目 录
摘要………………………………………………………………………………… i
Abstract…………………………………………………………………………… ii
1 绪论……………………………………………………………………………… 1
1.1电火花加工的基本原理…………………………………………………… 1
1.2 电火花加工的特点和适用范围…………………………………………… 2
2 机床总体设计…………………………………………………………………… 5
2.1 设计总体方案……………………………………………………………… 5
2.1.1 功能设计……………………………………………………………… 5
2.1.2 结构设计……………………………………………………………… 7
2.1.3 性能设计……………………………………………………………… 7
3 机械系统的设计………………………………………………………………… 10
3.1 脉冲当量的选择…………………………………………………………… 10
3.2 传动比的选择……………………………………………………………… 10
3.3 滚珠丝杆的选型和校核…………………………………………………… 11
3.4 步进电机的选用…………………………………………………………… 13
3.5同步带的设计选用………………………………………………………… 15
3.6 回转工作台的设计………………………………………………………… 18
3.6.1 工作原理……………………………………………………………… 18
3.6.2 蜗轮蜗杆的设计计算………………………………………………… 20
3.6.3 齿轮的设计计算与校核……………………………………………… 23
结论………………………………………………………………………………… 30
致谢………………………………………………………………………………… 31
参考文献…………………………………………………………………………… 32
摘 要
电火花加工技术是先进生产制造技术中的一个重要组成部分,是机械制造业中最广泛采用的机械切削和磨削加工的重要补充和发展。其最大特点是:工具和工件是非接触加工,加工中没有宏观的,因而可以用软的铜、石墨等材料加工任何硬度和强度的难加工金属材料;可以加工非常复杂的立体成型表面;可以加工低刚度、薄壁、深孔、微细孔等特殊精密零件。在各类模具制造业中,电火花加工技术是必不可少的关键技术。由于电火花加工技术是机电一体化技术,是机械、电工、电子、数控、自动控制、计算机应用等多门学科、专业知识的综合运用。
我的设计课题是DK7132数控电火花穿孔成型加工机床。DK为数控电加工机床,71为电火花穿孔,成型加工机床。32为机床工作台宽度。
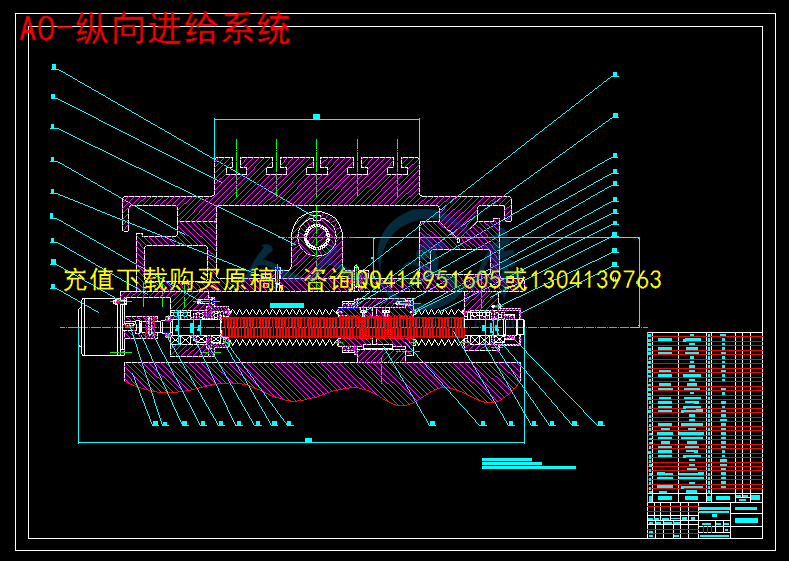
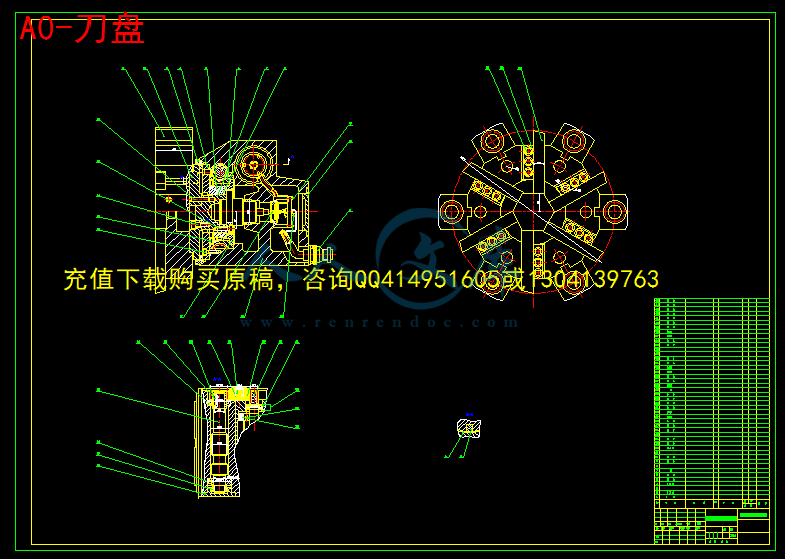
此次设计包括机床的总体机构设计,主轴运动的设计,横向进给,纵向进給,回转方向运动的设计。其中还包括带轮的强度计算,滚珠丝杆校核,轴承寿命的验算。
关键词:数控电火花加工 主轴运动 横向进给 纵向进给 步进电机
Abstract
The technology of electrical-discharge machining is an important part of advanced manufacture technology. And it is also an important complementarity and development of machine cutting and grinding machining in machine manufacture. The characteristic of electrical-discharge machining is that the tools and the work piece do not contact. There is no macroscopical cutting force. So we can use the material, such as soft copper and graphite, to machining metal materials regardless any rigidity and intension. The process is suited to the complicated solid molding surface. Electrical-discharge machining is also used for special precise part. In various tool making, the technology of electrical-discharge machining is the necessary key technology. Because the technology of electrical-discharge machining is the technology of mechatronics, and it is the integrate application of many subjects and professional knowledge , for example mechanism、electrician、electron、numerical control、auto control and computer application.
My design subject is DK7132 numerical control electrical-discharge perforation molding machining tool. DK means numerical control machining tool. 71 means electrical-discharge perforation molding machining tool. 32 means the width of tool’s worktable.
The design contains collectivity distribution design, principle axis design, landscape orientation feed design, portrait feed design, circumgyrate worktable design. It still includes intension calculation of gear wheel, the checking of ball bearing pole and the calculation of axis gearing life-span. The controlling system part contains the circuit of step-by-step electromotor control and the circuit of pulse electrical source. This part is the most important part of numerical control electrical-discharge machining tool, and it is very hard for me. The design of step-by-step electromotor control includes hardware circuit design and software system design. It explains the enlarging of CMOS chip and the design of keyboard display interface. The circuit of pulse electrical source uses high and low voltage pulse electrical source. The circuit is composed by transistor and unattached elements, it exports high and low voltage pulse, which can apply with two electrical-discharge interval and improve productivity.
Key words: Numerical control electrical-discharge machining, principle axis motion , step-by-step electromotor, pulse electrical source.
1 绪论
1.1电火花加工的基本原理
电火花加工的原理是基于工具和工件(正、负电极)之间脉冲性火花放电时的电腐蚀现象来蚀除多余的金属,以达到对零件的尺寸、形状及表面质量预定的加工要求。电腐蚀现象早在20世纪初就被人们发现,例如在插头或电器开关触点开、闭时,往往产生火花而把接触表面烧毛,腐蚀成粗糙不平的凹坑而逐渐损坏。长期以来,电腐蚀一直被人们认为是一种有害的现象,人们不断地研究电腐蚀的原因并设法减轻和避免电腐蚀的发生。但事物都是一分为二的,只要掌握规律,在一定条件下可以把坏事转成好事,把有害变为有用。1940年前后,前苏联科学院电工研究所拉扎连柯夫妇的研究结果表明,电火花腐蚀的主要原因是:电火花放电时火花通道中瞬时产生大量的热,达到很高的温度,足以使任何金属材料局部熔化、汽化而被蚀除掉,形成放电凹坑。这样,热门在研究抗电腐蚀办法的同时,开始研究利用电腐蚀现象对金属材料进行尺寸加工,终于在1943年拉扎连柯夫妇研制出利用电容器反复充电放电原理的世界上第一台使用化的电火花加工装置。


 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号