,输出传动盘和Variator传动盘组成。它们之间的接触点以润滑油作介质,金属之间不接触,通过改变Variator装置的角度变化而实现传动比的连续而无限的变化。
汽车的发展经历了三大革命,动力革命(内燃机的使用),传动革命(机械传动的完善和液体传动的使用)和控制革命(用传感器、微机和电液阀进行信息处理)。
从先进国家来看,动力革命和传动革命已经完成,目前正处于控制革命阶段,要解决的主要是机械太“机械”,没有灵性的问题,过去机械全靠人来操纵控制,然而人的生理和心理能力(感觉器官的功能、头脑分析的能力和体能)是有限的,操纵汽车这样复杂的机械对于人来说体力和脑力负担是很重要的,更主要的是单靠人力操纵将阻碍汽车的发展和其性能的提高。因此必须对汽车各部分(发动机、变速器、悬架、制动和转向机构等)进行自动控制,并从各部分的单独控制向整车一体化控制发展,从一般控制向智能控制发展。要解决机械信息处理能力问题,机械本身是无能为力的,液压控制在性能上也达不到要求,必须引入具有良好控制性能和信息处理能力的电子技术。但是仅仅采用机电液技术还不够,还需要应用声学、光学、和化学等多学科技术才能使机械具有良好的信息处理能力,实现高度自动化。
从技术发展角度来看,汽车传动技术中的关键是电子技术、电液控制技术和传感器技术。目前,世界主要的变速器制造生产厂家都致力于这些关键技术的研究与应用,极大地促进了自动变速器的发展[16]。
参考文献
[1] 臧杰,阎岩.汽车构造(下册)[M].北京:机械工业出版设,2005.8
[2] 刘惟信.汽车设计[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2001.7
[3] 王望予.汽车设计[M].第4版.北京:机械工业出版社,2004.8
[4] 余志生.汽车理论[M].第4版.北京:机械工业出版社,2006.5
[5] 杨可桢,程光蕴,李仲生.机械设计基础[M].第五版.北京:高等教育出版社,2006.5
[6] 殷玉枫.机械设计课程设计[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2006.6
[7] 李华敏,李瑰贤.齿轮机构设计与应用[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2007.6
[8] 周松鹤,徐烈烜.工程力学[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2003.2
[9] 刘朝儒,彭福荫,高政一.机械制图[M].第四版.北京:高等教育出版社,2001.8
[10] 刘品,李哲.机械精度设计与检测基础[M].第5版.哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社,2007.9
[11] 顾任安.东风EQ1090E(EQ140-1)载货汽车修理图册[M].北京:人民交通出版社,2005.6
[12] 王霄,刘会霞. Pro/ENGIHEER Wildfire 3.0典型机械零件设计手册[M].北京
化学工业出版社,2006,5
[13] 王铁,赵富强,李光辉.手动变速器建模实例教程:Pro/ENGINEER野火版[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2007.5
[14] 成大先.机械设计手册.单行本.轴承[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2004.1
[15] 李爱琴. 浅谈汽车变速器技术的发展.科技咨询导报[J].2007,15
[16] 胡朝峰,过学迅,汪斌.汽车变速器技术的发展与展望[J].汽车研究与开发,
2005,5
[17] Herbert E.Elliger.Automotive Engines.Prentic Hall,Inc.2001.
[18] Julian Happian Smith.An Introduction to Modern Vehicle Design.
Butterworth-HeinenMann. 2002.







 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号