门架式专用工业机械手设计
49页 14000字数+说明书+任务书+开题报告+外文翻译+6张CAD图纸【详情如下】
MyDesign1.ddb
任务书.doc
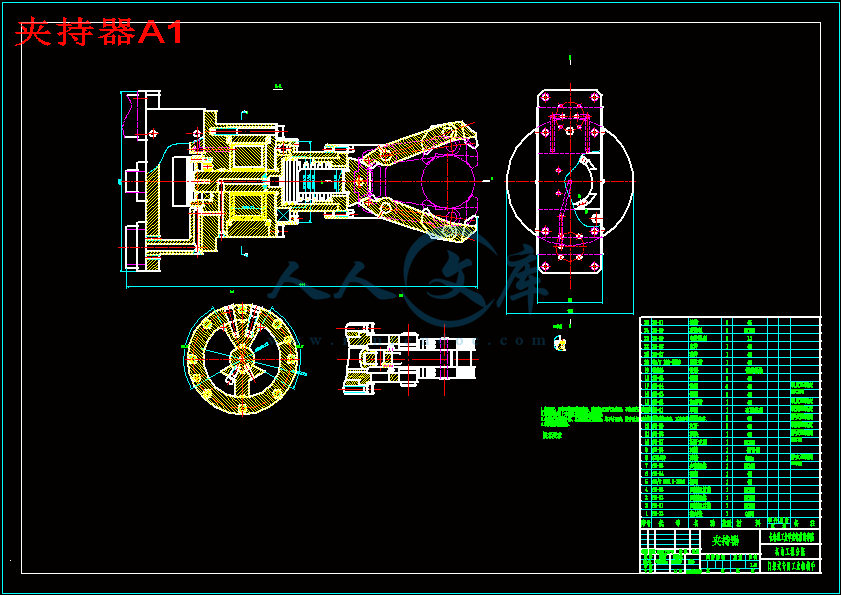
夹持器A1.dwg
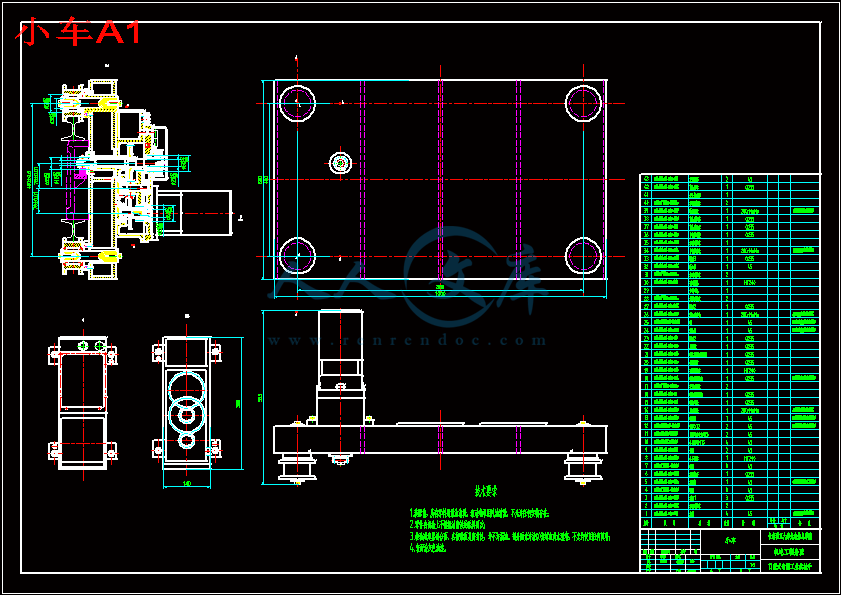
小车A1.dwg
成绩评定表理工.doc
机械臂A1.dwg
机械设计外文翻译.doc
输出轴A2.dwg
门架图A2.dwg
门架式专用工业机械手设计开题报告.doc
门架式专用工业机械手设计毕业论文.doc
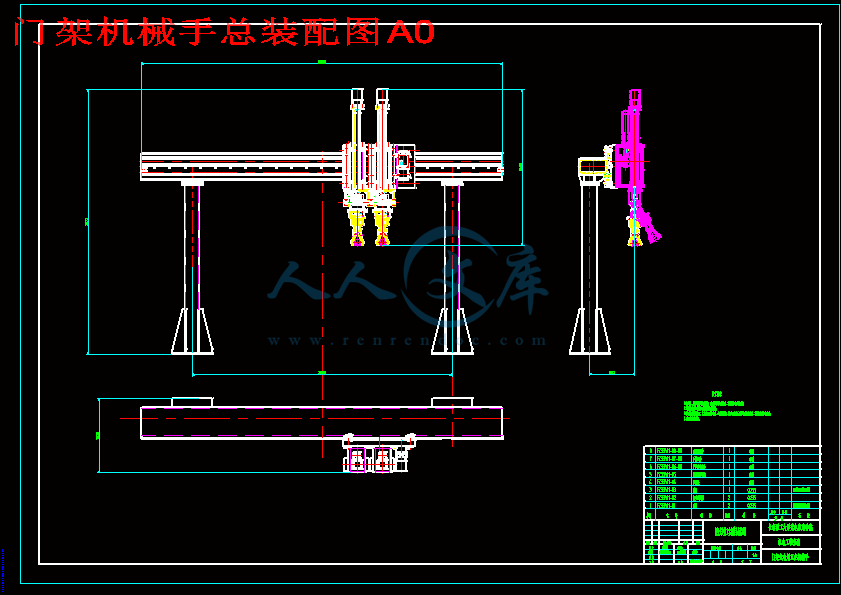
门架机械手总装配图A0.dwg




摘 要
本文以“门架式专用工业机械手设计”为题目,设计了一个多自由度固定机械手,使其具有水平旋转、上下摆动、并抓取一组物体等功能。
在先期工作中,对机械手进行功能原理分解。设计可行性方案并进行对比,选出最优方案。本文的重点有二个方面:
文中设计了机械手的机械结构部分,使用CAD和CATIA完成机械手的总体装配图和非标零件的设计,并结合力学知识对各非标零件进行校核计算。其中包括外观改进和结构优化。
结合设计参数和实践需要,对机械手的传动方案——液压传动进行设计,运用CAD绘制原理图。结合机械实体结构布置液压系统。
关键词:微型件 机械手 门架式
ABTRACT
This paper takes the project “The designing of a machinery manipulator for auto polishing of miniature parts” as the study background, designs a fixed manipulator which it has freedom 11.The manipulator has some functions, that it can turn in horizontal plane, swing in vertical plane and capture many miniature parts.
In the authors prior work, the manipulator of function is decomposed. Some of reasonable plans are designed. They are contrasted and the best plan is took. The focus of the paper is on three aspects:
At first, this paper designs the manipulator of machinery structure, use CAD and CATIA to finishes its Auto CAD and non-standard parts in mechanics. This part of the paper is consist of outward appearance and machinery construction, that they are improved and optimized.
The second, the paper designs a plan of manipulator’s transmission----hydraulic pressure transmission by parameters of design and practice of demand and finishes the schematic diagram in CAD. The system of hydraulic pressure is designed according the machinery structure.
At last, the paper finally puts forward the electric control strategy of the manipulator, and use the CAD and CATIA to finish the schematic diagram of electric control.
Keywords: Miniature parts Manipulator Polishing
目录
绪 论1
1机械手发展状况1
2课题背景及研究意义1
第一章 设计任务及方案评价3
1.1设计目标与功能原理分析3
1.2机械手的配置和工作原理3
1.3解决原理4
1.4方案的分析和决策5
第二章 结构评价设计7
2.1门架式专用工业机械手总体方案7
2.2机械手的部件设计8
2.2.1机械手的机架设计8
2.2.2小车的设计10
2.2.3机械手臂12
2.2.4夹持器设计13
第三章 部件计算与校核15
3.1横梁的计算15
3.2小车计算17
3.2.1 小车速度计算17
3.2.2 小车精度计算17
3.2.3 小车电机功率计算18
3.2.4 小车零件计算18
3.3手臂计算21
3.3.1 手臂汽缸计算21
3.3.2 手手腕处摆动减速电机计算21
3.4夹持器计算24
第四章 气动原理设计28
4.1驱动方式28
4.2工作原理28
4.2.1手臂升降汽缸28
4.2.2手臂回转汽缸29
4.2.3夹紧缸30
4.2.4气源处理30
第五章 机械手的控制设计32
5.1基本设计思路32
5.2单片机的选择32
5.3驱动芯片的选择34
5.4流程图36
5.5汇编程序37
总结40
参考文献41
致 谢42
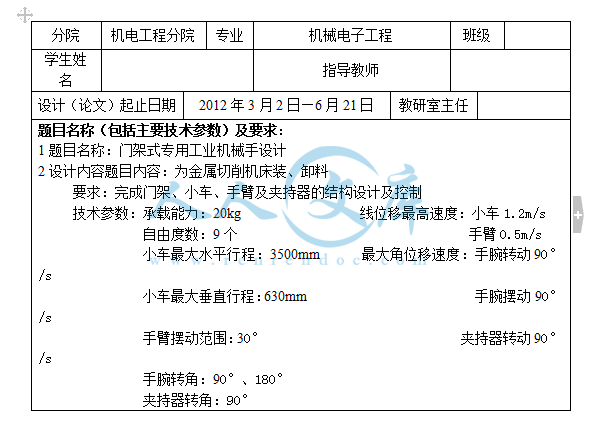
题目名称(包括主要技术参数)及要求:
1题目名称:门架式专用工业机械手设计
2设计内容题目内容:为金属切削机床装、卸料
要求:完成门架、小车、手臂及夹持器的结构设计及控制
技术参数:承载能力:20kg 线位移最高速度:小车1.2m/s
自由度数:9个 手臂0.5m/s
小车最大水平行程:3500mm 最大角位移速度:手腕转动90°/s
小车最大垂直行程:630mm 手腕摆动90°/s
手臂摆动范围:30° 夹持器转动90°/s
手腕转角:90°、180°
夹持器转角:90°
2课题背景及研究意义
机械手的发展已有近400年的历史了。现在全世界已有近100万台机械手在运行,机械手对国民经济和人民生活的各个方面,已产生重要的影响5 机械手技术已成为当今主导技术之一。随着工业机械化和自动化的发展,机械手已经广泛应用在生产自动化的各个行业。
工业机械手人又称通用自动机械手, 是一种“独立”的可变程序的自动机械手[2]。它是在五十年代末期出现, 近年来才迅速发展起来的重要自动化装置, 现已成为实现工业自动化的一种重要手段。抛光作业是一种非常艰苦的劳动。操作者总是处于噪音大,粉尘多的环境中。操作者总是技术熟练的老工人,也是必存在老龄化的问题。也给企业带来人手不足的问题。另外,随着技术快速发展,相关标准越来越高,零件越来越小,精度越来越高,手工艺不能满足其要求,此时
工业机械手开始发挥其潜能,并占有越来越重要的地位。
本课题设计的是机加自动线机械手,主要用于机床的上料卸料动作,例如在六角车床上。
手臂要求承载能力20KG,手臂数量2,自由度9,小车左右行程3500mm,手臂最大垂直行程630mm,手臂摆动范围30°。手腕转角90°。线位移最高速度:小车1.2m/s,手臂0.5m/s,最大角位移速度:手腕转动90°/S,手腕摆动90°/S,夹持器转动90°/S。驱动方式:机电,气压。
本课题研究不仅能大幅降低加工成本,还能显著提高微型件的表面质量。因此将机器人应用于微型件加工替代手工操作前景广阔,不仅能大幅度提高生产率,保证产品质量,而且还能解决熟练劳动力的短缺问题。第一章 设计任务及方案评价
1.1设计目标与功能原理分析
由于原理方案设计是机械手产品设计的第一步,是对产品成败、好坏起决定性的作用的工作,所以必须慎重。
可以从以下方面来考虑
能量方面、安全方面、人机工程方面、运动方面、创造方面、检查方面、作用方面、装配方面、运输方面、使用方面、材料方面、维修及回收方面、几何关系方面、费用方面、驱动方面、执行方面、设计期限方面
1.功能分析
(1) 明确功能目标
对所要求功能抽象化后,将系统功能合理的分成几组,以便设计需要。
(2) 功能组合
功能分解为功能组合提供了组合元素,功能组和的目的是形成多种形成以达到设计功能目标的集合化,即功能结构。显然功能结构形成的多样性与功能分解的合理与否有很大的联系[6]。
2.寻找解决方案原理
解决原理在机械设计及方法中又叫原理作用,所谓作用原理基本上就是把物理学中的物理效应体现在机械原理中的机构上,达到完成设计任务的目的。寻找作用原理目的,就是要找到一种物理效应,并将其与合理的机构最终形成解决问题的方案。
改变物理效应,改变几何特征都能获得实现某一功能的解决原理,大多数的设计中,参考已有资料,从物理效应着手寻找解决原理,利用表格和机械原理简图表达出来。
3.原理组合
根据功能结构把寻找到的作用原理。组合在一起,形成实现总功能的各种功能原理方案。
4.方案评价
在所中介的各个方案中,通过各方面要求进行评价,选择出最佳。
1.2机械手的配置和工作原理
门架机械手的配置,如图1-1所示。门架机械手设置在机床上方,机床主要为卧室机床,也可以为加工中心,取料和上料主要靠从机床上方空间完成动作[7]。机械手需要满足功能列举如下:
图1-1 机械手图示
1、在机床加工前后,需要门架机械手搬运毛坯和成品,输送线或者是料仓一半在机床旁,因此机械手需要有横向大范围的移动功能。能满足上料时毛坯库范围,下料后成品库范围。
2、每台机械手还需要具有升降功能,安装,取下产品都需要从机床上方经过,因此升降功能需要行程只要满足物料能够顺利通过。
3、在取料,上料过程中,为了提高节拍,需要马上取料后再装料,因此需要两只手同时操作。
4、安装,取料,根据不同工件毛坯的形态,需要机械手臂能够实现转动,摆动功能,以便于满足安装姿态的需要。
5、根据工件的尺寸大小,夹持需要满足多种尺寸的工件,因此范围夹持也是机械手的必须功能。
1.3解决原理
根据机械手各部分的工作原理及要求,列出原理模块图标如下表1-1
表1-1 机械手工作原理
功能ABC
1.机械臂平移齿轮齿条移动丝杆螺母驱动
2.机械臂升降气动丝杆螺母驱动齿轮齿条
3.手臂俯仰电机+齿轮气动液压
4.手臂回转电机气动液压
5.运动控制机电+气动机电+液压气动+液压
1.4方案的分析和决策
1 评价准则
评价准则是进行评价的依据。通常都使用多个评价准则,有的评价准则可用定量的参量表征,有的则不能。
评价准则来源于设计所要达到的目标,具体的说,就是从要求明细表里包含的各项要求和愿望中提取[8]。
2 衡量尺度
采用“价值”或“有效价值”作为方案评价的衡量尺度。
所谓价值,是基于实际的测量结果或估计结果相对评价准则进行比较得到的主观认识,具有很大的主观成分,故又可说这一工作是“主观步骤”。
3 评价方法
本文涉及采用排除法来解决方案选择问题,排除法是指针对多种方案,首先去掉不能满足功能的方案,再次去掉复杂繁冗方案最后所得的方案经过探讨而决定选用满足功能价格低廉的方案:
相比机电,气动,液压三种动力和控制方案,
液压驱动的特点有:
液压传动目前用得最多的一种传动方式,压力可在1~30Mpa,。液压驱动机械手多用于要求臂力较大而运动速度较低的工作场合。
1) 驱动力和驱动力矩较大,臂力可达100公斤;
参考文献
[1] 张建民.工业机器人[M].北京:北京理工大学,1988.47-261
[2] 波波夫.工业机械人的结构与应用 [M].北京:机械工业出版社,1997
[3] 机部情报所.国外工业机械手参考资料[M].重庆:科技文献出版社,1980
[4] 吴旭朝.工业机械手设计基础[M].天津:天津科技出版社,19877.0-92
[5] 高井宏幸(日).工业机械人的结构与应用[M].北京:北京工业机械出版社,19778.9-111
[6] 冈萨雷斯.机器人学[M].北京:中国科技出版社,1989
[7] 光列维奇?E?N.机器人和机械手控制系统[M].北京:北京新时代出版社,1985.2-3
[8] 陆祥生.机械手--理论与应用[M].北京:中国铁道出版社,1985.3-15
[9] 徐灏.机械手册第五卷[S].北京:机械工业出版社1992
[10] 蔡卫国.关节搬运机械手设计[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2009
[11] 龚青山.立式轴承压桩机上料机械手设计[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2010
[12] 杨永清.液压摆动机械手设计[M].上海:上海科技出版社,2008
[13] 樊明等. 封装及自动上料机械手 [M] 北京:机械工业出版社,2008
[14]侯沂等.装卸机械手设计研究。[M] 北京:机械工业出版社,2005
[15] Jacobsen S C ,Wood J.E.,Knutti D.F.et.a1 The UTAH/MIT dextrous hand; work in progress.The lnternationa1 Journa1 of Robotic Research[J], 1984.3(4):21-50
[16] Hyde J M ., Cutkosky M .R.Controlling contact transition.
IEEE Contro1 Systems[J],1994,14(1):25-30
[17] Ii Z.X.,Qin Z.,Jiang S.et a1.Coordinated motion generation
and real-time grasping force control for multi-fingered manipulation. Proceedings of the IEEE Internationa1 Conference on Robotics and Automation[M],1998,3631-3638.
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号