附件1张雯南通大学校级优秀毕业设计(论文)评选表.doc
脚盆注塑模具设计【6张图纸】【优秀】【word+CAD全套设计】
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:443833
类型:共享资源
大小:13.67MB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2015-06-26
上传人:小***
认证信息
个人认证
林**(实名认证)
福建
IP属地:福建
50
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
x0030
脚盆
注塑
模具设计
三维
- 资源描述:
-
摘要
模具设计的种类很多,其中以塑料模的设计最为主要。塑料产品的多样化和超大的市场需求量决定了塑料模设计的重要性。模具工业的发展有空间,前景很好。特别是中国加人WTO后,国际模具市场前景广阔,中国模具仍有一定的竞争优势。
本课题以脚盆为设计对象,主要研究了该零件的3D快速模具设计技术。通过对传统的2D设计,3D设计以及最新的参数化设计做比较,发现采用SolidWorks2004的模具设计平台,可以大大提高模具设计的效率,也提高了产品快速响应市场的能力。对此课题的研究让我们初步了解了模具设计的过程,对我们今后的发展有很大的帮助。
关键字:模具设计,SolidWorks,注塑模,快速设计
Abstract
Many types of mold design, plastic mold design with the most major. Plastic product diversification and market demand for super-plastic design has determined the importance of. Mold the development of industrial space, good prospects. Especially after China's WTO plus people, the international market prospects mold, China mold there is still a competitive advantage.
This topic takes the footbath machine as the target of mold design. It is main researched the 3D fast mould designing technique of this part. Through the comparion with the designing of traditional 2D design, 3D design and the latest designing of parameterize, we can find that if adopts the mold design platform of SolidWorks2004, it can improve the efficiency of mold design greatly, and also can improve the ability that the products respond the market fast. The study on mold design lets us find out the course of the design about the mould is very helpful to our development in the future.
Key words: Mold design, SolidWorks, Injection mold, Rapid design
目录
摘要II
AbstractIII
目录IV
第1章 绪论6
1.1注塑成型6
1.2模具工业发展现状6
1.3模具发展趋势7
1.4关于SolidWorks8
1.5本文的研究目的、内容和意义8
第2章 总体设计方案的确定10
2.1设计方案的提出与比较10
2.2设计方案的确定及导入12
2.3数据准备和项目建立13
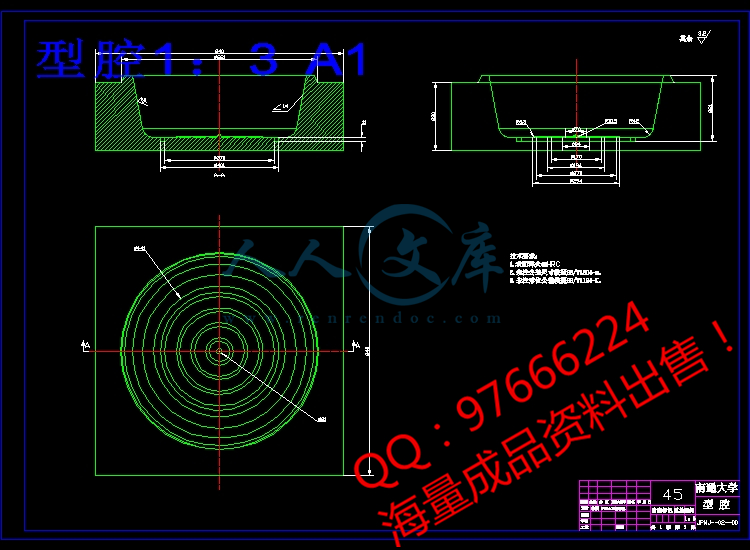
2.4 型芯型腔设计14
第3章 标准模架的选用22
3.1模板的选用22
3.2垫块的选用22
3.3导柱的选择23
3.4导套的选择24
3.5塑料注射模标准模架24
第4章 浇口与浇道的设计及计算26
4.1 添加智能螺钉26
4.2 添加定位圈27
4.3 添加浇口套27
4.4 浇口设计28
第5章 最终设计效果图29
5.1 模架最终效果图29
5.2 MasterCAM加工效果图30
第6章 总结32
参考文献33
致谢34




- 内容简介:
-
基于Windows的三维塑料注塑模具设计系统摘要三维实体建模革命已经是设计的主流。高端的三维实体造型系统已经在工程师工作站,大型航空航天,消费电子产品,汽车企业里使用很多年,还有许多小公司,现在做着从工作站到PC 机的转换。这样做的原因之一是为了达到转变灵活,并且基于Windows/NT平台,软件开发人员必须开发一种人们能负担得起,而且易于使用的应用程序。高端用户发现,中程固体模型如SolidWorks,正符合他们的需求。SolidWorks被选定为用于处理Windows的设计环境平台,它有强大的装配能力,易与使用,学习快速,以及实惠的价格。Windows的本地三维塑料注射模具设计系统已被用于一种通过NT接口的Visual C + +代码的商业软件,SolidWorks 99和API 。该系统为设计师提供了一个互动式电脑辅助设计环境,这既可以加快模具设计过程,又可以促进其标准化。 关键词:注塑模具; Windows; CAD; 零件1. 导言塑料零件被广泛的使用在一系列大范围生产中,从消费产品到机械,汽车和航空飞机,注塑过程已被确认作为一个重要的制造工艺。模具设计过程一般是一种新产品发展的关键。传统上来看,模具设计一直是非常“莫名其妙”的艺术,在成为一个可以相对精通它的人之前需要积累多年的经验。由于最初学习这种艺术十分困难,所以越来越少的人能从在这领域有经验和知识的专家那里受益了。要改变目前的状况,其中一种方法就是使用计算机辅助设计( CAD )系统。CAD作为日常术语已具有了非常广的能力范围,并已应用到一系列领域,从作为学校教学的教具,到三维机械设计。目前,大多CAD系统只提供几何造型功能,为草图绘制模具设计减小困难,但并没有为模具设计者提供必要的知识来设计铸模。因此,许多“附加”的软件,例如: IMOLD ,已被开发为高水平的3D建模平台用来减轻模具设计过程的困难。这样的安排在许多方面都是有利的。这种三维建模平台提供了插入软件与库的功能,还有作为一个既定的用户界面和风格的设计。其结果是,开发时间因为这些“附加”而大大减少。IMOLD (智能模具设计) 1 是一个基于知识下的,运行在综合绘图SolidWorks平台下的应用软件,并实现了以使用用户为条件的功能。它可用于Unix和Windows 操作系统。多年来,模具设计工程师必须处理两个不同的系统,UNIX和PC。前者是广泛应用在工程中,而后者主要用于中小型企业。 工程师们还需要将它运行于企业中,例如办公室中的文字处理,电子表格和项目管理工具,但这些并不是UNIX的工作范围。幸运的是,随着计算机技术的显着发展,在过去十年中已提供了一种方法来改变这种状况。最显着的变化是在计算机硬件区域,即实际的电子部分与数据处理,信息存储和显示技术,速度和记忆两方面。这些都使我们能更有效地利用固体建模功能在PC机的CAD / CAM 系统。随着提供更多的先进低成本的软件于Windows ,越来越多的工程师开始使用PC去完成他们的工作。因此,开发新的基于Windows平台上的模具设计应用软件已经有很高的需求。高端用户发现,中程固体模型,如SolidWorks,正符合他们的需求。从开始作为一个本地的Windows应用程序,如今SolidWorks已成为Windows下的一个3D机械设计软件。其独特的综合生产水平,易用性和经济性是无与伦比的。SolidWorks 99,第七次公司主要发布的机械设计软件用于Windows NT ,Windows 98和超越提供的平台,它是将更多的功能集成于一个集成模块的固体建模软件。常用的,如点击,拖放,剪切和粘贴,数据共享与其他导致其生产收益的Windows软件。其易用性和廉价性可以在没有广泛进行培训的公司使用并能够安装系统透射电镜在每一个工程师的桌面上。它其中一个应用是在模具设计中的塑料工业。这一最新的应用程序技术为模具设计过程增添了一个全新的层面。2. 注塑模具设计注塑模具使用温度依赖性变化的材料特性,通过使用铸模以获得最终形状的零散部分完成或接近完成的产品。在这种类型的制造过程中,液体材料被用来填充和塑造内腔造型 2 。首先,建立一个模型需要模具设计模型和载方块。设计模型代表成品,而载方块代表模具组件的总量。注塑模具设计涉及有关结构和功的组成部分模具的广泛经验知识(启发式知识)。一个新的模具开发典型过程可分为四个主要阶段:产品设计,模具的能力评估,细节零件设计,凸、凹模设计以及模具细节设计。最开始,一个产品的观念是一些人齐心协力想出的(通常是结合营销和工程)。开始的主要重点是分析市场机会和拟定合适的战略。在第一阶段,首先了解与进程相关的制造业的信息,然后设计制作详细的几何参数。设计的概念是转化为采用适当的生产信息制造。第二阶段在脱模方向和分型线的位置添加检查模具的能力。否则,零件的形状将被再次修改。第三阶段,部分几何参数是用来建立模具的型芯和型腔,以用于构成零件。一般收缩和膨胀需要被考虑以便模具在高温处理时形成正确的尺寸和形状。浇道,气孔也需要添加。将几何数据和分型信息结合是至关重要的一点。第四阶段涉及整体机械结构的模具,包括注塑机的连接模具,一种用于填充,冷却,排出和模具装配的机构。3. 方法论对于上述所有,SolidWorks 99已经被作为该平台的新模具设计投入应用。图1所示为Windows三维注塑模具设计系统与IMOLD的比较。用户的应用程序也可建立和运行作为一个独立的exe.文件或用户的DLL 或扩展DLL的SolidWorks。Solid Works的加载项管理器可以让用户在任何时候控制第三方软件装载在他们的SolidWorks上。一个软件包不止加载一次,还可以设置停留在SolidWorks上。3.1. SolidWorksSolidWorks最近成为了基于Windows操作系统的三维产品设计软件,它提供了一个最有力和直观的一流机械设计解决方案。对于SolidWorks,零件的形成是通过建立一个“基本特征” 并增加其他功能,如主体,切割,打孔,框架等。该基本特征可能是一种挤压,旋转,弯曲配置,或高抛。要创建一个基础特征,需要绘制一个二维几何图形并且移动图形到空间中来创造一个容块。几何图形可以被绘制在结构平面或其表面部分。基于特征的固体建模程序被用于二维设计的方法虽然已经过时,但由于基于Unix的固体建模软件很昂贵,所以我们采用基于微软Windows下的Solidworks ,它的成本价格低于之前的固体建模程序 3 。3.2 Parasolid作为三维内核SolidWorks使用Parasolid作为一个三维内核。 Parasolid内核建模工具包,是公认的世界领先的,生产验证的核心固体建模。设计上作为一种精确的边界代表性建模工具,Parasolid提供强大的固体建模,广泛的单元模型和集成面/层建模能力和被设计为简单的一体化的CAD / CAM / CAE系统,加快了投放市场的时间。其大量的功能被作为库的示例和面向对象的程序接口。它实质上是一个稳定的系统,可以用来 4 :(一)建立和操纵固体物体; (二)计算质量和转动惯量,并进行干扰检测;(三)用若干不同的表示方法输出的物体; (四)存储对象某种数据库或存档以及稍后的检索;(五)支持自形成表面。3.3 API 5 SolidWorks的应用编程接口(API)是一个对于SolidWorks的OLE编程接口。它包含数百个功能,可以被称为Visual Basic,VBA( Excel, Access等),C , C + + ,或SolidWorks的文件宏观调控。这些功能提供编程直接访问SolidWorks功能,如创建一条线,挤压,或核实参数表面。API的界面采用了面向对象的方法。全部该API函数的方法或属性,适用于一对象。图2是一个详细的鉴于SolidWorks的应用程序接口。SolidWorks的功能,通过公开的OLE自动化调度和使用派遣,也可通过标准的COM对象来进行。 调度接口 6 将打包不明确点并重新赋值为变量,这样的语言如Basic便可以处理他们。COM执行让您应用更多的可直接接触的基本对象和其他的部分,提高其性能。4. 执行实际上,SolidWorks API接口使用对象导向和API函数允许一个选择的一种面向对象的语言,例如:Visual C + +,作为的编程语言的方法。使用这种方法,应基于Windows的三维注塑模具设计,应用在Windows NT上通过接口的Visual C + +代码的商业软件, SolidWorks 99 。在此应用程序的模具设计过程分为几个阶段,提供模具设计一致的方法去创建模具设计。这个概述框架的显示如图 3 。每一个阶段可以被视为一个独立的模块的工程。这几个模块已被研制成功并使用在SolidWorks上。其中两个,模具基础模块和显示模块如下。4.1 模具基础模块模具基础模块可以自动创建参数标准模具基地,以及其所有组成部分和配件,如HASCO ,DME, HOPPT ,LKM和FUTABA。该模块可通过设计师轻松定制模具基地常用属性。主要特点包括提供标准模具的基础部件,例如支持支柱和浇道衬套, 2板和3板模具基地,和定制非标准模具基地。模具基础模块由四个主要部分组成,即组件库(包括标准和非标准件库),设计平台,部分从动功能,结构和连接管理。在这里,部分从动的功能提供了SolidWorks以支持该应用程序。模具基础模块详细显示如图 4 。( 1 )构件库在这个竞争日益激烈的世界,为了加强模具设计能力,降低设计成本和周期时间,减少人力, 自动化成为实现它的主要因素。换句话说,它必须有计算机软件,这个可以轻松地创建,修改和分析模具的设计组件,并更新变化设计模型。为了实现这一目标,必须提供一个三维构件库用来储存标准和非标准零部件数据,其尺寸都存储在Microsoft Excel中。指定适当的尺寸,这些构件便可以生成并插入装配结构。这个库是完全可定制的并且设计师能够增加自己需要的部分进入库。( 2 )尺寸驱动SolidWorks提供强大的尺寸驱动功能客观支持参数化设计。这是逻辑之间的关系在尺寸设置储存在Microsoft Excel的几何参数。当一整套尺寸被集成为相应参数的几何形状时,准确模型将可获得。( 3 )设计平台平台的设计使得设计师可以建立多种部分配置参数指定的Microsoft Excel电子表格。设计平台中保存文件的一部分,是用来存放尺寸,提供的功能和约束成形性能的,其中包括一些部分宣传材料,注释,和客户使用必要条件。当适当的尺寸被添加,在设计平台中将包含所有用以创建一个精确的模型装配的必要信息。( 4 )结构与管理这是一些结构关系模具的基础组件。当通过设计平台提供某些参数设置后,这个分模块将帮助模具设计师插入这些组件到装配的结构中,从而自动生成一个特定的模具基地装置。4.2 分模一些分模算法 7-10 已在前面讲过。这一过程中,分模模块用来处理建立型芯和型腔。它是电脑辅助注塑模具设计系统 11 最重要的模块。建立模具模型需要有一个设计模型,载方块,可用的分型面。设计模型代表了成品,而载方块代表模具组件总数。为了分开方块可形成型芯和型腔,设计模型首先要从方块中减去。然后将方块通过分型面分成两半,通常被称为型芯和型腔。当熔融塑料注入型腔的时候,最终产品即由两个对立的模具半凝固后,模具半摆脱部分沿分模方向D-D分开。那么实际的零件便可以获得。图 5显示分模设计进程。( 1 )确定脱模方向在沿相反方向的型芯和型腔脱开便是便是脱模方向(图6(a)条),产生分模线。脱模方向应首先确定。分模的方向影响分模线的方向,从而影响复杂的模具的确定。在大多数情况下,分模的方向在确定的同时应考虑几何方向和生产问题。( 2 )“通过”黑洞的认识和补丁当产生一些通过生产而成的漏洞时,设计者必须指出漏洞的分模位置和产生了分型面的漏洞。这个被称为“补丁”。表面需要并通过不定进行修复。由于上模具和下模具通过型腔连接,模具是不能分开型芯和型腔的。而且不能自动创建无补丁的洞(见图6条(b)。( 3 )确定分型线和挤压方向在成型时,一组部分的曲面成型由型芯与其他组的型腔组成。因此分型线之间的交叉关系使两组表面形成型芯和型腔。所以分模线应选在最大边回路的表面。从分模的边界线分开型芯或型腔的阻碍。挤压方向路径的分型线将在模糊时被跟随。这是垂直的脱模方向,而不是平行的分开表面正常的侧面的铸模(见图6(c)段)( 4 )生成分型面分型面是型芯和型腔相交的表面。分型面可以作为分裂的表面用以将模具分为两半。两种方法可用于产生分型面。扫描方法:在分型面生成由挤压的分型线向外推至外边界的型芯和型腔(见图6 (d)项) 。辐射的方法:在SolidWorks的分型面上也可以用辐射所产生的分型线与指定的辐射距离相结合达到延长以外的外表面的载箱(见辐射表面图6(e)。( 5 )建立载模块载模块可以将目标维起来,另外增加合适的空间围绕其周边进行计算。载模块的尺寸,模具的强度,和成型参数是决定物体尺寸的基础,可以有效地确定模具装配尺寸(图6(f)段)。( 6 )生成型芯和型腔为了创建型芯和型腔,载模块必须分成两个不同的模具半。首先,设计模型应从模块中减去。从而,一个空的空间内才能获得载模块。然后分型面和修补表面被用作分裂面,将载模块分成两个半模具的型芯块和型腔块。最后,模拟模具开模过程和检查干扰模具组件,模具半脱离部分表面不受任何外界干扰,沿方向d-d分模(图6(g段)。5 结束语本文介绍了塑料注射模具设计技术和方法以及CAD注射模具的基本概念。通过Windows NT平台,该方法已实施在SolidWorks99和API 。这使作为平台的Windows的本地设计环境具有强大的装配能力,易用性强,快速学习,而且价格便宜。CAD原型塑料注塑模具的设计使用Visual C + +已经通过Windows NT平台被发展和实施于SolidWorks99和API。这原型已开发和测试了几个模块,如数据筹备,填充设计,模具基地分模设计,模具设计等,已经获得了良好的效果。该程序为设计师提供了一个交互式CAD程序和Windows的本地设计环境,这既可以加快模具设计流程又可以增加标准化的便利性,同时又加速了模具制造。这一项目是一个面向对象的编程语言(Visual C + +),以确保其进一步发展和推广。 这种方法主要针对注塑模具设计过程,但它也可以用于压铸模具设计。参考资料1 IMOLD Version 3.0, Manusoft Plastic Pte Ltd., 1998.2 Y.S. Yueh, R.A. Miller, Systematic approach to support design for manufacturability in injection molding and die casting, in: Proceed-ings of the Computers in Engineering ASME Database Symposium,ASME, New York, USA, 1995, pp. 755765.3 SolidWorks 99 Users Guide, SolidWorks Corporation.4 Unigraphics Solutions Inc. Parasolid On-Line Documentation Web,Parasolid V SolidWorks 99 API Documentation, SolidWorks Corporation.6 J.J. Shah, H. Dedhia, V. Pherwani, S. Solkhan, Dynamic interfacing of applications to geometric modeling services via modeler neutral protocol, Comput. Aided Des. 29 (12) (1997) 811824.7 A.Y.C. Nee, M.W. Fu, J.Y.H. Fuh, K.S. Lee, Y.F. Zhang, De-termination of optimal parting directions in plastic injection mold design, CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 46 (1) (1997) 429432.8 Z.-Y. Zhou, S.-M. Gao, Z.-C. Gu, J.-Y. Shi, Automatic determination of the parting line in injection mold design, J. Comput. Aided Des.Comput. Graphics 12 (7) (2000) 512516.9 M.W. Fu, J.Y.H. Fuh, A.Y.C. Nee, Core and cavity generation method in injection mould design, Int. J. Prod. Res. 39 (1) (2001)121138.10 L. Kong, J.Y.H. Fuh, K.S. Lee, Auto-generation of patch surfaces for injection mould design, Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. B 215 (1) (2001) 105110.11 C.K. Mok, K.S. Chin, J.K.L. Ho, An interactive knowledge-based CAD system for mould design in injection moulding processes, Int.J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 17 (1) (2001) 2738.Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 8189A Windows-native 3D plastic injection mold design systemL. Kong, J.Y.H. Fuh, K.S. Lee, X.L. Liu, L.S. Ling, Y.F. Zhang, A.Y.C. NeeDepartment of Mechanical Engineering, National University of Singapore,10 Kent Ridge Crescent, Singapore 119260, SingaporeAbstract3D solid-modeling revolution has reached the design mainstream. While high-end 3D solid-modeling systems have been on engineersworkstation at large aerospace, consumer products, and automobile companies for years, many smaller companies are now making theswitch from workstations to PC. One reason for the shift is that the flexibility and advancement of Windows-native/NT has let softwaredevelopers create applications that are affordable and easy to use. High-end users are finding that mid-range solid modelers, such asSolidWorks, have met their needs.SolidWorks was chosen as the platform due to the Windows-native design environment, powerful assembly capabilities, ease-of-use,rapid learning curve, and affordable price. A Windows-native 3D plastic injection mold designs system has been implemented on an NTthrough interfacing Visual C+ codes with the commercial software, SolidWorks 99 and API. The system provides a designer with aninteractive computer-aided design environment, which can both speed up the mold design process and facilitate standardization. 2003 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.Keywords: Plastic injection mold; Windows; CAD; Parting1. IntroductionWith the broader use of plastics parts in a wide productrange, from consumer products to machinery, cars and air-planes, the injection molding process has been recognizedas an important manufacturing process. The mold designprocess is generally the critical path of a new product de-velopment. Conventionally, mold design has always been amuch “mystified” art, requiring years of experience beforeone can be relatively proficient in it. Due to the initial diffi-culty in learning this art, less and less people are benefitingfrom the experience and knowledge of the experts in thisfield. To change the current situation, one way is to use acomputer-aided design (CAD) system.CAD as an everyday term has grown to a broad range ofcapabilities and has applications in fields ranging from edu-cation for school teaching to three-dimensional mechanicaldesign. At the present time, most CAD systems provideonly the geometric modeling functions that facilitate thedrafting operations of mold design, and do not providemold designers with the necessary knowledge to design themolds. Thus, much “add-on” software, e.g. IMOLD, havebeen developed on high-level 3D modeling platforms toCorresponding author. Fax: +65-67791459.E-mail address: .sg (J.Y.H. Fuh).facilitate the mold design processes. Such an arrangementis advantageous in many ways. The 3D modeling platformprovides plug-in software with a library of functions as wellas an established user interface and style of programming.As a result, the development time for these “add-ons” issignificantly reduced.IMOLD(intelligent mold design) 1 is a knowledge-based software application, which runs on the UnigraphicsSolidWorks platform and is carried out by using the UserFunction provided. It is available on the UNIX and windowsoperation system. For years, mold design engineers havehad to deal with two different systems, UNIX and PC. Theformer is widely used in engineering applications whilstthe latter is used mainly in small and medium companies.Engineers also need to run corporate office applications suchas word processing, spreadsheets, and project managementtools, but these were not on their UNIX workstations.Fortunately, the remarkable development of computertechnology in the last decade has provided a way to changethis situation. The most significant change has been inthe area of computer hardware, i.e. the actual electroniccomponents associated with data processing, informationstorage, and display technology, in terms of both speedand memory. These have resulted in the more efficient useof the solid-modeling functions in a PC-based CAD/CAMsystem. With the increased availability of sophisticated,low-cost software for Windows, more and more engineers0924-0136/03/$ see front matter 2003 Elsevier Science B.V. All rights reserved.doi:10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00186-982L. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 8189are using PC applications to get their jobs done. Thus thedevelopment of a new mold design application based on theWindows platforms is in high demand.High-end users are finding that mid-range solid modelers,such as SolidWorks, have met their needs. Developed fromthe beginning as a native Windows application, SolidWorksis one of the 3D mechanical design softwares for Win-dows. Its unique combination of production-level power,ease-of-use, and affordability is unmatched. SolidWorks99, the seventh major release of the companys mechan-ical design software for Windows NT, Windows 98 andbeyond provides an increased power and functionality in afully integrated solid modeler. Familiar conventions such aspoint-and-click, drag-and-drop, cut-and-paste, and seamlessdata sharing with other Windows software lead to produc-tivity gains. The ease-of-use without extensive training andat affordable pricing enables companies to install the sys-tem on every engineers desktop. One of its applications isfor mold design in the plastics industry. This latest appli-cation technology has added an entirely new dimension tothe mold design process.2. Injection mold designInjection molding uses temperature-dependent changes inmaterial properties to obtain the final shapes of discreteparts to finish or near-finish dimensions through the use ofmolds. In this type of manufacturing process, liquid materialis forced to fill and solidify inside the cavity of the mold 2.Firstly, the creation of a mold model requires a designmodel and a containing box. The design model representsthe finished product, whereas the containing box representsthe overall volume of the mold components.Fig. 1. Relationship among user applications, SolidWorks, Unigraphics and Parasolid.Injectionmolddesigninvolvesextensiveempiricalknowl-edge (heuristic knowledge) about the structure and the func-tions of the components of the mold. The typical processof a new mold development can be organized into four ma-jor phases: product design, moldability assessment, detailedpart design, insert/cavity design, and detailed mold design.In Phase 0, a product concept is pulled together by afew people (usually a combination of marketing and engi-neering). The primary focus of Phase 0 is to analyze themarket opportunity and strategic fit. In Phase I the typicalprocess-related manufacturing information is then addedto the design to produce a detailed geometry. The concep-tual design is transformed into a manufacturable one byusing appropriate manufacturing information. In Phase IIthe parting direction and parting lines location are added toinspect the moldability. Otherwise, the part shape is againmodified. In Phase III, the part geometry is used to establishthe shape of the mold core and cavity that will be used toform the part. Generally shrinkage and expansions need tobe considered so that the molding will be the correct sizeand shape at the processing temperature. Gates, runners,overflows, and vents also need to be added. The associationbetween geometric data and parting information is criticalat this point. Phase IV is related to the overall mechanicalstructure of the mold including the connection of the moldto the injection machine, a mechanisms for filling, cooling,and for ejection and mold assembly.3. MethodologyFor the reasons described above, SolidWorks 99 has beenused as the platform for the new mold design application.Fig. 1 shows a Windows-native 3D injection mold designL. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 818983system compared with IMOLD. Users applications can becreated and run as a standalone exe file or as a User DLLor Extension DLL in SolidWorks. The SolidWorks Add-InManager allows users to control which third party softwareis loaded at any time during their SolidWorks session. Morethan one package can be loaded at once, and the settingswill be maintained across SolidWorks sessions.3.1. SolidWorksSolidWorksrecentlyemergedasoneofthe3Dproductde-sign software for Windows, providing one of the most pow-erful and intuitive mechanical design solution in its class. InSolidWorks, parts are created by building a “base feature,”and adding other features such as bosses, cuts, holes, fil-lets, or shells. The base feature may be an extrusion, revo-lution, swept profile, or loft. To create a base feature, sketcha two-dimensional geometric profile and move the profilethrough space to create a volume. Geometry can be sketchedon construction planes or on planar surfaces of parts.Feature-basedsolid-modelingprogramsaremakingtwo-dimensional design techniques obsolete. However,Unix-based solid-modeling software are expensive. Withthe introduction of SolidWorks for Microsoft Windows,the cost is less than the price of earlier dimension drivensolid-modeling programs 3.3.2. Parasolid as a 3D kernelSolidWorks uses Parasolid as a 3D kernel. Parasolid ker-nel modeling toolkit, is recognized as a worlds leading,production-proven core solid modeler. Designed as an exactFig. 2. SolidWorks API objects.boundary-representation solid modeler, Parasolid providesrobust solid-modeling, generalized cellular modeling and in-tegrated surface/sheet modeling capabilities and is designedfor easy integration into CAD/CAM/CAE systems to giverapid time to market. Its extensive functionality is suppliedas a library of routines with an object-oriented program-ming interface. It is essentially a solid modeler, which canbe used to 4: (i) build and manipulate solid objects; (ii)calculate mass and moments of inertia, and perform inter-ference detection; (iii) output the objects in various picto-rial ways; (iv) store the objects in some sort of database orarchive and retrieve them later; and (iv) support freeformsurfaces.3.3. API 5The SolidWorks application programming interface (API)is an OLE programming interface to SolidWorks. The APIcontainshundredsoffunctionsthatcanbecalledfromVisualBasic, VBA (Excel, Access, etc.), C, C+, or SolidWorksmacro files. These functions provide the programmer withdirect access to SolidWorks functionality such as creatinga line, extruding a boss, or verifying the parameters of asurface.The API interface uses an object-oriented approach. Allthe API functions are methods or properties that apply to anobject. Fig. 2 is one particular view of the SolidWorks APIobjects.SolidWorks exposes functionality through OLE automa-tion using Dispatch and also through standard COM objects.The Dispatch interface 6 will package arguments and re-turn values as Variants so that languages such as Basic can84L. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 8189handle them. A COM implementation gives your applica-tion more direct access to the underlying objects, and sub-sequently, increased performance.4. ImplementationsThe facts that SolidWorks API interface uses an object-oriented approach and the API functions allows one toFig. 3. System infrastructure for the mold design application.choose an object-oriented language, e.g. Visual C+, asthe programming language. Using this methodology, aWindows-based 3D injection mold design application is de-veloped on Windows NT through interfacing of the VisualC+ code with a commercial software, SolidWorks 99. Inthis application the mold design process is divided into sev-eral stages, providing the mold designer with a consistentmethod of creating the mold design. The overview of thisframework is shown in Fig. 3. Each stage can be consideredL. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 818985as an independent module of the program. Several moduleshave been successfully developed using SolidWorks. Twoof them, mold base module and parting module are shownbelow.4.1. Mold base moduleThe mold base module can automatically create parame-tric standard mold bases, with all its components andaccessories, like HASCO, DME, HOPPT, LKM andFUTABA. This module allows easy customization ofmold bases commonly used by designers. Key features in-clude availability of standard mold base components likesupport pillars and sprue bushings, 2-plate and 3-platemold bases, and customization of non-standard moldbases.The mold base module consists of four main sections,namely, the component library (including standard andnon-standard part library), the design table, the dimensiondriven functionality, and structure relation management.Here, the dimension driven functionality is provided bySolidWorks to support for the application. The details forthe mold base module are shown in Fig. 4.(1) Component libraryIn order to strengthen the mold design capability inthis increasingly competitive world, lowering the designcost and cycle time, reducing the man-power, and au-tomation are major factors in achieving this purpose. Inother words, it is necessary to have computer softwarethat is able to easily create, modify, and analyze themold design components, and update the changes in adesign model. To achieve this, a 3D component libraryis provided to store standard and non-standard partsdata, whose dimensions are stored in Microsoft Excel.By specifying the appropriate dimensions, these com-ponents can be generated and inserted into the assemblystructure. This library is completely customizable anddesigners are able to add their own parts into the library.(2) Dimension drivenSolidWorks provides strong dimension driven func-tionality to support parametric design. It is the logi-cal relationship between the dimension sets stored inMicrosoft Excel and the geometry. When a set of di-mension is integrated with the corresponding parameterset of the geometry of an object, the exact model canbe then obtained.(3) Design tableA design table allows a designer to build multipleconfigurations of parts by specifying parameters in anembedded Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. The designtable is saved in the part file and is used to store thedimensions, the suppression of features and the con-figuration properties, including part number in a billof materials, comments, and customer requirements.When appropriate dimensions are added, the designFig. 4. Details of the mold base module.table will contain all the information needed to createan accurate model of the assembly.(4) Structure relation managementThis section records the structure relations betweenmold base components. When supplied with certainparameter set from the design table, this sub-modulehelps the mold designer to insert these componentsinto the assembly structure, thus a specific mold baseassembly can be automatically generated.4.2. Parting moduleSome of the parting algorithms 710 have been reportedpreviously.Inthisdevelopment,partingmoduleisdevelopedto handle the creation of cores and cavities. It is one of themost important modules in a computer-aided injection molddesign system 11. The creation of a mold model needs tohave a design model, a containing box, and parting surfacesavailable. The design model represents the finished product,whereas the containing box represents the overall volume86L. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 8189Fig. 5. Parting design module.of the mold components. In order to split the box into thecore and cavity, the design model is first subtracted fromthe box. The parting surfaces are then used to separate thecontaining box into mold halves, often referred as the coreand cavity. When melt plastics is injected into the cavity, thefinished product is formed by the two opposing mold halves.After solidification, both mold halves move away from thepart along the parting directions d and d, respectively. Theactual part is then obtained. Fig. 5 shows the parting designprocess.(1) Determination of the parting directionThe pair of opposite directions along which the coreand cavity open are the parting directions (Fig. 6(a).L. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 818987Fig. 6. Parting design process: (a) determination of parting direction; (b) generation of patching surfaces; (c) determination of parting lines and extrudingdirections; (d) swept parting surfaces; (e) radiated parting surfaces; (f) creation of containing box; (g) generation of the core and cavity.88L. Kong et al./Journal of Materials Processing Technology 139 (2003) 8189To generate the parting lines, the parting directionshould be determined first. The parting direction in-fluences the orientation of the parting line that de-termines the complexity of the mold. In most cases,partingdirectionsaredeterminedbyconsideringboth geometry and manufacturing issues at the sametime.(2) Recognition and patching the “through” holesWhen there are some through holes in a product, thedesigners must indicate the parting location of the holesand generate the parting surfaces in these holes. Thisis called “patching” in this paper. Surfaces are neededand used to patch the through holes. Because the uppermold and the lower mold are connected at the throughhole, a mold cannot be separated and the core and thecavity cannot be created automatically without patchingthose holes first (see Fig. 6(b).(3) Determination of parting lines and the extrudingdirectionsIn molding, one group of the parts surfaces is moldedby the core, and the other group is molded by the cavity.The parting lines are therefore the intersection betweenthe two groups surfaces molded by the core and cavity.The parting lines are chosen from the largest edge-loopin the surface groups.From the parting lines to the boundary of the coreor cavity block, the extruding direction is the path thatthe parting lines will follow during sweeping. It is per-pendicular to the parting direction but parallel to thesurface normal of the side face of the mold box (seeFig. 6(c).(4) Generation of the parting surfacesThe parting surfaces are the mating surfaces of thecore and cavity. The parting surfaces can be used asthe splitting surfaces to cut a mold into two halves.Two methods can be used to generate the partingsurfaces.Sweep method: The parting surfaces are generatedby extruding the parting lines outwards to the outsideboundary of the core and cavity (see Fig. 6(d).Radiate method: In SolidWorks, the parting sur-faces can also be created by using radiating the partinglines with a specified radiate distance that is largeenough to extend the surface beyond the outsidefaces of the containing box (see radiate surfaces inFig. 6(e).(5) Creation of containing boxA containing box encloses the object and the addi-tional suitable space around its periphery is computed.The size of a containing box is determined based on thedimension of the object, the strength of the mold, andthe molding parameters that can effectively define thesize of the mold assembly (Fig. 6(f).(6) Generation of cores and cavitiesIn order to generate cores and cavities, the containingbox must be split into two separate mold halves. Firstly,the design model is subtracted out from the box. Thus,an empty space is obtained inside the containing box.Then parting surfaces and patching surfaces are used asthe splitting surfaces to separate the containing box intotwo mold halves, the core block and the cavity block.Fina
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
|
2:不支持迅雷下载,请使用浏览器下载
3:不支持QQ浏览器下载,请用其他浏览器
4:下载后的文档和图纸-无水印
5:文档经过压缩,下载后原文更清晰
|
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号