【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
[全部文件] 那张截图中的文件为本资料所有内容,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
摘 要
分析内平动齿轮传动的原理,提出由3 根偏心轴作平动发生器的实用新型齿轮传动机构一分流型内平动齿轮传动,并推导其传动比的计算公式.主要零件部件的计算设计.装置的装配设计和主要零件的设计。
分析内平动齿轮传动的原理,提出由3根偏心轴作平动发生器的实用新型齿轮传动机构一分流型内平动齿轮传动,并推导其传动比的计算公式.分析发现,为平衡机构的惯性力,采用2(或3)片平动齿轮时,设计啮合点相位差应取180° (120°);输入齿轮的齿数为3的倍数时,分流齿轮具有互换性;采用两片平动齿轮且内外齿轮齿数差为偶数时,平动齿轮具有互换性;采用3片平动齿轮且内齿轮齿数为3的倍数时,平动齿轮具有互换性.给出了啮合参数的编程计算方法.该新型传动具有承载能力强、传动比大(17—300)、体积小、质量轻、输入输出同轴线、加工安装简单等优点,是一种节能型的机械传动装置,也是减速器的换代产品.有广泛的应用前景。
关键词 :内平动齿轮传动;少齿差齿轮副;传动比
Abstract
Analysis of parallel move gear transmission principle, put forward by the three eccentric shafts for utility model translation generator gear mechanism within the translation of a shunt-type gear, and derive the formula for calculating the transmission ratio. The main components of the calculation of design components . Device design and assembly of major parts of the design.
Analysis of parallel move gear transmission principle, put forward by the three eccentric shafts for utility model translation generator gear mechanism within the translation of a shunt-type gear, and derive the formula for calculating the transmission ratio. Analysis, to balance the inertia force, using 2 (or 3) pieces of translation gear, the meshing point of the design phase should take 180 ° (120 °); input gear teeth as a multiple of 3, the shunt gear with interchangeability; with two translation gear and the internal and external gear tooth number difference is even, Ping gear has interchange ability; with three flat gear and internal gear teeth as a multiple of 3, the flat gear has interchangeability. Meshing parameters given programming account Calculation method. The new drive has a carrying capacity, transmission ratio (17-300), small size, light weight, input and output coaxial line, and simple installation process is an energy-efficient mechanical transmission device, is also a new generation product reducer . Have broad application prospects.
Keywords: Internal translation gear transmission;differential gears with small teeth; transmission ratio
目录
摘 要I
AbstractII
目录III
1 绪论1
1.1 平动减速器的发展概况1
1.2 市场需求分析1
1.3 本课题研究目的及意义以及国内外现状分析及展望1
1.4 课题的主要内容及要求1
2 传动方案及拟定3
2.1 平动啮合的定义和分类3
2.2 内平动齿轮传动工作原理3
2.4 分流式内平动齿轮传动机构4
2.5 传动比分析5
3 各主要部件选择及选择电动机7
3.1 各部件的选择7
3.2 电动机的选择7
4 减速器的整体设计8
4.1传动比的分配8
4.2传动的运动及动力参数计算8
4.3齿轮的设计计算8
4.3.1 分流齿轮的设计计算8
4.3.2 平动齿轮的设计计算12
4.4轴的设计计算15
4.4.1 输入轴的设计计算15
4.4.2 曲轴的设计计算19
4.4.3 输出轴的设计计算24
5 润滑与密封28
5.1润滑方式的选择28
5.2密封方式的选择28
5.3润滑油的选择28
6 箱体结构尺寸29
6.1箱体的结构尺寸29
7 设计总结30
致 谢32
参 考 文 献33
1 绪论
1.1 平动减速器的发展概况
随着科技技术的进步和发展,现代工业设备特别需要功率大 体积小 传动比范围大 效率高 承载能力强和使用寿命长的传动装置。因此,除了不断改进材料品质 提高工艺水平外,还要在传动原理和传动结构上深入探讨和创新,内平动齿轮传动原理的出现就是一例。它由北京理工大学张春林教授等人最先提出,并设计出了内平动齿轮减速器试验样机。该减速器属于节能型传动装置,除具有三环减速器的优点外还有着大的功率与重量比值 输入轴和输出轴在同一轴线上 既可以减速还可以增速以及震动小等优点,处于国内领先地位。
最先提出平动齿轮这一概念的是德国人,他们提出了摆线针轮行星齿轮传动原理。由于工艺和精度的限制,这种机构并没有快速发展起来,直到摆线磨床的出现。近些年国外在平动齿轮传动领域进行了一些新的研究,如日本住友重工研制的FA型高精度减速器和美国Alan-Newton公司研制的X Y减速器,就利用了平动齿轮传动的运动机理。
对平动齿轮传动研究,我国处于相对领先的地位。目前,平动齿轮的理论研究 机构设计和实验研究都取得了一些成果。例如:北京理工大学张春林教授 黄祖德教授等首次根据该传动的特点将其命名为平动齿轮传动机构。并通过对平动齿轮传动机构的运行机理进行分析研究,阐述了该机构的组成及机构变异方法,探讨了平动齿轮机构传动比和机械效率的计算方法,导出了计算公式,得出了平动齿轮机构效率与齿轮齿条传动机构 效率相当的结论。此后又根据机构的组合原理 演绎原理和同性异性变异原理对内平动齿轮机构的基本型进行演化变异,设计出一种传动比大,机械效率高 尺寸和重量小 结构紧凑 均载性好的新型平动此轮机构,并对平动齿轮传动机构连续运动条件及重合度方面进行了深入研究。
1.2 市场需求分析
用于冶金、矿山、机械、机器人、航海、轻工、航空、军工、纺织、化工、建筑等部门,亦可与各类电机直接联接,作成伺服电机。
1.3 本课题研究目的及意义以及国内外现状分析及展望
内平动齿轮减速器是一种新型的机械传动装置,它传动比大,机械效率高,结构简单,体积小,重量轻,能方便地与电机配套使用,避免了减速器体积比电机体积大的现象。该减速器是一种节能型的机械传动装置,具有国际先进水平。传动比可达到几千;机械效率大于90%;运转平衡性好,承载能力大,使用寿命长,体积小,重量轻,约为相似产品的1/3左右。
1.4 课题的主要内容及要求
主要研究内容:提出由3根偏心轴作平动发生器的实用新型齿轮传动机构一分流型内平动齿轮传动,并推导其传动比的计算公式。分析发现,为平衡机构的惯性力,采用2(或3)片平动齿轮时,设计啮合点相位差应取180。(120。);输入齿轮的齿数为3的倍数时,分流齿轮具有互换性;采用两片平动齿轮且内外齿轮齿数差为偶数时,平动齿轮具有互换性;采用3片平动齿轮且内齿轮齿数为3的倍数时,平动齿轮具有互换性。给出了啮合参数的编程计算方法。该新型传动具有承载能力强、传动比大(17—300)、体积小、质量轻、输入输出同轴线、加工安装简单等优点,有广泛的应用前景。

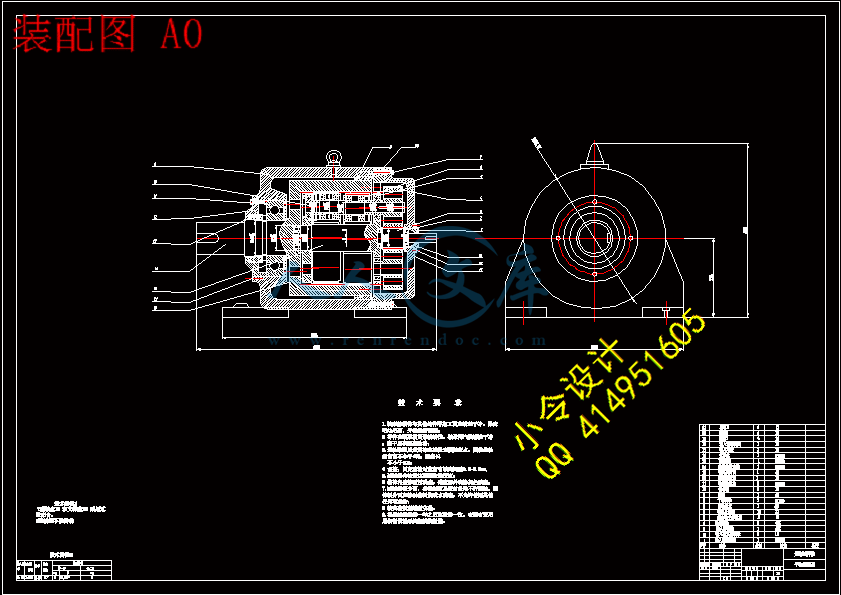
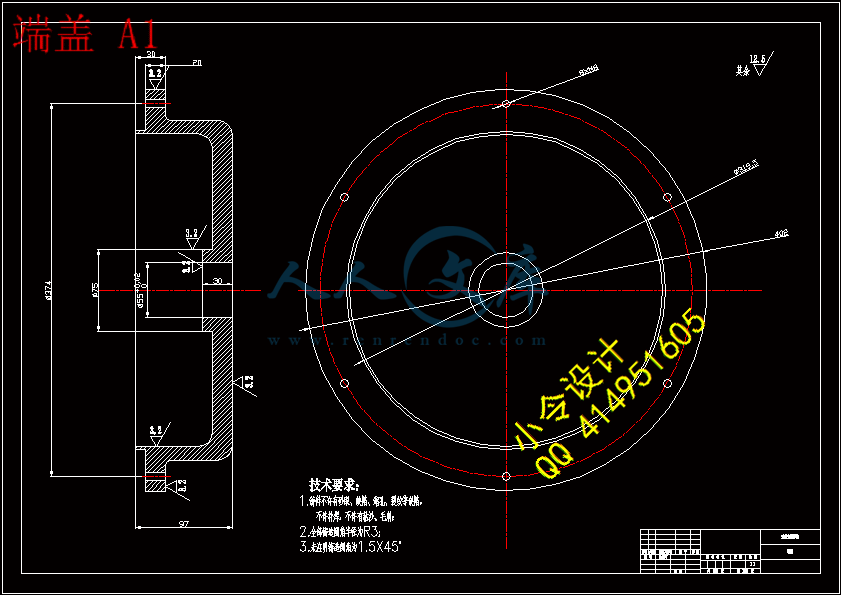
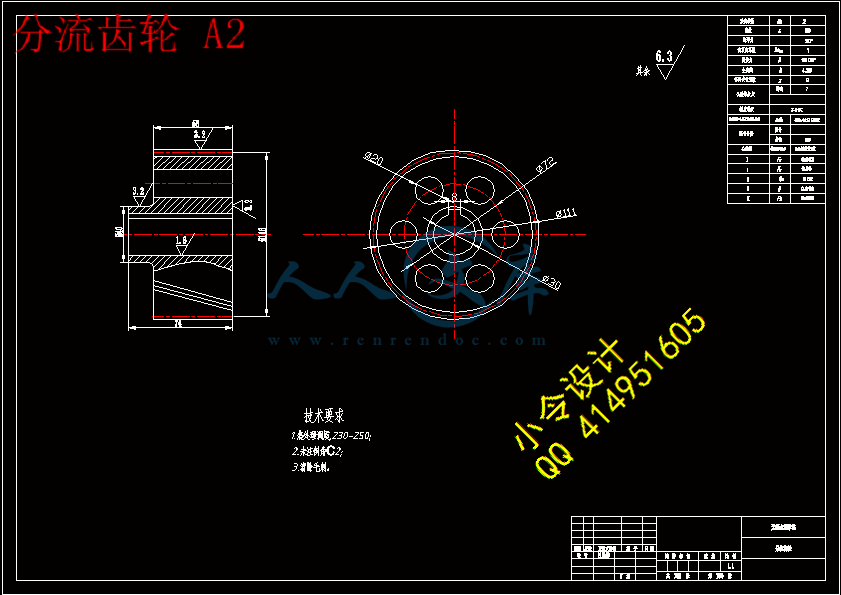


 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号