摘 要
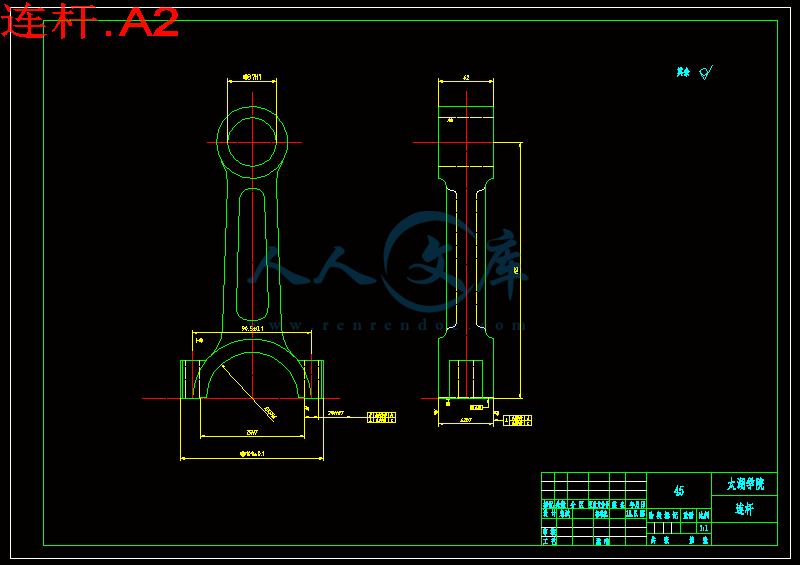
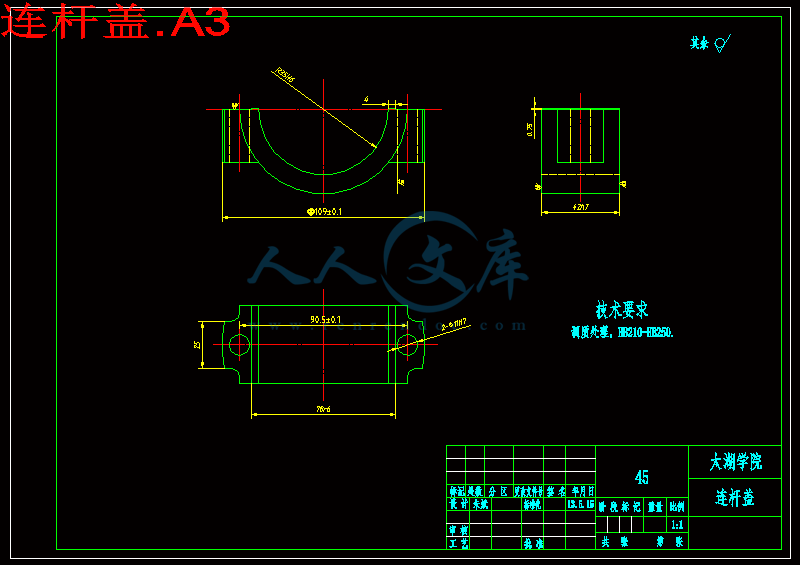
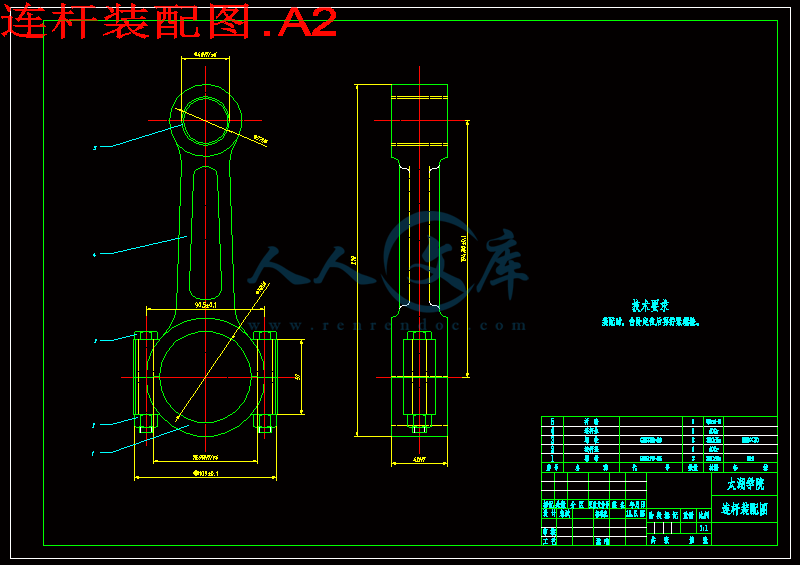
连杆是内燃机的主要传动件之一,正文主要论述了连杆的加工工艺及夹具设计。连杆的尺寸精度、形状精度以及位置精度的要求都很高,而连杆的刚性比较差,容易产生变形,因此在安排工艺过程时需要把各主要表面的粗精加工工序分开。逐步减少连杆加工余量、切削力及内应力的作用,以及修正加工后的变形,最后就能达到连杆的技术要求。连杆的主要加工表面为大、小头孔和两端面,较重要的加工表面为连杆体和盖的结合面及连杆螺栓孔定位面,次要加工表面为大头两侧面及螺栓座面等。
在连杆加工中有两个主要因素影响加工精度:
(1)连杆本身的刚度比较低,在外力(夹紧力、切削力)的作用下容易变形。
(2)连杆是模锻件,孔的加工余量较大,切削时将产生较大的残余内应力,并引起内应力重新分布。
通过对内燃机连杆的机械加工工艺及对粗加工大头孔夹具和铣结合面夹具的设计,主要归纳为以下两个方面:
第一方面:连杆件外形较复杂,而刚性较差。其技术要求很高,所以适当的选择机械加工中的定位基准,是能否保证连杆技术要求的重要问题之一。在连杆的实际加工过程中,选用连杆的大小头端面及小头孔作为主要定位基面,同时选用大头孔两侧面作为一般定位基准。为保证小头孔尺寸精度和形状精度,可采用自为基准的加工原则;保证大小头孔的中心距精度要求,可采用互为基准原则加工。
第二方面:关于夹具的设计方法及其步骤。
关键词:连杆;变形;加工工艺;夹具设计
ABSTRACT
The connecting rod is one of the main driving medium of diesel engine, this text expounds mainly the machining technology and the design of clamping device of the connecting rod. The precision of size, the precision of profile and the precision of position , of the connecting rod is demanded highly , and the rigidity of the connecting rod is not enough, easy to deform, so arranging the craft course, need to separate the each main and superficial thick finish machining process. Reduce the margin of processing, cutting force and internal stress progressively, revise the deformation after processing, can reach the specification requirement for the part finally .
In the Connecting rod is one of the main processing surface is large, the small head hole and both ends of the machined surface, is important for the connecting rod body and cover joint surface and the connecting rod bolt hole locating surface, secondary processing surface for bearing locking grooves, oil hole, head and body and a cover on the two sides of the bolt seat surface.
Machine of connecting rod are two major factors that affect the machining precision:
(1) Connecting rod itself stiffness is relatively low, in the external forces (cutting force, clamping force ) under the action of easy deformation.
(2) Connecting rod is die forgings, hole machining allowance, cutting will produce bigger residual stress, and stress redistribution caused by.
The automobile connecting rod machining process and the rough machining and milling combined with big hole clamp surface fixture design, mainly divided into the following two aspects:
The first aspect: connecting rod parts with complicated shape, while the poor rigidity. And the very high technical requirements, so the appropriate selection of mechanical processing in the locating datum, can ensure the connecting rod is one of the important problems of technical requirements. The connecting rod in the practical production process, selection of connecting rod to the size of the head end and the small head hole as the main positioning datum, and choice of big hole two side as a general locating datum. In order to ensure the size precision and shape precision of the small head hole, can be used for reference from the processing principle; ensure that the size of the first hole center distance accuracy requirements, can be used for reference each other the principle of processing.
Second: mainly on the fixture design method and steps.
Key words: Connecting rod;Deformation;Process;Fixture design
目 录
摘 要III
ABSTRACTIV
目 录V
1 绪论1
1.1 本课题的研究内容和意义1
1.2 国内外的发展概况1
1.3 本课题应达到的要求3
2 连杆的分析4
2.1 连杆的作用4
2.2 连杆的机械分析4
2.3 连杆的结构特点4
2.4连杆的主要技术要求5
2.4.1 大、小头孔的尺寸精度、形状精度5
2.4.2 大、小头孔轴心线在两个互相垂直方向的平行度5
2.4.3 大、小头孔中心距5
2.4.4 连杆大头孔两端面对大头孔中心线的垂直度5
2.4.5 大、小头孔两端面的技术要求5
2.4.6 有关结合面的技术要求5
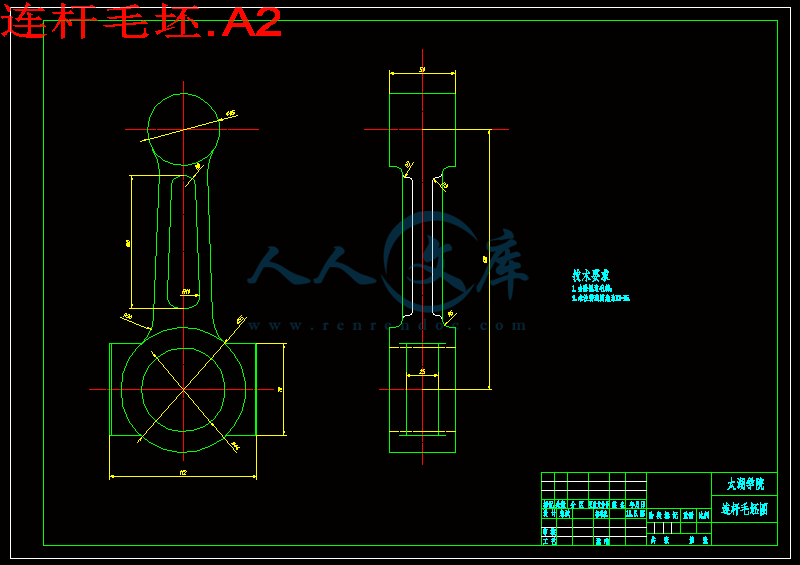
2.5 连杆的材料和毛坯分析5
3 连杆的加工工艺规程的制定7
3.1 加工工艺的基本概念7
3.2 选择定位基准7
3.3 确定加工余量8
3.4 拟订机械加工工艺路线8
3.5 连杆工艺计算10
3.5.1 粗铣两平面10
3.5.2 粗磨两平面11
3.5.3 钻小头小孔13
3.5.4 粗镗小头孔14
3.5.5 车大头外圆15
3.5.6 粗镗大头孔17
3.5.7 粗铣螺栓孔端平面17
3.5.8 精铣螺栓孔端平面17
3.5.9 铣开连杆大头18
3.5.10 精铣体盖分开面18
3.5.11 钻扩铰螺栓孔18
3.5.12 精磨体盖分开面20
3.5.13 精磨两端平面21
3.5.14 精镗小头孔21
3.5.15 粗镗大头孔22
3.5.16 精镗大头孔22
3.5.17 精镗小头孔22
4 夹具设计23
4.1 机床夹具的分类22
4.2 工件的加工工艺分析23
4.3 确定定位方案23
4.4 夹具的机构设计24
4.5 夹具的使用26
5 结论与展望28
6 致谢29
7.参考文献30
1 绪论
1.1 本课题的研究内容和意义
本课题研究的内容是:K2500内燃机车发动机NDS5主连杆工艺规程设计和系列夹具设计,其中包括了工艺流程的设计、工序的编写、系列夹具的设计,并有相关计算和说明书。
连杆的作用是将活塞承受的力传给曲轴,并使活塞的往复运动转变为曲轴的旋转运动。连杆由连杆体、连杆盖、连杆螺栓和连杆轴瓦等零件组成,连杆体与连杆盖为连杆小头、杆身和连杆大头。连杆小头用来安装活塞销,以链接活塞。连杆大头与曲轴的连杆轴颈相连。一般做成分开式,与杆身切开的一半称为连杆盖,二者靠连杆螺栓链接为一题。连杆轴瓦安装在连杆大头孔座中,与曲轴上的连杆轴颈装和在一起,是发动机中最重要的配合副之一。常用的减磨合金主要有白合金、铜铅合金和铝基合金。
不难看出,连杆对于内燃机来说是不可或缺并且起到关键性作用的零件。所以本课题的研究对于生产出优秀耐用的连杆起到至关重要的作用。同时对内燃机的安全性也起到关键作用。



 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号