康复机器人的系统设计
下肢康复机器人设计
下肢康复机器人的设计
基于步态控制的下肢康复机器人的设计【优秀机械手设计+25张CAD图纸】
【52页@正文17600字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609 】.bat
基于步态控制的下肢康复机器人的设计.doc
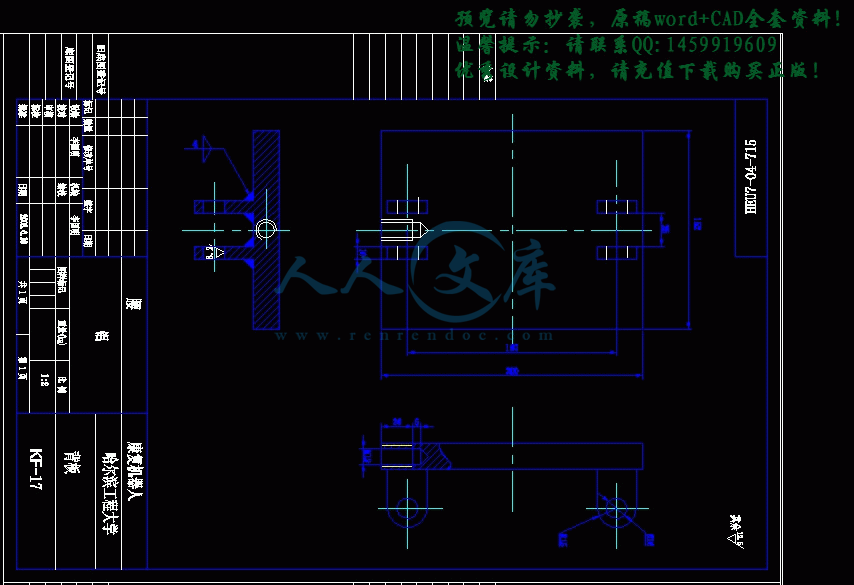
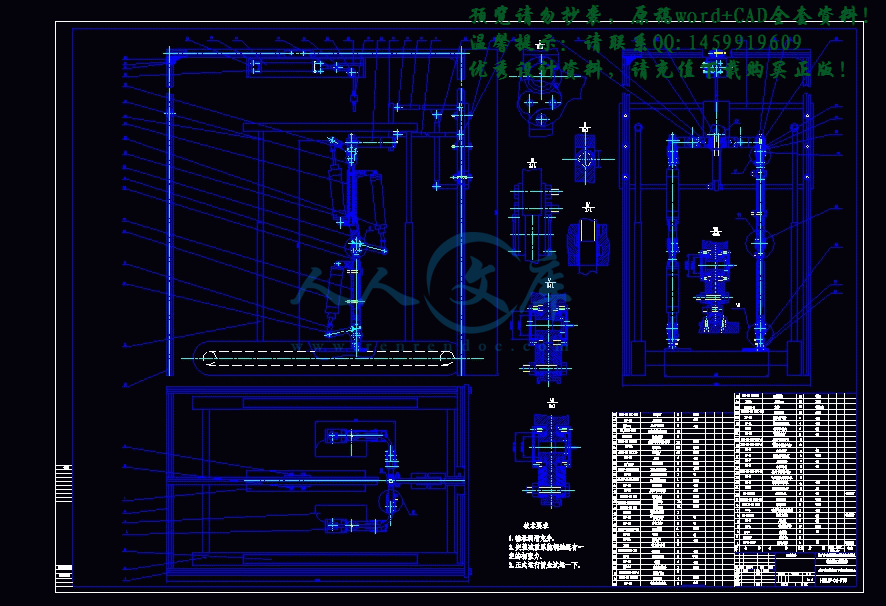
总装图.dwg
摘要2.doc
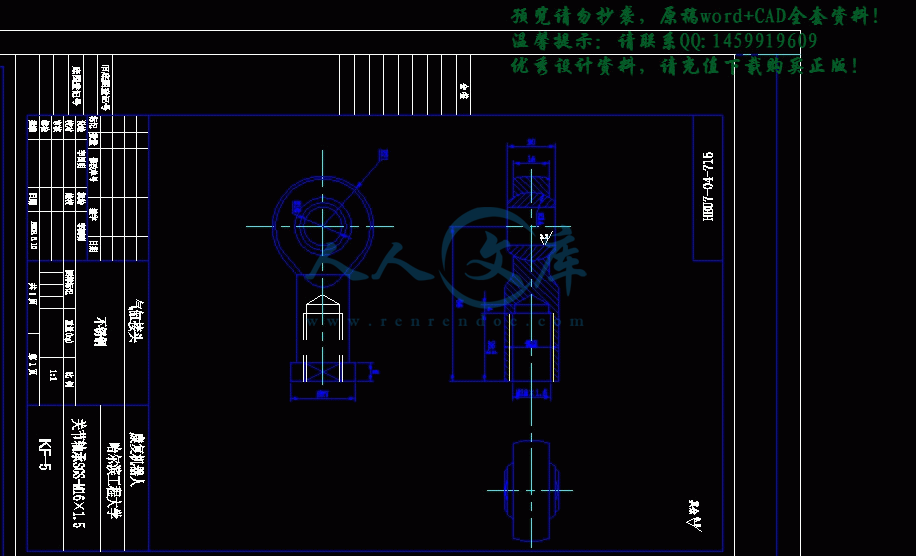
架子.dwg
背板.dwg
背板上杆.dwg
背板下杆.dwg
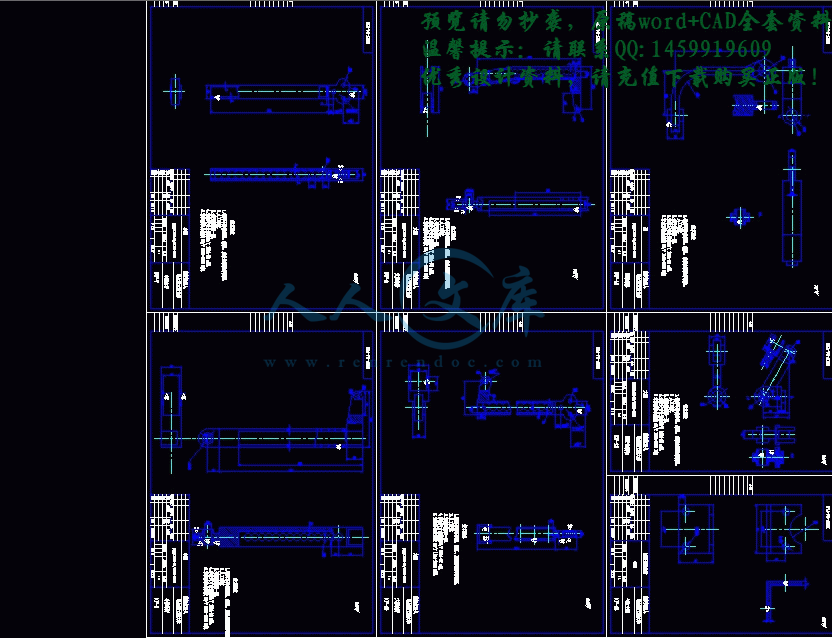
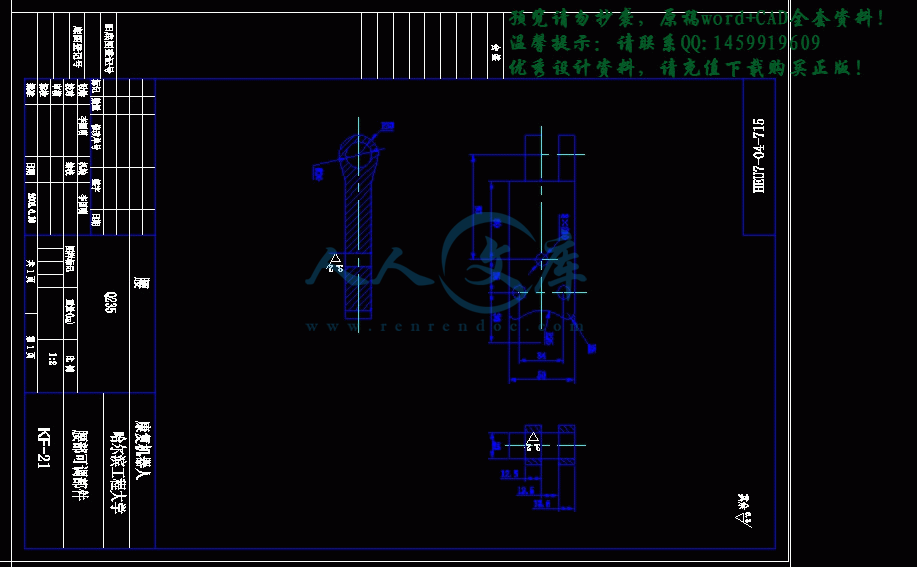
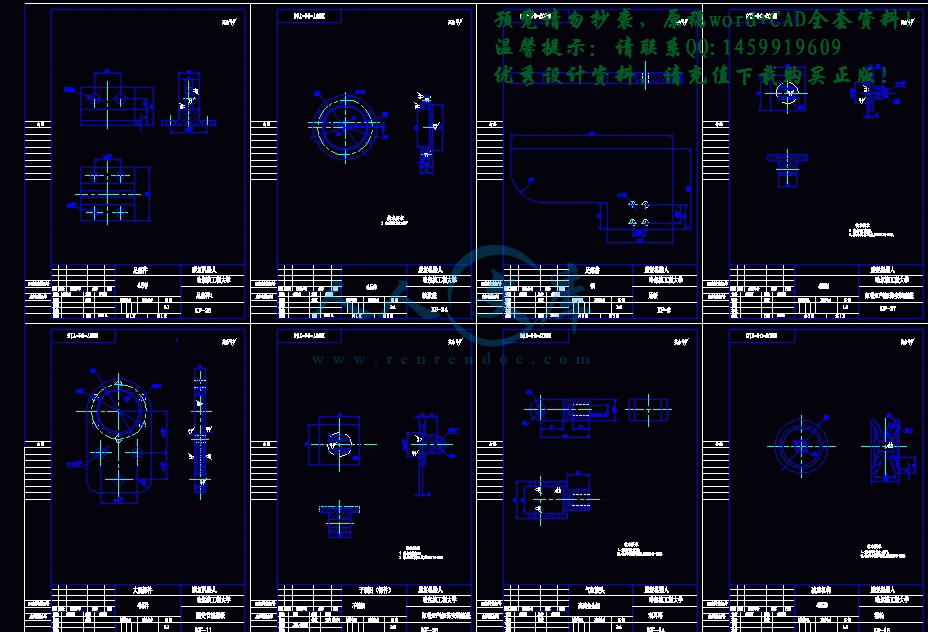
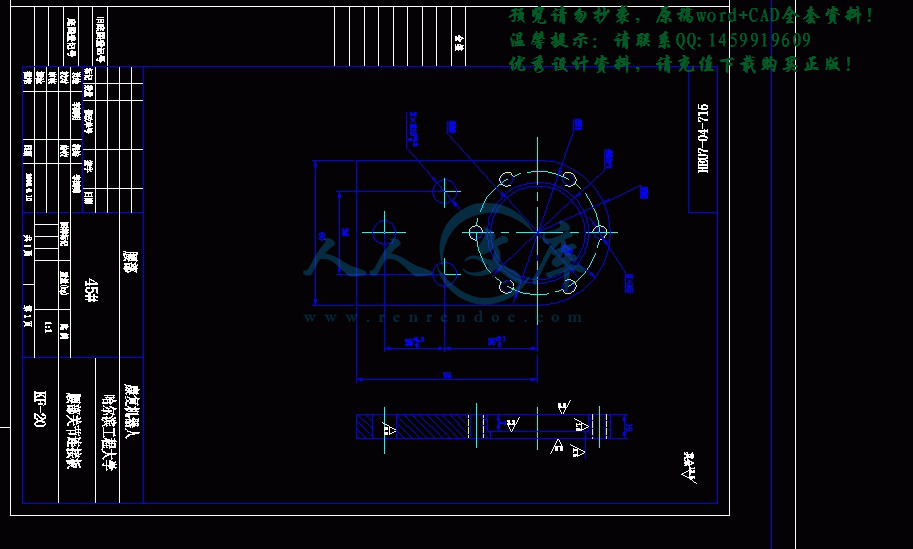
零件图合计13张.dwg
零件图合计9张.dwg
摘 要
康复机器人技术则是近年来迅速发展的一门新兴机器人技术,是机器人技术在医学领域的新应用;目前康复机器人已成为国际社会研究的热点之一。本课题主要研究的基于姿态控制步态康复训练系统的设计。
本文介绍了下肢康复机器人国内外发展现状和应用情况,进行了步态训练机器人的总体方案设计、结构设计,和总体控制方案设计等;对步态训练机器人进行三维建模,并对重要零件进行校核。本步态训练机器人共有7个自由度,其中每一条机械腿上有3个关节(3个自由度)模仿人体腿上的踝关节、膝关节、髋关节和一个用于减重的减重系统(包括1个自由度)。此系统能用于脑损伤、中风等病人的步态康复训练,帮助病人更好地进行康复训练,减轻他人的帮助,挺高效果。
关键词:康复训练;机器人;步态
ABSTRACT
The rehabilitation robot technology is a new robot technology developed rapidly recently, which is a new application in medical fields of robot technology. Currently the research on rehabilitation robot has been one of the focuses in the International Society. The rehabilitation robot technology is a synthesis of many subjects, which covers mechanics, electronics, control and rehabilitative medicine and so on; it has been a typical representation of the mechatronics research. The main research of this paper is based on the attitude control gait rehabilitation training system design.
In this paper, lower extremity rehabilitation and development of robot applications at home and abroad, a gait training robot's overall programme design, structural design, design and overall control; gait training on the robot for three-dimensional modeling, and important parts to check. The robot gait training has a total of seven degrees of freedom, each of which a mechanical leg joints have three (3 DOF) to imitate human leg ankle, knee, hip and a weight relief for weight relief system (including a degree of freedom). The system can be used for brain injury, stroke, and to help patients better rehabilitation training, and meets.the needs of different groups of people.
Key words:rehabilitation training; robot; gait
目 录
第1章 绪论1
1.1 概述1
1.2 康复机器人的国内外研究现状2
1.3 本课题主要研究内容7
第2章 总体方案设计与选择的论证8
2.1 步态分析8
2.2 方案的选择11
2.2.1 自由度的设计13
2.2.2 基本参数的选取13
2.2.3 驱动器的选择14
2.2.4 关节结构的选择14
2.2.5 连杆结构的选择14
2.2.6 腰部结构设计15
2.2.7 减重机构15
2.2.8 整体结构设计16
2.3 本章总结16
第3章 机械结构的设计与计算及驱动元件选型17
3.1 人体参数17
3.2 各关节运动学分析17
3.2.1踝关节的运动学分析18
3.2.2 膝关节的运动学分析18
3.2.3 髋关节的运动学分析19
3.3 关节力矩分析20
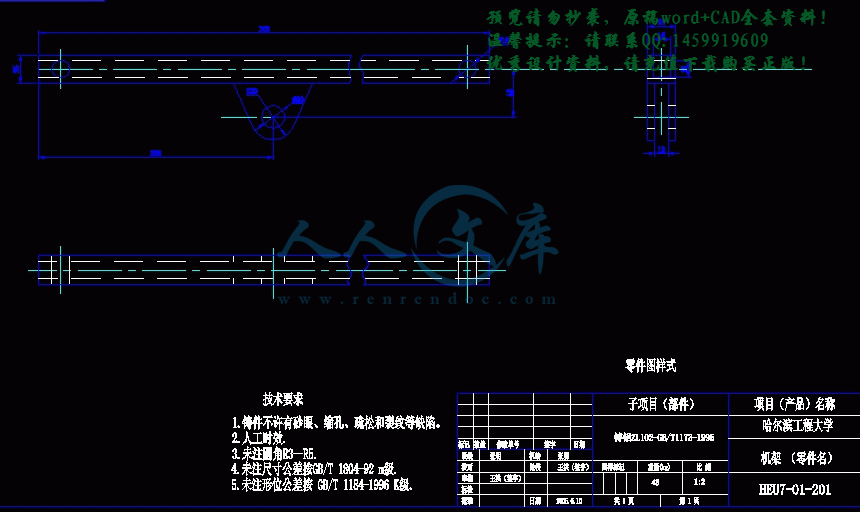
3.4 具体结构设计21
3.4.1 关节结构的选择21
3.4.2 连杆结构的选择22
3.4.3 腰部结构设计23
3.4.4 减重机构23
3.4.5 整体结构设计24
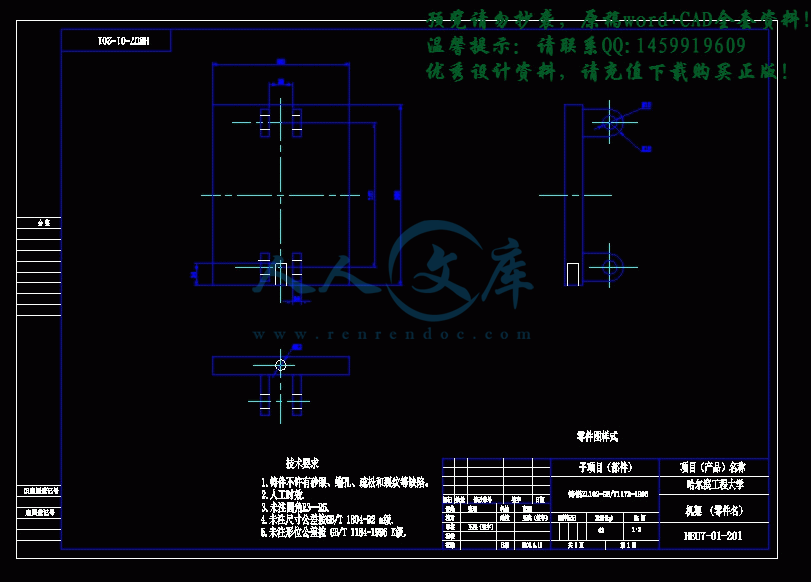
3.5 一些零件的设计和校核25
3.5.1 轴承的选择及校核25
3.5.2 气缸的选择25
3.5.3 连杆的计算与校核27
3.5.4 销轴的校核29
3.5.5 双头螺柱的校核30
3.5.6 传感器的选取30
3.6 减重系统分析及相关计算31
3.7 本章小结32
第4章 供气与控制系统的设计33
4.1 供气系统的设计33
4.1.1 供气回路设计33
4.1.2 气动元件的选择34
4.2 康复机器人的训练方式39
4.3 气动自动控制方框图39
4.4 本章小结40
结 论41
参考文献42
致 谢45
第1章 绪论
1.1 概述
据报道,我国60岁以上的老年人已有1.43亿,占全国人口的11%,到2050年将达到4.37亿。在老龄人群众中有大量的脑血管疾病或神经系统疾病患者,这类患者多数伴有偏瘫症状[1]。近年由于患心脑血管疾病使中老年患者出现偏瘫的人数不断增多,而且在年龄上呈现年轻化趋势。同时,由于交通运输工具的迅速增长,因交通事故而造成神经心痛损伤或者肢体损伤的人数也越来越多。在美国数以百万计的有神经科疾病病史和受到过意外伤害的患者需要进行康复治疗,仅以中风为例,每年大约有600,000中风幸存者,其中的二百万病人在中风后存在长期的运动障碍。随着国民经济的发展,这个特殊群体已得到了更多人的关注,为了提高他们的生活质量,治疗、康复和服务于他们的产品的技术和质量也在相应地提高。随着机器人技术和康复医学的发展,在欧洲、美国和日本等国家,医疗康复机器人的市场占有率呈逐年上升的趋势,仅预测日本未来机器人市场,2005年医疗、护理、康复机器人的市场份额约为250,000美元,而到2010年将上升到1,050,000美元,其增长率在机器人的所有应用领域中占据首位。因此,服务于四肢的康复设备的研究和应用有着广阔的发展前景[2]。
参考文献
[1] 张付祥,付宜利,王树国.康复机器人研究现状[J].河北工业科技,2005,22(2):100-105.
[2] 杜志江,孙传杰,陈艳宁.康复机器人研究现状[J].中国康复医学杂志,2003,18(5):293-294.
[3] Hogan N,Krebs I,Charnnarong J,Srikrishna P,Sharon A.MIT-MANUS:A Workstation for Manual and Training [J].IEEE International Workshop on Robot and Human Communication,1992:161 –165.
[4] Rehabilitation Center of DRMC./rehab.php,2008-06-12.
[5] Gait rehabilitation.http://userpage.fu-berlin.de/~bhesse/Gangreha/gte.html,2008,06,10.
[6] Saso Jezernik,Gery Colombo,Manfred Morari.Automatic Gait-Pattern Adaptation Algorithms for Rehabilitation With a 4-DOF Robotic rthosis[J].IEEE Transaction on Rehabilitation and automation,VOL.20,NO.3,JUNE2004.
[7] Rolf Bemhardt,Dragoljub Surdilovic.STRING-MAN:A New Wire Robot for Gait Rehabilitation.Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Conference On Robotics and Automation,New Orleans, LA,April 2004.
[8] Andrew Chu,H. Kazerooni,Adam Zoss.On the Biomimetic Design of the Berkeley Lower Extremity Exoskeleton (BLEEX).Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation Barcelona,Spain,April 2005.
[9] Hiroshi Kobayashi Hidetoshi Suzuki.Development of a New Shoulder Mechanism for a Muscle Suit[R].Department of Mechanical Engineering Science University of Tokyo,2004.
[10] 黄靖远,刘宏增等,“虚拟现实”康复工程前景初探.生物医学工程学杂志,Vol.16 No.2, 1999.
[11] 夏昊昕.下肢康复训练机器人的研究.哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学,2003.
[12] Winter,D.A.Kinematic and Kinetic patterns in Human Gait:Variability and Compensating Effects.Human Movement Science,3:51-76.
[13] Kirtley,C.CGA Normative Gait Database, Hong Kong Polytec3nic University,10 Young Adults.Available:http://.au/cga/data/.
[14] Winter A.International Society of Biomechanics,Biomechanical Data Resources,Gait Data.Available: /data/.
[15] Linskell,J.,CGA Normative Gait Database,Limb Fitting Centre, Dunde,Scotland,Young Adult. Available:http://.au/cga/data/.
[16] Fabio Gazzani,Antonello Fadda,Marina Torre,Velio Macellari.WARD:A Pneumatic System for Body Weight Relief in Gait Rehabilitation[J].IEEE Transaction on Rehabilitation Engineering,VOL.8,NO.4,DECEMBER 2000.
[17] F A Mussa-Ivaldi,J L Patton.Robots can teach people how to movetheirarm[R].Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation San Francisco,CA,April 2000.
[18] 孙建东,金德文.一种下肢被动运动康复训练器.中国康复医学杂志,Vol.16 No.5,2001.
[19] H. Kazerooni,Jean-Louis Racine,Lihua Huang,and Ryan Steger.On the Control of the Berkeley Lower Extremity Exoskeleton (BLEEX).Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics & Automation Barcelona,Spain,April 2005.
[20] 谭冠政,尉忠信,朱剑英.空间型两足步行机器人的运动学建模研究[J].航空学报,1992,13(12):1-8.
[21] 陈东辉,佟金,张书军,陈秉聪.人和动物的步态与步行机器人[J].中国农业机械学会成立40周年庆典暨2003年学术会论文集,2003,3:22-23.
[22] 胡宇川.人体下肢外骨骼工作机理研究[D].南京:南京理工大学,2006.
[23] 王斌锐.异构双腿行走机器人研究与开发[J].沈阳:东北大学,2005.
[24] 蔡自兴.机器人学[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2000年9月.
[25] [南斯拉夫]麦沃曼尔.伍科布拉托维奇 著,马培荪,沈乃勃 译.步行机器人和动力型假肢.科学出版社1983年7.
[26] 机器人技术手册.日本机器人学会编.科学出版社,1996年10月.
[27] 戢敏,袁中凡,林大全.仿真假人人体参数的计算和分析[J].中国测试技术,第4期 2003年7月.
[28] 张立勋,赵凌燕.下肢康复训练机器人的重心轨迹控制研究[J].应用科技,2005,4.
[29] Ounpu S.Terminology for clinical gait analysis (Draft #2). Prepared by American Academy of Cerebral Palsy Developmental Medicine Gait Lab Committee and distributed at North American Clinical Gait Lab Conference, Benson Hotel,Portland,Ore.April 6-9,1994.
[30] Inman V,Ralston HJ,Todd F.Human walking.Baltimore:Williams & Wilkins,1981.
[31] 郑秀瑗.运动生物力学进展[M].国防工业出版社,1998:82-92.
[32] SMC(中国)有限公司.现代实用气动技术[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2005:65-105,316-328,384-391.
[33] 徐炳辉.气动手册[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社,2005:38-45,50-54,155-158.




 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号