摘 要:
在生产过程中,使生产对象(原材料,毛坯,零件或总成等)的质和量的状态发生直接变化的过程叫工艺过程,如毛坯制造,机械加工,热处理,装配等都称之为工艺过程。在制定工艺过程中,要确定各工序的安装工位和该工序需要的工步,加工该工序的机车及机床的进给量,切削深度,主轴转速和切削速度,该工序的夹具,刀具及量具,还有走刀次数和走刀长度,最后计算该工序的基本时间,辅助时间和工作地服务时间。
关键词:
工序,工位,工步,加工余量,定位方案,夹紧力
Abstract :
Enable producing the target in process of production (raw materials, the blank , state of quality and quantity on part become always ) take place direct course of change ask craft course, if the blank is made, machining, heat treatment , assemble etc. and call it the craft course. In the course of making the craft , is it confirm every erector location and worker step that process need this of process to want, the locomotive of processing , this process , and the entering the giving amount of the lathe, cut depth , the rotational speed of the main shaft and speed of cutting, the jig of this process, the cutter and measuring tool, a one hundred sheets of number of times still leaves and a one hundred sheets of length leaves, calculate basic time of this process , auxiliary time and service time of place of working finally.
Keyword:
The process, worker one, worker's step , the surplus of processing, orient the scheme , clamp strength
目 录
第一章 概述……………………………………………………………………… 1
第二章零件的工艺分析…………………………………………………………2
2.1零件的工艺分析………………………………………………………… 2
2.2确定毛坯的制造形式…………………………………………………… 2
2.3箱体零件的工艺性……………………………………………………… 2
第三章 拟定箱体加工的工艺路线……………………………………………… 3
3.1 定位基准的选择……………………………………………………… 3
3.1.1 精位基准的选择……………………………………………………… 3
3.1.2 粗位基准的选择……………………………………………………… 3
3.2 加工路线的拟定……………………………………………………… 3
第四章 机械加工余量及工序尺寸的确定……………………………………… 7
4.1 机座主要平面加工的工序尺寸及加工余量…………………………… 7
4.2 机体主要平面加工的工序尺寸及加工余量…………………………… 7
第五章 确定切削用量及基本工时……………………………………………… 9
5.1 机座切削用量及基本工………………………………………………… 9
5.2 机体切削用量及基本工………………………………………………… 18
第六章夹具设计………………………………………………………………… 31
6.1 定位基准的选择…………………………………………………………… 31
6.2 定位元件的设计…………………………………………………………… 31
6.3 定位误差分析……………………………………………………………… 32
6.4 铣削力与夹紧力计算……………………………………………………… 33
6.5 夹紧装置及夹具体设计…………………………………………………… 33
6.6 夹具设计及操作的简要说明……………………………………………… 34
参考文献 ………………………………………………………………………… 35
致 谢……………………………………………………………………………… 36
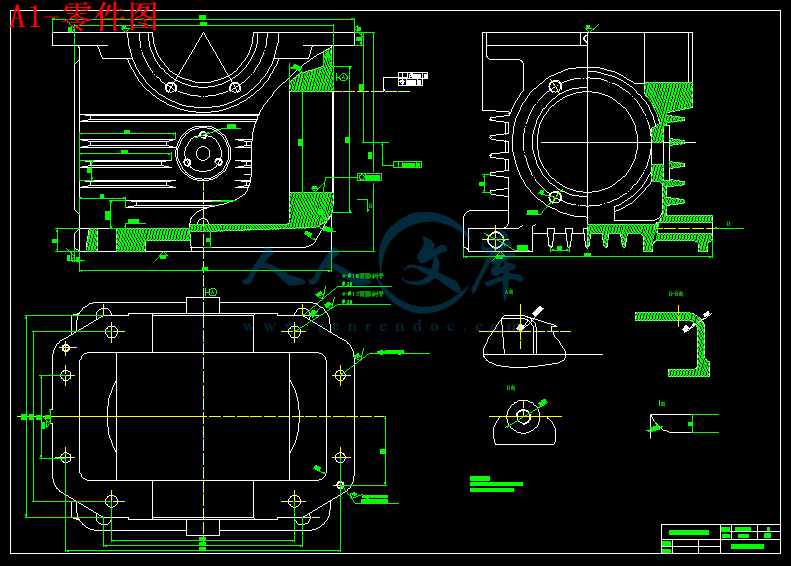
附 件 零件图和夹具图及加工工艺卡
第一章:概述
箱体零件是机器或部件的基础零件,它把有关零件联结成一个整体,使这些零件保持正确的相对位置,彼此能协调地工作.因此,箱体零件的制造精度将直接影响机器或部件的装配质量,进而影响机器的使用性能和寿命.因而箱体一般具有较高的技术要求.
由于机器的结构特点和箱体在机器中的不同功用,箱体零件具有多种不同的结构型式,其共同特点是:结构形状复杂,箱壁薄而不均匀,内部呈腔型;有若干精度要求较高的平面和孔系,还有较多的紧固螺纹孔等.
箱体零件的毛坯通常采用铸铁件.因为灰铸铁具有较好的耐磨性,减震性以及良好的铸造性能和切削性能,价格也比较便宜.有时为了减轻重量,用有色金属合金铸造箱体毛坯(如航空发动机上的箱体等).在单件小批生产中,为了缩短生产周期有时也采用焊接毛坯.
毛坯的铸造方法,取决于生产类型和毛坯尺寸.在单件小批生产中,多采用木模手工造型;在大批量生产中广泛采用金属模机器造型,毛坯的精度较高.箱体上大于30—50mm的孔,一般都铸造出顶孔,以减少加工余量.




![A4-工序卡[11张].gif](/ueditor/net/upload/2015-06-30/e838bda0-51df-4e1c-a09c-929d4da9ed30.gif)
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号