摘要
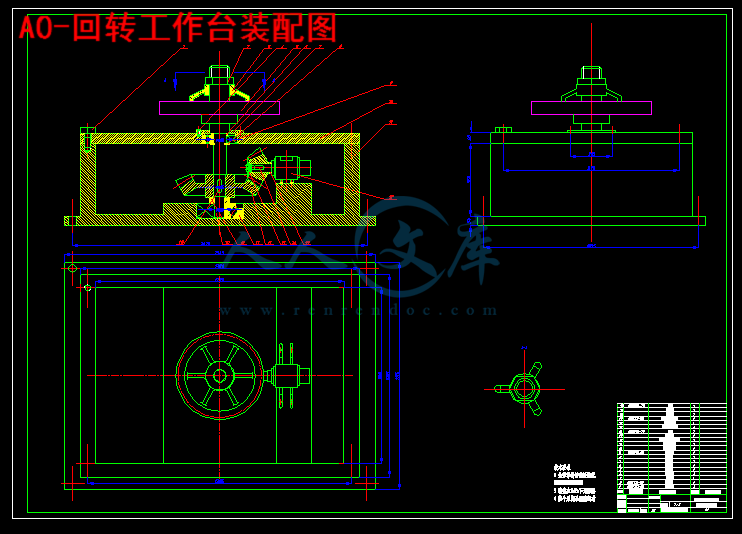
本课题是设计一种专门对法兰盘进行加工的带自动分度机构的回转工作台的设计,利用步进电动机进行自动分度的控制,再通过齿轮传动带动心轴和工件转动,配合钻床对法兰盘进行加工,使工件能任意角度的旋转。在单片机的控制下,步进电机每秒钟发出的脉冲数决定了工作台的转位角度。
关键词 步进电动机;自动分度;齿轮传动
Abstract
This subject is a special design to the flange with automatic processing of the rotary table, the subject is to use a stepper motor of automatic control, then through the drive spindle and the workpiece rotation, and then processing flange plate of the drilling machine, the work piece can be revolving random angle. Under the control of the microcontroller, the pulse per second from the stepper motor decides the table of the transfer point.
Keywords stepper motor automatic degrees gear
目 录
1 绪论1
1.1 回转工作台的简介和应用1
1.1.1 回转工作台的简介1
1.1.2 回转工作台的应用2
2 方案的选择3
2.1 数控回转工作台4
2.2 分度工作台4
2.2.1 开环数控转台4
2.2.2 闭环数控回转工作台5
3工作台的设计7
3.1 加工零件分析7
3.2步进电动机的选择8
3.2.1 步进电动机简介8
3.2.2 步进电动机的选择和参数9
3.2.3单片机控制步进电机原理11
3.2.4 单片机驱动工作台上步进电机设计12
3.3锥齿轮的选择和计算21
3.3.1齿轮设计输入参数21
3.3.2齿轮的材料及热处理21
3.3.3齿轮的基本参数21
3.3.4齿面接触疲劳强度校核23
3.3.5齿根弯曲强度校核24
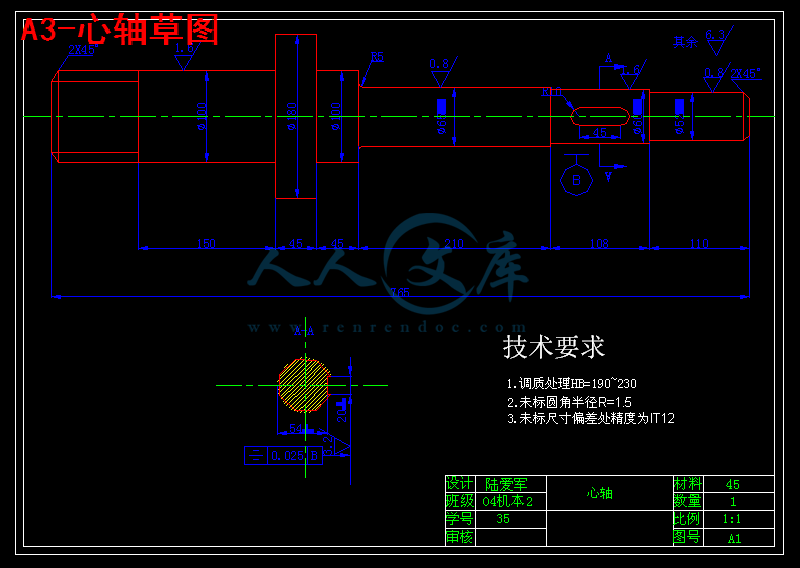
3.4心轴的设计25
3.4.1轴类零件的技术要求25
3.4.2轴类零件的材料、毛坯及热处理25
3.4.3心轴的较核25
3.5轴承的选择30
3.5.1轴承的分类30
3.5.2 推力球轴承的作用30
3.5.3 轴承的选定31
3.5.4轴承的动载荷和寿命计算31
3.6 夹紧装置的设计32
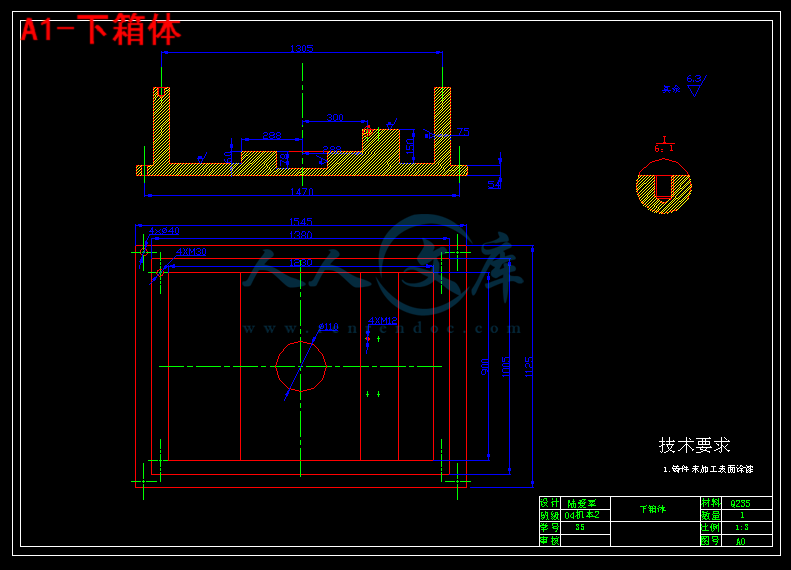
3.7箱体的设计33
结论33
致谢36
参考文献37
附录38
附录138
附录243
1 绪论
1.1 回转工作台的简介和应用
1.1.1 回转工作台的简介
回转工作台(以下称转台)根据其精度的不同分别是铣床、钻床和坐标镗床、坐标磨床的主要附件,高精度的转台还是计量检验工作中的测量仪器。
(1) 国内转台简介
工作台直径是转台主参数,目前我国专业生产厂制造的转台有手动和手动—机动(即通过万向节传动)两种,全是水平式,规格有200, 250, 320, 400和500五种,分度精度按部标为3′。去年获得一机部质量信得过产品奖的武汉机床附件厂生产的400mm转台。
(2) 国外转台简介
国外转台品种繁多,按驱动控制方式可分电动、气动、浓压和数控。按分度方式可分机械、光学、数显、端齿盘、钢球、电感和多面体。工业水平发达国家生产的转台品种多、规格全、精度高。没有单一的转台生产厂,如西德霍夫曼公司生产七十多个品种规格的转台,日本津田驹工业株式会社也有四十多种,这两家还生产多种分度头,有的产品既是转台又是分度头,而机床附件又都仅是这两家公司的一个分部。在分度精度上,首推美国莫尔公司的1440齿机械分度转台,其精度高达±0.1″。瑞士的西浦公司生产200-450 mm八种规格的转台,分度精度在4"-18"之间。以前的产品采用蜗轮副分度,近年则多采用光学分度。在锁紧机构上采用钢盘机构,不致使工作台面受力而产生变形。英国OMT光学测量工具公司生产的转台与其座标锉床配套,它采用圆柱销锁紧,.工作台面不受力、结构简单、工艺性也好,但操作不集中,它有12个品种规格,自Φ203一Φ914mm,分度精度在4 "-30″之间,全是光学转台。:日本工业株式会社以生产钢球分度超精密转台而著称,有手动和电气液压驱动两类11个规格,自Φ200-Φ1250mm,分度精度高达±1″。国外转台制造厂,据不完全统计约一百余家,以美、法、英、西德、日本、瑞士最多,下面简略介绍三家典型的公司:
美国莫尔公司(Moors)
1924年创立,五十年代制造转台,生产座标铣床、座标磨床,是美国精密机床厂代表之一,职工380人。莫尔转台,蜗轮副分度,不使用校正装置、操作方便、重复精度好,易于维修,制造难度大。它还可用步进电机调整角度增量,对转台进行程序控制,,实现简单的分度控制。蜗轮副加工是转台的关键,莫尔公司有一整套工艺予以保证,其分度精度为:标准级±12",精密级±6″、超精级±2″。转台直径仅有Φ726mm一种,立卧式,中心高200mm,可当分度头用。莫尔端面齿分度台,1440齿,分度精度高达±0.1″。1440齿分布在8寸的圆周长上即203×Л= 610mm,每齿间距仅为0.432mm,每一齿侧接触仅为百分之几毫米,可见端齿加工的难度。1440齿分度只能细分到十度,加装小角度发生器便可直接读到0.1"。1440齿分度盘是计量莫尔转合的仪器。
西德霍夫曼公司(Hofmann)
霍夫曼是生产分度头和转台颇具盛名的厂家,但这却是该公司一个很小的部分,霍夫曼仅有职工350人,一各类机床附件晶种达几十种,规格200余个,据统计仅转台一项就有30余种126个规格。霍夫曼GR型手动精密机械转台采用180齿的蜗轮,模数1.75,压力角10°。蜗杆升角2°13",因而分度精度高,且蜗轮副分度误差可由杠杆机构进行补偿,转台结构紧凑、密封性好,转合高度也较低,、分度精度为±5″和±10″两种。日本北川铁工厂生产的R、RI、WR和WRI型转台均自霍夫曼引进,以同型号共商标出厂。
日本津田驹工业株式会社
津田驹主要生产纺织机械,分度头、转台、平口钳等机床附件,约占生产能力10%。现有职工1500人。1937年开始生产转台,是日本最大的机床附件生产厂之一。津田驹生产14种转台、计41个规格, CTK型手动转台,快速进给的CTM型手动转台。
津田驹转台的几种方法简介如下:
1) 手动蜗轮分度:分度精度可达10"-15",鉴于蜗轮副节距误差和齿面接触精度直接影响分度精度,严格地控制了蜗轮的副加工和装配。
2) 伺服电机分度:利用数控装置发出信号、操纵伺服电机驱动转台。也采用蜗轮副,工作台主轴系用向心止推滚珠轴承,滑动部位用钢球支承,为适用于强力切削选用自动锁紧机构,分度精度为12"-15"。
3) 分度盘分度:为电动转台采用,在电机驱动主轴上装分度盘,分度数为一些固定量,在分度盘侧装有与分度数相等的信号销,电动机根据信号准确停止,一般可分24的约数,分度精度取决于分度盘,当然也受主轴和分度盘不同心度影响。
4) 分度盘:蜗轮并用分度。大型转台多采用并用分度,因为大规格转台定位销相应增大,使电磁吸铁吸力受到限制,大转台受冲击力,惯性力大,为此还采用了减速机构,分度精度可达3"。
5) 端齿盘分度: CTPM-300型转台系超精密自动分度转台,即是此法分度。分度精度可达4"。能承受重切削,自动定心精度高。



 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号