摘 要
【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
以下预览截图到的都有源文件,图纸是CAD,文档是WORD,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
随着信息技术的进步和全球化制造技术的进步,企业为了提高自身的竞争力,要求配置效率更高成本更低的加工设备,而传统机床在未来的加工业中会遇到难以克服的困难,例如在高速加工中(轨迹速度达到50m/min)和高效空间曲面加工及机床的通用性方面将无法满足现代加工技术的要求。因此探索和研究一种现代化机床具有十分重要的意义。
虚拟轴机床与传统的串联式数控机床相比具有很多优越性。传统数控机床各自由度是串联相接的,呈悬臂结构,且层叠嵌套致使传动链长,传动系统复杂,累计误差大,而精度低,成本昂贵,至今多数机床只是4轴联动,极少5轴。而虚拟轴机床的并联式加工中心结构特别简单,传动链极短,刚度大、质量轻、切削效率高、响应快,特别是很容易实现六轴联动,因而,能加工更复杂的三维曲面,且其加工精度和加工粗糙度都直接由控制程序来保证,因此,硬件成本低,而软件附加值高,是一种技术附加值极高的机电一体化产品。
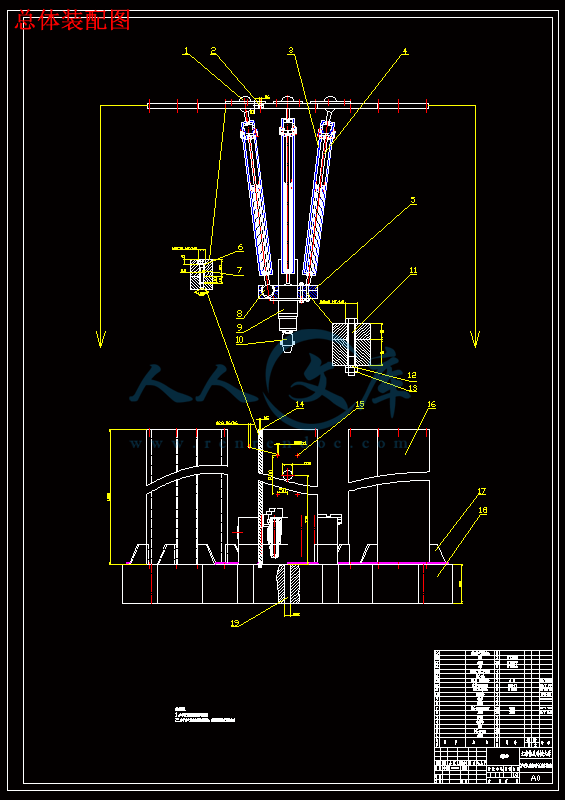
此研究课题针对现今的机加工趋向,制定了设计一部并联机床实验台的任务,作者与合作人共同设计。其中的并联部分分配给了合作者,作者主要负责并联机床实验台的总体框架结构设计。
平台大致由并联机构——三根并联丝杠(驱动电机)、铸铁机架、装卡平台和电主轴以及弹簧铣夹头组成。
关键词:并联机构、虚轴加工、雅可比矩阵、正解算法
Abstract
With the progress of the information technology and the development of the global manufacturing techniques, enterprises require more efficient and lower cost machines by reason of enhancing their competitive ability. But conventional machine tools will encounter many difficulties which are hard to overcome in the future, for instance of high-speed machining ( path speed exceeding 50m/min)and high efficient space curved surfacing machining as well as flexibility of machines. Thus, it is very important to explore and study kind of modern machines.
Be compared to the normal numerical control machine tool, it has larger rigidity, stronger carrying capacity, smaller error, higher precision, smaller ratio of self-weight and load, better dynamical capacity, less investment of hardware, but stronger function of software. All of these show its high additional technical valve.
This research topic for the current trend of the processing machine, developed a design of a parallel machine test-bed task, which the Author co-design and a partner. Some of them parallel to the allocation of the partner, the author mainly responsible for the PMT test-bed framework of the overall structural design.
Platform from roughly parallel bodies - three parallel screw (motor driven), cast iron rack, with card platform and Spindle and milling chucks of spring.
Key words: parallel instruction, virtual axis processing, Jacobian Matrix, positive solution algorithm
目 录
第1章 绪论1
1.1课题背景与意义1
1.2 并联机床发展历史及现状2
1.3本文主要研究内容5
第2章 重要零部件选型6
2.1依照主轴功率确定电主轴型号6
2.2 选择主轴下部刀具夹头7
2.3选择工件的装卡方式8
第3章 实验台支承部分及其连接的方案11
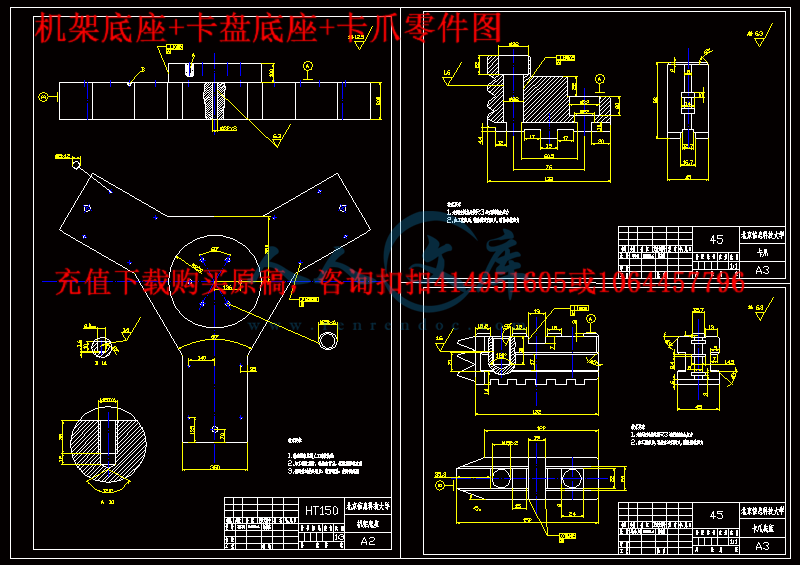
3.1机架的设计方案11
3.2铸造机架的材料及热处理14
3.3机架的截面形状、壁厚及周边筋的布置14
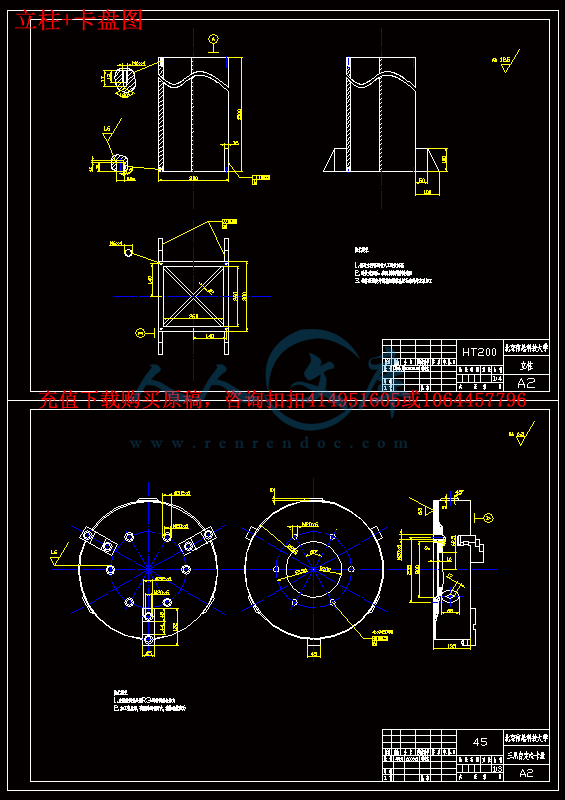
3.4立柱与底座的连接方式16
3.5底座的造型16
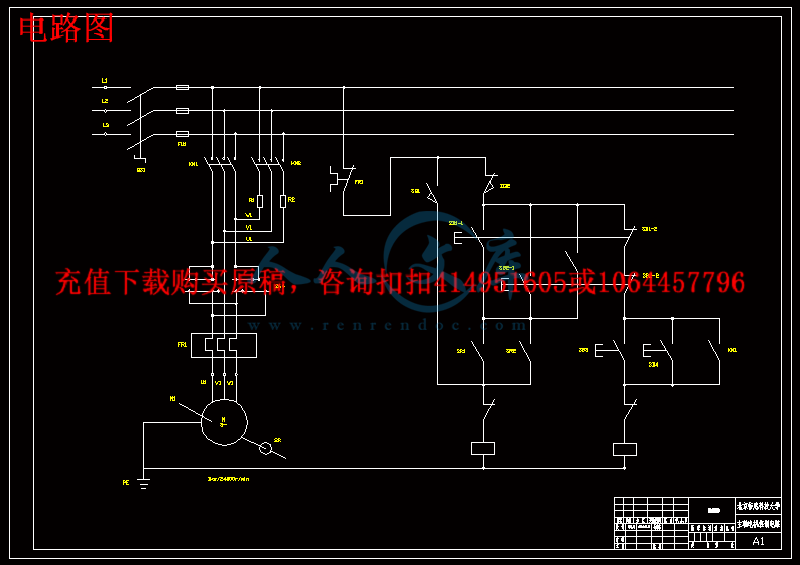
第4章 实验台驱动电路17
4.1 电路布线方案17
4.2 电路控制要求17
4.3电路控制连线原理图17
第5章 实验结果及三维建模18
5.1 设计并联实验台结果18
5.2 实验台solidworks建模18
第6章总结与展望19
参考文献20
致 谢20
第1章 绪 论
1.1课题背景与意义
为了提高对生产环境的适应性,满足快速多变的市场需求,近年来全球机床制造业都在积极探索和研制新型多功能的制造装备与系统,其中在机床结构技术上的突破性进展当属90年代中期问世的并联机床(ParallelMachineTool),又称虚(拟)轴机床(VirtualAxisMachineTool)或并联运动学机器(ParallelKinematicsMachine)。并联机床实质上是机器人技术与机床结构技术结合的产物,其原型是并联机器人操作机。与实现等同功能的传统五坐标数控机床相比,并联机床具有如下优点:
刚度重量比大:因采用并联闭环静定或非静定杆系结构,且在准静态情况下,传动构件理论上为仅受拉压载荷的二力杆,故传动机构的单位重量具有很高的承载能力。
响应速度快:运动部件惯性的大幅度降低有效地改善了伺服控制器的动态品质,允许动平台获得很高的进给速度和加速度,因而特别适于各种高速数控作业。
环境适应性强:便于可重组和模块化设计,且可构成形式多样的布局和自由度组合。在动平台上安装刀具可进行多坐标铣、钻、磨、抛光,以及异型刀具刃磨等加工。装备机械手腕、高能束源或CCD摄像机等末端执行器,还可完成精密装配、特种加工与测量等作业。
技术附加值高:并联机床具有“硬件”简单,“软件”复杂的特点,是一种技术附加值很高的机电一体化产品,因此可望获得高额的经济回报。
目前,国际学术界和工程界对研究与开发并联机床非常重视,并于90年代中期相继推出结构形式各异的产品化样机。1994年在芝加哥国际机床博览会上,美国Ingersoll铣床公司、Giddings&Lewis公司和Hexal公司首次展出了称为“六足虫”(Hexapod)和“变异型”(VARIAX)的数控机床与加工中心,引起轰动。此后,英国Geodetic公司,俄罗斯Lapik公司,挪威Multicraft公司,日本丰田、日立、三菱等公司,瑞士ETZH和IFW研究所,瑞典NeosRobotics公司,丹麦Braunschweig公司,德国亚琛工业大学、汉诺威大学和斯图加特大学等单位也研制出不同结构形式的数控铣床、激光加工和水射流机床、坐标测量机和加工中心。与之相呼应,由美国Sandia国家实验室和国家标准局倡议,已于1996年专门成立了Hexapod用户协会,并在国际互联网上设立站点。近年来,与并联机床和并联机器人操作机有关的学术会议层出不穷,例如第47~49届CIRP年会、1998~1999年CIRA大会、ASME第25届机构学双年会、第10届TMM世界大会均有大量文章涉及这一领域。由美国国家科学基金会动议,1998年在意大利米兰召开了第一届国际并联运动学机器专题研讨会,并决定第二届研讨会于2000年在美国密执安大学举行。1994~1999年期间,在历次大型国际机床博览会上均有这类新型机床参展,并认为可望成为21世纪高速轻型数控加工的主力装备。
我国已将并联机床的研究与开发列入国家“九五”攻关计划和863高技术发展计划,相关基础理论研究连续得到国家自然科学基金和国家攀登计划的资助。部分高校还将并联机床的研发纳入教育部211工程重点建设项目,并得到地方政府部门的支持且吸引了机床骨干企业的参与。在国家自然科学基金委员会的支持下,中国大陆地区从事这方面研究的骨干力量,于1999年6月在清华大学召开了我国第一届并联机器人与并联机床设计理论与关键技术研讨会,对并联机床的发展现状、未来趋势以及亟待解决的问题进行了研讨。



 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号