液压机械变速箱闭式试验台设计
液压机械变速箱闭式试验台的设计【优秀试验台全套课程毕业设计含2张CAD图纸】
【带外文翻译】【37页@正文17200字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】
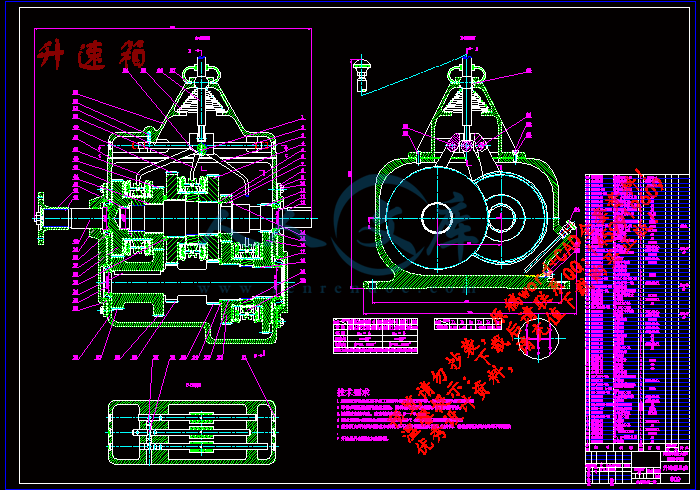
升速箱.dwg
摘要.doc
汽车发动机如何工作--中英文翻译.doc
液压机械变速箱闭式试验台设计.doc
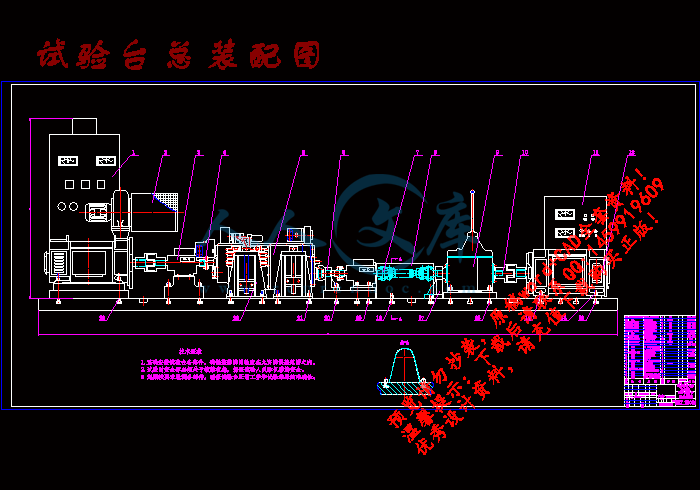
试验台总装配图.dwg
液压机械变速箱闭式试验台设计
摘 要
随着汽车工业的迅猛发展,变速箱作为汽车的重要传动部件,其操作性、传动性与安全性日显重要,为了缩短汽车变速箱的开发周期,降低研发成本,本论文以河南科技大学研发的1302R_HMT系统为基础,对液压机械变速箱的检测项目及检测方法进行了研究,设计和研发了“汽车变速箱性能检测系统”。本论文由以下几个部分组成:
1.系统的组成
试验台由直流电动机提供动力,利用快速安装机构定位、安装被测试的HMT;选NJ型转矩传感器作为力矩检测装置,选用直流发电机为加载装置,然后根据HMT的动力输出与加载装置的工作需求设计升速箱。
2.信号采集与处理
利用本校车动学院开发的PCM3132数据采集系统采集HMT的输入、输出转矩、转矩、油压、流量、温度等参数,为试验提供参考数据。通过A/D转换,由计算机屏幕显示。
根据以上分析,综合现有控制方案的特点的基础上给出了一种新型的变速箱试验台控制方案——直流电封闭机械传动试验台,并深入分析了其组成和工作原理,给出了硬件结构图和工作原理图,在此基础上根据模拟加载技术的要求提出了实现模拟加载功能的技术方案,对其中的一些关键环节进行了技术分析。该试验台实用性强,具有很高的推广价值。
关键词:功率封闭,电加载,变速箱,能量反馈
THE DESIGN OF THE DYNAMIC SIMULATION
BENCH FOR TRACTOR HYDRAULIC
MECHANICAL TRANSMISSION
ABSTRACT
With the rapid development of motorcar industries, the performance of gearbox is becoming more and more important. In order to shorten the development period of automatic transmissions of motorcar and reduce the research cost, this paper regards the HMT dynamic system of 1302R of Henan University of Science and Technology as the research background, and carried on a research about the test item and the method, then developed a test system for the performance of HMT. This article consists of several components below:
First, we introduce the system’s structure in general: the tester’s energy is provided by the direct current motive, making use of the quickly install equipment of fixed the position of HMT; choosing the NJ type’s torque equipment to test the torque, choosing the direct current generator as an add device, then design a gearbox according to the output power of the HMT.
Second, using the PCM3132 detecting the system’s oil pressure, controlling oil pressure, cooling flow or discharge etc, all these above parameters will contribute to diagnose the HMT. These signals can be output to the screen and displayed through an A/D change.
This paper introduces the components and working principle of the DC-power closed mechanical drive tester, on the basis of which the analog loading scheme of the DC power closed tester is presented an implemented, according to the requirement of analog loading technology. Some of the key links are described carefully. This test bench is useful and valuable to popularize.
KEY WORDS: Power closed, Electronically loading, Transmission, Energy return
目 录
摘要 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅Ⅰ—Ⅰ
Abstract ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅Ⅱ—Ⅱ
前言 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅3
第一章概 述┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅4
§1.1 设计(或研究)的依据或意义┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅4
§1.2 国内外同类设计(或同类研究)的概况 ┅┅┅┅4
§1.3 课题设计(或研究)的内容 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅5
第二章液压机械无级变速箱的结构原理及功用 ┅┅┅6
§2.1 液压机械变速箱的传动原理及其功用………………6
§2.2 液压机械变速箱的结构原理图…………………………7
第三章变速箱试验台设计方案研究 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅8
§3.1 试验台方案的确定 ………………………………………8
§3.2 试验台的组成及其基本功能 ………………………10
§3.3 试验台工作原理与HMT性能参数的测定 ………11
§3.4 动力输入(电动机) 的计算与选择…………………12
§3.5 联轴器的计算与设计 …………………………………15
§3.6 变速箱快速安装机构设计 ……………………………18
§3.7 传动机构的计算与设计…………………………………19
§3.8 加载装置(发电机)的计算与选择 ………………20
§3.9 试验台所用传感器的选择………………………………20
第四章升速箱的计算与设计┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅23
§4.1 升速箱的概述…………………………………………………23
§4.2 齿轮组的设计与校核 ………………………………………24
§4.3 轴的设计与校核 ……………………………………………29
§4.4 轴承的计算与选择……………………………………………29
§4.5 键的计算与选择 ……………………………………………30
§4.6 同步器的设计 …………………………………………………31
设计总结┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅33
§1.1 本次设计主要工作 ………………………………………33
§1.2 本次设计创新点………………………………………………33
参考文献 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅34
致谢 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅35
附录 ┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅┅36
前 言
车辆传动试验台是对车辆传动系的主要传动部件和装置变速器、差速与转向部件等进行综合性能测试的试验设备。通过试验来检验传动装置设计的合理性,加工、制造、装配和调试的工艺性。对试验结果的深入分析有助于了解和评定传动部件和装置的综合机械性能,同时也为工程设计人员提供实践的参考资料和设计依据。随着车辆传动系向高速比、大功率、低噪声等方向的飞速发展,人们对于车辆传动系的性能提出了更高的要求,因此,对传动试验台的深入研究具有重要的实际应用意义。
国外较早地开始了这方面的研究,如除美国Gleason公司在五十年代就设计出的用轮系作为加载系统的传动试验台的方案之外,比较著名的还有美国国家航空航天局(NASA)下属的Lewis研究中心、前苏联中央机械制造与设计研究院、美国通用动力公司、德国RENK公司、日本明电舍动力公司、日本丰田汽车公司、美国伊利诺斯大学机械工程系、法国Skoda公司等。从试验台方案的设计到最终的样品制造他们都进行了大量的研究工作,形成了系列化的设计模式。
参考文献
1.王祖麟、张振利 电加载变速箱试验台的设计《中国期刊网》2004.5.20
2.潘清明、刘启新 直流发电机自动稳压系统《中国期刊网》2000.9
3.王志鹏、马孝江等 汽车变速箱性能检测系统的设计《中国期刊网》2002.01
4.崔亚辉、马朝锋等 直流电封闭机械传动试验台模拟加载功能的设计《中国期刊网》2004.02
5.曾洁、张育华 车用自动变速器检测试验台的研制《中国期刊网》2004.06
6.《机械零件设计手册》 东北大学《机械零件设计手册》编写组 编
冶金工业出版社 1994年4月第三版
7.《电机与拖动基础》 许建国 主编
高等教育出版社 2004年8月第一版
8.《传感器、变送器、测控仪表大全》 徐学峰 主编
机械工业出版社1998年5月第一版
9.《机械设计课程设计》 席伟光、杨光、李波 主编
高等教育出版社2003年2月第一版
10.《机械制图》 刘小年 主编
机械工业出版社1999年5月第二版
11.《机械设计》 彭文生、李志明、黄华梁 主编
高等教育出版社2002年8月第一版
12.《互换性与测量技术基础》 陈于萍 主编
机械工业出版社2002年2月第一版
13.《工程力学》 陈殿云 主编
兰州大学出版社2003年5月第一版
14.《汽车构造》上、下册 吉林大学 陈家瑞 主编
机械工业出版社2005年3月第二版
15.《汽车设计》 吉林工业大学 王望予 主编
机械工业出版社2002年6月第三版
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号