摘 要
本次设计的任务是某冷凝器侧板冲压模具设计及制造工艺分析,根据冲压件的结构特点及技术要求,围绕如何提高生产率、降低生产成本、简化模具结构,对工件进行工艺分析,并提出了各种可能的冲压工艺方案,最终确定采用一套由落料、冲孔复合和弯曲、翻边复合组成的冲压工艺方案。
在工艺分析的基础上,计算工艺参数,详细设计了落料冲孔、弯曲翻边两套复合模具结构。在设计过程中,计算出了零件展开尺寸,并对模具的排样做出了合理的布置,使材料得到充分利用。通过计算各种冲裁力,对压力机进行合理吨位的选择,并确定了模具压力中心。再根据确定的工艺方案,进行模具的校核,最终,设计模具制造与装配工艺。
采用此工艺方案和模具结构,提高了冷凝器侧板的生产效率和产品质量。
关键词:冷凝器侧板;工艺分析;模具设计;落料冲孔复合模;弯曲翻边复合模
Abstract
The task of this design is design of Stamping die and manufacturing process analysis for Condenser side plate stamping die design. according to the structure of stamping parts and technical requirements, focusing on how to improve work efficiency and reduce the production cost and simplify the die structure, Process analysis was carried out on the workpieces, and puts forward the stamping process scheme for all possible, and ultimately determine the stamping process program with a set of blanking, punching composite and bending, flanging composite.
On the basis of technology analysis and calculation parameters, and the detailed design for blanking punching, bending, flanging two sets of compound die structure. In the process of design, calculated developed dimension of parts, and the layout of the mold made reasonable decorate for make full use of the material. By calculating the various blanking force on the tonnage presses a reasonable choice, and to determine the center of pressure of the mold. According to determine the processing plan, mold check, in the end, the design of mold manufacturing and assembly process.
With this process program and die structure, improved production efficiency and product quality condenser side plate.
Keywords:condenser side plate; process analysis; die design; blanking punching composite die; bending flanging composite die;
目 录
引言1
1毕业设计(论文)的要求与数据2
2零件的冲压工艺分析2
2.1制件总体方案分析2
2.2零件的力学性能分析2
2.3零件的精度和粗糙度3
2.4最小相对弯曲半径3
2.5最小弯曲边高度3
2.6最小圆角半径4
2.7冲裁件的最小孔直径4
2.8冲裁件的孔与孔之间,孔与边缘之间的最小距离4
2.9最大翻边高度4
3工艺方案的确定5
3.1冲压该零件所需要的基本工序5
3.2方案比较与确定5
4落料冲孔复合模设计6
4.1主要工艺参数计算6
4.1.1工件展开尺寸计算6
4.1.2排样设计与计算7
4.1.3冲裁力、卸料力、和推件力的计算8
4.1.4模具压力中心9
4.2压力机的选用11
4.2.1冲裁设备的选择11
4.2.2冲压设备规格的确定11
4.3模具刃口尺寸计算12
4.3.1刃口尺寸计算12
4.4模具设计13
4.4.1卸料装置13
4.4.2推件装置13
4.4.3凸凹模设计14
4.4.4凸模15
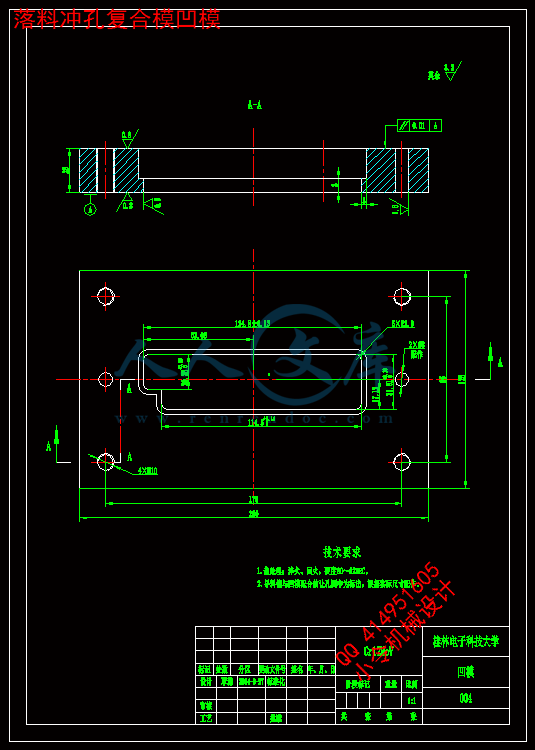
4.4.5凹模17
4.4.6模架的选择17
4.4.7模柄18
4.4.8固定件与定位元件19
4.4.9弹性元件20
4.4.10其他零件21
4.5模架闭合高度及压力机有关参数的校核22
4.5.1公称压力22
4.5.2滑块行程22
4.5.3闭合高度22
4.5.4压力机工作台面的尺寸23
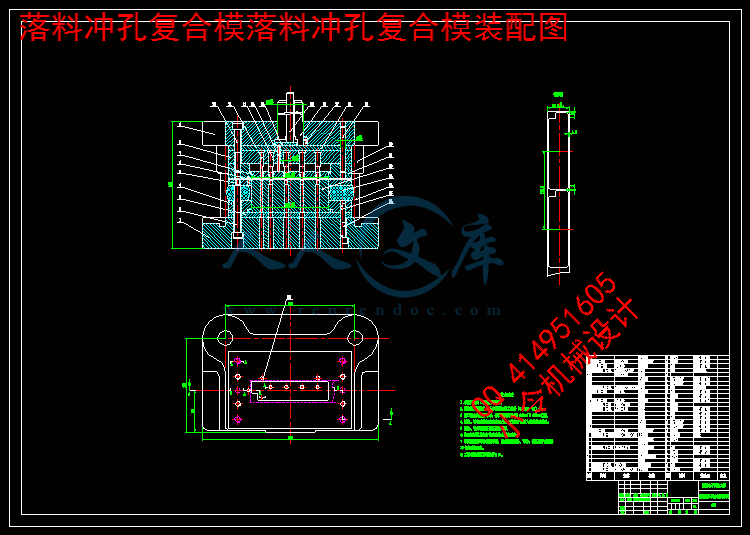
4.6落料冲孔复合模总装图设计23
4.6.1落料冲孔复合模工作过程23
4.7主要零件加工工艺的编制24
4.8落料冲孔复合模的安装与调试28
4.8.1模具装配顺序28
4.8.2模具的调试28
5翻边弯曲复合模29
5.1模具工作部分尺寸计算29
5.1.1弯曲工作部分计算29
5.1.2翻边刃口尺寸29
5.1.3弯曲时模具的圆角半径与凹模深度30
5.1.4弯曲回弹量30
5.2冲压力的计算和设备的选择30
5.2.1翻边力的计算30
5.2.2弯曲力的计算30
5.2.3选择冲压设备31
5.3模具设计32
5.3.1翻边凸模32
5.3.2凸凹模32
5.3.3凹模33
5.3.4凸模33
5.3.5凹模固定板34
5.3.6卸料装置34
5.3.7顶出装置34
5.3.8模柄35
5.3.9模架36
5.3.10固定于定位元件36
5.3.11其他零件36
5.4模具闭合高度和压力机有关参数的校核37
5.4.1公称压力37
5.4.2滑块行程37
5.4.3闭合高度37
5.4.4压力机工作台面的尺寸38
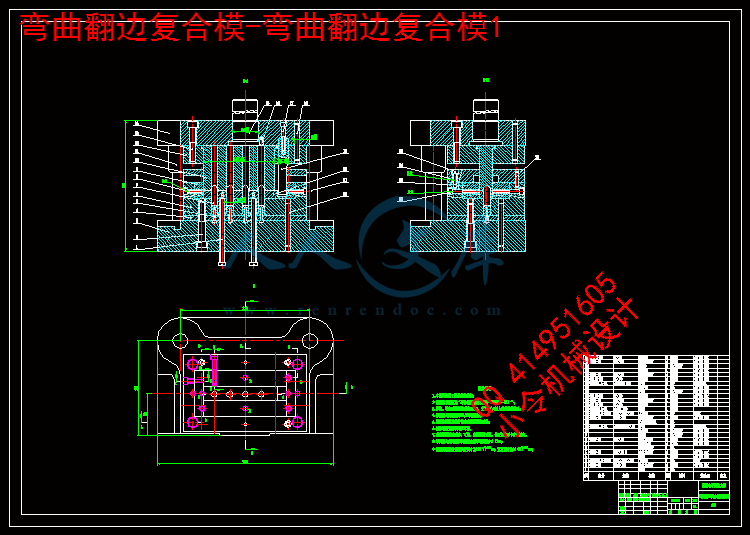
5.5弯曲翻边复合模总装图设计38
5.5.1弯曲翻边复合模的工作过程39
5.6主要零件加工工艺的编制39
5.7弯曲翻边复合模的安装与调整42
5.7.1模具的调整42
6总结45
谢 辞46
参考文献47
引言
在现代社会中,科技的进步促使工业生产行业发展得突飞猛进,许许多多的新鲜血液注入,实现了很多新型工艺、新型设备、新型技术以及新型材料在工业生产行业中的应用。从而使得冲压这项技术的不断改进与创新,模具设计及制造的水平实现快速的提升。
冲压加工应具有的三要素是:冲压设备、冲压模具以及冲压材料。而冲模是将金属或非金属材料单个加工及批量加工成型所需要冲件的专门的工具。只有合理的设计冲模、选择合适的冲压设备,并将它们安装调试准确,才能冲压出合格的制件。而冲压技术广泛运用于板料的加工中冲压成型中,在现代汽车、电器、航空等行业中,广泛应用到钣金件。而冲模在冲压工艺中非常重要,如果用不符合要求的冲模对工件进行加工,就会使得冲压件的质量不能达到设计要求,且进行批量冲压生产时效率极其低。可见,冲模在冲压加工中占有举足轻重的地位。在现代工业中,更多的是要求产品生产成本更加经济,生产周期越短越好,只有这样,才能在工业技术飞速发展的今天立于不败之地。当今工业生产的先进设计技术和新工艺的发展运用在模具的设计和制造中,让人们更能体会到模具在现代工业中的实用价值。
如今工业生产中,人们运用计算机技术和制造技术有机结合,实现了模具设计、制造加工一体化,与运用传统制造相比较,产品生产周期大大缩短了,产品质量有了很显著的提高,生产的成本与降低了很多,为工厂带来了更大的竞争优势和更高的经济效益。而我国的模具制造技术相对于发达国家而言,还存在着非常大的差距,根本无法满足国内市场对模具的需求,许多高精密等高档模具还需要从国外进口。我国的制造业技术正在迅猛发展,且模具制造在冲压加工行业在机械制造中扮演着越来越重要的角色,在市场环境高速发展的趋势下,不久的将来,我国将由模具大国向模具强国渐渐转变。
作为机械制造行业的后辈,学习模具相关的知识就显得尤为重要。本次设计是空调中常应用到的冷凝器侧板的冲压模设计,所以设计的任务主要是模具类型的选择和工作部分的制造,借此设计以巩固之前所学的模具知识。在满足工艺要求的基础上,尽可能使设计的模具结构简单,操作安全,还需要考虑模具的制造周期以及经济性是否符合现代工业的要求。这样不仅能设计和制造出先进的模具,也能充分地利用现代科技为工业的发展提供技术支持。



 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号