汽车制动系统设计及有限元分析(鼓式制动器设计含PROE三维图)
收藏
资源目录

压缩包内文档预览:
编号:22889968
类型:共享资源
大小:8.91MB
格式:ZIP
上传时间:2019-11-03
上传人:机****料
认证信息
个人认证
高**(实名认证)
河南
IP属地:河南
30
积分
- 关 键 词:
-
汽车
制动
系统
设计
有限元分析
制动器
PROE
三维
- 资源描述:
-
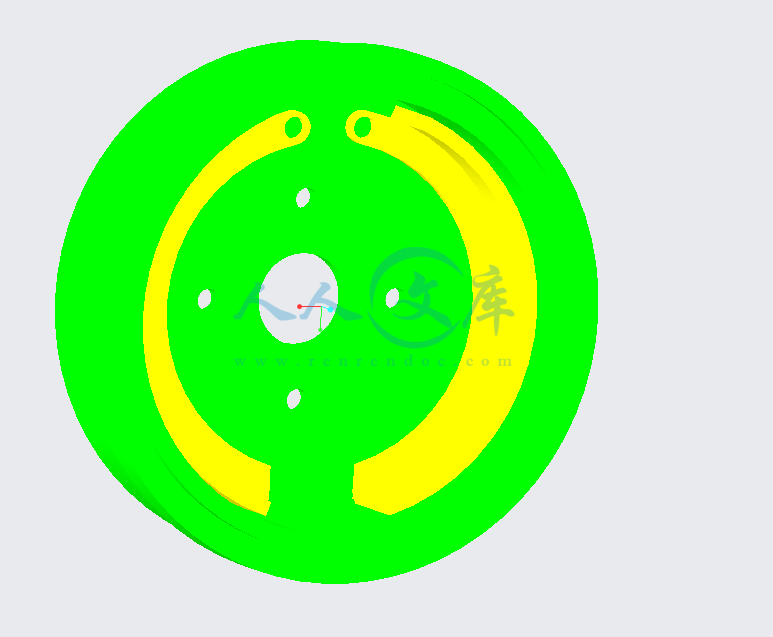

- 内容简介:
-
毕 业 设 计(论 文)外 文 参 考 资 料 及 译 文译文题目: Automotive brake systems 汽车制动系统 学生姓名:专业:所在学院:指导教师:职称:说明:要求学生结合毕业设计(论文)课题参阅一篇以上的外文资料,并翻译至少一万印刷符(或译出3千汉字)以上的译文。译文原则上要求打印(如手写,一律用400字方格稿纸书写),连同学校提供的统一封面及英文原文装订,于毕业设计(论文)工作开始后2周内完成,作为成绩考核的一部分。AutomobileBrakeSystemThebrakingsystemisthemostimportantsystemincars.Ifthebrakesfail,theresultcanbedisastrous.Brakesareactuallyenergyconversiondevices,whichconvertthekineticenergy(momentum)ofthevehicleintothermalenergy(heat).Whensteppingonthebrakes,thedrivercommandsastoppingforcetentimesaspowerfulastheforcethatputsthecarinmotion.Thebrakingsystemcanexertthousandsofpoundsofpressureoneachofthefourbrakes.Twocompleteindependentbrakingsystemsareusedonthecar.Theyaretheservicebrakeandtheparkingbrake.Theservicebrakeactstoslow,stop,orholdthevehicleduringnormaldriving.Theyarefoot-operatedbythedriverdepressingandreleasingthebrakepedal.Theprimarypurposeoftheparkingbrakeistoholdthevehiclestationarywhileitisunattended.Theparkingbrakeismechanicallyoperatedbywhenaseparateparkingbrakefootpedalorhandleverisset.Thebrakesystemiscomposedofthefollowingbasiccomponents:the“mastercylinder”whichislocatedunderthehood,andisdirectlyconnectedtothebrakepedal,convertsdriverfootsmechanicalpressureintohydraulicpressure.Steel“brakelines”andflexible“brakehoses”connectthemastercylindertothe“slavecylinders”locatedateachwheel.Brakefluid,speciallydesignedtoworkinextremeconditions,fillsthesystem.“Shoes”and“pads”arepushedbytheslavecylinderstocontactthe“drums”and“rotors”thuscausingdrag,which(hopefully)slowsthecar.Thetypicalbrakesystemconsistsofdiskbrakesinfrontandeitherdiskordrumbrakesintherearconnectedbyasystemoftubesandhosesthatlinkthebrakeateachwheeltothemastercylinder(Figure).Basically,allcarbrakesarefrictionbrakes.Whenthedriverappliesthebrake,thecontroldeviceforcesbrakeshoes,orpads,againsttherotatingbrakedrumordisksatwheel.Frictionbetweentheshoesorpadsandthedrumsordisksthenslowsorstopsthewheelsothatthecarisbraked.Inmostmodernbrakesystems(seeFigure15.1),thereisafluid-filledcylinder,calledmastercylinder,whichcontainstwoseparatesections,thereisapistonineachsectionandbothpistonsareconnectedtoabrakepedalinthedriverscompartment.Whenthebrakeispusheddown,brakefluidissentfromthemastercylindertothewheels.Atthewheels,thefluidpushesshoes,orpads,againstrevolvingdrumsordisks.Thefrictionbetweenthestationaryshoes,orpads,andtherevolvingdrumsordisksslowsandstopsthem.Thisslowsorstopstherevolvingwheels,which,inturn,sloworstopthecar.Thebrakefluidreservoirisontopofthemastercylinder.Mostcarstodayhaveatransparentreservoirsothatyoucanseethelevelwithoutopeningthecover.Thebrakefluidlevelwilldropslightlyasthebrakepadswear.Thisisanormalconditionandnocauseforconcern.Iftheleveldropsnoticeablyoverashortperiodoftimeorgoesdowntoabouttwothirdsfull,haveyourbrakescheckedassoonaspossible.Keepthereservoircoveredexceptfortheamountoftimeyouneedtofillitandneverleaveacamofbrakefluiduncovered.Brakefluidmustmaintainaveryhighboilingpoint.Exposuretoairwillcausethefluidtoabsorbmoisturewhichwilllowerthatboilingpoint.Thebrakefluidtravelsfromthemastercylindertothewheelsthroughaseriesofsteeltubesandreinforcedrubberhoses.Rubberhosesareonlyusedinplacesthatrequireflexibility,suchasatthefrontwheels,whichmoveupanddownaswellassteer.Therestofthesystemusesnon-corrosiveseamlesssteeltubingwithspecialfittingsatallattachmentpoints.Ifasteellinerequiresarepair,thebestprocedureistoreplacethecompeteline.Ifthisisnotpractical,alinecanberepairedusingspecialsplicefittingsthataremadeforbrakesystemrepair.Youmustneverusecoppertubingtorepairabrakesystem.Theyaredangerousandillegal.Drumbrakes,itconsistsofthebrakedrum,anexpander,pullbacksprings,astationarybackplate,twoshoeswithfrictionlinings,andanchorpins.Thestationarybackplateissecuredtotheflangeoftheaxlehousingortothesteeringknuckle.Thebrakedrumismountedonthewheelhub.Thereisaclearancebetweentheinnersurfaceofthedrumandtheshoelining.Toapplybrakes,thedriverpushespedal,theexpanderexpandstheshoesandpressesthemtothedrum.Frictionbetweenthebrakedrumandthefrictionliningsbrakesthewheelsandthevehiclestops.Toreleasebrakes,thedriverreleasethepedal,thepullbackspringretractstheshoesthuspermittingfreerotationofthewheels.Diskbrakes,ithasametaldiskinsteadofadrum.Aflatshoe,ordisk-brakepad,islocatedoneachsideofthedisk.Theshoessqueezetherotatingdisktostopthecar.Fluidfromthemastercylinderforcesthepistonstomovein,towardthedisk.Thisactionpushesthefrictionpadstightlyagainstthedisk.Thefrictionbetweentheshoesanddiskslowsandstopsit.Thisprovidesthebrakingaction.Pistonsaremadeofeitherplasticormetal.Therearethreegeneraltypesofdiskbrakes.Theyarethefloating-calipertype,thefixed-calipertype,andthesliding-calipertype.Floating-caliperandsliding-caliperdiskbrakesuseasinglepiston.Fixed-caliperdiskbrakeshaveeithertwoorfourpistons.Thebrakesystemassembliesareactuatedbymechanical,hydraulicorpneumaticdevices.Themechanicalleverageisusedintheparkingbrakesfittedinallautomobile.Whenthebrakepedalisdepressed,therodpushesthepistonofbrakemastercylinderwhichpressesthefluid.Thefluidflowsthroughthepipelinestothepowerbrakeunitandthentothewheelcylinder.Thefluidpressureexpandsthecylinderpistonsthuspressingtheshoestothedrumordisk.Ifthepedalisreleased,thepistonreturnstotheinitialposition,thepullbackspringsretracttheshoes,thefluidisforcedbacktothemastercylinderandbrakingceases.Theprimarypurposeoftheparkingbrakeistoholdthevehiclestationarywhileitisunattended.Theparkingbrakeismechanicallyoperatedbythedriverwhenaseparateparkingbrakinghandleverisset.Thehandbrakeisnormallyusedwhenthecarhasalreadystopped.Aleverispulledandtherearbrakesareapproachedandlockedinthe“on”position.Thecarmaynowbeleftwithoutfearofitsrollingaway.Whenthedriverwantstomovethecaragain,hemustpressabuttonbeforethelevercanbereleased.Thehandbrakemustalsobeabletostopthecarintheeventofthefootbrakefailing. Forthisreason,itisseparatefromthefootbrakeusescableorrodsinsteadofthehydraulicsystem.Anti-lockBrakeSystemAnti-lockbrakesystemsmakebrakingsaferandmoreconvenient,Anti-lockbrakesystemsmodulatebrakesystemhydraulicpressuretopreventthebrakesfromlockingandthetiresfromskiddingonslipperypavementorduringapanicstop.Anti-lockbrakesystemshavebeenusedonaircraftforyears,andsomedomesticcarwereofferedwithanearlyformofanti-lockbrakinginlate1990s.Recently,severalautomakershaveintroducedmoresophisticatedanti-locksystem.InvestigationsinEurope,whereanti-lockbrakingsystemshavebeenavailableforadecade,haveledonemanufacturetostatethatthenumberoftrafficaccidentscouldbereducedbysevenandahalfpercentifallcarshadanti-lockbrakes.Sosomesourcespredictthatallcarswillofferanti-lockbrakestoimprovethesafetyofthecar.Anti-locksystemsmodulatebrakeapplicationforceseveraltimespersecondtoholdthetiresatacontrolledamountofslip;allsystemsaccomplishthisinbasicallythesameway.Oneormorespeedsensorsgeneratealternatingcurrentsignalwhosefrequencyincreaseswiththewheelrotationalspeed.Anelectroniccontrolunitcontinuouslymonitorsthesesignalsandifthefrequencyofasignaldropstoorapidlyindicatingthatawheelisabouttolock,thecontrolunitinstructsamodulatingdevicetoreducehydraulicpressuretothebrakeattheaffectedwheel.Whensensorsignalsindicatethewheelisagainrotatingnormally,thecontrolunitallowsincreasedhydraulicpressuretothebrake.Thisrelease-applycycleoccursseveraltimepersecondto“pump”thebrakeslikeadrivermightbutatamuchfasterrate.Inadditiontotheirbasicoperation,anti-locksystemshavetwootherthingsincommon.First,theydonotoperateuntilthebrakesareappliedwithenoughforcetolockornearlylockawheel.Atallothertimes,thesystemstandsreadytofunctionbutdoesnotinterferewithnormalbraking.Second,iftheanti-locksystemfailinanyway,thebrakescontinuetooperatewithoutanti-lockcapability.Awarninglightontheinstrumentpanelalertsthedriverwhenaproblemexistsintheanti-locksystem.ThecurrentBoschcomponentAnti-lockBrakingSystem(ABS),isasecondgenerationdesignwildlyusedbyEuropeanautomakerssuchasBWM,Mercedes-BenzandPorsche.ABSsystemconsistsof:fourwheelspeedsensor,electroniccontrolunitandmodulatorassembly.Aspeedsensorisfittedateachwheelsendssignalsaboutwheelrotationtocontrolunit.Eachspeedsensorconsistsofasensorunitandagearwheel.Thefrontsensormountstothesteeringknuckleanditsgearwheelispressedontothestubaxlethatrotateswiththewheel.Therearsensormountstherearsuspensionmemberanditsgearwheelispressedontotheaxle.Thesensoritselfisawindingwithamagneticcore.Thecorecreatesamagneticfieldaroundthewinding,andastheteethofthegearwheelmovethroughthisfield,analternatingcurrentisinducedinthewinding.Thecontrolunitmonitorstherateochangeinthisfrequencytodetermineimpendingbrakelockup.Thecontrolunitsfunctioncanbedividedintothreeparts:signalprocessing,logicandsafetycircuitry.Thesignalprocessingsectionistheconverterthatreceivesthealternatingcurrentsignalsformthespeedsensorsandconvertsthemintodigitalformforthelogicsection.Thelogicsectionthenanalyzesthedigitizedsignalstocalculateanybrakepressurechangesneeded.Ifimpendinglockupissensed,thelogicsectionsendscommandstothemodulatorassembly.ModulatorassemblyThehydraulicmodulatorassemblyregulatespressuretothewheelbrakeswhenitreceivescommandsfromthecontrolutuit.Themodulatorassemblycanmaintainorreducepressureoverthelevelitreceivesfromthemastercylinder,italsocanneverapplythebrakesbyitself.Themodulatorassemblyconsistsofthreehigh-speedelectricsolenoidvalves,twofluidreservoirsandaturndeliverypumpequippedwithinletandoutletcheckvalves.Themodulatorelectricalconnectorandcontrollingrelaysareconcealedunderaplasticcoveroftheassembly.Eachfrontwheelisservedbyelectricsolenoidvalvemodulatedindependentlybythecontrolunit.Therearbrakesareservedbyasinglesolenoidvalveandmodulatedtogetherusingtheselect-lowprinciple.Duringanti-brakingsystemoperation,thecontrolunitcyclesthesolenoidvalvestoeitherholdorreleasepressurethebrakelines.Whenpressureisreleasedfromthebrakelinesduringanti-brakingoperation,itisroutedtoafluidreservoir.Thereisonereservoirforthefrontbrakecircuit.Thereservoirsarelow-pressureaccumulatorsthatstorefluidunderslightspringpressureuntilthereturndeliverypumpcanreturnthefluidthroughthebrakelinestothemastercylinder.汽车制动系统制动系统是汽车上最重要的系统。如果制动系统坏了,结果会很严重。制动器实际上是能量转化装置,制动器能将车辆的动能(动量)转化为热能(热)。当司机踩制动踏板时,司机施加的使汽车停下的力相当于推动汽车的力的十倍。制动系统能施加在每个制动器上的力有几千磅。汽车上装有两套完全独立的制动系统,即行车制动系统和驻车制动系统行车制动用来减速、停车或者控制正在正常行驶的车辆,它是通过司机踩下和释放刹车踏板来控制的。驻车制动的主要目的是使车辆在无人看管时保持静止状态。驻车制动是机械式操作,司机可以通过一个独立的驻车制动刹车脚踏板或者刹车手柄来操控。制动系统由下列基本部分组成:“制动主缸”,安装在发动机罩的下面,直接与制动踏板相连,将司机脚部的机械压力转化为液压压力。钢制的“制动管路”和柔韧的“制动软管”将制动主缸与安装在各个车轮上的“制动轮缸”连接起来。制动液,特别设计工作在极端环境下,充满制动系统。“制动蹄”和“制动衬块”在制动轮缸的推动下分别与“制动鼓”和“制动盘”接触而产生阻力,从而(有希望)使汽车减速。典型的制动系统由前部的盘式制动器和后部的盘式或鼓式制动器组成,制动器用管道与制动主缸相连。基本上,所有的汽车制动器都是摩擦式制动器。当司机开始制动时,控制装置迫使制动蹄或者制动衬块挤压车轮上的旋转的制动鼓或者制动盘。制动蹄与制动鼓或者制动衬块与制动盘之间的摩擦使车轮减速或者停下,从而使汽车被刹住。大多数现代制动系统里都有一个充满液体的缸体,叫做制动主缸,它包含两个独立的部分,每个部分都有一个活塞,每个活塞都和司机驾驶室的刹车踏板相连。当踩下制动踏板时,制动液就被从制动主缸压到各个车轮。在各个车轮处,制动液推动制动蹄或制动衬块与旋转的制动鼓或制动盘接触。静止的制动蹄或制动衬块与转动的制动鼓或制动盘之间的摩擦,使制动鼓或制动盘减速或停止,这将使车轮减速或者停止,进而使汽车减速或者停止。制动液储液罐在制动主缸的顶部。今天大部分的汽车的制动液储液罐都是透明的,以便你不必打开盖子就能看到液面的高度。制动液的液面会随着制动衬块的摩擦而下降,这是正常状况不必担心。如果液面高度在短时间内明显下降或者下降了三分之二,请尽快检查你的制动系统。保持制动液储液罐的盖子是关闭状态,除非你需要加油,绝不要让凸轮制动液暴漏着。制动液必须保持非常高的沸点,暴漏在空气中将造成制动液吸收水分而沸点降低。制动液通过一系列钢制管路和强化的橡胶管从制动主缸到达车轮处。橡胶管路仅仅用在对柔韧性有要求的地方,如前轮处,管路会随着形式上下移动。剩下的系统管路用不锈无缝钢管通过特殊配件相连。如果钢制管路需要修理,最好的方式是更换相同的管路,如果这不实际,也可以用为制动系统维修专门生产的专用接头配件来修理。决不能用铜制管路来维修制动系统,那样很危险而且违反规定。鼓式制动器,包括制动鼓、一个制动轮缸、回位弹簧、一个制动底板、两个带摩擦片的制动蹄和支承销。制动底板固定在驱动桥壳的法兰盘上或者转向节上。制动鼓安装在轮毂上。制动鼓的内表面与制动蹄摩擦片之间有一段间距。制动时,司机踩下踏板,制动轮缸是制动蹄张开压在制动鼓上。制动鼓与摩擦片之间的摩擦使车轮制动,使车辆停止。解除制动时,司机放开踏板,回位弹簧拉回制动蹄从而使车轮能自由转动。盘式制动器,有一个金属盘代替了制动鼓。制动盘两侧各装有一个平的制动蹄或者叫盘式制动摩擦衬块。制动衬块挤压旋转的制动盘使汽车停止。来自制动主缸的制动液迫使轮缸的活塞向制动盘移动,从而推动摩擦衬块紧紧地压在制动盘上。摩擦衬块与制动盘之间的摩擦使制动盘减速和停止,这就是制动的过程。活塞是塑料或者金属制的。盘式制动器有三种基本类型,浮钳盘式制动器、定钳盘式制动器和滑动钳盘式制动器。浮钳盘式制动器和滑动钳盘式制动器用一个活塞,定钳盘式制动器有两个或者四个活塞。制动系统装配组件驱动方式有机械式、液压式或者气压式。机械式杠杆机构适用于所有汽车的驻车制动。当踩下制动踏板时,推杆推动制动主缸的活塞移动,制动液从油管流到动力制动单元再流到制动轮缸,制动液的压力推开轮缸的活塞,从而使摩擦片挤压制动鼓或制动盘。如果放开制动踏板,活塞回到初始位置,回位弹簧使制动蹄回位,制动液被压回主缸,制动停止。驻车制动的主要作用是使车辆在无人看管时保持静止,驻车制动是机械式操作,司机通过一个独立的制动手柄来操纵。手刹通常在汽车已经停下时使用。当拉动手刹时,后制动系统被刹住并被锁在“打开”的位置,现在可以把汽车扔下而不用担心它自己移走了。当司机想要再次移动汽车时,他必须按一个按钮才能使手刹拉杆松开。手刹还必须能在脚刹
- 温馨提示:
1: 本站所有资源如无特殊说明,都需要本地电脑安装OFFICE2007和PDF阅读器。图纸软件为CAD,CAXA,PROE,UG,SolidWorks等.压缩文件请下载最新的WinRAR软件解压。
2: 本站的文档不包含任何第三方提供的附件图纸等,如果需要附件,请联系上传者。文件的所有权益归上传用户所有。
3.本站RAR压缩包中若带图纸,网页内容里面会有图纸预览,若没有图纸预览就没有图纸。
4. 未经权益所有人同意不得将文件中的内容挪作商业或盈利用途。
5. 人人文库网仅提供信息存储空间,仅对用户上传内容的表现方式做保护处理,对用户上传分享的文档内容本身不做任何修改或编辑,并不能对任何下载内容负责。
6. 下载文件中如有侵权或不适当内容,请与我们联系,我们立即纠正。
7. 本站不保证下载资源的准确性、安全性和完整性, 同时也不承担用户因使用这些下载资源对自己和他人造成任何形式的伤害或损失。

人人文库网所有资源均是用户自行上传分享,仅供网友学习交流,未经上传用户书面授权,请勿作他用。
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号