SY5190THB 25混凝土输送泵车液压系统设计
混凝土输送泵车液压系统设计全套课程毕业设计
SY5190THB 25混凝土输送泵车液压系统设计【优秀含16张CAD图纸课程毕业设计】
【带任务书+开题报告+课题申报表+评阅表+外文翻译】【54页@正文25600字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】
S管阀A0 A3.dwg
中英文.doc
任务书.doc
任务书1.doc
内容提要.doc
封面.doc
封面1.doc
开题报告1.doc
开题报告书.doc
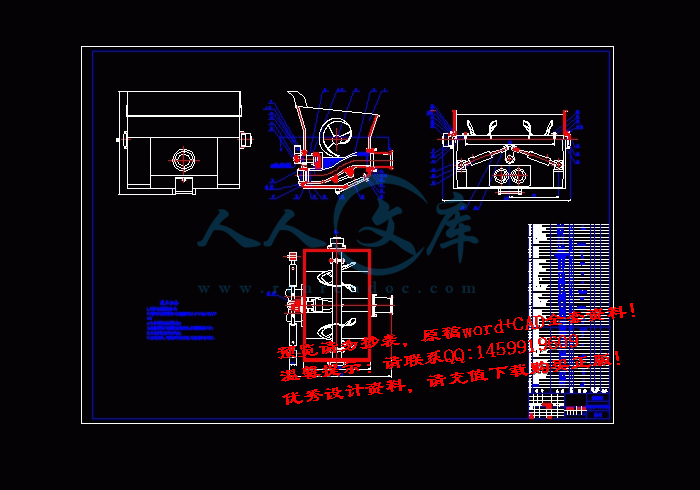
搅拌料斗A1.dwg
搅拌轴A2.dwg
搅拌轴及搅拌叶片.dwg
摆动杆A3.dwg
正文.doc
泵车分配液压原理图A3.dwg
泵车搅拌回路液压原理图A3.dwg
泵车泵送回路液压原理图A2.dwg
泵车液压原理图A2.dwg
泵车臂架系统液压原理图A2.dwg
目录.doc
眼镜板A2.dwg
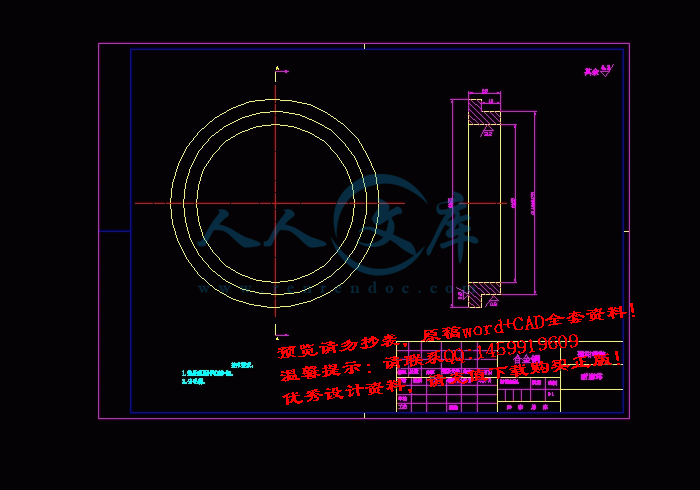
端盖A3.dwg
评阅表.doc
课题申报表.doc
轴A4.dwg
轴瓦A4.dwg
进度考核表.doc
附件封面.doc
马达座A3.dwg
高低压切换回路液压原理图A3.dwg
任务书
课题名称SY5190THB 25混凝土输送泵车液压系统设计
一、课题研究的目的与主要内容
二、目的:
培养学生综合运用所学知识的能力,能够独力的解决较为简单的工程问题,树立正确的设计思想的工作作风。本课题是SY5190THB 25混凝土输送泵车液压系统设计,该课题来源于三一集团,通过课余时间参观学习和实地考察,给毕业设计提供参考。具体要求通过毕业设计使学生用所学的知识解决实际问题,培养学生理论联系实际的能力。
主要内容:
第一部分:指出混凝土泵车液压系统需要满足的技术要求。
第二部分:对泵的理论输送量、泵送混凝土额定压力、泵送能力指数进行分析,在此基础上对液压系统进行设计。
第三部分:详细说明各功能实现回路的原理。
三、基本要求
1.独立完成相关设计原理图。
2.按学院毕业设计的编写规格要求,撰写设计说明书(1~2万字)。
3.完成与设计有关的3000—5000个字的外文资料翻译,译文要求准确,语言流畅。
2.此表1式3份,学生、系、教务处各1份。
三、课题研究已具备的条件(包括实验室、主要仪器设备、参考资料)
现具有《机械设计手册》、《液压传动与气压传动》、《电子技术》、《零件设计手册》等相关资料和液压泵、液压阀等液压元件的相关资料。除了以上的资料,还有AUTOCAD、PRO/E、OFFICE等相关的绘图软件和工作软件。
内容提要
混凝土泵车作为我国工程机械的主力机种,被广泛应用于浇注混凝土施工作业中。泵车的核心技术就是液压系统的设计,由于泵车的工作条件恶劣,要求实现的动作较复杂,于是对液压系统的设计提出了较高要求,其液压系统也是工程机械液压系统中较为复杂的。因此,对泵车液压系统的分析设计对推动我国泵车发展具有十分重要的意义。
本次设计的课题是SY5190THB 25混凝土输送泵车液压系统设计,内容首先陈述了课题提出的背景,分析了泵车的发展趋势及市场需求,再对泵车的基本构造进行确定。通过对泵车液压系统总体分析设计了开式回路,制定了液压系统工作原理图和各回路液压系统工作原理图。最后完成对泵送机构进行设计与计算和配套件选型。
此设计在整体上结构布局合理,液压元件的选择和使用具有较好的经济性和实用性,并且性能方面得到了最好的发挥。
Summary
Concrete pump as the main force of China's construction machinery models, are widely used in concrete pouring operations. The core technology is the hydraulic pump system design. As the truck's poor working conditions, requested action to achieve more complex, so the design of the hydraulic system put forward high requirements, its hydraulic system in the hydraulic system is more complex. Therefore, pump hydraulic system analysis and design of the pump to promote the development of China is of great significance.
This design issue is the design of the hydraulic system pump of SY5190THB 25,The contents of the first statement of the issues raised in the background, Analysis of the pump and market demand trends, Then the basic structure of the pump were determined. On-pump hydraulic system analysis and design of the overall open circuit, developing the work of the hydraulic system and the circuit schematic diagram of hydraulic system work. Finally completed the design and calculation of pump body and accessories selection.
The design on the whole reasonable structure, selection and use of hydraulic components has a better economy and practicality, and performance was the best play.
目录
内容提要……… ……………………… ……………………………..Ⅰ
SUMMARY … …………… ………………………………………....…..Ⅱ
1 前言………………………… ……………………………....… .. .. 1
1.1 课题提出的背景…………… ……………………………………1
1.2 泵车的分类………………………………………….. ……. …. ..4
1.3 泵车的功用…………… …………..………………….. ….. .. .. ..6
1.4 泵车的发展趋势……………….. ……… ………….. ….. .. .. .. ..7
2 泵送机构的基本构造及工作原理……… ………… ……………. .9
2.1 混凝土泵车的基本构成………… ……………… ………. …. ...9
2.2 泵送机构……………. ………………………… …… …. …. ... .9
2.3 分配机构…………………………….. …………………. …. ....10
2.4 清洗机构………………….. ……….. ……… …………. …. ....10
2.5 料斗与搅拌机构………….. ……….. ……… …………. …. ....11
3 液压系统设计………………… …………………. …. .... …….. ..13
3.1 液压系统发展前景………………………………. ………. .......13
3.2 液压系统的设计及步骤要求……………….. …… …. …. .......14
3.3 液压系统图的拟定………………………………. ………. .......15
3.4 液压系统图的绘制………………………………. ………. .......17
3.5 液压系统动作说明………………………………. ………. .......18
4 混凝土泵缸摆动系统计算…………………………………………26
4.1混凝土泵分配阀……………………………………………………26
4.2料斗与搅拌系统……………………………………………………31
4.3管阀及摆动阻力矩设计…………………………………………..36
4.4摆动系统设计计算…………………………………..…………..41
5 液压成品件列表……………………… …….…………… .....…....45
5.1 液压阀的选择………………………………. .. ..…… .....……...45
5.2 液压元件成品列表…………………… …………. ………. .......45
总 结………………………………………………………...….…47
参考文献……………………………………………………………….48
致谢…………………………………………..…………………….…49
1 前言
混凝土泵车是输送混凝土的施工设备,具有行驶、泵送、布料三种功能为一体的一种机械设备,自带底盘和布料臂架,具有机动灵活、方便高效、安全环保施工强度低等特点,它能一次性完成水平运输和垂直运输,它安装有运动和动力传动装置、泵送和搅拌装置以及其他一些辅助装置。混凝土泵车通过动力装置的动力传给液压泵,液压泵推动活塞带动混凝土泵工作。然后利用布料机和输送管,将混凝土输送到一定的高度和距离。在作业中,混凝土泵车的动力装置的动力驱动泵送机构、搅拌机构、分配机构和臂架机构等工作装置。而液压系统作为泵车最重要组成部分,随着施工要求的提高,人们对液压系统的要求也越来越高。
参考文献
[1] THE DESIGN AND ANALYSIS OF VIBRATIONSTRUCTURE OF VERTICAL DYNAM ICBALANCING M ACHINE
[2] 成大先. 机械设计手册. 第四版 [M] 北京:化学工业出版社,2002
[3] 申永胜. 机械原理教程 [M]. 北京:清华大学出版社,1999
[4] 刘鸿文 材料力学. 北京:高等教育出版社,1992
[5] 贾培起. 液压缸. 北京:科学技术出版社,1987
[6] 何存兴 张铁华 液压传动与气压传动. 第二版. 武汉:华中科技大学出版社,2000
[7] 机械零件设计手册编写组 . 机械零件设计手册[M] . 北京:冶金工业出版社,1979
[8] 张富洲. 机械设计课程设计[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,1993
[9] 黄凤云.工程材料及应用[M] . 武汉:华中理工大学出版社,1999.10
[10] 雷天觉.液压工程手册[M] . 北京:机械工业出版社,1990
[11] 上海第二工业大学液压教研室. 液压传动与控制[M] . 北京:机械工业出版社,1993
[12] 刘鸿文,材料力学[M] .高等到教育出版社





















 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号