锁芯套冷冲压工艺及级进模设计
43页 13000字数+说明书+任务书+开题报告+外文翻译+18张CAD图纸【详情如下】
任务书.doc
冷冲压工艺卡片-A4.doc
外文翻译--冲压变形.doc
相关资料.doc
计划周记进度检查表.xls
设计图纸18张.dwg
锁芯套冷冲压工艺及级进模设计开题报告.doc
锁芯套冷冲压工艺及级进模设计论文.doc
摘 要
冲压模具的工作原理主要是根据零件的外形及工艺要求选用合适的凸模和凹模将板料分离或成形而得到所需制件。因为模具主要用于工件的大批量生产,而且模具需要保证冲压产品的尺寸精度和产品质量,所以要考虑模具的设计能否满足工件的工艺性,能否加工出合格的零件,以及后来的维修和存放是否合理等。本次设计中不仅要确保设计的模具做出的零件能满足工作要求、模具要有足够的使用寿命,还要考虑到它的实际工作环境和必须完成的设计任务。根据一系列的分析、设计、查表、计算,最终确定模具的模架采用对角型模架,凸模凹模采用分别加工法,这样可以采用线切割等数控设备来一次完成全部的工序加工。卸料方式采用弹性卸料,排样方式采用有废料斜排的方式以及采用级进冲压。
关键词:落料;翻边;冲孔;级进模
目 录
摘 要III
AbstractIV
目 录V
1 绪论1
1.1 本课题的研究内容和意义1
1.2 国内外的发展概况1
1.3 本课题应达到的要求1
2 工艺性分析和工艺方案的确定3
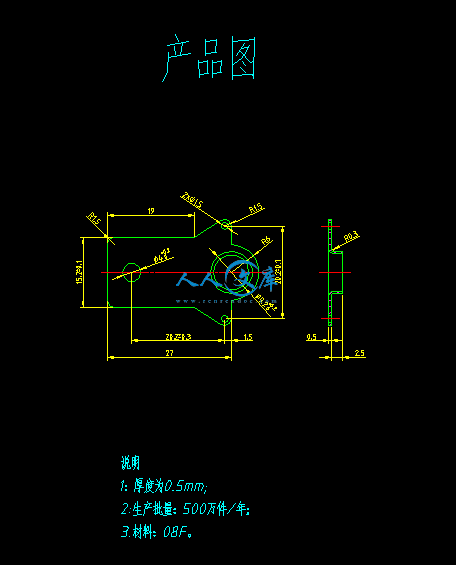
2.1零件图3
2.2零件的工艺性分析3
2.3模具材料的选用4
2.3.1冷冲模材料的选用要求4
2.3.2材料的选择原则4
2.4冲裁工艺方案的确定4
2.5排样5
2.5.1排样方法5
2.5.2搭边值与条料宽度及工位的确定6
3 设计计算9
3.1 翻边力的计算9
3.1.1 预冲孔大小的确定9
3.1.2 翻边系数9
3.2 冲裁力的计算10
3.3 卸料力、推件力、顶出力的计算11
3.4 冲压力的计算12
3.5 冲模压力中心的确定12
3.6 冲压设备的确定14
4 结构设计16
4.1凹模凸模设计16
4.1.1 凸、凹模分别加工时的计算法16
4.1.2 凸、凹模配作加工时的计算方法21
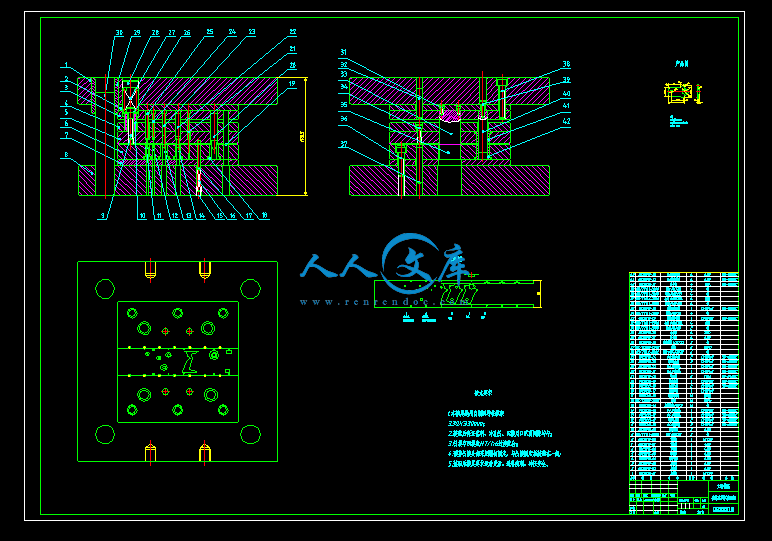
4.2定位方式的选择24
4.2.1 浮升两用销24
4.2.2 引导销25
4.3卸料、出件方式的选择27
4.4 模架及零件27
4.5其余零部件的选择与尺寸的确定29
5 总结和展望33
5.1 结论33
5.2 不足之处及未来展望33
致 谢34
参考文献35
1 绪论
1.1 本课题的研究内容和意义
本课题研究对锁芯套零件的连续模设计,其中包括冲压工艺、排样方案、模具结构分析等方面,通过平时的学习和专业老师的精心指导以及查阅大量资料,从而进行的模具设计。
首先,要对零件的工艺进行分析,课题的锁芯套零件的方按,采用先冲孔、再预剪、之后翻边,最后落料的工艺。其次,是对零件的排样方按的设定,通过计算,选择最优的排样方按。之后,则是对冲压凹凸模的设计计算,合理的冲裁间隙关系着冲裁模的冲裁质量和冲裁模具本身的寿命,也是模具设计中较为重要的一个环节。最后是模架和压力机的选用。
模具是机械工程及其自动化专业的一个专业方向,选择模具方向的毕业设计题目完全符合本专业的要求,从应用性方面来说,模具又是生产效率极高的工具之一,能有效保证产品一致性和可更换性,具有很好的发展前途和应用前景。连续模在模具中技术含量高,制造、装配难度大,因此本课题研究连续模的冲压工艺、排样方案、模具结构分析等方面,同时要求学生要有良好的心理素质和仔细认真的作风,对学生也是一次很好的锻炼机会。
1.2 国内外的发展概况
随着电子、信息等高新技术的不断发展,模具CAD/CAE/CAM正向集成化、三维化、智能化和网络化方向发展。模具CAD/CAE/CAM技术是模具设计、制造技术的发展方向,模具和工件的检测数字、模具软件功能集成化、模具设计、分析及制造的三维化、模具产业的逆向工程以及模具软件应用的网络化是主趋势。 3.发展多功能模具 为了提高效率和保证制品的质量,要采用多工位级进模及具有组合功能的双色,多色塑料注射模等。
4.发展高寿命模具 高效率必然需要高寿命,为了达到高寿命,除模具本身结构优化外,还要对材料的选用和热处理,表面强化技术予以开发和创新。
5.发展高精度模具 要实现模具的高精度,在模具的设计与加工中必然要使用高精度加工设备和高技术加工工艺。要进一步发展数控机床和加工中心的使用,要发展CAD/CAE/CIM等高新技术。
目前,我国的模具工业与国外发达国家相比,精密加工设备在模具加工设备中的比重还比较低,CAD/CAE/CAM技术的普及度不高,许多先进技术应用还不够广泛,特别是在大型,精密,复杂和长寿命模具技术上存在着明显的差距。
1.3 本课题应达到的要求
综合应用各种所学的专业知识,在规定的时间内对产品进行冷冲压工艺分析,制订完整的冲压工艺方案,并完成整副模具设计、数据计算和图纸(所有图纸折合A0不少于2.5张)绘制,具体内容如下:
1.完成模具装配图:1张(A0或A1);
2.零件图:主要是非标准件零件图(不少于5张);
3.冷冲压工艺卡片:1张 ;
4.设计说明书:1份(15000字以上,其中参考文献不少于10篇,外文不少于5篇);
5.翻译8000以上外文印刷字符,折合中文字数约5000字的有关技术资料或专业文献,内容要尽量结合课题。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号