【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
以下预览截图到的都有源文件,图纸是CAD,文档是WORD,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
摘 要
本设计分析研究了CA6140车床变速箱中拔叉零件的夹具设计。由于拔叉零件的工序较多且结构较为复杂,所以为了保证加工精度和提高生产效率,考虑采用数控机床进行加工,以下内容进行了拨叉零件工艺性分析、加工顺序和工艺方案的确定,并通过对拨叉零件数控加工工艺规程设计和钻孔工序的夹具设计,为拨叉零件在数控机床上加工提供了理论依据和有力的硬件保证。
关键词:数控加工工艺,定位,夹紧,专用夹具
Abstract
The design of the gearbox on the lathe is in CA640 parts fork and drill a point of order processing Φ20, Φ50 hole of this special fixture design process. Fork parts as a result of the more complex the structure, processes more; therefore in order to ensure the accuracy of processing to increase productivity and reduce labor intensity, consider the use of CNC machine tools for processing and preparation of the CNC machining process. In order to ensure Φ20, Φ50 hole on the vertical datum tolerance, CNC machine tools to meet the processing requirements on their design of a special fixture, the fixture using automatic clamping device, clamping a reliable, easy to operate. Higher production efficiency, therefore, applicable to high-volume, the processing pipeline. Able to meet the design requirements.
Keywords: NC machining process, positioning, clamping, special fixture
目 录
摘要1
Abstract2
目 录3
1 绪论5
2 数控加工工艺概述5
2.1 数控加工工艺分析的一般步骤与方法5
2.2 机床的合理选用5
2.3 数控加工零件工艺性分析6
2.3.1 零件图样上尺寸数据的给出应符合编程方便的原则6
2.3.2 零件各加工部位的结构工艺性应符合数控加工的特点6
2.4 加工方法的选择与加工方案的确定6
2.4.1 加工方法的选择6
2.4.2 加工方案确定的原则7
2.5 工序与工步的划分及加工顺序安排7
2.5.1 工序的划分7
2.5.2 工步的划分7
2.5.3 加工顺序安排8
2.6 零件的安装与夹具的选择8
2.6.1 定位安装的基本原则8
2.6.2 选择夹具的基本原则8
2.7 刀具的选择与切削用量的确定8
2.7.1 刀具的选择8
2.7.2 切削用量的确定9
2.8 对刀点与换刀点的确定9
2.9 加工路线的确定9
3 拨叉零件数控加工工艺分析10
3.1 拨叉零件的作用10
3.2 拨叉零件的工艺分析11
3.3 确定拨叉零件生产类型11
3.4 确定拨叉零件毛坯类型11
3.4.1 确定毛坯种类11
3.4.2 确定铸件加工余量及形状11
3.4.3 绘制铸件零件图12
3.5 拨叉零件数控加工工艺规程设计12
3.5.1 选择定位基准12
3.5.2 制定数控加工工艺路线12
3.6 机械加工余量、工序尺寸及公差的确定13
3.6.1 圆柱表面工序尺寸13
3.6.2 平面工序尺寸14
3.6.3 确定切削用量及时间定额14
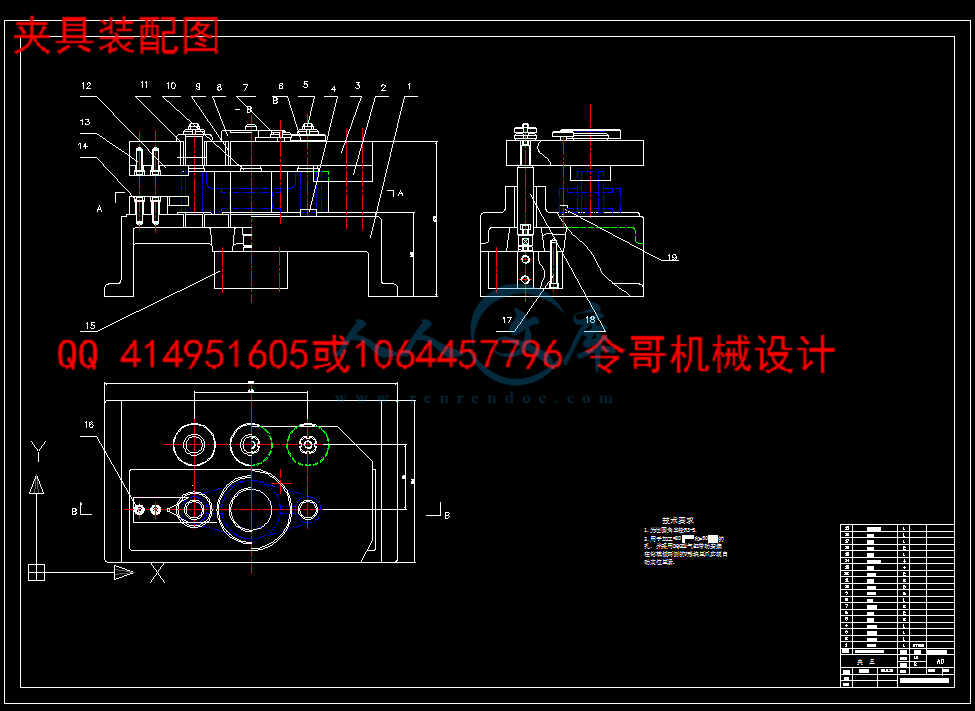
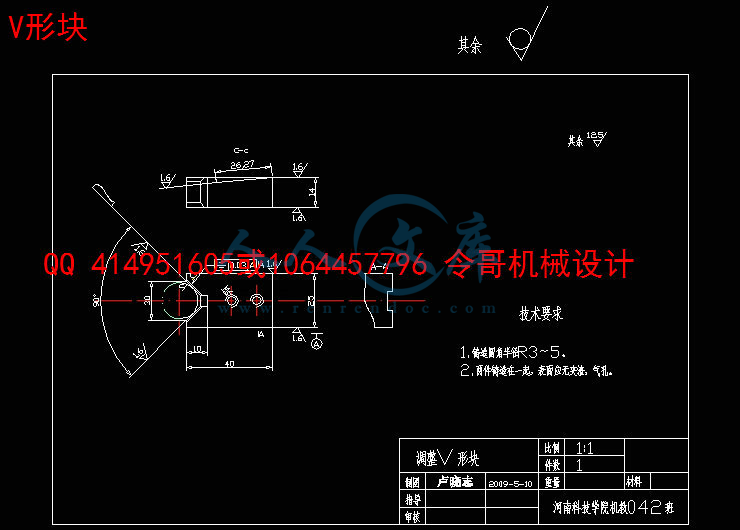
4 夹具设计23
4.1 问题的提出23
4.2 夹具设计23
4.2.1 定位基准选择23
4.2.2切削力及夹紧力计算24
4.3定位误差分析24
4.3.1定位元件尺寸及公差的确定24
4.3.2计算钻套中心线与工作台的垂直度误差24
4.3.3计算定位销轴与工作台的平行度误差25
4.4夹具设计及操作的简要说明25
5结束语26
致谢27
参考文献28
1 绪论
随着我国现代制造技术的发展,数控机床的普及和从事数控加工人员的增多,数控加工越来越受到人们的重视。拨叉零件广泛应用于我们的日常生活及生产当中,拨叉零件的制造精度能不能够满足技术要求,如何更大限度的降低机加工的基本劳动时间及提高单位时间内的生产率,都成为机械行业势待解决的技术性问题。随着数控技术的不断发展及数控技术应用的不断广泛化、深入化,我们意识到,采用数控机床来加工拨叉零件既能够提高零件的精度又能够完成采用普通机床加工应运受限的瓶颈,对提高加工效率、以及降低劳动强度都有不可估量之好处。
随着计算机科学、信息技术的迅速发展,传统的制造业已发生了十分显著的变化,发达国家正进行由传统的制造技术向现代制造技术的转变,并提出了全新的制造模式。数控加工技术将逐步引航现代机械制造业的发展。数控机床的应用范围日益扩大,其产生的经济效益与社会效益十分明显。
对传统零件的数控加工技术也得到越来越广泛的应用。面对新技术、新工艺的不断出现,提高数控加工技术在传统拨叉类零件的应用也受到越来越多的重视。如何使数控技术在加工这一类零件中表现出其高质量、高精度、高效率,都成为各国争先要解决的问题。因此研究它对我国的制造行业很有借鉴作用。
2 数控加工工艺概述
2.1 数控加工工艺分析的一般步骤与方法
工作人员在进行工艺分析时,要有机床说明书、编程手册、切削用量表、标准工具、夹具手册等资料,根据被加工工件的材料、轮廓形状、加工精度等选用合适的机床,制定加工方案,确定零件的加工顺序,各工序所用刀具,夹具和切削用量等。
2.2 机床的合理选用
在数控机床上加工零件时,一般有两种情况。第一种情况:有零件图样和毛坯,要选择适合加工该零件的数控机床。第二种情况:已经有了数控机床,要选择适合在该机床上加工的零件。无论哪种情况,考虑的因素主要有,毛坯的材料和类、零件轮廓形状复杂程度、尺寸大小、加工精度、零件数量、热处理要求等。概括起来有三点:
(1)要保证加工零件的技术要求,加工出合格的产品;
(2)有利于提高生产率;
(3)尽可能降低生产成本(加工费用)。
2.3 数控加工零件工艺性分析
数控加工工艺性分析涉及面很广,在此仅从数控加工的可能性和方便性两方面加以分析。
2.3.1 零件图样上尺寸数据的给出应符合编程方便的原则
(1)零件图上尺寸标注方法应适应数控加工的特点在数控加工零件图上,应以同一基准引注尺寸或直接给出坐标尺寸。在保持设计基准、工艺基准、检测基准与编程原点设置的一致性方面带来很大方便。由于零件设计人员一般在尺寸




 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号