摘要
本次设计主要讲述收音机中框零件塑件进行模具设计的毕业设计。论文综述了国内模具设计的研究进展及研究现状、分析课题的研究背景、阐述课题研究的意义和内容。
首先分析塑件工艺结构,了解塑件的技术要求,测量塑件尺寸,绘制塑件图,选用ABS材料,设计出一套一模一腔的塑料模具。同时,详细叙述了设计过程如何分析塑件制品的结构、性能,确定成型方案,成型部分的设计,导向机构、浇注系统、顶出机构、排气、冷却系统等,接着分析了如何选择模具钢种、模具标准件。
本套模具设计结合了机械制图,CAD,公差配合,模具设计,机械制造技术模具工艺学,UG等专业课程的知识,讲述了塑料模具结构设计的步骤,详细介绍了一套塑料模具设计的全部过程。
关键词:型腔;型芯;模具设计
Design of injection mold frame radio parts
Abstract
This instruction booklet main narration the radio frame models the graduation project which carries on the mold to design.The paper summarizes the analysis of the status quo, and research progress of study on the hydraulic technology at home and abroad and the significance of research background, describes the research topics.
First analyzes models the craft structure, understood models the specification, the survey models a size, the plan models a chart, selects the ABS material, designs set of the one plastic mold with one mold holes. At the same time, how in detail narrated the design process to analyze models a product the structure, the performance, determined took shape the plan, took shape the partial designs, the guidance organization, pours the system, goes against the organization, the exhaust, the cooling system and so on, how then analyzed has chosen the mold aluminum, the mold standard.
This set molding tool design combined the machine graphics, CAD, the business trip match, molding tool design, machine manufacturing the technique molding tool craft learn, the UG waits professional lesson, relating the plastics molding tool structure a design of step, detailedintroduced a set of plastics molding tool to design of all processes.
Key Words: Cavity core;mold;design
目 录
1绪论1
1.1模具介绍1
1.2模具在加工工业中的地位1
1.3模具的发展趋势1
1.4设计在学习模具专业中的作用2
2该塑件材料分析和工艺性分析3
2.1材料分析3
2.2工艺分析3
3拟定的成型工艺4
3.1塑件的成型方法4
3.2塑件的成型参数4
3.3确定型腔数目4
3.3.1计算制品的体积和重量4
3.3.2确定型腔数目4
4浇注系统的设计6
4.1塑件在模具中的位置6
4.1.1型腔的布置6
4.1.2分型面的选择6
4.2确定浇口形式及位置7
4.3主流道的设计8
4.4分流道设计8
4.5冷料穴设计9
5成型零部件的设计10
5.1成型零部件的结构设计10
5.2成型零部件工作尺寸计算11
5.3成型零部件的强度与刚度计算12
6结构零部件的设计14
6.1选用注射机及模架14
6.1.1初选注射机14
6.2.2选标准模架15
6.2定模板与动模板的设计16
6.3合模导向机构的设计16
7推出机构的设计18
7.1推件力的计算18
7.2确定顶出方式及推杆位置18
8侧向分型与抽芯机构设计20
8.1外侧抽芯机构设计20
8.1.1计算斜导柱倾斜角21
8.1.2计算斜导柱直径D21
8.2.3计算斜导柱长度21
8.2内侧抽芯机构设计21
8.2.1计算斜导柱倾斜角21
8.2.2计算斜导柱直径22
8.3.3计算斜导柱长度22
9温度调节系统设计23
10排气系统设计24
10.1排气不良的危害性24
10.2排气方法24
10.3排气槽结构24
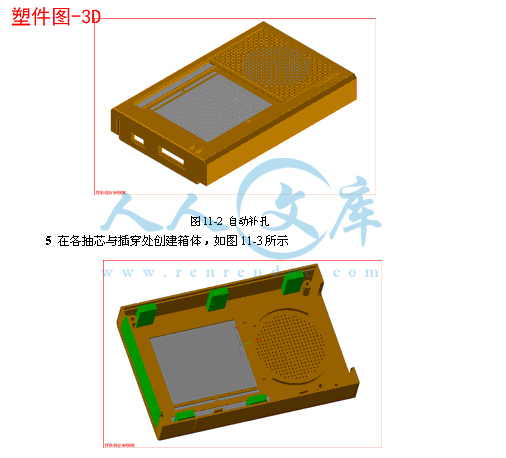
11产品及模具的三维造型25
12注塑机参数校核29
12.1最大注射量、锁模力、注射压力、模具厚度的校核29
12.2开模行程的校核29
12.3模具与注射机安装相关部分尺寸校核29
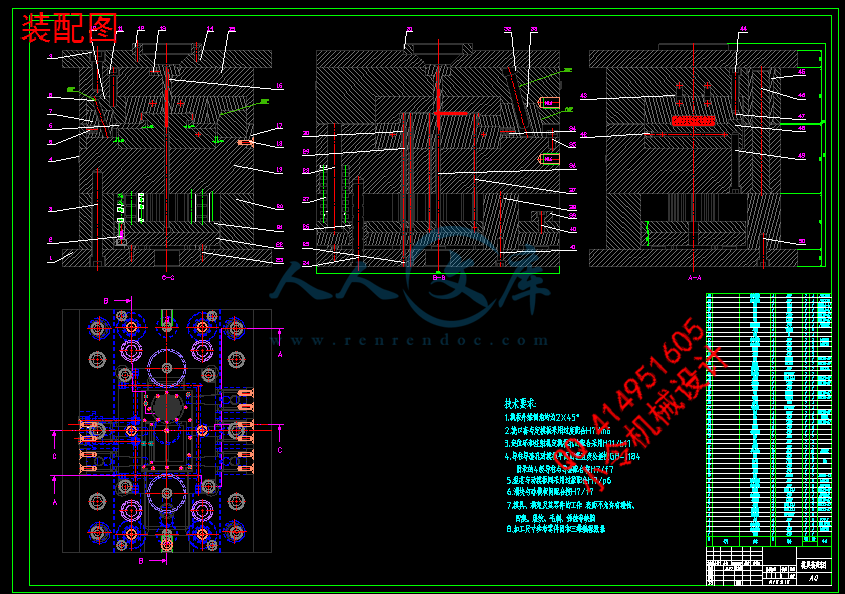
13绘制图纸并编写技术文件30
13.1绘制各非标准零件图纸30
13.2编写加工工艺和装配技术31
13.2.2装配要求32
13.2.3综合要求32
设计总结34
致谢35
参考文献36
毕业设计(论文)知识产权声明37
毕业设计(论文)独创性声明38
1 绪论
1.1模具介绍
模具的作用是控制和限制材料(固态或液态)的流动,使之形成所需要的形体。用模具制造零件以其效率高,产品质量好,材料消耗低,生产成本低而广泛应用于制造业中。模具主要类型有:冲模、锻摸、塑料模、压铸模、粉末冶金模、玻璃模、橡胶模、陶瓷模等。除部分冲模以外的上述各种模具都属于腔型模,因为它们一般都是依靠三维的模具型腔是材料成型。其中塑料模约占模具总数的35%,分额最大而且有继续上升的趋势。塑料模主要包括压塑模,挤塑模,注射模,此外还有挤出成型模,泡沫塑料的发泡成型模,低发泡注射成型模,吹塑模等。
1.2模具在加工工业中的地位
模具是工业生产中的重要工艺装备,模具工业是国民经济各部门发展的重要基础之一,是国际上公认的关键工业。模具生产技术水平的高低是衡量一个国家产品制造水平高低的重要标志。它在很大程度上决定着产品的质量,效益和新产品的开发能力。模具工业既是高新技术产业的一个组成部分,又是高新技术产业化的重要领域。模具在机械,电子,轻工,汽车,纺织,航空,航天等工业领域里,日益成为使用最广泛的主要工艺装备,它承担了这些工业领域中60%~90%的产品的零件,组件和部件的生产加工。振兴和发展我国的模具工业,正日益受到人们的关注。
1.3模具的发展趋势
20世纪80年代开始,发达工业国家的模具工业已从机床工业中分离出来,并发展成为独立的工业部门,其产值已超过机床工业的产值。改革开放以来,我国的模具工业发展也十分迅速。近年来,每年都以15%的增长速度快速发展。许多模具企业十分重视技术发展。加大了用于技术进步的投入力度,将技术进步作为企业发展的重要动力。此外,许多科研机构和大专院校也开展了模具技术的研究与开发。模具行业的快速发展是使我国成为世界超级制造大国的重要原因。今后,我国要发展成为世界制造强国,仍将依赖于模具工业的快速发展,成为模具制造强国。
尽管我国模具工业有了长足的进步,部分模具已达到国际先进水平,但无论
是数量还是质量仍满足不了国内市场的需要,每年仍需进口10多亿美元的各类大型,精密,复杂模具。与发达国家的模具工业相比,在模具技术上仍有不小的差距。今后,我国模具行业应在以下几方面进行不断的技术创新,以缩小与国际先进水平的距离。
(1) 注重开发大型,精密,复杂模具;随着我国轿车,家电等工业的快速发展,成型零件的大型化和精密化要求越来越高,模具也将日趋大型化和精密化。
(2) 加强模具标准件的应用;使用模具标准件不但能缩短模具制造周期,降低模具制造成本而且能提高模具的制造质量。因此,模具标准件的应用必将日渐广泛。
(3) 推广CAD/CAM/CAE技术;模具CAD/CAM/CAE技术是模具技术发展的一个重要里程碑。实践证明,模具CAD/CAM/CAE技术是模具设计制造的发展方向,可显著地提高模具设计制造水平。
(4) 重视快速模具制造技术,缩短模具制造周期;随着先进制造技术的不断出现,模具的制造水平也在不断地提高,基于快速成形的快速制模技术,高速铣削加工技术,以及自动研磨抛光技术将在模具制造中获得更为广泛的应用。

 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号