目录
第1章 概述 1
1.1课题的提出 1
1.1.1课题产生的背景 1
1.1.2 课题的意义 1
1.2国内外实验机研究的回顾、现状及发展趋势 2
1.2.1国内外试验机发展及其趋势 2
1.2.1国内外各种实验机的介绍 5
1.3课题的内容: 7
第2章 万能材料试验机总体设计 9
2.1加载方式 9
2.2 试验机式样的选择 9
2.3传动方式的对比与选择 9
第3章 运动动力设计与验算 14
3.1滚珠丝杠副的运动动力设计计算 14
3.1.1静载荷条件 14
3.1.2丝杠寿命计算 15
3.1.3丝杠强度计算 15
3.1.4丝杠的稳定性 16
3.1.5丝杠的刚度 17
3.1.6丝杠的传动效率功率 19
3.1.7滚珠丝杠几何参数 19
3.2电机的选择 20
3.3各轴功率,转速,转矩的计算 21
3.4各级传动的设计计算 21
3.4.1带传动设计计算(同步) 21
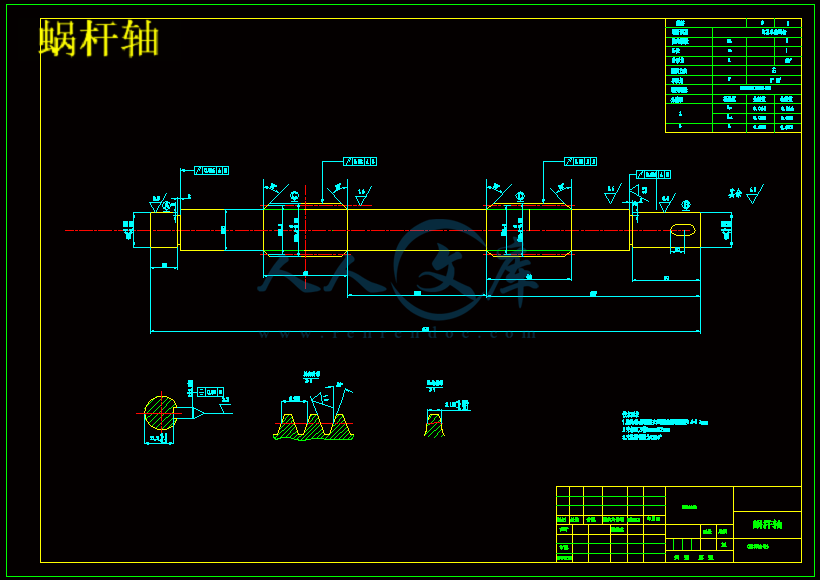
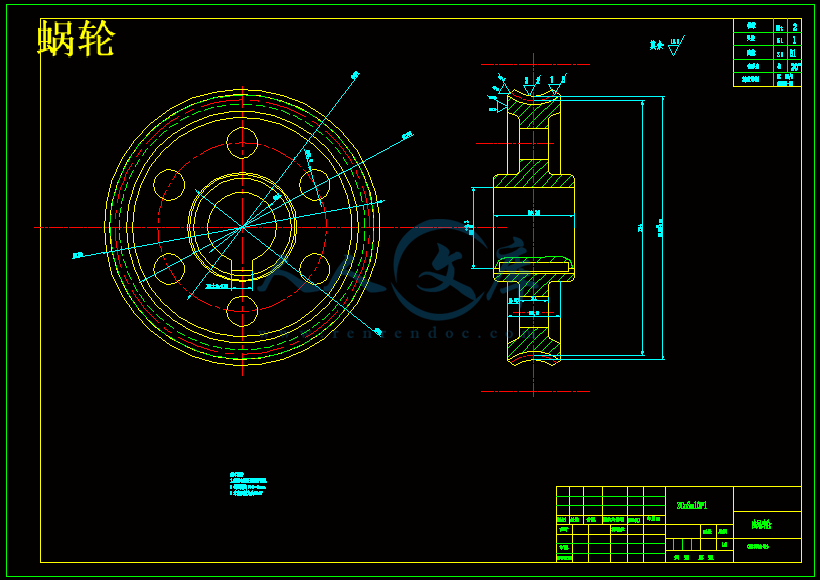
3.4.2蜗轮蜗杆减速器的计算 22
3.5支撑滚珠丝杠的轴承的选择及验算 26
3.6动静横梁变形的验算 28
3.6.1动横梁变形的验算 28
3.6.2静横梁变形的验算 29
第4章 总结 31
参考文献: 32
摘 要
试验机是在各种条件、环境下测定金属材料、非金属材料、机械零件、工程结构等的机械性能、工艺性能、内部缺陷和校验旋转零部件动态不平衡量的精密测试仪器,可以对材料进行拉伸、压缩、弯曲、剪切、扭转、冲击、疲劳、蠕变、持久、松弛、磨损、硬度等试验。近年来,试验机行业技术突飞猛进。试验机向着两个方向即超微外力检测与超大外力检测发展。高检测精度、高灵敏度、运动平稳、易于操纵是目前试验机的主要发展方向。
本文首先概述了试验机的基本定义、分类与国内外一些重要生产商的成果。第二部分论述了所想到的四种方案并对这些方案优缺点作了分析和对比。在彼此比较后决定选第一种方案。第三部分则是说明了试验机的主要机械传动部分的设计以及对它们的校核过程。试验机的传动部分主要由蜗轮蜗杆、皮带、滚珠丝杠三部分组成。经过校核后所有设计均符合要求。在文章的最后简明的介绍了做本次毕业设计的一些心得体会。
关键词 试验机;蜗轮蜗杆;齿形带;滚珠丝杆;
ABSTRACT
Test machine in various conditions and environment in metal materials, non-metallic materials, machinery accessory, engineering structures such as mechanical properties, technics performance, Internal defects and checking dynamic imbalance rotating parts of sophisticated testing equipment, such as materials tension, compression, bending, shear, reversing, impact, fatigue, creep, lasting and relaxation, wear, hardness tests. In recent years,the technic of the test machine industry advances rapidly. Test machine is the direction toward the development of the super-tiny force detection and the development of super-large external force testing. Detection of high-precision, high sensitivity, smooth motion, easily operated test machine is the main development direction presently.
This paper first summarizes the test machine's basic definition, classification, and some important domestic and foreign manufacturers results. The second part, discussing about the experiences of the four projects as well as advantages and disadvantages of these projects are analyzed and compared . In comparison with each other decide the first option. The third part is the experiment, the major part of the mechanical drive design and the process of checking them. The main drive system of the test machine includes the worm, toothed belts, ball screw three components. After checking all the design had complied with the request. In the end concisely introduce the meeting and what had learned in the graduate design experiences.
Keywords: Test Machine, Worm Gear & Worm,Toothed Belts,Ball Screws,
第1章 概述
1.1课题的提出
1.1.1课题产生的背景
作为专业本科毕业生,为了能在走上工作岗位之后更快地进入职业角色、我们需要在通过毕业设计这一环节初步地将自己在大学四年中所学习到的知识应用到实践中去。所以在指导老师的引导之下,我选择了万能材料试验机设计这个题目。
1.1.2 课题的意义
通常,把测定材料机械性能的仪器和设备称为材料试验机。但是,有些国家有时把测定材料物理性能(甚至化学性能)的仪器和设备也称为材料试验机。
国外,在工业比较发达的国家中,对于试验机的研制和生产,都是比较重视的。这是因为,材料试验机作为一个基础工业部门,对于工业生产和科研工作有直接的不容忽视的影响。
实际上,对于工业生产和各种工程设计来说,材料试验机是确保各种机器,车辆,船舶和结构物的合理设计与安全运行的重要测试设备。因为,为了既经济又安全可靠地从事各种工程设计,必须根据材料的机械性能选取合适的材料。否则,可能造成浪费,或者导致发生严重的事故。而要获得准确的材料机械性能数据,只有使用材料试验机。
在工业生产特别是军事工业生产中,为了保证产品质量,常常需要对各种材料和零部件或整机进行检定和测试。许多重要性的热处理零部件,如轧钢机的钢辊,机器的主轴和汽车的连杆等,都要百分之百的进行硬度检定。
在冶金工业生产中,随着科学技术的飞速发展,也提出了许多新问题。例如现代技术的发展,需要一些具有特殊性能的,能在高温,低温,高压,高速以及各种复杂条件下工作的材料,因此必须研制新型材料与合金。钢铁厂生的钢材,也需要随时检验。显而易见,所有这些研究和检验工作,离开材料试验机是无法进行的。
上述几点,已足以说明材料试验机的发展对航空,冶金,机械,建筑和造船等工业部门,在合理设计工程结构,节约材料,提高产品质量,改进工艺和降低成本方面具有重要的意义。





 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号