并联机床实验台总体结构设计
23页 15000字数+说明书+答辩稿+开题报告+外文翻译+8张CAD图纸【详情如下】
solidworks三维图.rar
三爪自定心卡盘.dwg
三维图.doc
主轴电机控制电路图.dwg
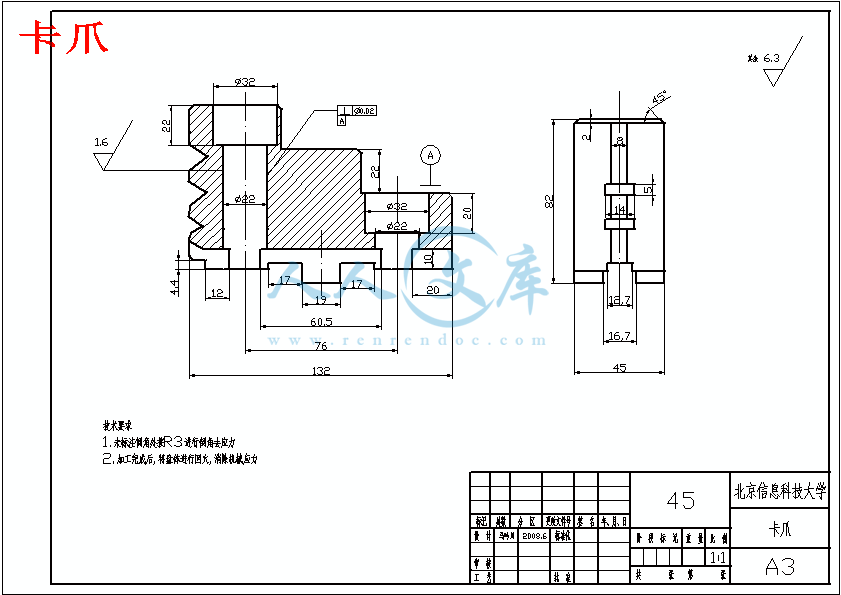
卡爪.dwg
卡爪底座.dwg
外文翻译--设计并联机床使用kinetostatic标准的表现.doc
并联机床实验台总体结构设计开题报告.doc
并联机床实验台总体结构设计答辩稿.ppt
并联机床实验台总体结构设计论文.doc
并联机床实验台总装图.dwg
摘要目录.doc
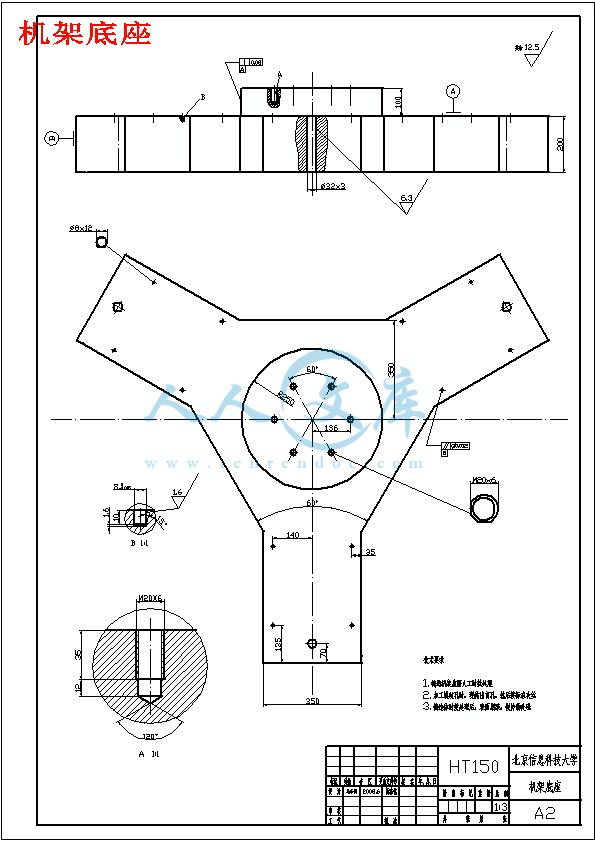
机架底座.dwg
机架装配图.dwg
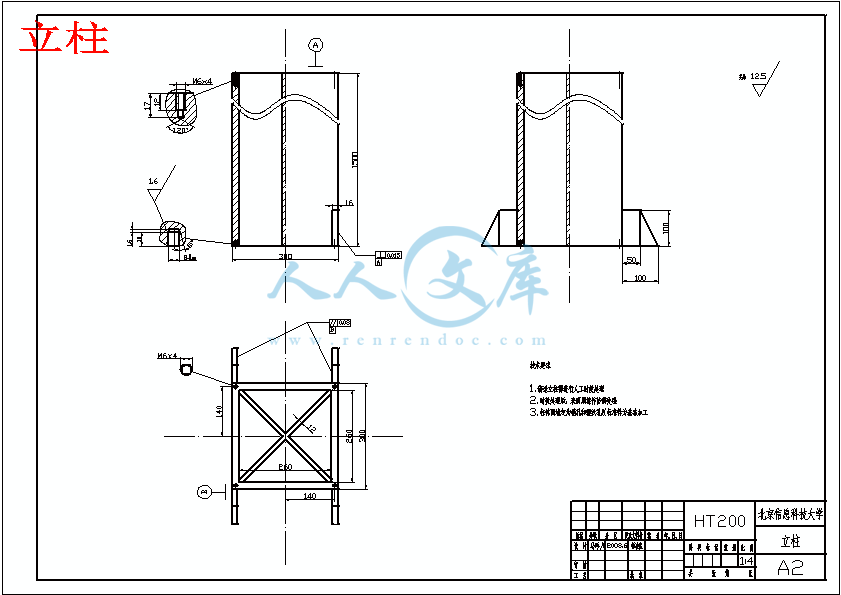
立柱.dwg







摘要
随着信息技术的进步和全球化制造技术的进步,企业为了提高自身的竞争力,要求配置效率更高成本更低的加工设备,而传统机床在未来的加工业中会遇到难以克服的困难,例如在高速加工中(轨迹速度达到50m/min)和高效空间曲面加工及机床的通用性方面将无法满足现代加工技术的要求。因此探索和研究一种现代化机床具有十分重要的意义。
虚拟轴机床与传统的串联式数控机床相比具有很多优越性。传统数控机床各自由度是串联相接的,呈悬臂结构,且层叠嵌套致使传动链长,传动系统复杂,累计误差大,而精度低,成本昂贵,至今多数机床只是4轴联动,极少5轴。而虚拟轴机床的并联式加工中心结构特别简单,传动链极短,刚度大、质量轻、切削效率高、响应快,特别是很容易实现六轴联动,因而,能加工更复杂的三维曲面,且其加工精度和加工粗糙度都直接由控制程序来保证,因此,硬件成本低,而软件附加值高,是一种技术附加值极高的机电一体化产品。
此研究课题针对现今的机加工趋向,制定了设计一部并联机床实验台的任务,作者与合作人共同设计。其中的并联部分分配给了合作者,作者主要负责并联机床实验台的总体框架结构设计。
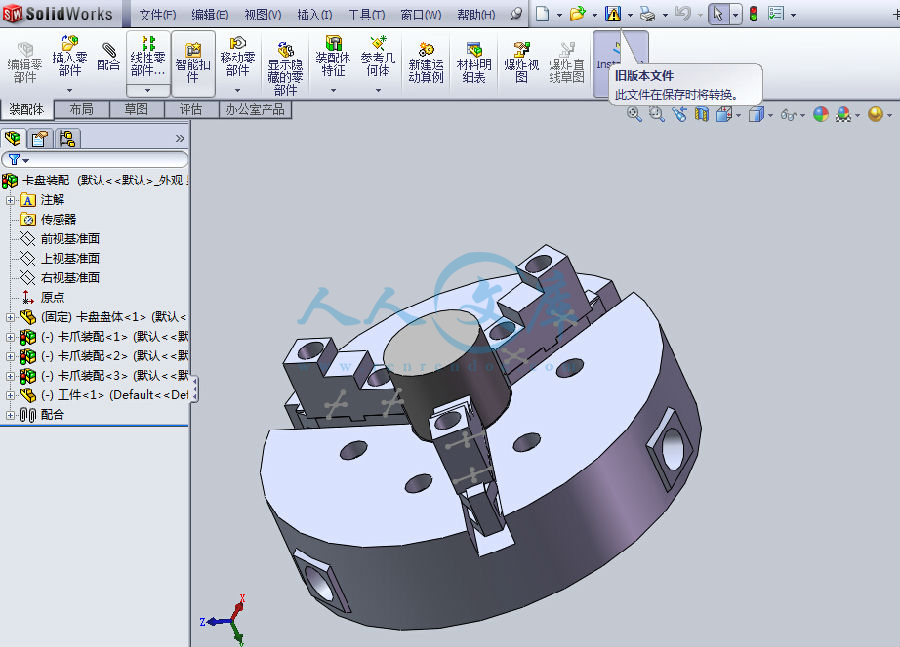
平台大致由并联机构——三根并联丝杠(驱动电机)、铸铁机架、装卡平台和电主轴以及弹簧铣夹头组成。
关键词:并联机构、虚轴加工、雅可比矩阵、正解算法
Abstract
With the progress of the information technology and the development of the global manufacturing techniques, enterprises require more efficient and lower cost machines by reason of enhancing their competitive ability. But conventional machine tools will encounter many difficulties which are hard to overcome in the future, for instance of high-speed machining ( path speed exceeding 50m/min)and high efficient space curved surfacing machining as well as flexibility of machines. Thus, it is very important to explore and study kind of modern machines.
Be compared to the normal numerical control machine tool, it has larger rigidity, stronger carrying capacity, smaller error, higher precision, smaller ratio of self-weight and load, better dynamical capacity, less investment of hardware, but stronger function of software. All of these show its high additional technical valve.
This research topic for the current trend of the processing machine, developed a design of a parallel machine test-bed task, which the Author co-design and a partner. Some of them parallel to the allocation of the partner, the author mainly responsible for the PMT test-bed framework of the overall structural design.
Platform from roughly parallel bodies - three parallel screw (motor driven), cast iron rack, with card platform and Spindle and milling chucks of spring.
Key words: parallel instruction, virtual axis processing, Jacobian Matrix, positive solution algorithm
目录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1课题背景与意义 1
1.2 并联机床发展历史及现状 2
1.3本文主要研究内容 5
第2章 重要零部件选型 6
2.1依照主轴功率确定电主轴型号 6
2.2 选择主轴下部刀具夹头 7
2.3选择工件的装卡方式 8
第3章 实验台支承部分及其连接的方案 11
3.1机架的设计方案 11
3.2铸造机架的材料及热处理 14
3.3机架的截面形状、壁厚及周边筋的布置 14
3.4立柱与底座的连接方式 16
3.5底座的造型 16
第4章 实验台驱动电路 17
4.1 电路布线方案 17
4.2 电路控制要求 17
4.3电路控制连线原理图 17
第5章 实验结果及三维建模 18
5.1 设计并联实验台结果 18
5.2 实验台solidworks建模 18
第6章总结与展望 19
参考文献 20
致 谢 20
并联机床的研究方向:
(1)并联机床组成原理的研究
研究并联机床自由度计算、运动副类型、支铰类型以及运动学分析、建模与仿真等问题。
(2)并联机床运动空间的研究
包括运动空间分析及仿真、可达工作空间求解(如数值求解法、球坐标搜索法等)、机床干涉计算及位置分析等。
(3)并联机床结构设计的研究
并联机床的结构设计包括很多内容,如机床的总体布局、安全机构设计、数控系统设计(包括数控平台建造、数控系统编程、数控加工过程仿真等)。
(4)并联机床刚度、精度、柔度、灵巧度的研究
并联机构封闭回路的特性,使并联机床较传统串联结构机床具有更高的刚度,但这个特性引起的耦合问题,相对的形成在动力分析上很大的困扰,因此对其研究应予以足够的重视。关于并联机床精度的研究仍是国际难题,包括机床系统硬件研究(及机床制造前精度设计和精度描述)和系统输出精度研究(及机床制造后输出数据处理和精度评价)。并联机床柔度的研究包括柔度分析、柔度评价指标及其在工作空间内的分布等方面。灵巧度主要研究灵巧度指标及其分布等。
(5)并联机床误差研究
包括误差分析、建模及误差精度保证、测量系统设计等问题。
(6)并联机床模块设计与创建
根据工件加工的空间型和平面型,相应地把并联机床分为空间型并联机床和平面型并联机床两大类。并联机床按功能和结构可分为以下几个功能模块:①执行模块;②机座模块(静平台模块);③动平台模块;④机架模块;⑤定位模块;⑥驱动模块;⑦控制和显示模块;⑧润滑与冷却模块。
(7)新型虚拟轴数控机床的研究
虚拟轴数控机床是“要用数学制造的机床”。因为这种机床的设计与运行要用到非常复杂的数学计算与推理。目前对于Stewart平台的理论研究已取得一些关键结论,还需进一步研究Stewart平台的综合分析,为虚拟轴数控机床的研制提供理论基础。
(8)并联机床控制的研究
包括高速、高精度的控制算法,刀具运动轨迹的直接控制、开放式数控系统等。虚拟轴机床的最大特点是机械结构简单而控制复杂,因此这方面的研究在并联机床的研究中具有举足轻重的作用。1.3 本文主要研究内容
给定主轴功率1kw,加工范围半径为350的半球体,主轴倾角±25°
以上述参数,自行设计并联机床总体零部件及装配方案。
涉及到电主轴、刀具夹头、装卡夹具、立柱、底座、电源走向、安装定位等的选用及其设计。
动力学问题
刚体动力学逆问题是并联机床动力分析、整机动态设计和控制器参数整定的理论基础。这类问题可归结为已知动平台的运动规律,求解铰内力和驱动力。相应的建模方法可采用几乎所有可以利用的力学原理,如牛顿-尤拉法、拉格朗日方程、虚功原理、凯恩方程等。由于极易由雅可比和海赛矩阵建立操作空间与关节空间速度和加速度的映射关系,并据此构造各运动构件的广义速度和广义惯性力,因此有理由认为,虚功(率)原理是首选的建模方法
动态性能是影响并联机床加工效率和加工精度的重要指标。并联机器人的动力性能评价完全可以沿用串联机器人的相应成果,即可用动态条件数、动态最小奇异值和动态可操作性椭球半轴长几何均值作为指标。与机器人不同,金属切削机床动态特性的优劣主要是基于对结构抗振性和切削稳定性的考虑。动态设计目标一般可归结为,提高整机单位重量的静刚度;通过质量和刚度合理匹配使得低阶主导模态的振动能量均衡;以及有效地降低刀具与工件间相对动柔度的最大负实部,以期改善抵抗切削颤振的能力。由此可见,机器人与机床二者间动态性能评价指标是存在一定差异的。事实上,前者没有计及对结构支撑子系统动态特性的影响,以及对工作性能的特殊要求;而后者未考虑运动部件惯性及刚度随位形变化的时变性和非线性。因此,深入探讨并联机床这类机构与结构耦合的、具有非定长和非线性特征的复杂机械系统动力学建模和整机动态设计方法,将是一项极富挑战性的工作。这项工作对于指导控制器参数整定,改善系统的动态品质也是极为重要的。第6章 总结与展望
此次课题《并联机床实验台》,在设计过程中,作者与合伙人遇到了许多的困难。相比较,并联机床机械结构简单,但并联机构的活动范围计算复杂,需要考虑的问题不计其数。在课题中难免有我们考虑不到的地方,望各位老师予以谅解。
传统机床的发展已有数百年的历史,而并联机床的出现才不过几年的时间,期望短期内一下子就能解决并联机床在理论和实践上的一系列难题是不现实的;同样,在并联机床发展过程中暂时碰到一些难题就认为并联机床没有前途、难以最终走向市场同样是不可取的。
并联机床的优点有许多,能够完成表面形状极其复杂的零件,加工形式类似于数控加工中心,而且具有高刚度、高精度等诸多优点。相比于普通铣床,加工性能大大提高。是机具发展前途的新型金属切削机床。
参考文献
1.黄真, 《空间机构学》, 北京:机械工业出版社, 1991
2. 熊有纶, 《机器人学》, 北京:机械工业出版设, 1989
3. 邵俊鹏, 《机床数控技术》, 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 1990
4. 濮良贵, 《机械设计》, 高等教育出版社, 1989
5. 徐灏, 《机械设计手册》, 北京:机械工业出版社, 1991
6. 刘兴良, 《机器人和机械手控制系统》,北京:机械工业出版社,1984
7. 孔令富等, 《模型参数自摄影控制设计的一种方法》,信息与控制,1991,NO.4:29-32
8. 蒋松新, 《机器人及机器人学中的控制问题》 机器人, 1990,12(5):1-6
9. 梁崇高等, 《一种Stewart平台型机械手位移正解》,机械工程学报,1991,27 (2):26-30
10.胡汗才, 《单片机原理及其接口技术》,北京:清华大学出版社,1996
11.文福安,李静宜等,《并联机器人位置正解》, 机械科学与技术, NO.3,1993
12.黄真,孔令富,方跃法,《并联机器人机构学理论及控制》,北京:机械工业出版社,1997,2-4
13.陈文家,王宏光等,《并联机床的发展现状与展望》, 机电工程, 2001,18(4):5-8
14.Soumya Bhattacharys On the Optimum Design of Stewart Platform Type Parallel
Manipulators [J] Robotica.1995,13:133-1
15.Waldron K J., Raghavan M. and Roth B. Kinematics of a Hybrid serial-Parallel
Manipulation System. ASME J. of Dyn. Sys. Meas. And Cont.,1989,111,211-221
16. Sklar M. and Teasar D. Dynamic Analysis of Hybrid Serial Manipulator System
Containing Parallel Modules. J. Mech. Trans. and Aut. Des., 1988,109-11
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号