HD6120混合动力城市客车总体设计
38页 18000字数+说明书+外文翻译+3张CAD图纸【详情如下】
HD6120混合动力城市客车总体设计说明书.doc
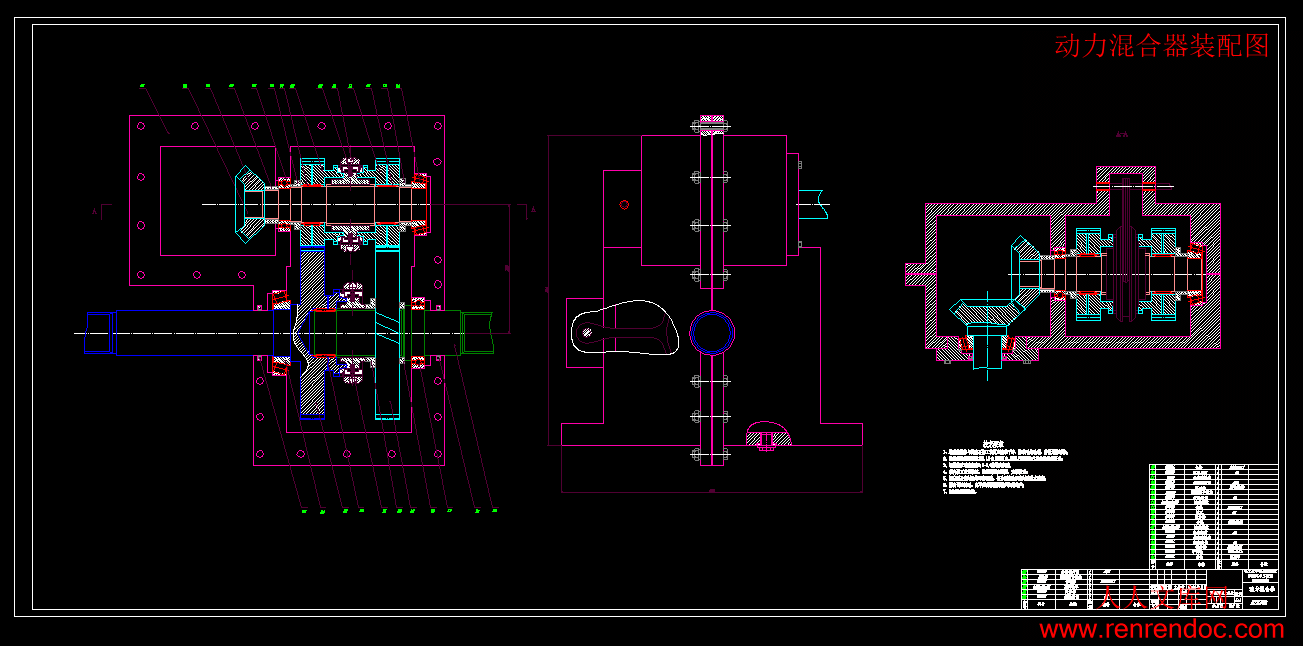
动力混合器装配图.dwg
外文翻译--混合动力驱动.doc
总布置图.dwg
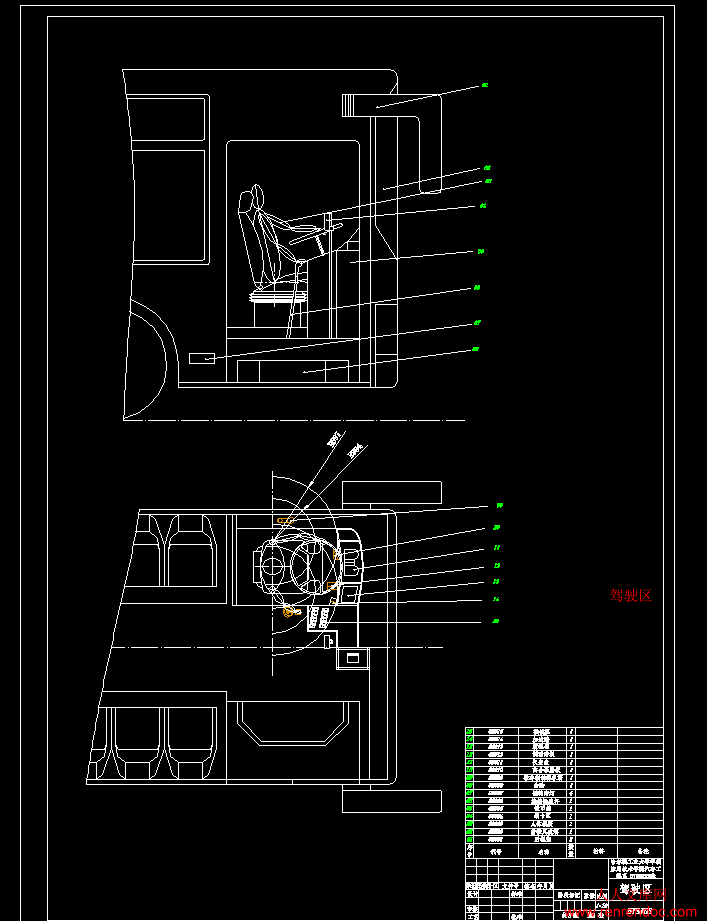
驾驶区.dwg
摘 要
城市客车是市民出行的首选,在各个城市中承担着人口流动的任务,应用广泛,数量众多。同时城市客车的运行工况特殊,城市中信号灯多,站点之间距离短,运行路线固定,城市客车频繁的起步,加速,制动,怠速时间长,平均运行速度低。由于汽车设计时需要满足最高行驶车速和最大爬坡度等动力性要求,需要装备大功率发动机,使得城市客车经常处于功率过剩状态,造成了严重的能源浪费和环境污染。
油电混合动力汽车融合了传统燃油汽车和纯电动汽车的优点,具有传统内燃机车动力性好和电动汽车清洁环保的特点,能够有效的降低能源消耗,减少污染排放,具有重要的研究意义。
关键词:混合动力;并联;城市客车;人机工程学
目 录
摘要……………………………………………………………………………………Ⅰ
Abstract ……………………………………………………………………………Ⅱ
第1章 绪论…………………………………………………………………………1
1.1选题的背景和意义…………………………………………………………1
1.2国内外研究动态………………………………………………………………2
1.3 研究内容与方法……………………………………………………………3
第2章 混合动力城市客车驱动系统选型…………………………………4
2.1 混合动力客车的分类 ………………………………………………………4
2.1.1 串联式混合动力城市客车 …………………………………………4
2.1.2 并联式混合动力城市客车 ………………………………………5
2.1.3 混联式混合动力城市客车 …………………………………………6
2.2混合动力城市客车驱动系统的选择…………………………………………7
2.2.1混合动力城市客车动力系统对比……………………………………7
2.2.2混合动力系统结构选型依据…………………………………………9
2.3本章小结……………………………………………………………………10
第3章 混合动力城市客车动力系统设计……………………………………11
3.1动力系统参数计算…………………………………………………………11
3.1.1驱动电机的选择……………………………………………………11
3.1.2动力电池的选择……………………………………………………13
3.2发动机的选择………………………………………………………………15
3.3本章小结……………………………………………………………………16
第4章 混合动力城市客车动力混合器的设计………………………………17
4.1动力混合器的作用 …………………………………………………………17
4.2动力混合器的设计…………………………………………………………17
4.1.1齿轮几何参数的计算……………………………………………18
4.1.2齿轮的校核……………………………………………………20
4.3本章小结……………………………………………………………………21
第5章 基于人机工程学的驾驶区布置………………………………………22
5.1人机工程学………………………………………………………………22
5.2二维人体模板的结构…………………………………………………22
5.3人体尺寸………………………………………………………………23
5.3.1人体主要尺寸………………………………………………………23
5.3.2人体水平尺寸………………………………………………………23
5.4本章小结……………………………………………………………………25
第6章 整车经济性计算…………………………………………………………26
6.1燃油经济性的评价指标……………………………………………………26
6.2燃油经济性的计算…………………………………………………………27
6.3本章小结……………………………………………………………………29
结论………………………………………………………………………………30
参考文献 …………………………………………………………………………31
致谢……………………………………………………………………………………33
附录………………………………………………………………………………34
第1章 绪 论
1.1 选题的背景和意义
汽车自诞生以来,其发展速度不断加快,与人们生活的联系越来越紧密。汽车已经不再是一个简单的代步和运输工具,它已成为许多人的生活必需品和文化生活的一部分。汽车的普及程度和技术水平甚至已经成为一个国家或地区现代化程度的标志。随着汽车工业的发展,汽车的产销量和保有量逐年增加,同时也带来了能源消耗、环境污染等许多负面影响。传统汽车对石油资源的需求越来越大,对生态环境的影响也越来越大。更糟糕的是,汽车排放的尾气中二氧化碳对气候变暖有着很大的影响;汽车尾气中氮氧化合物、一氧化碳、未燃碳氢化合物和颗粒排放物等有害物质,对人类的生态环境都产生了不利的影响。每年全球汽车排放有害气体约2亿吨以上,约占大气污染总量的60%,是大气污染的“头号杀手"。为此,各国制定了一系列十分严格的排放法规,要求汽车生产厂家设法减少汽车排放,开发无污染和超低污染汽车。面对世界能源匮乏,油价高居不下,环境污染严重的现实,节油环保便成为社会关注的焦点,新能源车的开发和应用也就成了世界范围内的新课题和大趋势。
在诸多解决方案中,目前成功实现产业化的只有混合动力汽车。混合动力汽车既具有内燃机动力性好、工作时间长的优点,又有电动机无污染和低噪声的好处,达到了发动机和电动机的最佳匹配。由于混合动力系统本身也具有充电功能,因此不需要建设配套的充电基础设施,对蓄电池的要求,与纯电动汽车相比也大大降低。混合动力汽车在技术、经济和环境等方面具有突出的综合优势。
而城市客车,是大部分市民出行的首选交通方式,承担着巨大的人流量,由于城市客车大部分运行在市区内,具有经常起步加速,制动停车,站台之间运行距离短,平均速度低等特殊工况,内燃机大部分时间工作在最佳工作转速范围以外,造成了能源的浪费、环境的污染以及加速了车辆本身的磨损。混合动力系统则可以优化内燃机的工作区间,大大改善上述问题,因此,发展研究混合动力城市客车具有很重大的现实意义。
1.2 国内外研究动态
融合了纯电动汽车和燃油汽车优点的混合动力汽车,由于较好地满足了汽车低排放、低油耗、高性价比的综合要求,较好地解决了汽车节能与环保问题,因而逐渐成为世界各大汽车生产企业开发的热点,其市场前景也越来越被看好。目前,丰田公司是混合动力汽车领域的佼佼者,1997年12月,日本丰田汽车公司首先在日本市场上推出了世界上第一款批量生产的混合动力汽车“普锐斯(PRIUS)”,该轿车于2000年7月开始出口北美,同年9月开始出口欧洲。普锐斯在达成高水平的燃油经济性和环保性能的前提下,实现了出色的动力性和舒适性。“PRIUS”的正式量产上市标志以混合动力汽车为代表的新一轮汽车研发竞争的开始。为保持领先地位,丰田公司加大了对混合动力车的投入,2005年,丰田投资1000万美元在美国肯塔基州工厂改造设备和训练员工。2006年,丰田汽车公司在美国市场上推出了4款从现有车型改造成的混合动力汽车,这些混合动力汽车的外形、操控以及车内的设备和普通车完全一样。丰田的目标是最终将推出旗下几乎所有车型的混合动力版,并在2012年把混合动力汽车的产量提高到100万辆。本田公司推出了“insight”、“CIVIC”等混合动力汽车.福特公司紧随其后,推出了“ESCAPE”混合动力汽车,戴克、通用、雪铁龙、日产等公司也纷纷加快了混合动力技术的产业化开发。通用、戴克、宝马三家公司在混合动力技术发展方面结成了技术联盟,携手发展双模混合动力技术,并在2005年的北美车展上引入了一款结合了V8柴油发动机和最新一代混合动力驱动系统的S级轿车。3.1动力系统参数计算
3.1.1驱动电机的选择
电动机是混合动力汽车的驱动单元之一,电动机驱动系统包括电动机、功率电子电路及控制部分。混合动力汽车对电机驱动系统的基本要求为:
1、电机驱动系统具有宽广的调速范围,有着与汽车行驶一致的动力特性。简言之,低转速时恒转矩,高转速时恒功率。最高转速越高,在同样的额定输出功率下,转速越高,电动机尺寸、重量越小;
2、动态性能好——电动机应具有较大的启动转矩和较大范围的调速性能,使HEV具有良好的起动性能和加速性能,以获得所需要的起动、加速、行驶、减速、制动所需的功率和转矩。电动机具有自动调速功能,因此,可以减轻驾驶员的操纵强度,提高家是舒适性,并且能够达到与内燃机汽车加速踏板同样的控制响应;
3、为了减少汽车的非有效载荷,要求电机驱动系统体积小、重量轻,功率密度大,在短时间内具有较高的过载能力;
4、高效率—这对于电动汽车意义尤其重大;
5、电气系统安全性和控制系统安全性——抗振动、耐腐蚀、低噪音;抗干扰,具有较好的电磁兼容性;各种动力电池组和电动机的工作电压,可以达到300V以上,对电气系统安全性和控制系统的安全性,都必须符合国家或国际有关车辆电气控制的安全性能的标准和规定;
6、能够四象限运行,实现正反转和再生制动,进能量回收,再生制动回收的能量一般可达到总能量的10%-15%,这点在内燃机汽车上是不能实现的;
7、高电压——在允许的范围内,尽可能采用高电压,电压越高,电动机尺寸越小、重量越低,特别是可以降低功率转换器成本;

 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号