GQ50型钢筋切断机的结构设计与运动仿真
钢筋切断机的结构设计与运动仿真全套课程毕业设计
钢筋切断机的结构设计
GQ50型钢筋切断机的结构设计与运动仿真【优秀机械设备设计含三维建模及23张CAD图纸】
【带任务书+开题报告+文献综述+外文翻译】【54页@正文12200字】【详情如下】【需要咨询购买全套设计请加QQ1459919609】
Autodesk Inventor建模
Ⅰ轴.dwg
Ⅱ轴.dwg
Ⅱ轴大齿轮.dwg
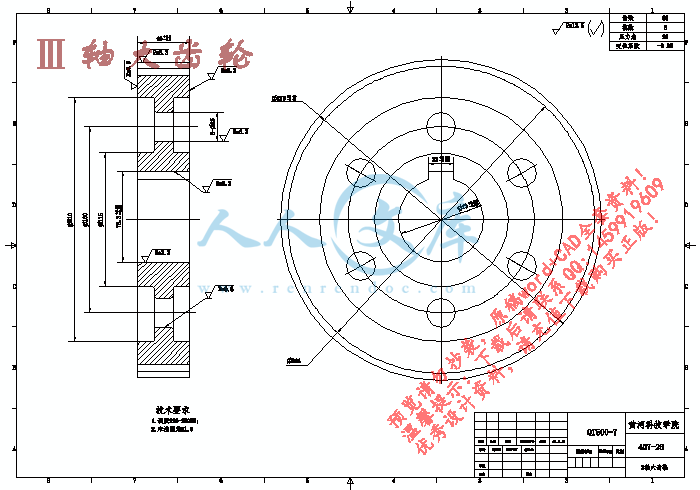
Ⅲ轴.dwg
Ⅲ轴大齿轮.dwg
任务书.doc
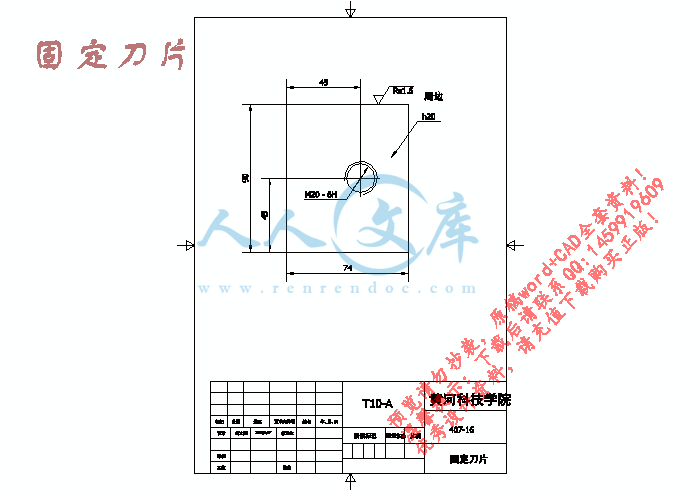
固定刀片.dwg
固定板.dwg
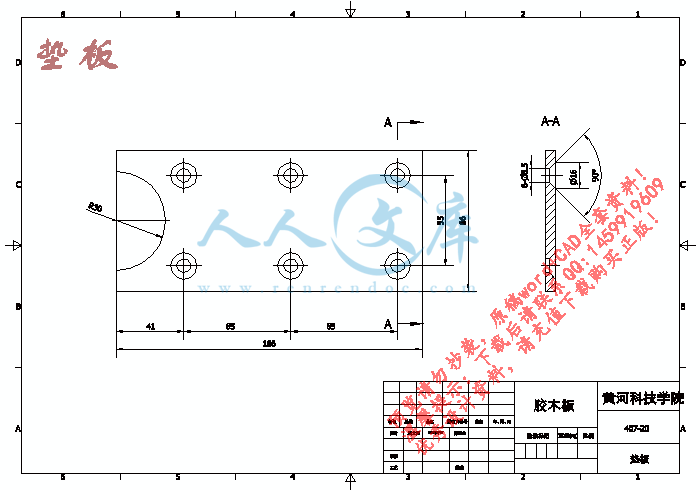
垫板.dwg
大侧盖.dwg
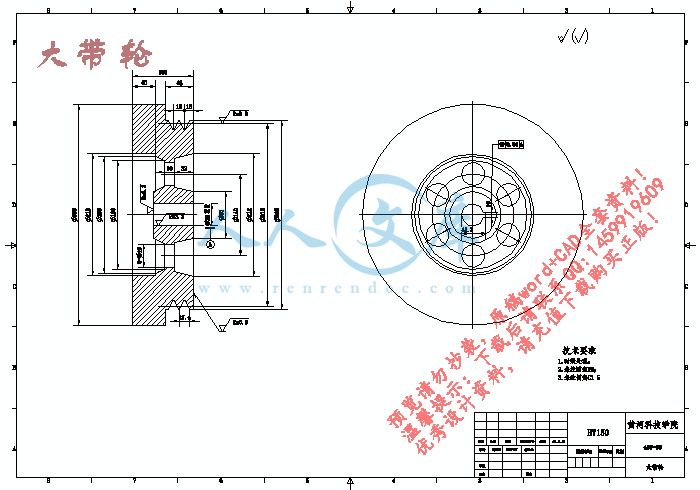
大带轮.dwg
带台轴瓦.dwg
开题报告.doc
总目录.doc
总装—运动仿真.avi
效果图图片
文献综述.doc
文献翻译.doc
文献翻译.pdf
无台轴瓦.dwg
曲轴.dwg
活动刀座.dwg
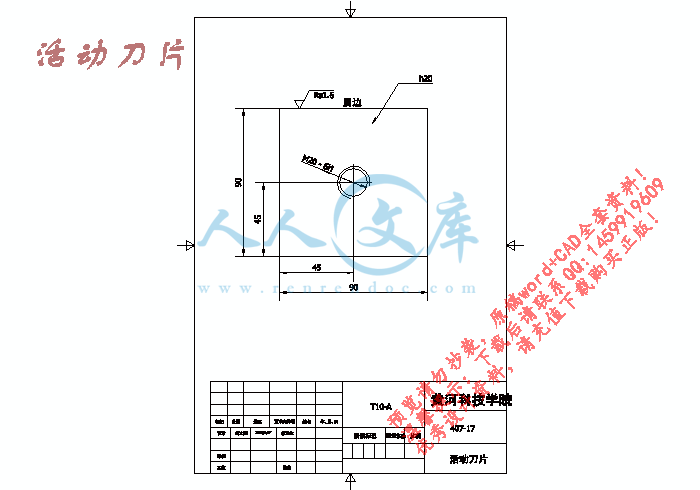
活动刀片.dwg
游动大齿轮.dwg
芯套盖.dwg
装配图.dwg
说明书.doc
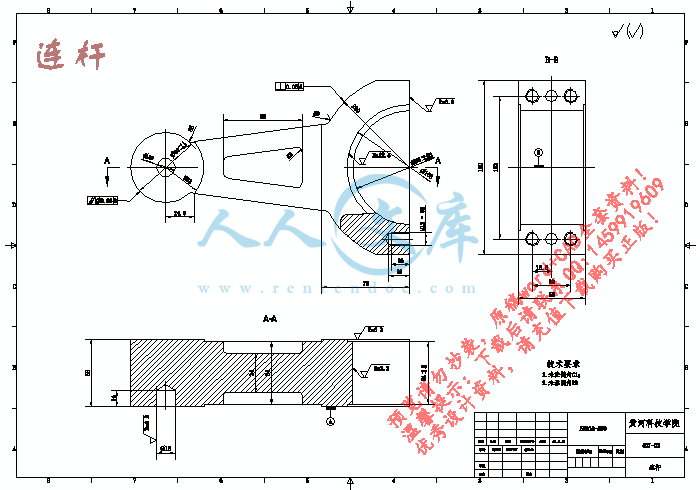
连杆.dwg
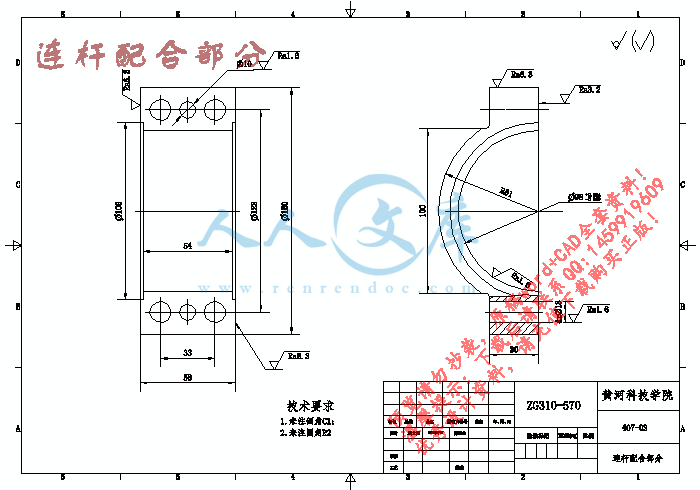
连杆配合部分.dwg
连杆铜瓦.dwg
送料轴.dwg
顶盖.dwg
任务书
毕业设计(论文)题目 GQ50型钢筋切断机的结构设计与运动仿真
毕业设计(论文)工作内容与基本要求(目标、任务、途径、方法,应掌握的原始资料(数据)、参考资料(文献)以及设计技术要求、注意事项等)
一、设计技术要求、原始资料(数据)、参考资料(文献)
1、设计要求:
1)建立运动分析模型 ,分析曲柄滑块机构的位移、速度、加速度。
2)完成50型钢筋切断机的结构设计。
3)完成传动系统的计算机的仿真分析(采用三维软件建模并仿真)。
2、原始资料(数据):
切断机的电机,4kw;切断次数,28(次/分);切断行程:40mm。
3、参考资料
1)筑路机械工程著作;
2)建筑机械杂志。
二、设计目标与任务
设计出满足要求的钢筋切断机,并完成其装配图与部分零件图,查阅文献资料不少于12篇,其中外文资料不少于2篇。
1、文献综述一篇,不少于3000字,与专业相关的英文翻译一篇,不少于3000汉字。
2、毕业设计说明书一份,内容与字数都不少于规定的任务量。
3、图纸若干(折合后不少于A1图纸3张,可以用计算机绘图)。
4、包含本次设计的所有内容的光盘一张。
GQ50型钢筋切断机的结构设计与运动仿真
摘要
本产品的设计是根据黄河科技学院工学院机械系2012届毕业设计的要求,在参观调研的基础上,对大学四年已学知识的总结、实践与提高。按照指导老师的要求,我首先查阅了大量关于此产品设计的资料,做好初期准备。然后到河南省长葛市黄河旋风股份有限公司参观,深入了解钢筋切断机的工作原理及使用要求,在此基础上,形成自己初步的设计思路。
本产品设计给定的原始参数是:切断能力为(φ6-φ50)mm的圆钢;电机功率为4kw;冲切次数为28次/min;切断行程为40mm。此次设计的主要研究内容和技术关键是:根据钢筋切断机的使用要求,确定其工作原理,在此基础上进行钢筋切断机的结构设计,确定主要结构尺寸。主要包括以下几点:1、电动机的选择;2、传动装置的设计和计算;3、轴承的选择;4、曲轴连杆机构的设计;5、机体的设计;6、刀片的设计选择。然后根据这些设计数据进行产品的建模及运动仿真。
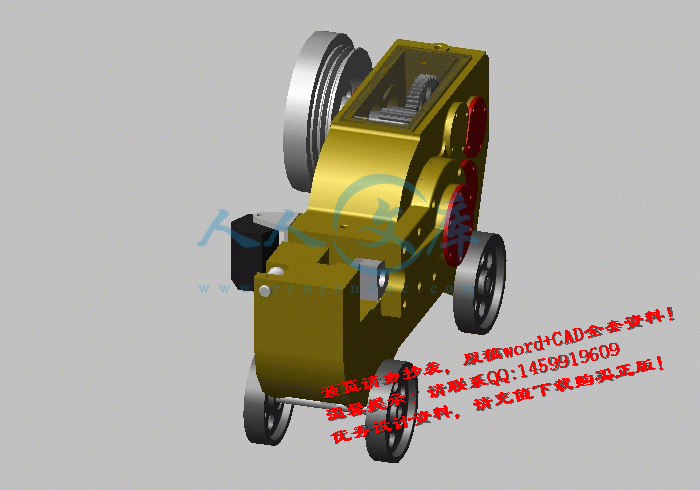
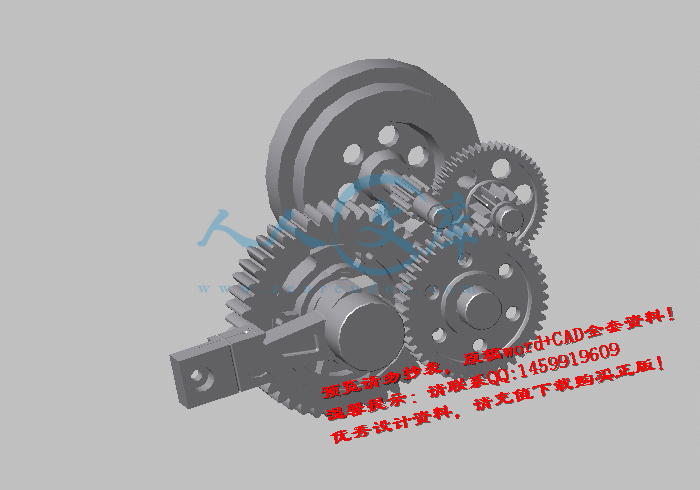
本次产品建模使用的是美国Autodesk公司的三维设计软件Inventor 2011。首先是根据设计数据建立各个零件的草图,在草图的基础上运用零件特征生成三维实体;然后在Inventor 2011软件的虚拟环境中进行虚拟装配,建立数字样机;最后进行应力分析、运动干涉分析及运动仿真。
本设计可以大幅降低钢筋切断机的研发周期及成本,从而提高产品的市场竞争力和企业的经济效益。
关键词:钢筋切断机,结构设计,Inventor 2011,虚拟装配,运动仿真
Disc Centrifuge Spindle Box Design
Author:Wenchao Liu
Tutor:Liangwen Wang
Abstract
This product is designed according to the college of engineering science and technology of 2012 member of graduation design requirements, during a visit to a research, on the basis of the university for four years have already learn knowledge summary, practice and improve. According to the requirements of the guiding teacher, I first looked a lot about this product design information, do well to the early. And then to the Yellow River in henan province ChangGe city whirlwind visit to a joint stock limited company, understand reinforced cutting machine and working principle of the use requirement, and based on this, the preliminary design to form their own ideas.
This product design parameters are given of the original: cutting ability for (phi 6-phi 50) mm round steel; The motor power for 4 kw; For punching number 28 times/min; Cut off the trip to 40 mm. The design of the main research contents, technology and the key is: according to the use requirement reinforced cutting machine, determine its working principle, and based on the structure of the steel cutting machine design, confirming the main structure size. Mainly include the following: 1, the choice of the motor; 2, the design and calculation of transmission device; 3, bearing choice; 4, crankshaft connecting rod design of organization; 5, the body's design; 6, the blade design choices. Then according to the design data modeling of products and movement simulation.
This product modeling is using the company's 3 d design Autodesk Inventor 2011 software. First of all is according to the design data to set up the various parts of the sketch, in the sketch of the use part features based on 3 d entity; And then in the Inventor 2011 software virtual environment in virtual assembly, to build digital prototype; Finally in stress analysis, motion interference analysis and simulation movement.
This design can dramatically reduce the reinforced cutting machine development cycle and cost, so as to improve the market competitiveness of products and the economic efficiency of enterprises.
Keywords: steel cutting machine, the structure design, Inventor 2011, virtual assembling, movement simulation
目 录
1 绪论1
2 设计前的准备3
2.1计划任务书3
2.1.1 产品设计的依据3
2.1.2 计划任务书3
2.2 设计前的准备3
3钢筋切断机的总体设计4
3.1钢筋切断机的工作原理4
3.2钢筋切断机的基本结构4
4传动方案的设计5
4.1 基本传动数据计算5
4.1.1分配传动比5
4.1.2计算各州的运动及动力参数5
4.2 带传动的设计6
4.2.1带型的选择6
4.2.2带轮基准直径的确定6
4.2.2带速的确定6
4.2.3中心距、带长及包角的确定。6
4.2.4 确定带的根数7
4.2.5 带轮结构与尺寸7
4.3 齿轮传动的设计7
4.3.1选材料、确定初步参数7
4.3.2齿面疲劳强度计算8
4.3.3齿根抗弯疲劳强度验算10
5 Autodesk Inventor 201112
5.1 Inventor 2011的组成12
5.2三维绘图软件Inventor 2011的优点12
5.2.1 二维工程图处理能力比较好12
5.2.2 具有良好的设计项目管理功能13
5.2.3 参数化技术和变量化技术13
5.2.4 简便的操作风格13
5.2.5 精彩的显示功能13
6 主要零件的设计及建模14
6.1机体的设计流程14
6.2其他主要零件的建模效果展示23
7钢筋切断机的装配29
7.1装配流程29
7.2大侧盖的装配步骤29
7.2.1新建文件30
7.2.2装入所有零件30
7.2.3向机体安装大侧盖30
7.3装配效果图展示33
8应用Inventor软件进行干涉检查34
8.1检查零部件之间的干涉34
8.2 连杆及连杆铜瓦的干涉检查34
9绘制各主要零件的工程图37
10 传动结构的运动仿真41
10.1建立一个简单的装配41
10.2运动仿真步骤41
致谢45
参考文献46
附 录48
1 绪论
钢筋切断机是建筑机械的一种。它是钢筋加工必不可少的设备之一,主要用语房屋建筑、桥梁、隧道、电站、大型水利等工程中对钢筋的定长切断。钢筋切断机与其他切断设备相比,具有重量轻、耗能少、工作可靠、效率高等特点,因此近年来逐步被建筑工地和小型轧钢厂等广泛采用,在国民经济建设的各个领域发挥了重要的作用。
新中国成立初期,建筑工程中钢筋加工技术非常落后,主要依靠手工或者简单工具,劳动强度大、生产效率低、工程质量很难保证。太原重型机械学院是国内最早生产钢筋切断机的单位之一。他们于1958年首次引进苏联的卧式钢筋切断机图纸,生产了国内第一台钢筋切断机。随后又于1985年引进了日本立式钢筋切断机和德国卧式钢筋切断机,并在此基础上研发了GQ40、GQ50、GQ65等一系列开式、封闭式及半封闭式切断机。该系列的钢筋切断机均是采用机械轮剪切进行切断的。此外,沈阳建筑工程学院工厂、陕西渭南农业科技股份有限公司、黑虎建筑机械公司等企业也生产过不同类型的机械式钢筋切断机。
参考文献
[1] 孙恒,陈作模,葛文杰主编.机械原理(第七版)[M].高等教育出版社,2006.5.
[2] 郑修本主编.机械制造工艺学(第二版)[M].机械工业出版社,2011.2.
[3] 濮良贵,继明刚主编.机械设计(第八版)[M].高等教育出版社 2006.5.
[4] 吴宗泽,罗胜国主编. 机械设计课程设计手册(第三版)[M].高等教育出版社,2006.5.
[5] 机械设计委员会主编.机械设计手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2007.
[6] 朱张校主编.工程材料(第三版)[M].北京:清华大学出版社.2000.
[7] 胡仁喜,赵伟,刘昌丽等主编.Inventor 2009中文版机械设计高级应用实例[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2009.
[8] 刘极峰主编.计算机辅助设计与制造[M].北京:高等教育出版社,1979.1.
[9] Aberdeen Group, Inc. Managing Product Relationships: Enabling Iteration and Innovation in Design[M]. USA: Aberdeen Group.2006 . 8 .
[10] 施平主编.机械工程专业英语[M].北京:北京电子工业出版社,2003.
[11] Aberdeen Group, Inc. Product Lifecycle Collaboration Benchmark Report: The Product Profitability “X Factor”? [M]. USA: Aberdeen Group. 2006.8.
[12] 灏主编.机械设计手册(第四卷)[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1991.9.
[13] 灏主编.机械设计手册(第二版)[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2000.
[14] 邹宜候主编.机械制图(第四版)[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2001.
[15] Aberdeen Group, Inc. The Product Lifecycle Management for Small to Medium-Size Manufacturers Benchmark Report[M]. USA: Aberdeen Group. 2006.3.
[16] 邱宣怀等主编.机械设计(第四版)[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2004.
[17] Aberdeen Group, Inc. Design for Sourcing: Improving Product Lifecycle Profitability[M].USA: Aberdeen Group. 2006.3.
[18] 文英主编.金属工艺学上册(第四版)[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2003.5.
[19] 刘鸿文编著.材料力学[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2004.1.
[18] 韩进宏主编.互换性与测量技术基础[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社,2004.7.
[20] Aberdeen Group, Inc. The Global Product Design Benchmark Report[M]. USA: Aberdeen Group.2005.12.
[21] Aberdeen Group, Inc.The Product Innovation Agenda Benchmark[M]. USA: Aberdeen Group. 2005.9.
[22] 徐灏主编.新编机械师手册上、下册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1995.
[23] 辛一行主编.现代机械设备设计手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2001.
[24] 卜炎主编.机械传动装置设计手册上、下册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1998.12.
[25] 朱龙根主编.简明机械零件设计手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2003.
[26] 合肥通用机械研究所主编.机械工程手册[M].北京:机械工业出版社,1979.1:16-24.
[27] 陈伯雄,董仁扬,张云飞等主编. Inventor Professional 2008机械设计实战教程[M].北京:化学工业出版社,2008.1:702-720.



















 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号