双离合器式自动变速器的七挡齿轮变速器设计【优秀含16张CAD图纸+汽车车辆工程毕业设计】
【带开题报告+外文翻译】【84页@正文25800字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609 】
图纸总汇16张.dwg
开题报告.doc
设计说明书.doc
说明书封皮.doc
开题报告
题目名称双离合器式自动变速器的七挡齿轮变速器设计
一、课题研究现状、选题目的和意义
1、研究现状:
我国是以平行轴式变速器生产为主的国家,生产双离合器自动变速器可以充分利用原有手动变速器的生产设备,只需增加少量的生产设备即可,生产继承性好,可以大大的减小成本,因此发展和研究双离合器自动变速器将是实现汽车自主创新的一个重要方向。虽然国外已经批量生产双离合器式自动变速器并应用到了多款轿车上,但国内的研究与国外相比正处于起步阶段。
1940年,Darmstadt大学教授Rudolph Franke第一个申请了双离合变速器专利,并在货车上进行了装车试验,但始终没能投入批量生产。随后保时捷也发明了专用于赛车的双离合变速器。到了20世纪90年代,国内外各大汽车厂商都投入了较大力量对DCT进行研究和开发,并开发出了多种型式的DCT产品。较为突出的是德国大众公司和美国博格华纳(BorgWarner)集团合作开发的第一款能适用于大批量生产的双离合变速器—直接换挡变速器(Direct Shift Gearbox简称DSG)。大众公司已将DSG应用于Audi TT、第五代高尔夫等多种主流车型上。在大众汽车DSG一马当先的带领下,其他国家厂商纷纷投入人力物力加入”双离合器变速器”的队伍。与大众不同的是,其他厂商更专注于提高双离合器变速器所承受的最大扭矩,将双离合器变速器装备到跑车上。
宝马M部门在第3代SMG(Sequential Manual Gearbox)顺序式手动变速器的基础上开发出了最新的专门为最高转速可达9000r/min的V8发动机而设计的M-DCT(Dual Clutch Transmission)7挡双离合器变速器。M-DCT双离合器变速器已经率先装备在宝马最新一代M3轿跑车和敞篷跑车上。 保时捷一直是使用手动变速器和Tiptronic手/自动一体变速器的。目前,保时捷将自己“雪藏”多年的PDK双离合器变速器应用于民用跑车领域。保时捷PDK双离合器变速器的结构和运行原理与大众汽车公司DSG双离合器变速器相同。 除了宝马和保时捷,日产研发出配合GT-R跑车的双离合器变速器,三菱汽车研发出用于EVO跑车的双离合器变速器。不久的未来,以大众DGS为领头羊的双离合器变速器将成为变速箱技术的主流,各种级别的轿车都将会广泛应用双离合器变速器。在渝举行的“中国工程科技论坛——2010中国汽车自主创新”上获悉,上汽正加速研发我国自主创新、拥有国际领先技术的湿式双离合器自动变速箱,并表示该项产品将于不久正式面世。同时,2011年2月比亚迪称其将推出自主研发的双离合器式自动变速器。
正是这样的两个离合器配合换挡的结构,在挡位切换时齿轮早已衔接,DSG双离合自动变速器实现了,平顺换挡、快速换挡、动力“无间断”地输出,节约燃油的设计目的。据大众官方数据,目前普及型的双离合变速器换挡时间只有0.2秒左右。即使是全球最好的赛手换挡速度也不可能与双离合变速器相比。双离合变速器换挡时间也远超出人类操作的极限。
双离合器变速器是脱胎于半自动变速器技术的一项衍生技术,目前大众已经在高尔夫汽车上成功使用了的DSG-7双离合器自动变速器,其技术核心是从机械传动的手动变速器发展而来,内部构造却与传统手动变速器相似。因此它继承了手动变速器工作可靠和便于维护的技术优势。同时,双离合器变速器在使用方面与普通自动变速器并无太大差别,方便省力。
总之,双离合器自动变速器既继承了传统手动变速箱传动效率高、结构紧凑、重量轻、价格便宜等许多优点,又实现了液力机械自动变速器和金属带式无级自动变速器动力换挡,换挡品质好的优点,使车辆具有很好的动力性和燃油经济性,具有优异的性能和广阔的应用前景。
2、选题目的和意义:
为了解决中断动力换挡给车辆性能带来的影响,需要对电控机械式自动变速器的换挡过程进行精确的控制。特别是为了减少换挡过程中的冲击度,需要对发动机与变速器构成的动力总成在转速差、转矩等方面进行精确匹配和控制,但是这些仅在一定程度上改善其换挡性能,并不能从根本上解决问题。如果要进一步提高电控机械式自动变速器的性能,则需要增加发动机起、停等一些其它控制手段,反而增加了车辆的复杂程度和成本,得不偿失。所以,电控机械式自动变速器在对车辆舒适性等方面要求不高的车型上,例如低挡轿车、军用车辆、公共汽车、载重车等,由于其具有结构简单、成本低等优点,仍具有优势,但是在对舒适性要求高的车型上,其应用就具有了局限性。为了既可以充分利用AMT所具有的优点,又可以消除AMT中断动力换挡的缺点,双离合器式自动变速器(DCT)应运而生,它基于平行轴式手动变速器发展而来,其转矩传递能力适用于各种排量的车辆,同时继承了手动变速器传动效率高、结构简单、安装空间紧凑、重量轻等优点。这种自动变速器的出现已经成为了许多汽车厂家所关注的热点。本课题在国内外研究的基础上,旨在通过对双离合器自动变速器的结构、工作原理进行研究,对本课题的研究能够使我了解双离合器自动变速器的设计方法和原则,通过本课题的研究我可以完成专业课程的实践总结,获得一定的工程设计工作方法,以后的设计研究工作提供一定的参考。
二、设计(论文)的基本内容、拟解决的主要问题
1.设计的基本内容:
依据现有生产企业在生产车型的变速器作为设计原型,在给定发动机输出转矩、转速及最高车速、等条件下,设计出符合要求的变速器。
(1)了解双离合器式自动变速器结构及工作原理、设计步骤与设计方法。
(2)对所设计的双离合器式七挡自动变速器进行总体方案论证。
(3)双离合器式自动变速器中各部件的主要参数进行选择与设计计算。
(4)同步器主要参数的确定。
2.拟解决的主要问题:
(1)各档位传动比计算及齿轮齿数分配
(2)各档位齿轮的设计和校核
(3)各轴的设计和校核
(4)确定同步器结构及主要参数
三、技术路线(研究方法)
四、进度安排
(1)调研、资料收集,完成开题报告 第1、2周
(2)研究双离合器式自动变速器的七挡齿轮变速器的结构原理、设计步骤与设计方法 第3周
(3)双离合器式自动变速器的七挡齿轮变速器主要参数的选择与设计计算 第4~9周
(4)完成所设计装配图与零件图图纸 第10~12周
(5)完成设计说明书的撰写,指导教师审核 第13周
(6)毕业设计(论文)修改、完善 第14周
(7)毕业设计(论文)审核、预审 第15周
(8)毕业设计(论文)修改、完善 第15、16周
(9)毕业设计(论文)答辩准备及答辩 第17周
五、参考文献
[1] 唐德江.双离合器式自动变速器的研究.[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2005.
[2] 吴光强,杨伟斌,秦大同.双离合器式自动变速器控制系统的关键技术[J].机械工程学报., 2007,43(2).
[3] 陈然,孙冬野,刘永刚,. 双离合器式自动变速器建模与控制系统仿真[J]. 重庆大学学报,2010,(9).
[4] 董小洪. 双离合器自动变速器干式双离合器设计与分析[D].2010.
[5] Xubin Song, Jason Liu, Daniel Smedley. Simulation Study of Dual Clutch Transmission for Medium Duty Truck Applications[J].SAE,2005(01):3590-3593.
[6] 赵志强.湿式双离合器自动变速器建模及仿真分析[D].长沙:湖南大学,2009.
[7] 赵玉省.双离合器自动变速系统的综合控制[D].重庆:重庆大学,2009[18].
[8] Andreas Hegerath,Bergheim(DE).Dual Clutch For A Transmission With Two Input Shafts.US,Patent No.:6929107B2,2005[20].
[9] 康海涛.双离合器式自动变速器的研究.[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2004.
[10] 刘振军,秦大同,叶明.等.车辆双离合器自动变速传动技术研究进展分析[J].农业机械学报,2005.36(11):161~164.
[11] 杨伟斌,秦大同.双离合器式自动变速器控制系统的关键技术[J].机械工程学报,2007,43(2):13~21.
[12] AUDI A G.Audi TT 3.2 quattro with shift gear-box(DSG)[J] Audi Word, 2003(2:20-4).
[13 [13] 陈家瑞.汽车构造[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2000:10-97.
[14] 王望予.汽车设计(第4版)[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2010:78-113.
[15] 刘维信.汽车设计[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2001:158-207.
[16] 余志生.汽车理论(第三版)[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2000:1-88.
摘 要
双离合器自动变速器由电控机械式自动变速器发展而来,它综合了液力机械自动变速器(AT)和电控机械自动变速器(AMT)的优点,能够实现动力换挡、减少了换档时间、提高了换档品质、极大地提高了汽车的舒适性和操纵性。
本设计以双离合器式自动变速器的结构和工作原理为基础,针对干式双离合器自动变速器的设计方法,分析了各种不同变速器的布置方案并选定了本变速器的最终布置方案。对变速器中的主要零件包括齿轮形式、换挡结构形式作了阐述并进行了选择并对变速器的传动比的范围、中心距做初步的选择和设计。对变速器中的齿轮的模数、压力角、螺旋角、进行了选择并计算出齿轮其他的相关参数和对齿轮的校核。对轴的结构尺寸进行设计和轴承的选用并对其进行了校核。
关键词:双离合器;自动变速器;传动比;齿轮;轴
ABSTRACT
DCT duo to Mechanical Transmission.Itinherits the advantages of Automatic Transmission(AT) and Automated Mechanical Transmission (AMT).It has the ability of power shifing that can reduce shift time andimprove shift quality.And the comfort and maneuverability of vehicle will be greatly improved.
In this thesis,the study of dry type Dual Clutch Transmission is based on the Structural characteristics and working principle of DCT. For dry-type dual-clutch automatic transmission design, analyzed the layout of the various transmission options and selected the final layout of the transmission scheme. The major part of gear, including gear form, elaborated shift structure and make the choice and range of transmission gear ratio, center distance a preliminary selection and design. The gear on the transmission module, pressure angle, helix angle, were calculated gear selection and other relevant parameters and checking on the gear. Structural dimensions of the shaft and bearing design and its selection was checked.
Key words: Dual Clutch Transmission;Automatic transmission;Transmission Ratio;Gear ;Axis
目 录
摘要I
AbstractII
第1章 绪论1
1.1 课题研究的目的和意义1
1.2 课题的研究现状3
1.3 课题的研究内容及技术路线4
第2章 双离合器自动变速器传动方案的确定6
2.2 DCT结构的分析6
2.2 DCT双离合器形式的分析9
2.2.1 干式双离合器性能分析9
2.2.2 湿式双离合器性能分析10
2.3 DCT基本结构方案的确定11
2.4 本章小结11
第3章 双离合器自动变速器的设计与计算12
3.1 变速器主要参数的选择12
3.1.1 传动比范围12
3.1.2 变速器各档传动比的确定12
3.1.3 中心距的选择15
3.1.4 变速器的外形尺寸15
3.1.5 齿轮参数的选择15
3.1.6 各档齿轮齿数的分配及传动比的计算17
3.1.7 变速器齿轮的变位21
3.2 变速器齿轮强度校核26
3.2.1 齿轮材料的选择原则26
3.2.2 变速器齿轮弯曲强度校核27
3.2.3 轮齿接触应力校核32
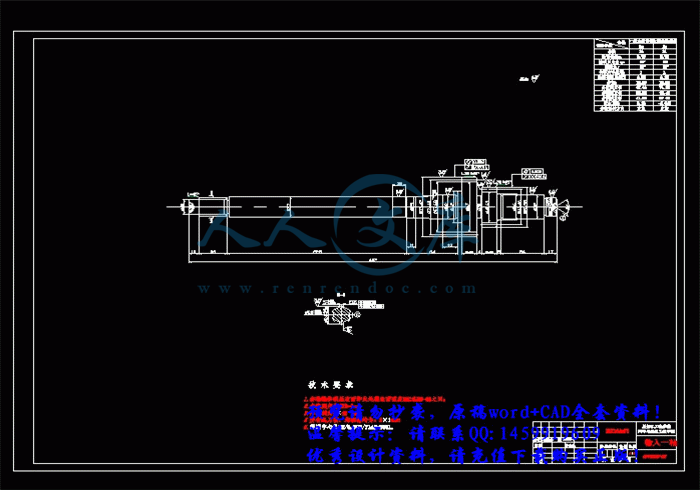
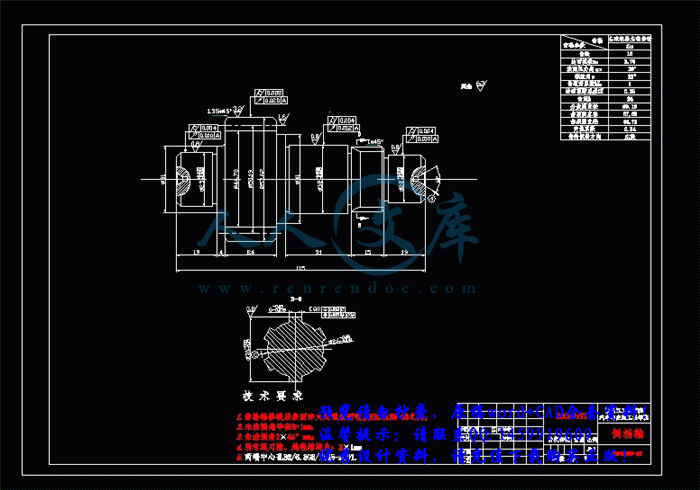
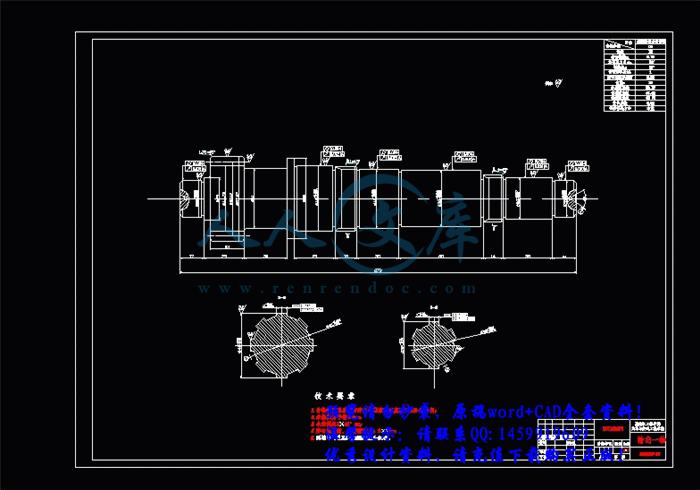
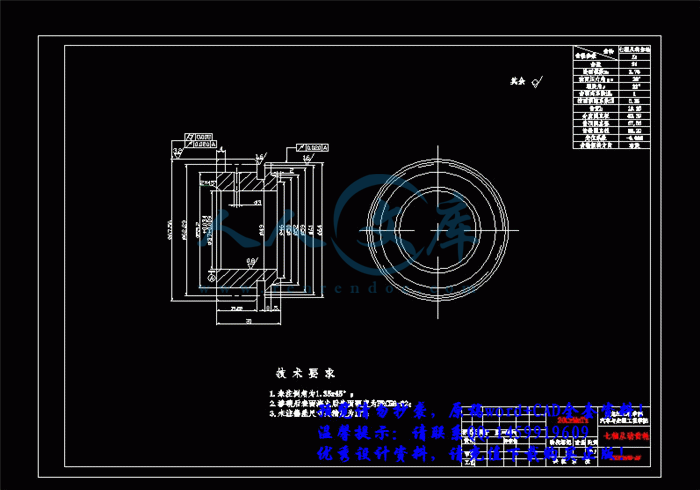
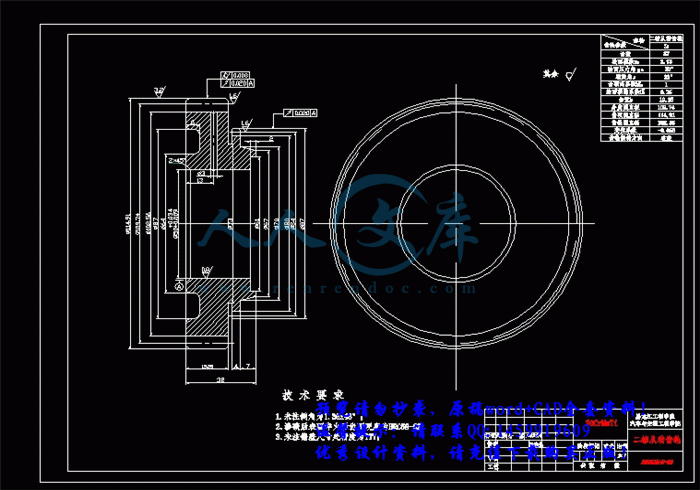
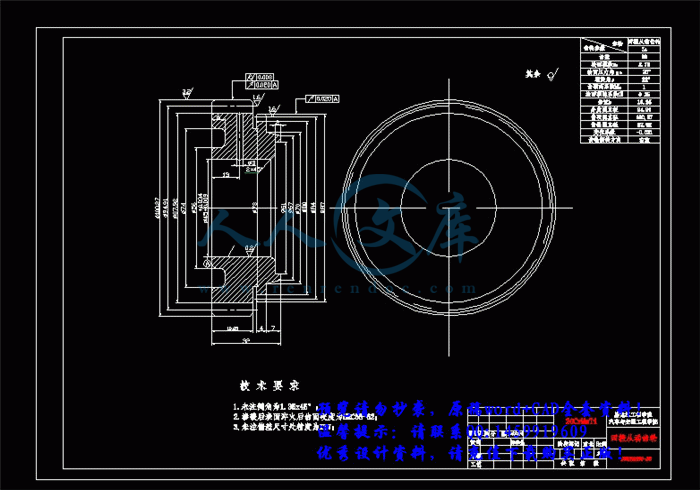
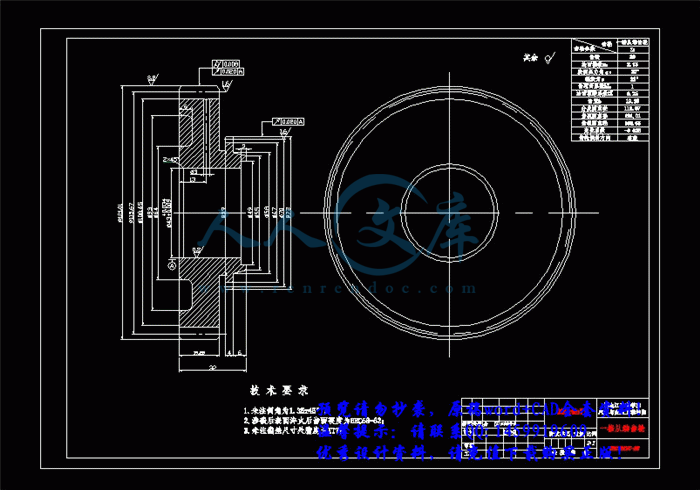
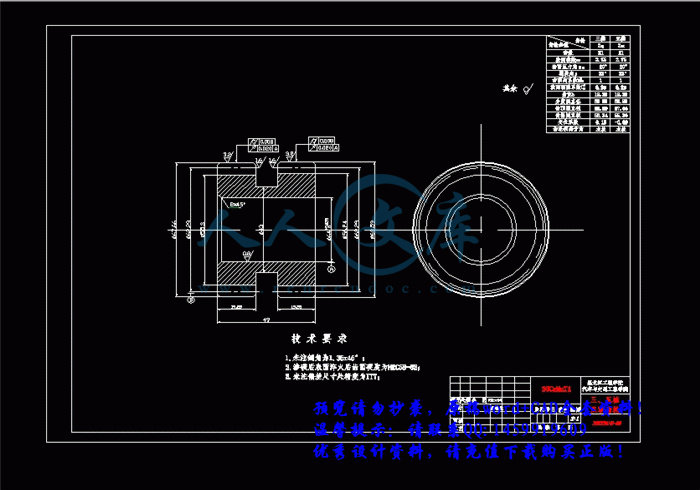
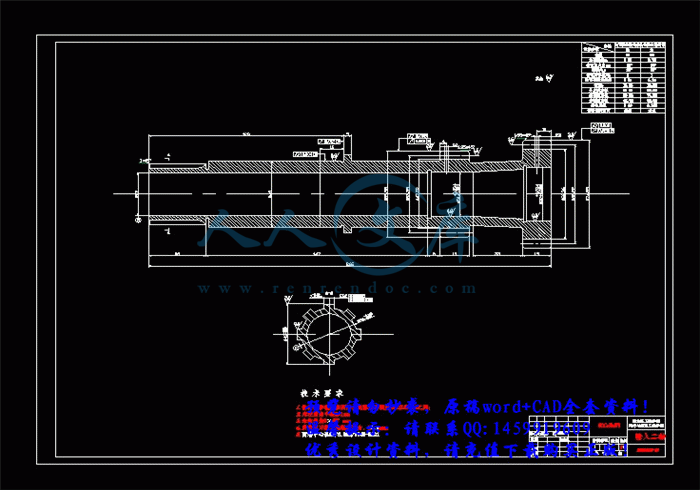
3.3 轴的结构和尺寸设计34
3.3.1 初选轴的直径35
3.4 轴的强度验算36
3.4.1 轴的刚度计算36
3.4.2 轴的强度计算56
3.5 轴承选择与寿命计算63
3.5.1 输出一轴轴承的选择与寿命计算63
3.5.2 输出二轴轴承的选择与寿命计算68
3.6 本章小结71
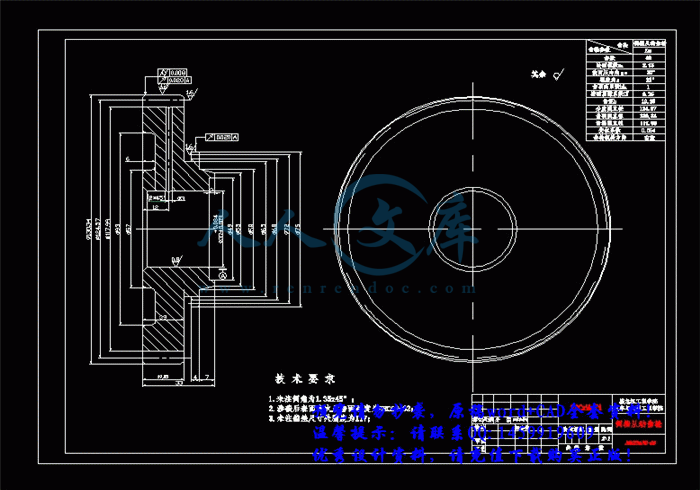
第4章 变速器同步器及结构元件设计72
4.1 同步器设计72
4.1.1 同步器的功用及分类72
4.1.2 锁环式同步器72
4.1.3 锁环式同步器主要尺寸的确定73
4.1.4 主要参数的确定74
4.2 变速器壳体76
4.3 本章小结76
结论77
参考文献78
致谢80
附录81
附录A 外文文献原文81
附录B 外文文献翻译92
第1章 绪 论
汽车自动变速技术是人们长期以来一直努力追求的目标,是车辆改进和完善传动系统的重要方向。自动变速技术始于1960年左右,到现在车辆的自动变速技术已取得了长足的进步。装备自动变速器的汽车,具有操纵方便、起步平稳、乘坐舒适性好、燃油经济性高、安全可靠等一系列优点,使得市场上对装备自动变速器的汽车的需求日渐高涨。汽车自动变速器的研究和应用有着更加重要的现实意义,各主要工业国家均在这方面投入了大量人力和财力,研制出种类繁多的各类自动变速器。自动变速器技术越来越完善,在越来越多的车辆上得到应用,成为现代汽车与现代工业发展的标志之一。随着我国的经济发展,家庭汽车的普及程度越来越高,且对乘用车的乘坐舒适性、燃油经济性和排放性能有了更高的要求。因此研究和开发既有高质量、操纵方便又有经济实用等特点的车辆具有广阔发展前景,来满足日益增长的广大消费者的需求。要实现这些功能,满足这些要求,就必须开发和研制出传动系中既能够高效传递发动机动力,又具有操纵方便的自动变速器[1]。
1.1 课题研究的目的和意义
由于汽车传动方式和控制方式的不同,汽车自动变速系统存在多种不同的类型。根据传动方式的不同,可以分为以下五类:液力传动、液压传动、机械传动、储能传动、电传动。汽车上应用较多的自动变速器主要有液力机械自动变速器(Automatic Transmission,AT)、无级变速器(Continuously Variable Transmission,CVT)和电控机械自动变速器(Automated Manual Transmission,AMT)以及最近发展的双离合器自动变速器(Dual Clutch Transmission,DCT)等四种。







 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号