【温馨提示】 购买原稿文件请充值后自助下载。
[全部文件] 那张截图中的文件为本资料所有内容,下载后即可获得。
预览截图请勿抄袭,原稿文件完整清晰,无水印,可编辑。
有疑问可以咨询QQ:414951605或1304139763
摘 要
本次设计是以三菱FX2n为核心的电梯控制系统的硬件组成及软件设计,采用PLC来控制轿箱提升电机的起、停和正、反转。这里主要是对电梯曳引机的参数进行设计、计算、(包括电动机、减速器、轴、轴承、联轴器、制动器)以及工艺的编排和相关图形的绘制,另外对PLC控制系统的设计,主要是PLC控制电路图、程序流程图以及PLC编程。
其中对曳引机的设计重点是减速器的选择和箱体零件的设计和加工。减速器选择的是蜗杆减速器,轴承是调心滚子轴承,联轴器选择的是弹性柱销联轴器。PLC控制程序设计是考虑到电梯的上升和下降逻辑,以及楼层显示,运作时的加速和减速。
现在电梯都采用传统的继电器群的控制方法,由于所用的继电器较多,控制柜体积庞大,控制系统成本高,而且众多继电器的动作会产生较大的噪音,污染环境。采用PLC配合接口进行控制,可将传统的继电器控制逻辑变为计算机程序控制逻辑,去掉所有用于逻辑控制的中间继电器,使电梯系统的成本和噪音大大降低,控制柜的体积也可大大缩小。
关键词:PLC ;曳引机 ;电动机 ;减速器 ;联轴器 ;制动器
Abstract
This design is take FX2n as the core elevator control system hardware composition and the software design, uses the PLC integrated circuit to control the sedan box to promote the electrical machinery, to stop with, the reverse. Here mainly is carries on the design, the computation to the elevator tractor parameter, (including electric motor, reduction gear, axis, bearing, shaft coupling, brake) as well as the craft arrangement and the correlation graph plan, moreover to the PLC integrated circuit control system design, mainly is the PLC integrated circuit control circuit diagram, the program flow diagram as well as the PLC integrated circuit programming.
The most important of this design is changed huge parts of contents. The new version increases plenty of new technical contents and new calculation method.PLC integrated circuit control system design. Besides a few parts are changed according to the Chinse lift situations, this revised version is basically compliant
Now the elevator all uses the method of traditional the relay group control, because of many relay have been used, control the cabinet volume huge, the cost of control system is high, most of the multitudinous relay movement have the big noise, the pollution environment. Uses the PLC integrated circuit coordination connection to carry on the control, may become the traditional black-white control logic the computer program control logic, removes all uses in the logical control intermediate relay, causes the cost of the elevator system and the noise reduces greatly, controls the cabinet the volume also to be possible to reduce greatly.
Key words:PLC integrated circuit;Tractor;Electricmotor;Reduction gear;Shaft coupling;Brake
目录
1绪论……………………………………………………………………………………………1
1.1电梯的起源…………………………………………………………………………………1
1.2电梯的种类…………………………………………………………………………………1
1.2.1按用途分类………………………………………………………………………………1
1.2.2按速度分类………………………………………………………………………………2
1.2.3按拖动电动机类型分类…………………………………………………………………2
1.2.4按驱动方式分类…………………………………………………………………………2
1.2.5按控制方式分类…………………………………………………………………………3
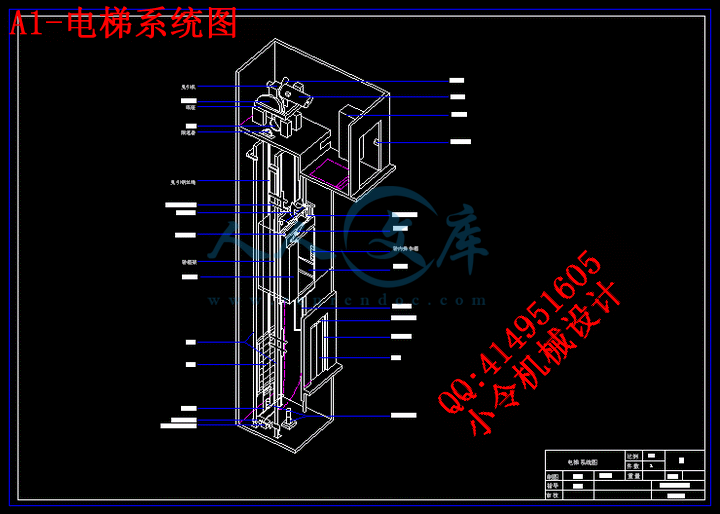
1.3电梯主要组成及结构……………………………………………………………………3
1.3.1曳引机构的组成…………………………………………………………………………4
1.3.2曳引机构的减速器………………………………………………………………………5
2有关参数的计算………………………………………………………………………………7
2.1曳引机的确定……………………………………………………………………………7
2.1.1选择曳引机………………………………………………………………………………8
2.1.2曳引机容量的计算………………………………………………………………………8
2.1.3曳引力计算………………………………………………………………………………8
2.2减速器设计…………………………………………………………………………………9
2.2.1常用减速器的型式及其应用……………………………………………………………9
2.2.2减速器的基本构造……………………………………………………………………10
2.2.3蜗杆减速器设计………………………………………………………………………12
2.3轴的设计与计算…………………………………………………………………………16
2.3.1轴的分类………………………………………………………………………………16
2.3.2轴的常用材料…………………………………………………………………………16
2.3.3轴的结构设计…………………………………………………………………………16
2.3.4轴的强度计算…………………………………………………………………………16
2.4轴承的设计与计算………………………………………………………………………20
2.5联轴器的设计与计算……………………………………………………………………22
2.5.1联轴器选择应考虑的问题 ………………… ………………………………………22
2.5.2联轴器的理论转矩……………………………………………………………………22
2.5.3主要尺寸计算…………………………………………………………………………23
2.6制动器的设计与计算……………………………………………………………………23
2.7工艺………………………………………………………………………………………24
2.7.1零件的分析……………………………………………………………………………24
2.7.2工艺规程设计…………………………………………………………………………26
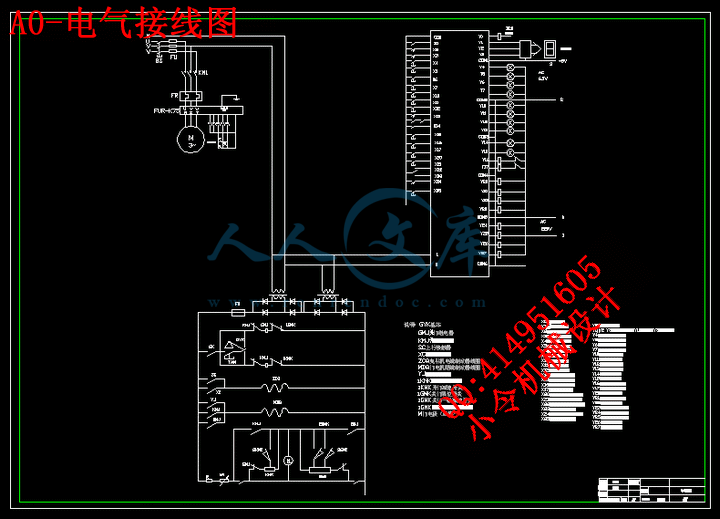
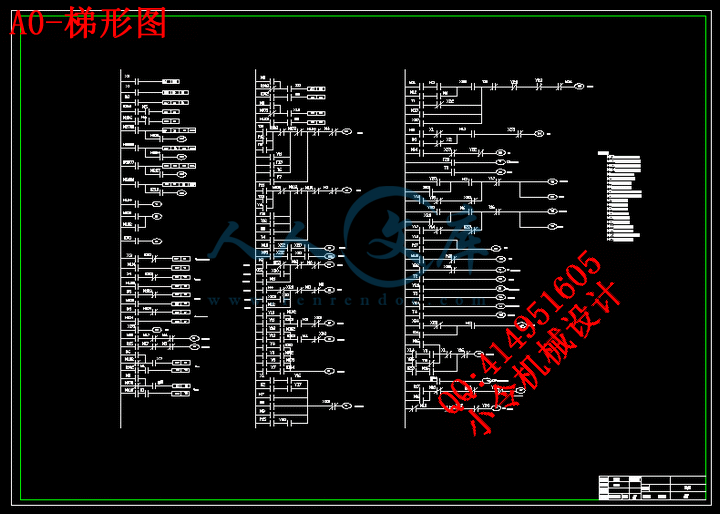
3 PLC 电梯控制系统的设计………………………………………………………………29
3.1 PLC 系统概述…………………………………………………………………………29
3.1.1 PLC 的定义………………………………………………………………………29
3.1.2 PLC 的特点…………………………………………………………………………30
3.1.3PLC 与继电器控制系统的比较………………………………………………………32
3.1.4 PLC 的基本结构………………………………………………………………………33
3.1.5 PLC 的工作原理………………………………………………………………………35
3.2 PLC 控制系统的设计分析………………………………………………………………37
3.2.1 PLC 控制系统的设计基本原则………………………………………………………37
3.2.2PLC 控制系统的设计的主要内容……………………………………………………38
3.2.3.PLC 控制系统程序设计的步骤……………………………………………………39
3.3 电梯PLC控制系统的设计……………………………………………………………40
3.3.1电梯的运行过程…………………………………………………………………40
3.3.2选择 PLC…………………………………………………………………………41
3.3.3PLC 规模的估算……………………………………………………………………42
3.3.4PLC 输入输出模块的选择……………………………………………………………43
3.3.5PLC 的选择……………………………………………………………………………44
4结论……………………………………………………………………………………………46
5参考文献………………………………………………………………………………………47
6翻译……………………………………………………………………………………………48
6.1外文资料……………………………………………………………………………………48
6.2译文………………………………………………………………………………………54
7致谢…………………………………………………………………………………………59


 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号