锻压机自动上料机械手执行系统设计
29页 11000字数+说明书+外文翻译+10张CAD图纸【详情如下】
外文翻译--工业机器人及电动驱动系统.doc
手指.dwg
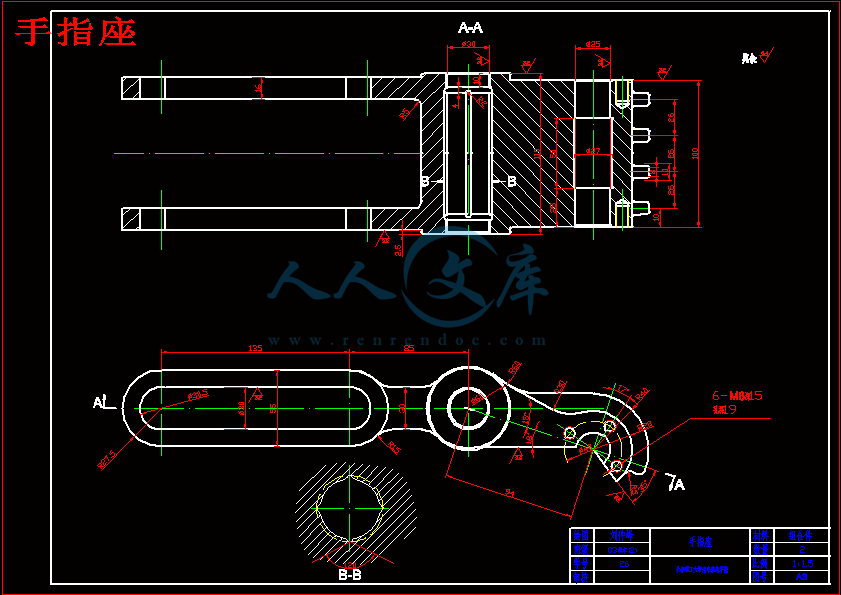
手指座.dwg
手架.dwg
手臂伸缩机构装配图.dwg
手部结构.dwg
手部结构组合图.dwg
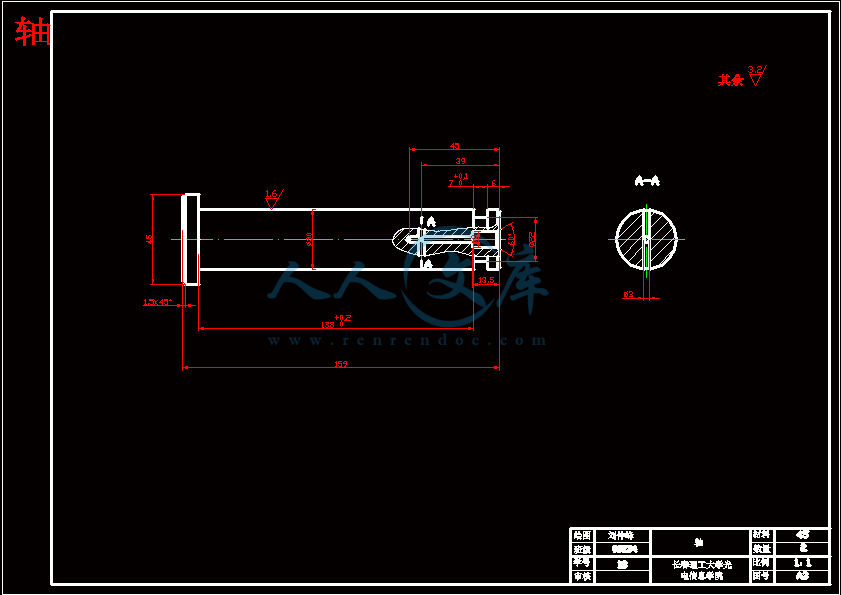
轴.dwg
轴环.dwg
轴盖.dwg
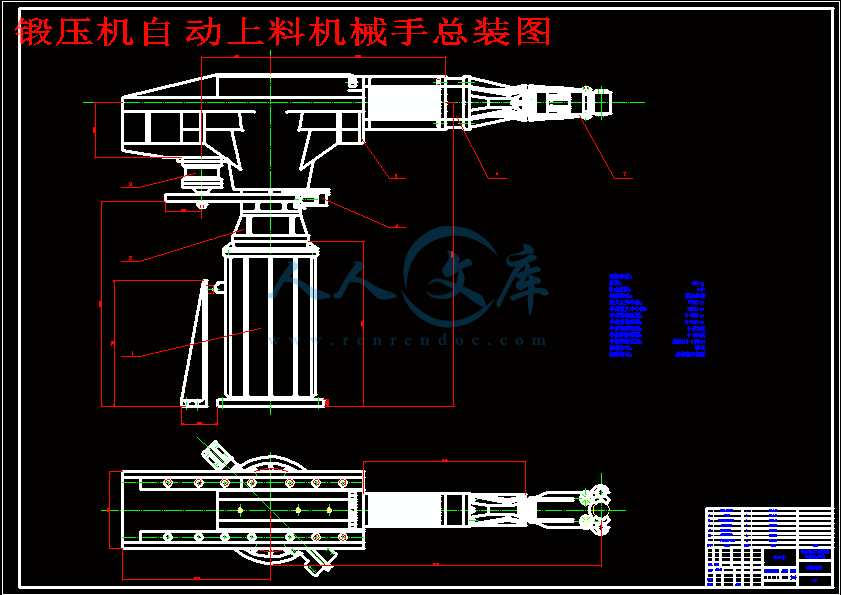
锻压机自动上料机械手总装图.dwg
锻压机自动上料机械手执行系统设计说明书.doc










摘要
锻压机自动上料机械手的作用是将被加热的坯料从上料位置将热坯料搬运到立式精锻机上锻打,其成品锻件由下料机械手从立式精锻机上取下并送到转换机械手上,转换机械手先把锻件反转 90度成水平位置,由丙烷切割装置将两端切齐,切割完毕运送到车间外面的仓库。该机械手包括执行系统、驱动系统和控制系统,本文主要设计了机械手的执行系统即手部.腕部和臂部的设计,实现了手部的夹持、腕部的回转和臂部的伸缩等功能,用 CAD完成了该机械手的总装图及手部和臂部的绘制,并分析操作该机械手的各种力学参数 ,讨论了其工作空间的情况。同时对其进行动力学分析,得到各传动关节所需的驱动力,得出了最终方案。
关键词: 锻压机 执行系统 力学参数
Abstract
The forge press automatic high-quality goods manipulator's function is the semifinished materials which heats up from the high-quality goods position the hot semifinished materials is transported to the vertical fine forging machine on hammers, its end product forging takes down by the yummy treats manipulator from the vertical fine forging machine and delivers transforms on the manipulator, transforms the manipulator to reverse the forging 90 degrees to become the first horizontal position, cuts neat by the propane cutter device the both sides, cutting finished ships to the workshop outside the warehouse. Manipulator including the implementation of the system, drive system and control system, this paper designed a robot hand that the implementation of the system. Wrist and arm of the design, implementation of the hand's grip, wrist rotation and arm stretching functions use CAD to complete assembly of the mechanical hand and hand and arm map rendering, and analysis to operate the various mechanical parameters of the manipulator, discussed the situation of their work space. At the same time the dynamic of its analysis, the driving force needed to drive joint, come to the final program.
Keyword: forging machine the implementation of the system the mechanical parameters
目录
第一章 绪论…………………1
1.1 机械手发展状况1
1.1.1 发展历史1
1.1.2现代研究趋势2
1. 1. 3 国内发展状况3
1.1.4应用举例4
1. 2机械手的研究意义6
1.3应用价值7
第二章 功能原理和结构评价设计8
2.1参考数据8
2.2 工作要求9
2.3系统组成9
2.4总体方案10
2.5具体结构方案11
第三章机械手执行系统设计与计算…13
3.1机械手执行系统设的各部分设计结构13
3.1.1手部结构13
3. 1.2腕部结构14
3.1.3臂部结构14
3.2.机械手手部设计:15
3.2.1手部结构:15
3.2.2夹紧力计算:15
3.2.3 手臂的设计计算16
3.3液压缸结构尺寸液压缸内径计算:17
3.4.液压缸壁厚计算18
3.5.液压缸零件的连接计算20
总结…………………………………22
致谢…………………………………23
参考文献……………………………24
1. 2机械手的研究意义
机械手能模仿人手和臂的某些动作功能,用以按固定程序抓取、搬运物件或操作工具的自动操作装置。它可代替人的繁重劳动以实现生产的机械化和自动化。随着科学技术的发展,机械手广泛应用于机械制造、冶金、电子、轻工和原子能等部门。
在机械制造方面机械手最早应用在汽车行业,常用于焊接、喷漆、上下料和搬运。机械手延伸和扩大了人的手足和大脑功能,它可以替代人从事危险,有害,有毒,低温和高热等恶劣环境中的工作;替代人完成繁重,单调重复劳动,保证生产质量,提高生产效。目前主要应用于制造业中,特别是电器制造、汽车制造、塑料加工、通用机械制造及金属加工等工业,机械手与数控加工中心,机械手和计算机集成制造系统 实现生产自动化。随着生产的发展,功能和性能的不断改善的提高,机械手的应用领域日益扩大。
1.3应用价值
用于轴类零件精锻自动生产线上,将加热后的坯料从运输车上取下搬运到立式精锻机上。机械手固定安装在 JD100立式精锻机前。
第二章 功能原理和结构评价设计
2.1参考数据
抓重: 60公斤
自由度数: 4个
座标型式: 圆柱坐标
最大工作半径: 1700毫米
手臂最大中心高: 2300毫米
手臂运动参数: 手臂伸缩范围: 0~500毫米
手臂伸缩速度: 200mm/s
手臂升降范围: 0~600毫米
手臂升降速度: 150mm/s 手臂回转范围: 0~200
手臂回转速度: 630/s
手腕运动参数: 手腕回转范围: 0~180
手腕回转速度: 201/s
手指夹持范围: Φ30-Φ120mm
缓冲方式及定位方式:
手臂伸缩: 伸出时由行程开关适时发信切断油路,手臂滑行缓冲,死挡块快定位,伸缩时无缓冲措施,由活塞和油缸端盖相碰定位
手臂升降: 上升时是靠可调碰铁触动行程开关而发信,使电液换向阀变为 O 型划块机能,切断油路而实现缓冲定位,下降时靠油缸端部节流缓冲,以导向套和升降缸支撑座相碰而定位。
手臂回转: 采用行程节流阀减速缓冲,用定位油缸驱动定位销而定位。
手腕回转: 采用行程开关发信,切断油路滑行缓冲,死挡块定位。
驱动方式: 液压
控制方式: 点位程序控制
机械结构设计的基本要求,包括对机器整机的设计要求和对组成零件的设计要求两个方面,两者相互联系、相互影响。
2.2 工作要求
机械手的工艺流程
机械手原位→机械手前伸→机械手上升→机械手抓取并夹紧→机械手退
机械手左转→机械手前伸→机械手松开→机械手下降→机械手右转→退至位
2.3系统组成
本机械手系统由执行系统、驱动系统和控制系统组成。执行系统包括手部、手臂、手腕。驱动系统包括动力源、控制调节装置和辅助装置组成。控制系统由程序控制系统和电气系统组成
参考文献
【1】.张福学机器人技术及其应用.北京:电子工业出版社,2000
【2】.蒋新松 Robotics.沈阳:辽宁科学技术出版社,1994
【3】.王承义机械手及其应用.北京:机械工业出版社,1981
【4】.何发昌邵远多功能机器人的原理及应用.北京:高等教育出版社,1996
【5】.王华坤范元勋机械设计基础.北京:兵器工业出版社,2000
【6】.邱宣怀机械设计第四版.北京:高等教育出版社,1997
【7】.郑志峰链传动设计与应用手册.北京:机械工业出版社,1992
【8】.唐世恭李慧中工程材料及成型工艺.北京:兵器工业出版社,1996
【9】.徐锦主机械设计手册.第 3卷.北京:机械工业出版社,1995
【10】.王特典工程材料.南京:东南大学出版社,1996
【11】.马香峰机器人机构学 .北京:机械工业出版社,1991
【12】.郑洪生气压传动.北京:机械工业出版社,1981
【13】.季明善液气压传动.北京:机械工业出版社,2002
【14】John J.Craig,Introduction to Robotics Mcchanics And Control[M],Second Edition,Addison-Wesley, Rcading,MA,1989
【15】.Beom-Sahag Ryuh, Gordon R.Pennock. An automatic tool changer and infegrated software for a robotic die polishing station[J].American: Mechanism and Machine Theory. August 2005
【16】.高井宏幸(日)等编著.工业机械人的结构与应用.北京:机械工业出版社,1997
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号