摘 要
近年来,我国的模具发展迅速,尤其是塑料模具提出了越来越高的要求,最近几年,塑料模具在整个模具行业所占的比例上升到30%左右,相信在未来的时间里,中国塑料模具工业还将保持年均增长速度达到10%以上较高速度的发展,国内塑料模具市场以注塑模具需求量最大。将来注射模具发展的方向向更精密、更高效、复合和多功能、更大型、更精密、更复杂、更绿色及更经济的方向发展,模具产品的技术含量将不断提高,模具制造周期将不断缩短。
注射成型是塑料成型的一种重要的方法,它主要适用于热塑料的成型,可以一次成型简单或复杂的精密塑件。本课题是将音箱作为设计模型,将注塑模具的相关知识作为依据,介绍塑件结构形状,塑件的材料选择,及塑件的结构工艺性,注射机成型的设备组成分类及型号规格。
本课题通过对音箱外壳成型工艺的分析,设计了一副一模两腔的塑料模具。设计成型零部件时,根据塑料的特性、塑件的结构和使用要求,确定型腔的总体布局,选择分型面,确定脱模方式,设计浇注系统、冷却系统。计算成型零部件的工作尺寸。运用Pro/E软件完成音箱外壳模具的整体设计;应用Pro/E中的塑料顾问模块(Plastic Advisor),对塑料制品进行注射仿真分析。最后对三维造型使用Pro/Engineer形同转出dwg文件进行出图。
关键词:注塑模具;注射机;Pro/Engineer;EMX(模架设计专家)
Abstract
. In recent years, China's rapid development of the mold, especially the plastic mold of the increasingly high demand, in recent years, the plastic mold in the mold industry the proportion of up to 30% jobs, I believe in the coming years, China plastic mold industry will maintain an average annual growth rate of more than 10% high speed development, the domestic market to plastic mold injection mold greatest demand. The future development direction of injection mold to more sophisticated, more efficient, complex and multi-purpose, larger, more sophisticated, more complex, more green and more economic development, mold the technical content of the product will continue to improve, the manufacturing cycle of the die will shorten ceaselessly.
Plastic molding injection molding is an important method, which is mainly applied to the thermal plastic molding, molding can be a simple or complex precision plastic parts. This topic is the speaker as a design model, the injection mold related knowledge as the basis, elaborates the structure process of plastic products, injection molding machine equipment composition classification and specifications.
Through proper analysis of the speaker molding process, I designed a double-cavity plastic mould.While designing molding components, based on the characteristics of plastic, plastic parts of the structure and use requirements, the overall layout of the cavity, the joint face, the stripping methods, design of gating system, exhaust system should be determined. the working size of the molded parts is calculated. Then use Pro / E software to complete the overall design hair dryer shell mold; and finally the plastic module consultant (Plastic Advisor) in Pro / E is applied for plastic injection simulation analysis. finally the3D modeling using Pro / Engineer DWG file is transferred out of a map.
Key words: Injection molding; injection machine; Pro/Engineer; EMX (formwork design expert)
目 录
摘要
Abstract
第一章 绪论1
1.1模具及模具工业的发展与现状1
1.2塑料成型模具的及其分类1
1.3注射模具的发展趋势1
第二章 塑料成型工艺2
2.1 塑件材料的选择2
2.2确定成型方法2
2.3注塑成型工艺过程3
2.3.1 成型前的准备3
2.3.2 注塑成型过程3
2.3.3、塑件的后处理4
2.4塑件的结构工艺性4
2.5 塑件成型工艺参数5
2.5.1 温度5
2.5.2 压力6
2.5.3 成型周期7
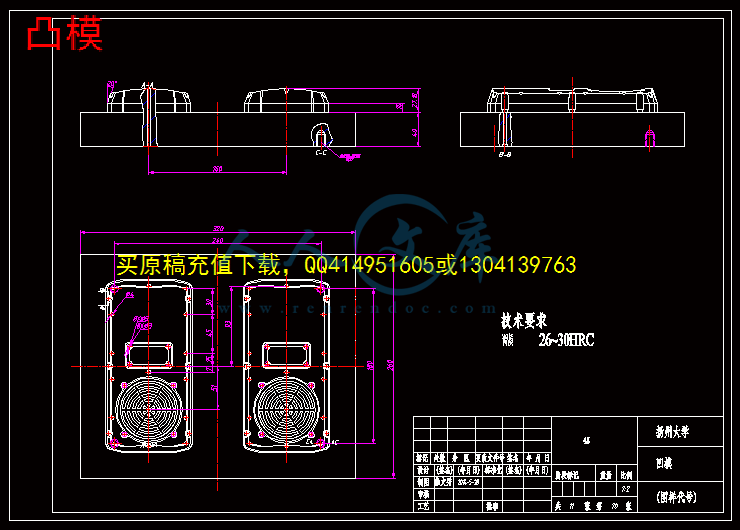
第三章 音箱面壳模具设计9
3.1注塑成型设备9
3.1.1注塑机结构组成9
3.1.2 注塑机的分类9
3.1.3 注塑机的型号规格10
3.2注射模具分类及典型结构10
3.2.1注射模分类10
3.2.2注射模典型结构10
3.3音箱模具的结构设计12
3.3.1分型面的设计12
3.3.2型腔数目的确定13
3.3.3 浇注系统的设计14
3.3.4 成型零件设计16
3.3.5 合模导向机构的设计19
3.3.6 推出机构设计20
3.3.7 模具温度调节系统设计22
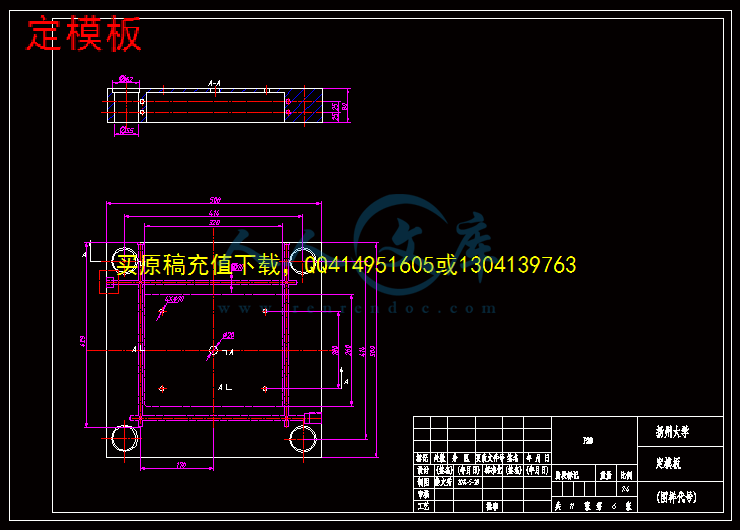
3.3.8 标准模架的选用24
3.4 注射模具与注射机的关系25
3.4.1 选择注塑机25
3.4.2最大注射量的校核26
3.4.3 注射压力的校核26
3.4.4 锁模力的校核27
3.4.5 安装部分尺寸校核27
3.4.6 开模行程的校核27
3.4.7 推出装置的校核27
3.4.8 喷嘴的校核28
第四章 音箱面壳模具三维设计29
4.1音箱面壳三维造型及模具设计29
4.2 模架设计30
4.2.1 定义模具模架30
4.2.2 添加设备31
4.2.3 设计顶出机构33
4.2.4 设计冷却系统33
4.2.5 动画模拟开模35
第五章 音箱面壳模具注射仿真分析36
5.1 Pro/e塑料顾问的简介36
5.1.1注射仿真分析的优点36
5.1.2注射仿真分析的缺点36
5.2塑料顾问模块的进入36
5.3分析功能应用37
5.4分析结果38
5.4.1注射压力38
5.4.2注射温度38
5.4.3塑料熔体温度39
5.4.4熔接痕39
5.4.5气泡40
第六章 小结与展望41
6.1小结41
6.2展望41
致 谢42
参考文献43
附 录44
第一章 绪论
1.1模具及模具工业的发展与现状
在模具工业的总产值中,冲压模具约占50%,塑料模具约占33%,压铸模具约占6%,其他各类模具约占11%。在模具生产方面,国内已经能够生产精度达21µ m的精密多T位级进模、新轿车的部分覆盖件模具、48in(约122cm)大屏幕彩电塑壳注射模具、6.5kg大容量洗衣机全套塑料模具以及汽车保险杠和整体仪表板等塑料模具,还有照相机塑料件模具、多型腔小模数齿轮模等精密塑料模具。





 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号