摘 要
本设计为中型四柱式液压机,主机最大工作负载设计为2000KN。主机主要由上梁、导柱、工作台、移动横梁、主缸、顶出缸等组成。本文重点介绍了液压系统的设计。通过具体的参数计算及工况分析,制定总体的控制方案。经方案对比之后,拟定液压控制系统原理图。液压系统选用插装阀集成控制系统,插装阀集成控制系统具有密封性好,通流能力大,压力损失小等特点。为解决主缸快进时供油不足的问题,主机顶部设置补油油箱进行补油。主缸的速度换接与安全行程限制通过行程开关来控制;为了保证工件的成型质量,液压系统中设置保压回路,通过保压使工件稳定成型;为了防止产生液压冲击,系统中设有泄压回路,确保设备安全稳定的工作。此外,本文对液压站进行了总体布局设计,对重要液压元件进行了结构、外形、工艺设计,对主机、电气控制系统进行了简要设计。
通过液压系统压力损失和温升的验算,本文液压系统的设计可以满足液压机顺序循环的动作要求,能够实现塑性材料的锻压、冲压、冷挤、校直、弯曲等成型加工工艺。
关键词:液压系统;液压机;毕业设计
ABSTRACT
This paper design for the medium frame of hydraulic machines, the mainframe’s largest work load design for 2000KN. Mainframe mainly by the beam、guided、worktable、mobile beams、master cylinder、cylinder head out of components etc. This paper focuses on the hydraulic system design. Through specific parameters and hydraulic mechanic situation analyzes, formulation of a master control program. By contrast, developed hydraulic control system diagram.Hydraulic systems use cartridge valve integrated control system, integrated cartridge valve control system has good sealing, flow capacity, small pressure loss characteristics etc. To solve the master cylinder express entered the shortage of oil supply in the top of the mainframe installed oil tank. Master cylinder for the speed of access restrictions and security through the trip exchanging to control switches.To ensure the quality of the work-piece molding, in the hydraulic system installed packing loop through packing work-piece stability molding; To prevent hydraulic shocks, pressure relief system with a loop to ensure that this equipment can be a safe and stable work. In addition, the paper hydraulic station on the overall layout of the key components of the hydraulic structure、shape、technique for a specific design.
By the loss of hydraulic system pressure and temperature checked. Hydraulic system is designed to meet the hydraulic action sequence and cycle requirements can be achieved by forging plastic materials, stamping, cold extrusion, straightening, bending, and other molding processes.
Keywords: Hydraulic System ;Hydraulic Pressure machine;Graduation design
目 录
第1章 绪论1
1.1 液压机现状概要1
1.2 本文拟达到的要求2
第2章 四柱液压机总体方案设计3
2.1 四柱液压机主要设计参数3
2.2 四柱液压机工作原理分析3
2.2.1 四柱液压机的基本组成3
2.2.2 四柱液压机的工作原理4
2.3 四柱液压机工艺方案设计6
2.4 四柱液压机总体布局方案设计6
2.5 四柱液压机零部件设计7
2.5.1 主机载荷分析7
2.5.2 主机工作台设计10
2.5.3 控制台设计10
第3章 四柱液压机液压系统设计10
3.1 液压传动的优越性概述11
3.2 液压系统设计要求11
3.2.1 液压机负载确定11
3.2.2 液压机主缸工艺过程分析12
3.2.3 液压系统设计参数12
3.3 液压系统设计12
3.3.1 液压机主缸工况分析12
3.3.2 液压机顶出缸工况分析15
3.3.3 液压系统原理图拟定16
3.3.4 液压系统基本参数计算21
3.4 液压系统零部件设计28
3.4.1 液压机主缸设计28
3.4.2 液压机顶出缸设计32
3.4.3 液压油管设计33
3.4.4 液压油箱设计35
3.5 液压站布局设计36
3.5.1 液压站设计需要考虑的问题36
3.5.2 液压站的结构设计36
3.6 液压系统安全、稳定性验算37
3.6.1 液压系统压力损失验算37
3.6.2 液压系统温升验算41
第4章 四柱液压机电气系统设计42
4.1 电气控制概述42
4.2 四柱液压机电气控制方案42
4.2.1 四柱液压机电气控制方式选择42
4.2.2 电气控制要求与总体控制方案42
4.3 四柱液压电气控制电路设计43
4.3.1 四柱液压机主电路设计43
4.3.2 四柱液压机控制电路设计43
4.3.3 电气控制过程分析45
第5章 四柱液压机安装调试和维护46
5.1 四柱液压机的安装47
5.2 四柱液压机的调试47
5.3 四柱液压机的保养维护47
结论48
参考文献49
致谢51
附录152
附录253
第1章 绪 论
1.1液压机现状概要
液压传动技术发展到今天已经有了较为完善、成熟的理论和实践基础。液压传动技术与传统的机械传动相比,操作方便简单,调速范围广,很容易实现直线运动并且还具有自动过载保护功能。液压传动容易实现自动化操作,采用电液联合控制后,可以实现更高程度的自动控制以及远程遥控。由于液压传动的工作介质是流体矿物油,有较大的沿程和局部阻力损失。当系统的工作压力比较高时,还会产生比较大的泄漏,泄漏的矿物油将直接对环境造成污染,有时候还容易引起安全事故。油液受温度的影响很大,因此液压油不能在很高或很低的温度条件下工作。由于液压油的可压缩性和泄漏,液压传动不能保证恒定的传动比和很高的传动精度,这是液压传动的最大不足之处。此外,液压传动的故障排除不如机械传动、电气传动那样容易,因而对使用和维护人员有较高的技术水平要求。虽然液压传动存在这些缺陷,但总体上优点还是盖过了缺点,因而应用还是很广泛。
液压机自19世纪问世以来得到了很快的发展,在工业生产中已经有了广泛的应用,成了产品压力加工成型不可或缺的机械设备。随着科学技术的日新月异,电子技术、液压技术的不断成熟,液压机也得到了更进一步的发展。到目前为止,液压机的最大公称压力已经达到了750MN,控制技术也由原来传统的继电器控制变为可编程控制器和工业计算机控制,这使液压机的运行平稳性、控制精度、产品质量有了保证,同时生产效率得到了很大的提高。
液压机加工与传统机械加工相比属于无屑加工,应用范围广泛,一般用于塑性材料的冷挤、校直、弯曲、冲裁、拉伸等。此外液压机还用于粉末冶金、翻边、压装等产品的成型加工工艺。液压机还能实现复杂工件和不对称工件的加工,产品废品率较低。液压机根据加工工件的不同性质,还可进行适当的压力行程调整,满足产品的加工要求。液压机主要由主机、液压系统、电气系统三部分组成。液压机的整个工作过程的实现,首先是由电气系统来控制液压系统,然后再由液压系统控制主机主缸和顶出缸的顺序动作。总的来说,液压机操作简单,维护方便。
虽然液压机目前应用十分广泛,但是潜在的问题还很多。液压机属于高压工作设备,进行压力加工时,随着压力的不断升高泄漏也会不断增大,这样不利于保证零件的加工精度,同时还会对环境造成污染。除此之外,液压机还存在如下缺陷,液压机压力加工完成后,卸压时存在很大的液压冲击,这样对液压元件及其它设备损害很大;按下启动按钮后,动作灵敏性不及电气控制;液压机出现故障不能够正常工作,故障不容易及时找到并排除,给维护带来了一定的技术难题和不便;液压机工作时产生的液压冲击、气蚀等现象,会缩短液压元件的使用寿命。
为了催生更大的生产力,液压机的设计需要改进。液压油路设计、控制系统的优化设计将是液压机今后值得研究的方向。
(1)油路设计方面
为了防止泄油和外界的污染,液压机油路的设计趋于集成化、封闭循环式,这样可以延长设备的使用寿命。除此之外,液压元件设计尽量标准化,集成化。集成液压系统减少了管路连接,可以降低泄漏和污染。液压元件的标准化给维护带来了方便。
(2)控制系统方面
液压机属于高压设备,控制系统除控制设备安全可靠的工作之外,还应该让控制精度变得更高,人机交互变得更简单,操作更方便,自动化、高速化、智能化程度更好。
综上所述,液压机的发展促进了生产力的发展。伴随着电气控制技术、液压传动技术的不断发展,液压机的自动化程度、加工精度将进一步得到提高,实现智能化控制。
1.2本文拟达到的要求
(1)液压机总体方案设计,其中包括主机的结构设计和工艺设计、零部件的结构设计和工艺设计、部件装配方案设计;
(2)通过液压系统总体设计方案的对比,确定合理的液压系统设计方案。主要包括液压系统原理图设计、液压元件结构、工艺设计、液压站总体布局设计;
(3)电气控制系统设计,包括主电路和控制电路电路图设计;
(4)设计方案确定时,必须考虑选用什么样的制造材料,达到什么样的表面加工质量,采用什么样的机械加工设备,选择什么样的热处理方式等;
(5)整个设备满足拆装方便,运输方便的要求;
(6)四柱液压机能够准确完成如下工作循环:主缸活塞滑块快速下行、主缸活塞滑块慢速加压、主缸保压、主缸卸压、主缸活塞滑块回程、顶出缸顶出、顶出缸退回等;
(7)设备达到总体布局合理,结构紧凑、工作稳定可靠、操作简单、维护方便、环境污染小、工作的时候噪音低、自动化程度高等,能够完成冲压、冷挤、校直、弯曲、粉末冶金压制成型、薄板拉伸、压装成型等加工工艺。
第2章 四柱液压机总体设计
2.1四柱液压机主要设计参数
(1)拟设计的四柱液压机主要技术参数见表2.1
表2.1 液压机技术参数
参 数 项参 数
公称力(最大负载)2000KN
工进时液体最大工作压力25MPa
主缸回程力400KN
顶出缸顶出力350KN
主缸滑块行程700mm
顶出活塞行程250mm
主缸滑块距工作台最大距离1100mm
主缸滑块快进速度0.08m/s
主缸滑块工进最大速度0.006m/s
主缸快退速度0.03m/s
顶出活塞顶出速度0.02m/s
顶出活塞退回速度0.05m/s
(2)四柱液压机的主要功能
通过液压传动系统传递动力,完成零件的压力成型加工。
(3)四柱液压机的适用范围
液压机主要用于冷挤、校直、弯曲、冲裁、拉伸、粉末冶金、翻边、压装等成型工艺。
2.2 四柱液压机工作原理分析
2.2.1 四柱液压机的基本组成
四柱液压机主要由主机、液压控制系统、电气控制系统三部分组成。 其中主机包括工作台、导柱、滑块、上缸、顶出缸等结构;液压系统由控制元件、执行元件、辅助元件、动力装置、工作介质等组成;电气控制控制系统主要由继电器、接触器、按钮、行程开关、电器控制柜等组成。
2.2.2 四柱液压机的工作原理
(1)四柱液压机主机组成简图2.1
1-滑块 2-导柱 3-工作台 4-安装地基
5-顶出缸 6-主缸 7-上横梁 8-辅助油箱
图2.1 四柱液压机主机组成简图
(2)四柱液压机工作原理分析
四柱液压机的动作顺序通过电气系统、液压系统控制,控制顺序框图如图2.2。
图2.2 四柱液压机控制顺序图
从上面的控制顺序框图可以看出,液压机的工作原理由电气控制系统控制液压系统,液压控制系统再控制主机工作,主机动作触及行程开关,将信号反馈给电气控制系统,实现循环控制。
(3)四柱液压机工作循环分析
四柱液压机工作循环如图2.3所示。
图2.3 四柱液压机工作循环图
四柱液压机工作循环如图2.3(a),滑块在自重的作用下快速下行,碰到行程开关后由快进变为工进,随后进行加压、保压。保压时间完成后,滑块快速回程,直到回到原来的位置,停止运动;图2.3(b)表示顶出缸的工作循环过程,主缸快进、工进、保压、退回停止后,顶出缸才运动,将工件顶出。

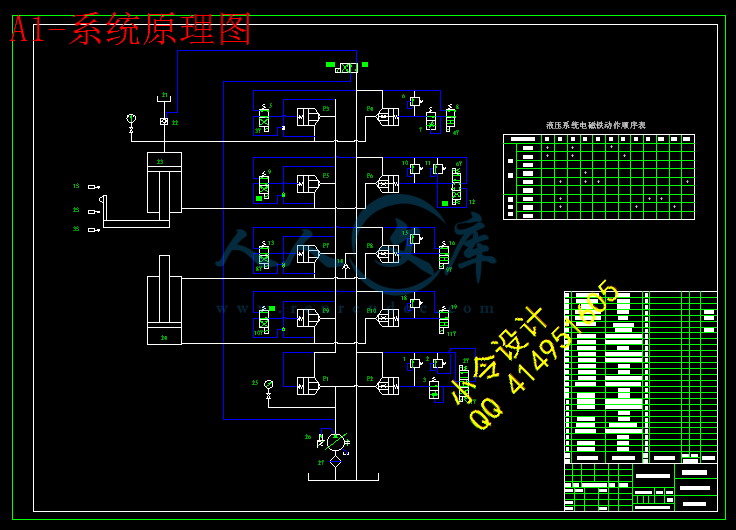

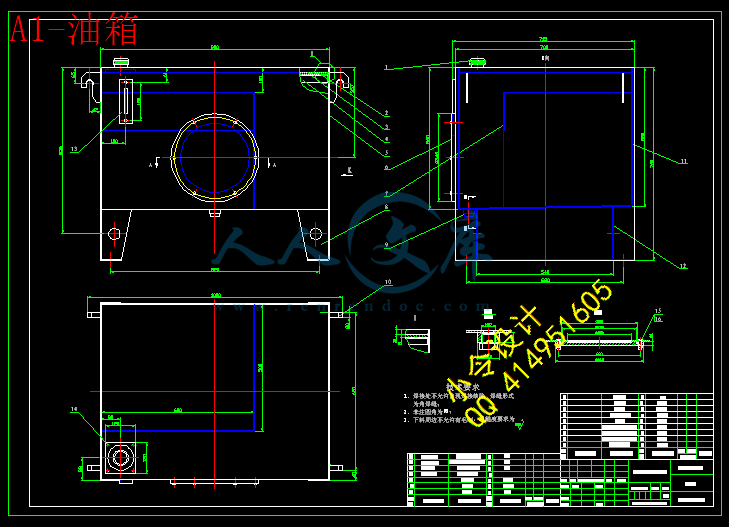

 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号