液压机械传动开式试验台设计
液压机械传动开式试验台的设计【优秀试验台全套课程毕业设计含4张CAD图纸】
【带任务书+外文翻译】【39页@正文17500字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】
任务书.doc
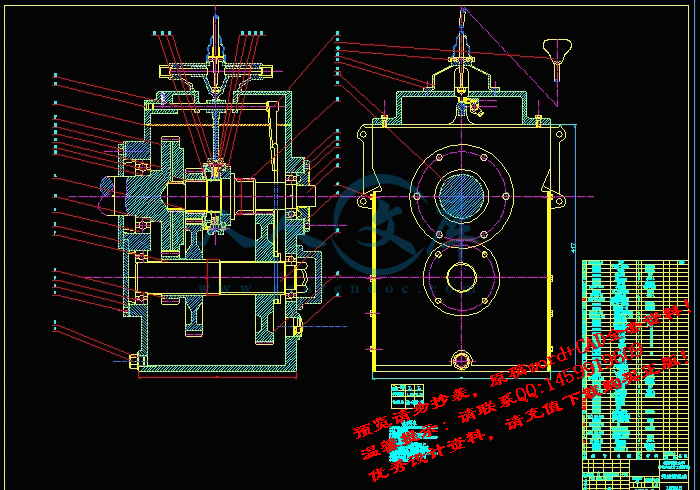
升速箱总成图.dwg
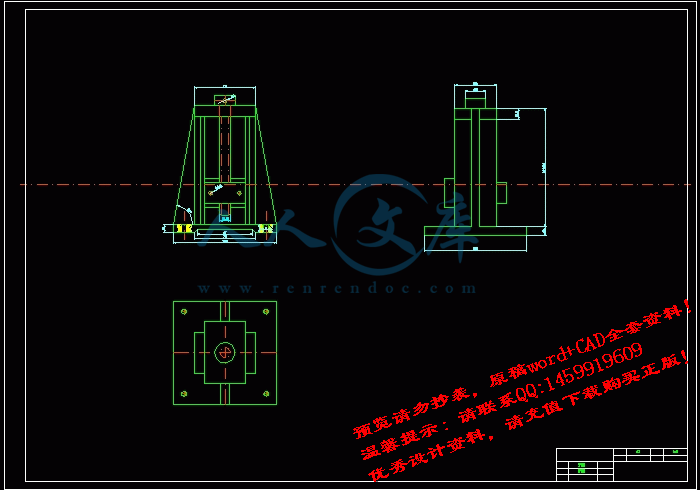
夹具.dwg
差速器和车桥--中英文翻译.doc
液压机械传动开式试验台设计.doc
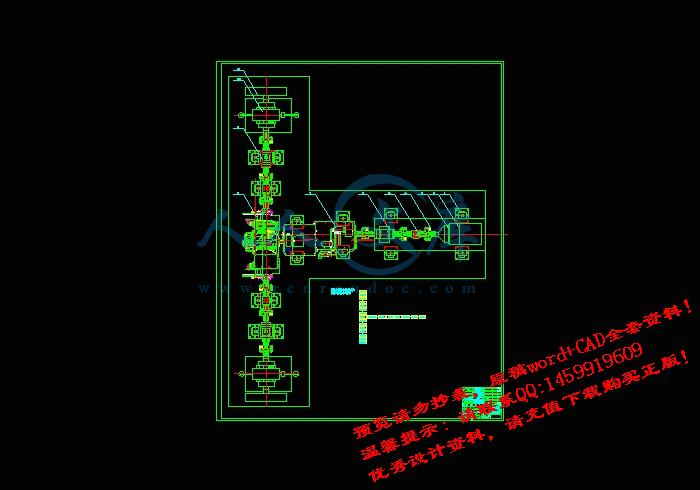
装配俯视图.dwg
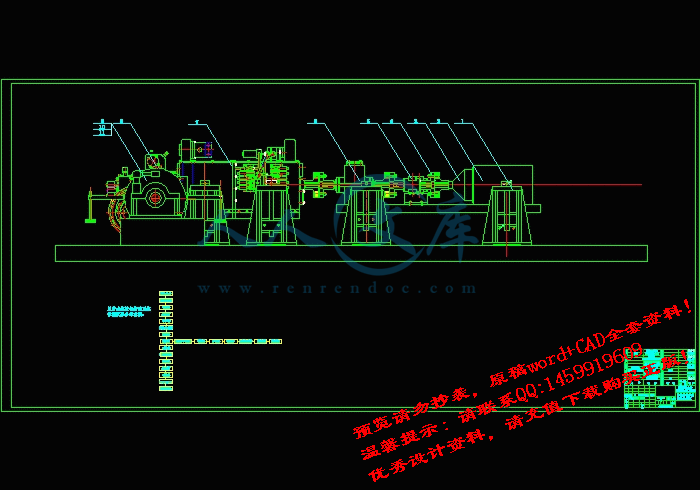
装配图.dwg
驾驶模拟器 防抱制动系统(ABS)--文献翻译.doc
液压机械传动开式试验台设计
任 务 书
设计(论文)题目液压机械传动系统开式试验台
主要研
究内容新型传动系统性能试验台;汽车、拖拉机燃油经济性的测试等。
试验台吸收功率:200KW,转速200~3000转/分
对试验台的试验原理进行设计,选择电涡流测功机为功率吸收装置和其他组件;设计或选择升速装置;
数据采集和处理利用车辆研究所开发的数据采集系统。
主要技
术指标(或研究目标)绘制实验台的总体布置图;对总体参数进行计算;
绘制总量不低于A0号的图纸3张,其中计算机图纸1张;
不低于12000字的设计计算说明书,10000外文字符资料翻译;
设计步骤:
①课题调研,查阅文献资料,明确设计任务;②选择设计方案;③总体设计④详细设计⑤撰写设计说明书;⑥毕业设计答辩。
进度计划①调查研究,熟悉设计内容,收集文献,时间占10%(约1周)
②实际任务分析与实施方案的确定,写出开题报告;时间占10%(约1周)
③实施设计、计算、绘图,论文起草时间占45%~50%(约5周)
④整理论文,时间占10%(约1周)
摘要
燃油经济性和较少的有害气体排放和日益增大的舒适性等要求是现代汽车十分重要的研究课题. 液压机械差速转向机构是利用液压机械无级传动原理,将液压传动与齿轮传动恰当组合的一种新型封闭双功率流传动机构。本文介绍了机——电——液一体化动态仿真试验台的系统结构及性能特点。讨论了系统的动态性能及恒转速控制的原理和基本规律。对部分试验和理论结果进行了分析和研究,分析了车辆动力传动试验台机械测功器的结构和工作原理,提出了机械测功器的控制方案,并进行了仿真计算。针对已有机械传动系统试验台存在的局限性提出了适合于不同传动形式及测试要求的多功能试验台的设计思路,对所涉及的多功能试验台的组成和工作原理进行了分析讨论,给出了不同组合形式时试验台结构及测试控制方法。计算表明,合理的选择可以使测功器获得较好的动态特性。试验结果表明该系统运行稳定、加载方便、节能效果显著,满足了设计的要求。
关键词: 车辆传动,动力传动试验台,性能分析,惯量模拟
Structure and performance Analysis of the Dynamic
Simulation Bench for Vehicle Transmission System
ABSTRACT
To satisfy the demand for greeted fuel economy, fewerem jssion and enhanced comfort, which are very important themes for modern automat boilers.The bydro-mechanical differential turning mechanism using hydro-mechanical infinite transmission theory is the new close double flow transmission mechanism being suitably made up of hydraulic transmission and gear transmission.This paper introduces the structure and performance characteristics of an integrated electro-hydro-mechanical control system of the dynamic simulation bench for vehicle transmission. The dynamic performance and the theory and basic law of the constant speed control are discussed.Some theoretical and experimental results are analyzed.The construction and working principles of a power-trans mission test bench and a mechanical dynamometer analyzed .Control policy about the mechanical dynamometer is described,then the matching method of the control system and the pivotal parameter are gained. Dynamic analysis of this model is finally demonstrated in detail。This paper analyses and discusses both composition of the multifunction test and operating principle,and presents test, method of cont to and structures of various combining test .A design idea of multifunction test bed is put forward which is suitable for different driving form and test requirement.The test results show that system runs steadily,saves energy remarkably,loads conveniently, andsatisfies requirement of design。
Keywords: Vehicle transmission,Test bench,Performance analysis,Inertia simulat
前 言
近几年来,我国的工程车辆工业发展迅猛,而随着汽车工业的崛起也伴随着对于产品的实验与检测手段的落后。尤其是目前,我国制造汽车尚在起始阶段,还不成熟.但作为经济发展支柱的汽车工业,必然要在当今技术潮流中疾进,而以后汽车传动系统发展方向是以自动变速器技术(自动变速器和液压机械转向装置)为核心,所以为了给汽车自动传动产品完善设计理念、交检产品性能,控制产品的质量,提高汽车的品质,势必对其零部件提出更高更严格的要求。传动系是汽车实现发动机动力输出到行驶的必须系统,变速器是汽车传动系中一个重要总成,为了对变速器产品结构和零部件的性能、寿命进行测试和分析。为产品设计与质量评价提供可靠的科学依据,缩短产品的开发周期和提高产品质量;避免在用户使用中出现质量问题,减少售后服务的工作量,节约资金,降低成本,提高产品的市场信誉度。所以传动系统试验台的研究将为汽车、拖拉机的新技术改造提供试验平台,有力推动农业机械行业科研水平的提高具有特别重要的意义。
车辆传动系是车辆的重要组成部分,其作用不仅是为了实现减速(或者增速)、转换系统的运动传递路线、使各运动构件协调配合工作;同时还把原动机输出的功率和转矩传递到驱动轮、或者其它执行机构上克服行驶阻力或工作阻力而做功。实现传动路线、传动方向的转换和传递动力是车辆传动系的两个基本任务。
1传统系统结构介绍及功用
传统的履带式车辆传动系和汽车传动系相似,主要由用于切断动力的离合器、变换档位的变速器、起主要减速作用的主减速器、起差速作用的差速器、轮边差速及用于转向的轮边制动器组成;现代履带车辆传动系不断采用新技术、新结构,经过多年的发展和改进,逐步形成了现代履带车辆传动系。现代履带车辆传动系,将液压机械无级变速传动技术应用于变速机构取代了原来的离合器与固定轴式齿轮箱组成的变速机构,其中以双(多)功率流多段无级变速传动为代表;差速及转向装置由液压机械复合转向取代,形成主要由行星排和液压马达、液压泵组成的液压机械连续无级传动的复合转向。
液压机械无级变速传动以液压机械式无级自动变速器(HMT)为主,主要由多档自动变速器、液压变量泵和定量马达构成的液压变速装置、将机械和液压动力合成的行星齿轮机构三部分构成。液压机械传动是一种液压功率流与机械功率流并联的新型传动形式,通过机械传动实现传动高效率,通过液压传动与机械传动相结合实现机械传动无级变速。与传统的机械式变速器相比,液压机械式无级自动变速器有以下特点:
①能自动适应负荷和行驶阻力的变化,实现无级调速,保证发动机工作在最佳工作点,有利于提高其动力性、燃油经济性和工作效率。
②以液体为传力介质,使传动系动载大为减轻,易防止超载和发动机熄火,可大大提高有关零部件的寿命,对工作条件恶劣的农业机械和工程机械尤为重要。
③行驶平稳,能吸收衰减振动、冲击和噪声,提高乘坐舒适性。
④能以很低的车速稳定行驶,可提高坏路上的通过性和低速作业质量。
⑤操作轻便,便于实现换档自动化,降低驾驶员劳动强度。
⑥体积小,重量轻,惯性小,结构紧凑,节省材料,易于布置。
国外实际试验资料表明:装备无级自动变速器的拖拉机的作业性能显著提高,不仅能降低操作强度,提高车辆作业速度,改善作业质量,而且可以大幅度提高拖拉机的动力性和燃油经济性,统计对比数据表明生产效率提高12~16%,燃油消耗率降低8~10%,具有明显经济性,并减少了排放。
有此可见液压机械无级变速传动系统有着很广阔的市场,它不仅提高了工作效率,而且改善了驾驶员工作的环境。车辆传动试验台是对车辆传动系的主要传动部件和装置变速器、差速与转向部件等进行综合性能测试的试验设备。通过试验来检验传动装置设计的合理性,加工、制造、装配和调试的工艺性。对试验结果的深入分析有助于了解和评定传动部件和装置的综合机械性能,同时也为工程设计人员提供实践的参考资料和设计依据。随着车辆传动系向高速比、大功率、低噪声等方向的飞速发展,人们对于车辆传动系的性能提出了更高的要求,因此,对传动试验台的深入研究具有重要的实际应用意义。
参考文献
[1] 刘惟信.《汽车设计》.清华大学出版社,2001年
[2] 张文春.《车辆传动试验台论证报告》 .河南科技大学 ,2004年
[3] 机械工程手册编辑委员会.《机械工程手册》.机械工业出版社,1997
[4] 彭文生.《机械设计》.高等教育出版社,2003年
[5] 刘惟信.张宁一.《汽车转向机构设计的研究》.北京汽车,1991
[6] 刘惟信,吴明常.《同步器优化设计的研究》.汽车工程,1990
[7] 李伟,刘惟信.《汽车四档变速器的设计》.当代汽车,1987
[8] 葛安林.《车辆自动变速理论与设计》北京:机械工业出版社,1993
[9] 刘惟信.《圆锥齿轮与双曲面齿轮传动》.北京:人民交通出版社出版,1993
[10] 刘惟信.《机械可靠性设计》北京:清华大学出版社,1994
[11] 陈家瑞.《汽车构造》.北京:人民交通出版社,1993
[12] 张洪欣.《汽车设计》.北京:机械工业出版社,1989
[13] 余志生.《汽车理论》.北京:机械工业出版社,1981
[14] 刘惟信,戈平,李伟.《汽车发动机与传动系参数最优匹配的研究》.汽车工程,1991
[15] 戈平,刘惟信.《汽车发动机与传动系的匹配分析和优化设计》.汽车技术,1993


 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号