【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
以下预览截图到的都有源文件,图纸是CAD,文档是WORD,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
摘要:CA6140车床作为主要的车削加工机床,在机械加工行业中得到了普遍的应用。CA6140车床主轴箱的主要功用是支撑并且传动主轴,使车床的主轴带动工件用特定的转速转动。本次毕业设计运用计算、验算、实验等方法,确定了运动方案和实现结构优化设计,通过功能设计与计算,运用Solidworks三维软件完成了零部件的建模与装配、实现装配动态仿真。将CA6140车床主轴箱的内部结构以及工作原理,更生动形象的表达出来。
关键词:CA6140机床主轴箱;建模与装配;三维结构设计;运动仿真
Three dimensional design and Simulation of the transmission of the CA6140 lathe main axle box
Abstract:The CA6140 lathe as the main turning processing machine tool, has been popular applied in the manufacturing industry. The main function of CA6140 lathe headstock is the support and transmission shaft, the lathe spindle drives the workpiece rotate with the prescribed speed. The design is based on the computation, analogy and experimental methods, completed to determine the motion scheme and structure design, the design and calculation, modeling and assembly, using Solidworks 3D software complete parts assembly,dynamic display. the internal structure of CA6140 lathe headstock and working principle, more vivid image expression。
Keywords: CA6140 machine; headstock; dimensional animation
目 录
摘要…………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅰ
Abstrat ……………………………………………………………………………………Ⅱ
目录…………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅲ
1 绪论..................................................................1
1.1 研究意义.............................................................1
1.2 研究现状.............................................................1
1.3 课题研究内容与方法...................................................1
1.4 设计方案可行性分析...................................................2
1.5 小结.................................................................2
2 总体设计方案..........................................................3
2.1 主轴箱的组成和特点...................................................3
2.2 主轴箱的主要参数.....................................................3
2.3 传动系统及其方案的确定...............................................4
3 车床主轴箱的设计计算..................................................6
3.1 主轴箱的箱体.........................................................6
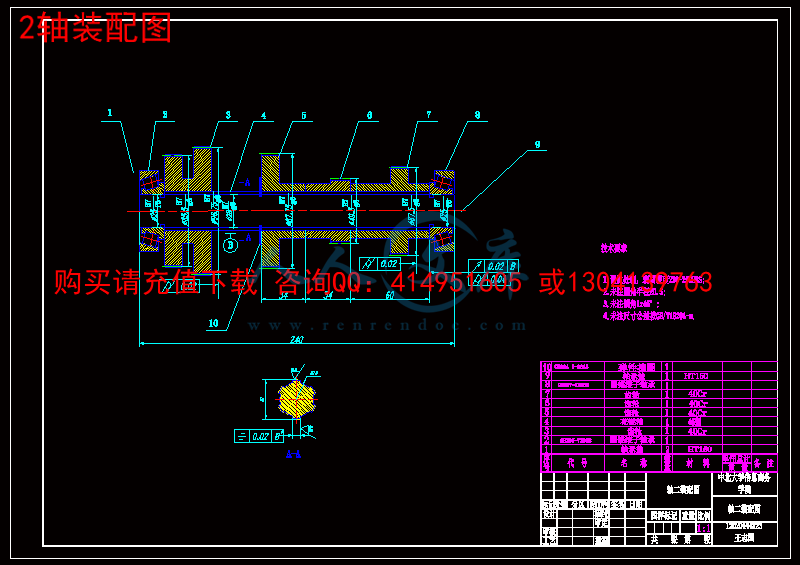
3.2 Ⅰ轴主要零件设计计算.................................................7
3.3 Ⅱ轴主要零件设计计算................................................16
3.4 Ⅲ轴主要零件设计计算................................................22
3.5 Ⅳ轴主要零件设计计算................................................28
3.6 Ⅴ轴主要零件设计计算................................................31
3.7 Ⅵ轴主要零件设计计算................................................34
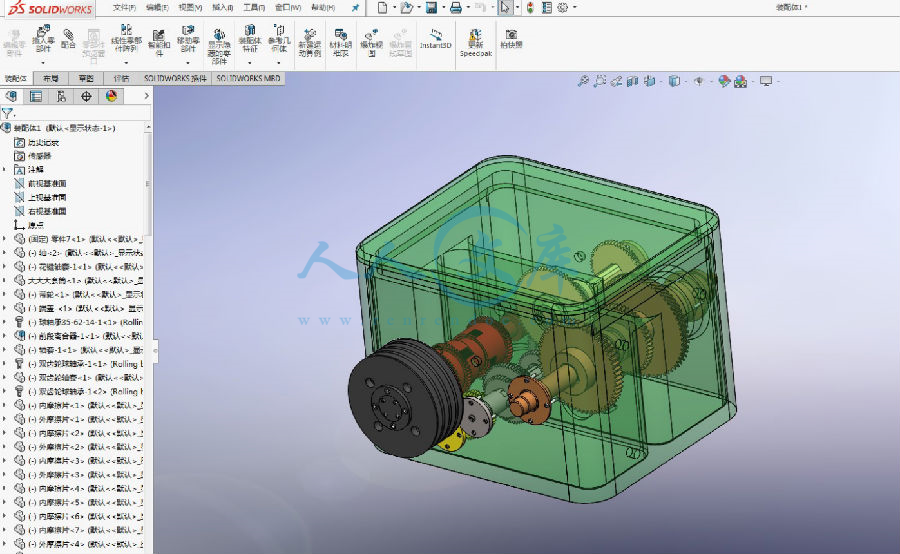
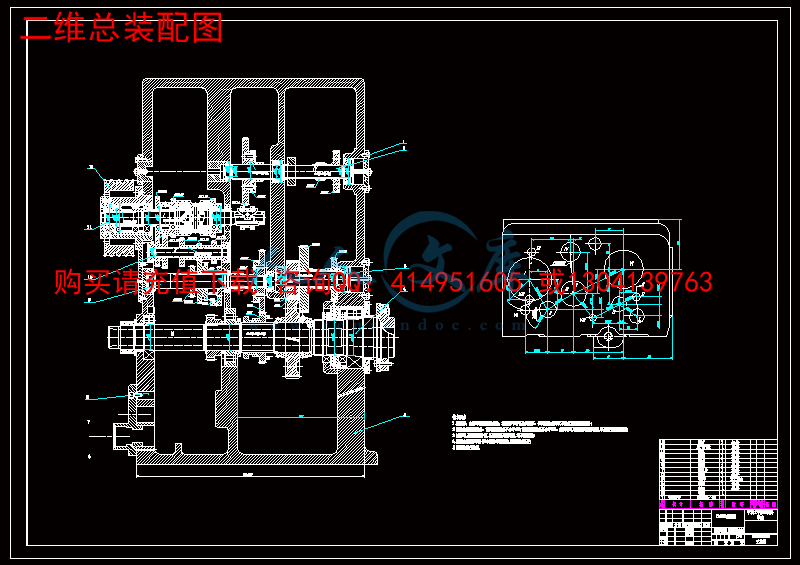
3.8 主轴箱的装配效果图..................................................36
3.9 小结................................................................39
4 车床主轴箱的运动仿真........................................................41
总结与展望.......................................................................43
致谢.............................................................................44
参考文献.........................................................................45
1 绪论
1.1 研究意义
车床的应用极为广泛,主要用于加工各种回转表面,其中 CA6140车床是卧式车床应用最广泛的一种。
CA6140型普通车床的主要组成部件有:主轴箱、刀架、溜板箱、进给箱、尾架、床身等[1]。
1)检验理论知识:本次关于CA6140车床主轴箱的三维设计,对过去所学的机械设计专业理论知识进行了全面检验,在设计过程中发现自身在以前学习过程中所忽略和不会的部分,并进一步加强和学习。
2)完善理论知识:在完成本次毕业设计的过程中,发现了许多我从未学过的新知识,对新知识的学习,扩大了自己的知识面,完善了自己的基础理论知识。并且提高了自己对于三维设计软件(Solidworks)的使用能力、三维设计、三维建模的能力。
3)应用理论知识:在本次毕业设计过程中,应用所学的机械专业理论知识,对车床主轴箱做了外观和部分零部件尺寸方面的优化设计,并借助Solidwork三维软件,绘出主轴箱整体及其零部件的三维设计图,并且生成装配体效果图,直观的表现出调整后主轴箱的整体及零部件的外观、形状、尺寸及装配特点。
1.2 研究现状
传统的车床主轴箱设计方法比较复杂,尤其是在制造新零件时需制造模具和调整机床,有准备时间周期长,误差大,加工零件的精度很难达到标准要求等缺点,在设计过程中图纸和数据更改也比较费事,需要投入大量的时间和精力,如果使车床主轴箱的设计一开始从三维实体造型开始,整个产品的设计过程从草图,实体,装配,虚拟样机,都可以利用三维呈现出来。将大大减少了产品的设计过程时间,提高了开发设计效率,使产品变得更加形象、具体,更利于开发者的观察和修改。现在流行的三维软件Solidworks完全符合这个要求,为机械三维产品的设计提供了一种便捷的方式。






 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号