履带拖拉机变速器的改进设计
履带拖拉机变速器的改进设计【优秀拖拉机变速器全套课程毕业设计含2张CAD图纸】
【带任务书+外文翻译】【34页@正文13900字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】.bat
任务书.doc
封皮.doc
履带拖拉机变速器的改进设计.doc
摘要.doc
目录.doc
英文翻译.doc
资料译文.doc
cad图集2张.dwg
任 务 书
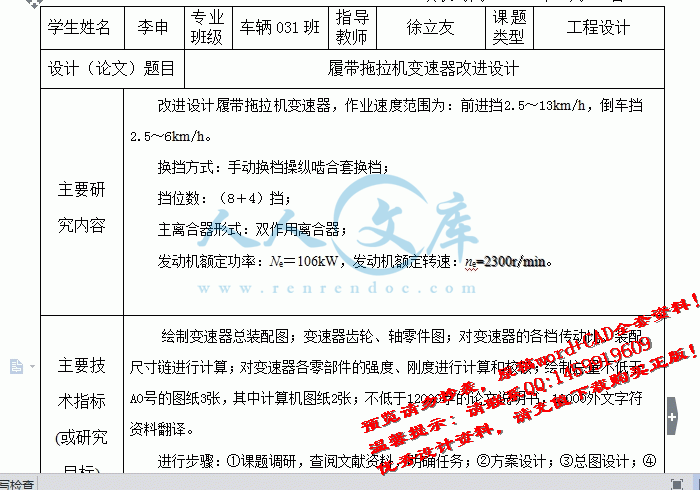
设计(论文)题目履带拖拉机变速器改进设计
主要研究内容改进设计履带拖拉机变速器,作业速度范围为:前进挡2.5~13km/h,倒车挡2.5~6km/h。
换挡方式:手动换档操纵啮合套换档;
挡位数:(8+4)挡;
主离合器形式:双作用离合器;
发动机额定功率:Ne=106kW,发动机额定转速:ne=2300r/min。
主要技术指标(或研究目标)绘制变速器总装配图;变速器齿轮、轴零件图;对变速器的各档传动比、装配尺寸链进行计算;对变速器各零部件的强度、刚度进行计算和校核;绘制总量不低于AO号的图纸3张,其中计算机图纸2张;不低于12000字的论文说明书,10000外文字符资料翻译。
进行步骤:①课题调研,查阅文献资料,明确任务;②方案设计;③总图设计;④
撰写论文:③毕业论文答辩。
进度计划①调查研究,熟悉设计内容,收集文献资料,时间占20%~25%(约2.0~3周);
②设计任务分析与实施方案的确定,写出开题报告;时间占3%~5%(约1周);
③实施设计、计算、绘图,论文起草时间占45%~50%(约6周);
④整理论文,时间占5%~8%(约1.5周);
⑤毕业论文答辩,时间占3%~5%(约1.5周)。
履带拖拉机变速器的改进设计
摘 要
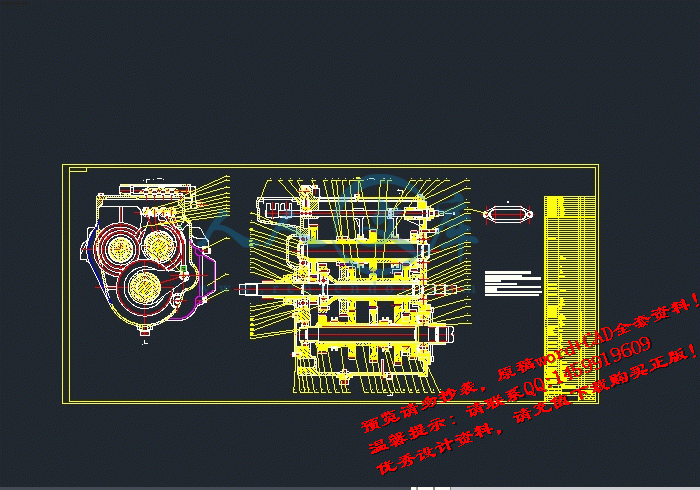
本篇文章详细介绍了本次的设计内容和设计思想,这次设计主要是在东方红拖拉机原型1302R变速器的基础上进行的分析改进,重点介绍了原型的设计不足和存在的问题,在分析履带拖拉机的工作环境和农业作业要求的基础上重新布置了传动比的分配,操纵机构的优化,啮合方式的改进,比如增加了传动比的范围,增加了低速作业挡,有利于拖拉机在复杂的环境工作,换挡方式由原来的直接拨动齿轮换挡变为啮合套换挡,使换挡更加方便、可靠,防止打齿。为了改善拖拉机的原地起步性能,该为双作用离合器的结构形式,使动力输出和传递轴在不同的时刻进行结合,这种按先、后依次结合的特点在农业生产中是很必要的。
对于结构设计采用结构紧凑的三轴式,在满足强度的基础上使结构紧凑,节省材料,对于齿轮的布置,尽量节省空间,布置合理。外形轮廓采用大量圆形弧线过渡,使铸造性能提高,结构合理,外形美观。在农业机械化的今天这种多挡位,随着农业的发展振兴,大功率的拖拉机还具有广阔的市场前景。
关键词: 啮合套, 双作用离合器,拖拉机,变速器
IMPROVED DESIGN OF THE TRACKED
TRACTOR TRANSMISSION
ABSTRACT
This article describes in detail the design of this content and design ideas. The design is mainly in the DFH 1302R prototype on the basis of the analysis improvements, focus on the prototype design deficiencies and the problems. Analysis of crawler tractor in the work environment and agriculture operations on the basis of a re-arrangement of the distribution of transmission ratio, manipulation of the optimization, and improving the mode of engagement are done, such as increasing the scope of the transmission ratio, increasing a low-speed operation block, and the favorable environment for the complex, shifting the original style of direct pull shift into gear meshing sets shift, shifting more convenient and reliable. In order to prevent tooth playing with greater impact and improve the tractor started in suit performance of the dual role of the structure of the clutch, the output power and transmission shaft in different light moment, and combining the features were in agricultural production is very necessary.
For structural design using compact three-axis, it can meet the compact structure, material savings. For gear settings, as far as possible to save space, a reasonable layout is done. Using contour shape of a large number of circular arc transitions so that the casting performance enhancement, reasonable structure, pleasing in appearance. Agricultural mechanization in the number of such gear today, with the development and revitalization of agriculture, high-power tractor, they have broad market prospects.
Key words : meshing sets, double-clutch, tractor,transmission
目 录
第一章 前言……………………………………………………1
第二章 履带拖拉机变速箱的改进方案的探讨与确定……2
§2.1 变速箱存在的问题………………………………………2
§2.2 变速器的功用………………………………………………2
§2.3 变速器的类型……………………………………………3
§2.4 变速器传动方案的确定…………………………………4
第三章 变速器的结构参数的设计及选择…………………………6
§3.1确定变速器的外形尺寸………………………………………6
§3.1.1变速箱齿轮中心距…………………………………………6
§3.1.2 变速箱的轴参数确定…………………………………6
§3.2 传动比的确定…………………………………………………7
§3.2.1 最高档传动比的选择………………………………………7
§3.2.2最低档传动比的确定………………………………………8
§3.3 变速箱齿轮设计计算…………………………………………9
§3.3.1齿轮的设计准则……………………………………………9
§3.3.2变速箱各档齿轮基本参数的选择…………………………10
§3.3.3 齿轮参数的计算………………………………………12
第四章 变速器齿轮的校核…………………………………………15
§4.1齿轮的损坏形式……………………………………………15
§4.2 轮齿弯曲强度计算……………………………………………15
§4 .3 齿轮接触应力计算……………………………………………17
第五章 变速器轴的强度校核…………………………………………19
§5.1轴的刚度校核……………………………………………19
§5.2 轴的刚度校核……………………………………………20
第六章 变速器轴承的校核 ……………………………………………22
第七章 变速器操纵机构的设计说明…………………………………23
§7.1 功用和要求…………………………………………………23
§7.2 换档机构…………………………………………………23
§7.3 锁定机构………………………………………………24
第八章 结论………………………………………………………27
参考文献…………………………………………………………28
致谢………………………………………………………………29
第一章 前 言
在拖拉机制造的多年发展历史中,变速箱的技术进步和水平一直处于举足轻重的地位。拖拉机性能的好坏,不仅取决于发动机,而且很大程度上依赖于变速器的性能。为有效的拖拉机的动力性和燃油经济性,以前直接拨动齿轮的两轴式变速器已经不能满足时代的发展要求,本设计就是根据拖拉机变速器存在的问题,进行的一次改进设计。
随着农业机械化的展开,各种大型农用机械车辆的使用越来越广泛。本设计东方红1302R履带拖拉机为为原形,以其的基本参数为依据,查阅相关资料,完成履带拖拉机变速器的相关设计,履带拖拉机车适用于在大型农场和工作量较大的农村作业,主要应用在深耕,旋耕,收获谷物,播种等农业生产场合。为此在动力性、通过性、工作稳定速度,可靠性,耐用,等方面对设计者提出了更高的要求!
我国是一个农业大国,拖拉机的制造和使用在数量上一直处于世界的前列,但其技术含量和发达国家相比差距较大,改变落后的拨齿换挡式变速器,提高工作效率和使用性能,进一步提高动力性和经济性,对我们国家来说具有重要的意义,对可持续发展战略具有深远的影响。但是本次设计只是在原有的基础上进行的改进,虽然变速器的性能有所提高,但是仍然同性能优良的国外变速器有很大差距。随着电子技术的发展,自动变速和电子控制的变速器必然成为主流。
为了满足这次变速器的设计要求,本人充分利用现代通讯工具、机械设计软件、导师资源等一切便利条件,收集资料,细心计算、积极与其他相关系统或总成的设计者沟通与交流。力求最后设计的产品能够达到:好造、好用、好看的目标。
参考文献
[1].机械电子工业部洛阳拖拉机研究所 主编.拖拉机设计手册(上册). 机械工业出版社,1994
[2].吉林工业大学,北京农机学院,洛阳农机学院等 合编.拖拉机底盘结构设计图册.北京:机械工业出版社,1974
[3].中国农业机械化科学研究所编.农业机械设计手册(上、下册).北京:中国工业出版社,1970
[4].彭文生,李志明,黄华梁 主编.机械设计.北京:高等教育出版社,2002.8
[5].梁正强 编.机械零件设计计算实例.北京:中国铁道出版社,1986
[6].吉林大学 王望予 主编.汽车设计第4版.北京:机械工业出版社,2004.8
[7].吉林工业大学诸文农 主编.底盘设计(上册).北京:机械工业出版社,1981
[8].清华大学 余志生 主编.汽车理论 第3版.机械工业出版社,2006
[9].华中农学院 主编.拖拉机汽车学 第四册 拖拉机理论.北京:农业出版社,1983
[10].华中农学院 主编.拖拉机汽车学 第二册 拖拉机汽车底盘构造.农业出版社,1983
[11].吉林大学 陈家瑞 主编.汽车构造第2版(下册).机械工业出版社,2006
[12].吴宗泽 主编.机械设计实用手册.化学工业出版社,1999
[13].江苏工学院 刘星荣 主编.拖拉机构造(下册).北京:机械工业出版社,1988
[14] 鲁智雄. 底盘构造与车辆理论. 北京:中国农业出版社,2005年98-101
[15] 刘小芳等.汽车工程手册设计篇.北京:人民交通出版社.2000年
[16] 机械设计手册编委会.机械设计手册.3版.北京:机械工业出版社,2004年,
[17]. 程悦荪 主编.拖拉机设计.北京:机械工业出版社,1989


 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号