离合器壳体中心大孔冲孔、成型、修边复合膜设计【优秀】【word+9张CAD图纸全套】【冲压复合模具类】【毕业设计】
【带任务书+开题报告+评阅评语表+指导教师评阅表+外文翻译+实习报告】【42页@正文20100字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】
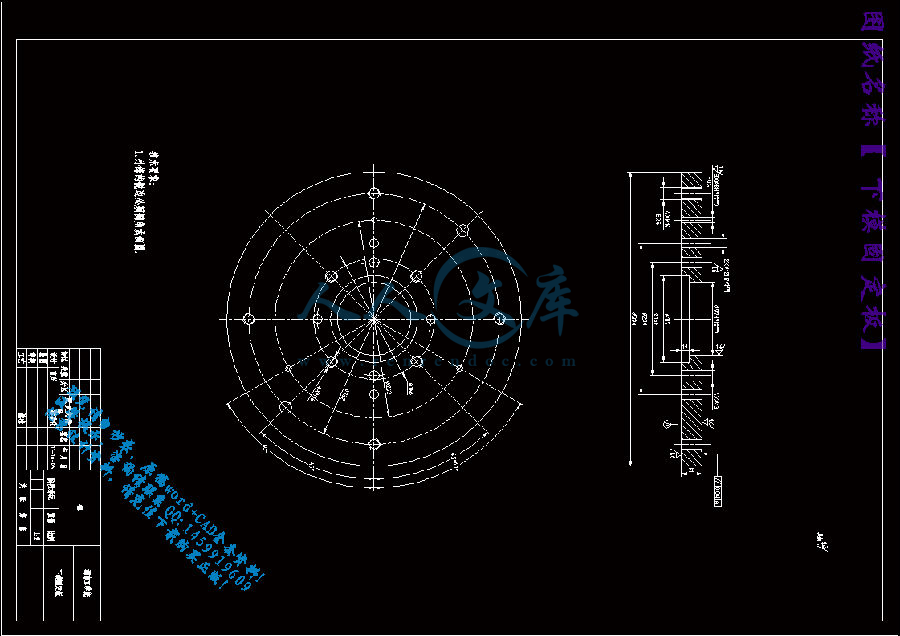
下模固定板.dwg
中期检查表.doc
任务书.doc
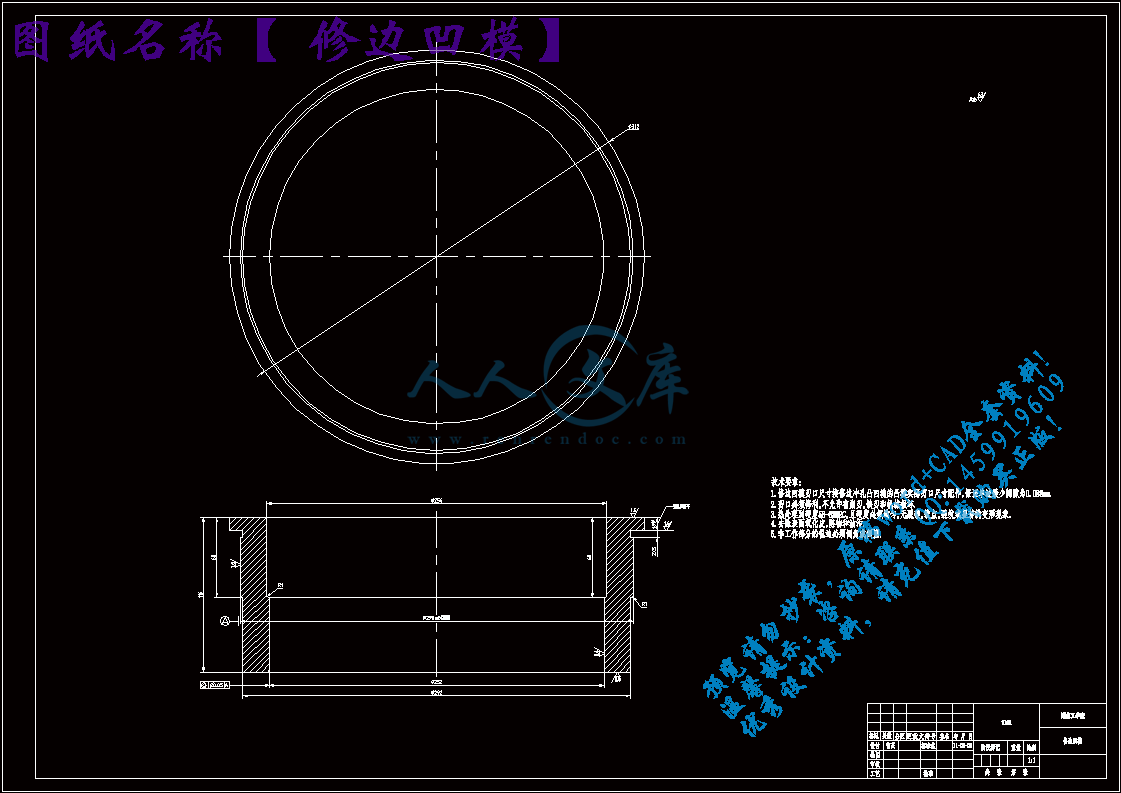
修边凹模.dwg
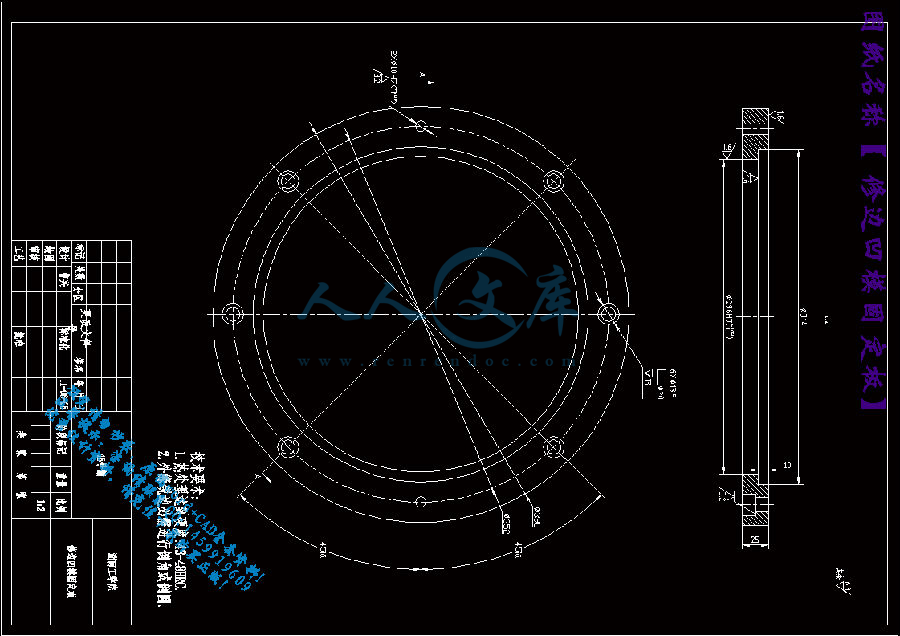
修边凹模固定板.dwg
冲孔凸模.dwg
外文翻译---冲压模具设计中侧壁起皱的分析 中文版.pdf
实习报告.doc
封面.doc
开题报告.doc
御料板.dwg
成形修边凸凹模.dwg
成形冲孔凸凹模.dwg
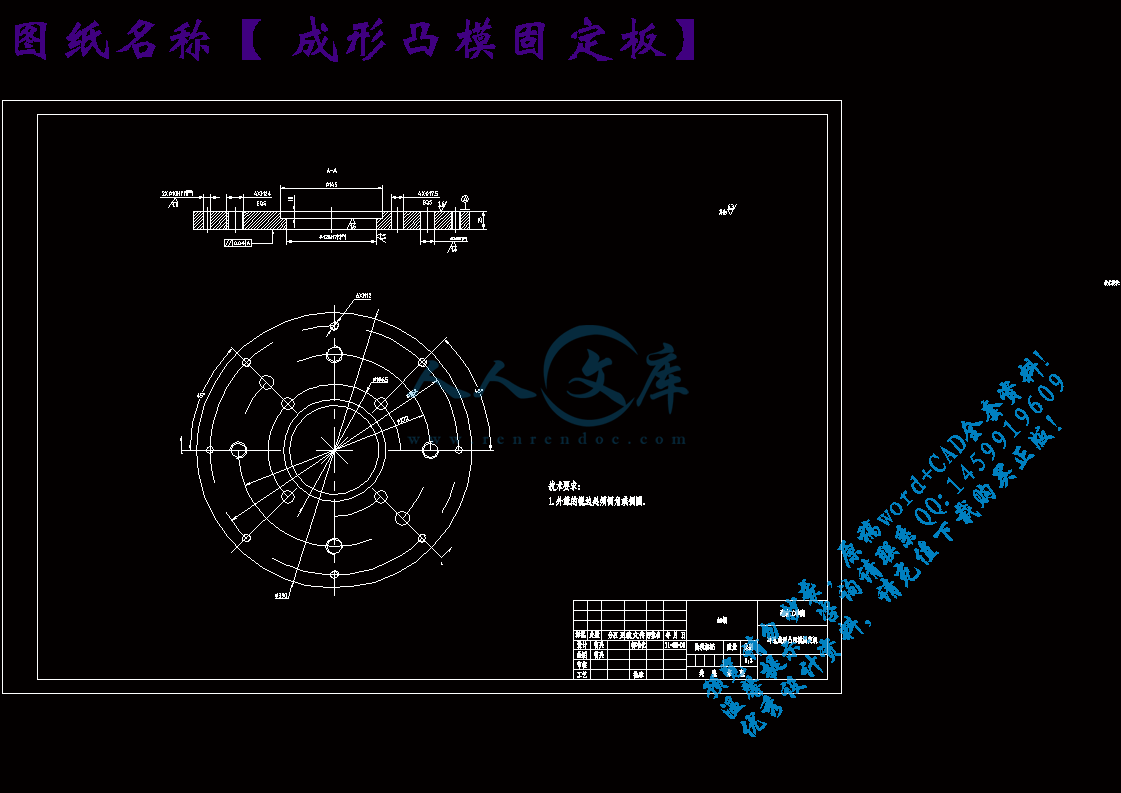
成形凸模固定板.dwg
指导教师评阅表.doc
正文.doc
答辩资格审查表.doc
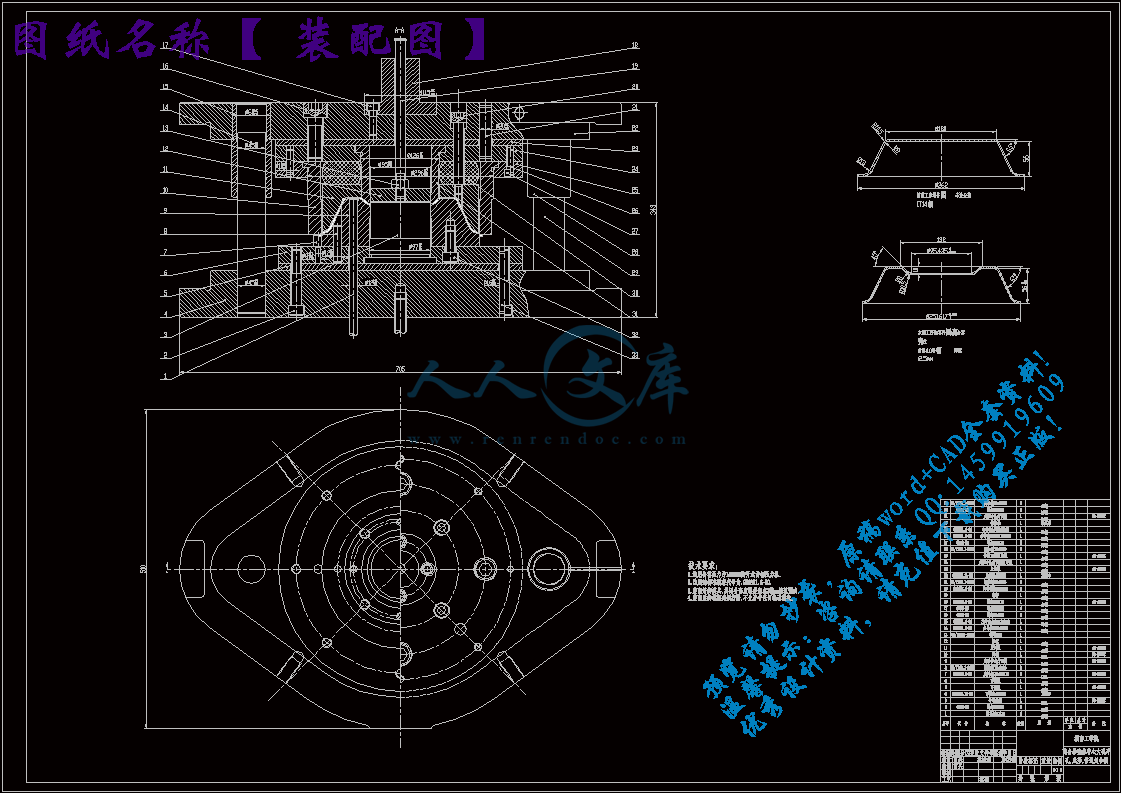
装配图.dwg
评阅评语表.doc
湖南工学院2011 届毕业设计(论文)课题任务书
系: 机械工程系 专业: 材料成型及控制工程
指导教师郭雪娥学生姓名曹兴
课题名称离合器壳体中心大孔冲孔,成型,修边复合模设计
内容及任务
模具零件图
模具总装图一张
全部模具零件图纸(其中至少有一张电脑绘图)
所有图纸折合成0号图不得少于3张。
自选一个重要模具零件编制加工工艺路线,进行相关的计算,并编制加工工艺卡和工序卡。
设计说明书
1、资料数据充分,并标明数据出处。
2、计算过程详细、完全。
3、公式的字母含义应标明,有时还应标注公式的出处。
4、内容条理清楚,按步骤书写。
5、说明书要求有计算机打印。
拟达到的要求或技术指标1、保证规定的生产率和高质量的冲压件的同时,力求成本低、模具寿命长。
2、设计的冷冲模必须保证操作安全、方便。
3、冲模零件必须具有良好的工艺性,即制造装配容易、便于管理。
4、便于搬运、安装、紧固到冲床上并且方便、可靠。
5、保证模具强度前提下,注意外形美观,各部分比例协调。
进度安排起止日期工作内容备注
3月1日
3月2日 ~ 4月1日
4月2日 ~ 5月4日
5月5日 ~ 5月7日
5月7日 ~ 5月20日
5月21日 ~5月23日
5月24日 ~5月25日
5月26日 ~5月29日
6月1日 ~ 6月10日
选取课题及编写开题报告;
英文论文翻译;
查询相关资料,产品基本要求分析。根据CAD二维图纸对设计模型进行Pro/E三维造型;
塑件材料选择、注射机的选择、成型方法及其工艺的选择;
模具相关结构的设计;
成型零件的制造工艺分析设计;
整理设计说明书,按照学院得规范要求排版打印设计说明书;
上交毕业设计资料,评阅;
准备答辩。
主要参考资料1、《冷冲压工艺及模具设计》刘心治主编重庆大学出版社
2、《冲压工艺及模具设计》万战胜主编 铁道出版社
3、《冲模设计》 吉林人民出版社
4、《实用冲压技术》 机工出版社
5、《冷冲压及塑料成型工艺与模具设计资料》 机工出版社
6、《模具设计与制造简明手册》 冯炳尧等编 上海出版社
7、《冲压工艺模具设计实用技术》 郑家贤编 机械工业出版社
8、《实用板金冲压工艺图集》 梁炳文主编 机械工业出版社
摘 要
复合模是冷冲压模具中加工精度、效率较高的一种设备。对于需经过几道工序才能冲压完成的零件来说,应尽可能根据零件的工艺要求采用复合模加工。本文就是对离合器壳体的前道工序半成品的进一步加工时,所需的复合模设计。这套模具适合于离合器壳体的中心大孔冲孔、成形、修边加工,其后尚有几道加工工序。在对该复合模进行设计时,主要的问题是对原工序件的底部成形方式的设计,由于要保证原工序件的大致形状精度,在这里采用局部成形的方法对底部的凸起进行加工。因此,确定合适的压边力就成了起伏成形能否成功的关健。同时,成形锥形凸包时,成形凸凹模的设计也较重要。为了设计的标准化,尽可能选用了标准件,如模架,模座,压边机等。最后对模具的一个主要零件导套进行了简单的加工工艺路线的制定。本设计对于进行起伏成形模具设计有一定的参考作用。
关键词:模具设计;复合模;压延成形
ABSTRACT
Compound die is an efficient and precise provision of normal stamp die. For
the part can not finished in only one stamp working procedure,it is better machining on the compound die according to the technical demands of the part. In the thesis, designed a compound mold used to machining the half-finished clutch shell. This set of mold suits in the clutch shell punch central hole, stamp bottom convex shape, and shave fringe, after that still had several processing working procedures. When carries on the design of this compound mold, the main question is to confirm the way of stamp the bottom convex figuration. Because it is have to guarantee the fore working procedure’s approximate shape precise, uses partial-undulate stamp in here to processing the bottom bulge. Therefore, the key role to succeed of the partial-undulate stamp is to define reasonable blank holding force. At the same time, when stamped conical convex bulge, the design of convex-concave die is also important. In order to the standardized design, has selected the standard part as far as possible. Such as die frame, die bed plates, press machine and so on. Finally, set down the machining technical procedure of sleeve, a major mold component. The design in the thesis has some referenced value for analogical calendaring molding design.
Keywords: mold design; compound die; calendaring molding
目 录
摘 要2
1 分析冲压件的工艺性7
1.1 冲裁工艺性7
1.2 成形工艺性8
2 分析计算确定工艺方案9
2.1 确定所需的冲压基本工序9
2.2 确定工序数目9
2.2.1 确定拉伸次数9
2.2.2 顶面起伏成形加工次数的确定10
2.2 确定工序顺序11
2.3 确定工序的组合11
3 主要工艺参数的计算13
3.1 计算毛尺寸13
3.2 计算冲压力15
3.2.1 起伏成形的压力计算15
3.2.2 中心冲大孔的冲裁力15
3.2.3 修边时的冲裁力16
3.2.4 冲中心大孔时的御料力16
3.2.5 外缘修边时的御料力16
3.2.6 冲孔时的推件力17
3.2.7计算压边力17
3.3 初选压力机17
3.4 计算压力中心18
3.5 计算凸凹模刃口尺寸及公差18
3.5.1 冲中孔时凸、凹模刃口尺寸计算19
3.5.2 修边凸凹模刃口尺寸计算20
3.5.3 成形凸凹模的刃口尺寸计算20
4 模具整体结构设计22
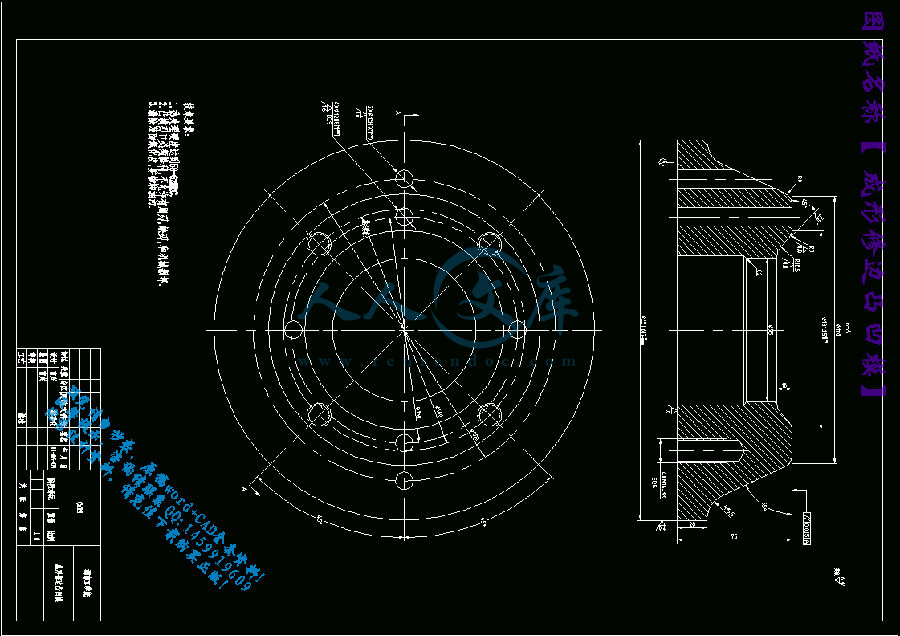
4.1 修边凹模的设计22
4.1.1 凹模的尺寸计算22
4.1.2 凹模的结构形式23
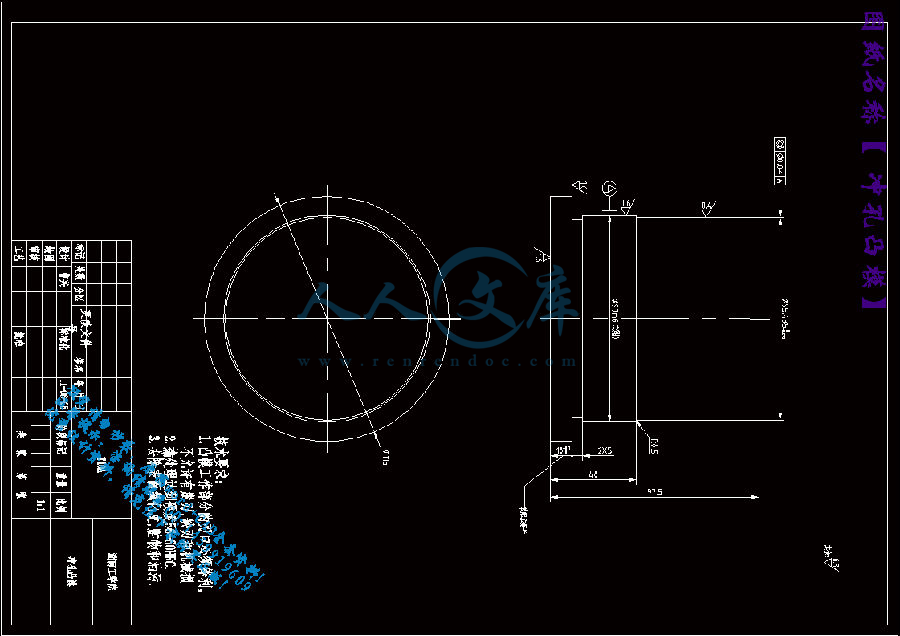
4.2冲孔凸模的设计24
4.2.1 计算24
4.2.2 凸模的结构设计25
4.3凸凹模(冲孔凸模和修边凹模)的设计26
4.4 冲模的导向装置27
4.4.1无导向冲裁27
4.4.2导板导向28
4.4.3模架的导向28
4.5定位装置31
4.5.1条料的横向定位装置:31
4.5.2.条料的纵向定位装置:32
4.6卸料装置33
4.6.1.固定卸料装置的形式33
4.6.2.固定卸料板的固定方式33
4.7推件装置的设计33
4.7.1.推件板的结构形式34
4.7.2.推件板的尺寸与公差34
4.7.3.推件板的极点位置34
4.7.4.打杆与打板的设计34
5 其它冲模零件设计35
5.1模柄的类型及选择35
5.2凸模固定板36
5.3垫板36
5.4紧固件37
5.5定位销37
6 模具的装配38
6.1复合模的装配38
6.2凸、凹模间隙的调整38
7 具体零件的工艺方案39
总结41
参考文献42
致 谢43
1 分析冲压件的工艺性
1.1 冲裁工艺性
冲裁件的工艺性是指冲裁件对冲压工艺的适应性,即冲裁件的结构形状、尺寸大小、精度等级是否符合冲裁加工的工艺要求。良好的结构工艺性应保证材料消耗少,工序数目少,模具结构简单而寿命高,产品质量稳定,操作简单等等。通常对冲裁件的工艺性影响最大的是几何形状尺寸和精度要求。对几何形状的要求是冲裁件的形状应尽可能简单、对称,最好采用圆形、矩形等规则的几何形状或由这些形状所组成,使排样时废料最少;冲裁件的凸出悬臂和凹槽的宽度不宜太小,以免凸模折断;冲裁件的外形或内形的转角出,要避免夹角出现,应以圆弧过渡,以便于模具加工,减少热处理或冲压时的在尖角处开裂的现象,同时可以防止尖角部位的刃口磨损过快而使模具寿命降低。对精度的要求是冲裁件的经济精度一般不高于IT11级,最高可达IT8~10级,冲孔比落料的精度约高一级。
该零件的形状如图1,其冲裁工艺性为:
⑴结构与尺寸:该零件结构较简单、形状对称,完全由圆弧和直线组成,没有长的悬臂和狭槽。
⑵精度:零件尺寸最大凸缘尺寸精度为IT11,高度尺寸略低于IT12,其余尺寸均为自由尺寸,中心大孔的冲孔尺寸要求不高,可以经过普通的冲裁方法加工形成。
修边时,相应的尺寸要求和冲孔时相比较高,其凸缘尺寸为IT11级精度,因此,进行模具设计时,应保证修边时所用模具的精度。另外,零件图中还对下顶面与下底面的平行度,下底面的平面度有一定要求,因此加工时最好能使外缘的修边和顶面的成形在同一付模具上进行加工,以保证相对的位置精度和形状精度,而在冲模加工方法中,复合模能在一付模具上对工件进二道或更多的工序加工,而保持被加工零件没有相对的位移,有利于得到较高精度的加工件。因此,相对来说,该零件的冲裁加工要求可以得到保证。
⑶材料:该零件材料为10号钢,屈服强度为206Mpa,此材料具有良好的结构强度和塑性,其冲裁加工性较好。
⑷生产批量:大批量生产。
根据以上分析,该零件的冲裁性较好,可以冲裁加工。
参考文献
[1] 肖景荣、姜奎华.冲压工艺学[M]. 机械工业出版社
[2] 万战胜.冲压工艺及模具设计[M]. 铁道出版社
[3] 夏具谌、李志刚.中国冲模设计大典[M]. 江西科学技术出版社
[4] 实用冲压技术[M]. 机工出版社
[5] 冷冲压及塑料成型工艺与模具设计资料[M]. 机工出版社
[6] 冯炳尧.模具设计与制造简明手册[M]. 上海出版社
[7] 郑家贤.冲压工艺模具设计实用技术[M]. 机械工业出版社
[8] 梁炳文.实用板金冲压工艺图集[M]. 机械工业出版社
[9] 甘永立.几何量公差与检测[M]. 上海科学技术出版社
[10] 章跃主.机械制造专业英语[M]. 机械工业出版社
[11] 刘心治.冷冲压工艺及模具设计[M]. 重庆大学出版社
[12] 冲模设计手册[M]. 机械工业出版社
[13] 杨玉英.实用冲压工艺及模具设计手册[M]. 机械工业出版社



 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号