Polo轿车三轴五档手动变速器设计
48页 15000字数+说明书+外文翻译+6张CAD图纸【详情如下】
Polo轿车三轴五档手动变速器设计论文.doc
三轴五档变速器装配图.dwg
变速器操纵机构装配图.dwg
外文翻译--一个短期课程自动变速器.doc
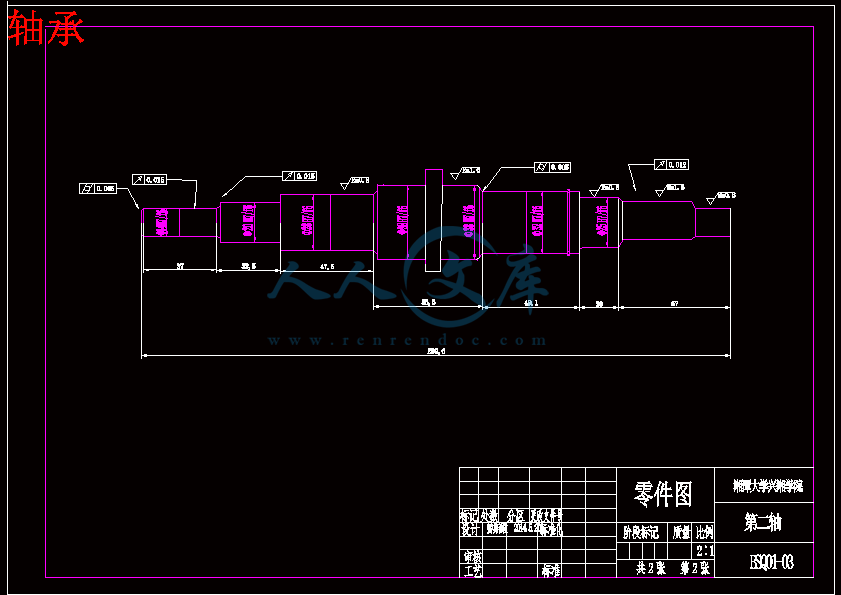
轴承.dwg
齿轮.dwg



摘 要
本设计的任务是设计一台用于轿车上的五档手动变速器。合理的设计和布置变速器能使发动机功率得到最合理的利用,从而提高汽车动力性和经济性。变速传动机构的主要作用是改变转距和转速的数值和方向;操纵机构的主要作用是控制传动机构,实现变速器传动比的改变,即实现换挡,以达到变速变距。
本文参阅了国内外大量文献,首先简单地叙述了机械式变速器的发展历史、变速器的地位和作用,讨论了其现状以及未来发展趋势。进而研究了机械式变速器的基本结构和变速原理,其中重点研究了传动机构(主要是轴和齿轮)的基本结构、特点及工作原理,对机械式变速器各挡传动路线进行了简要分析。文章包括大量的计算过程,具体内容有:变速器的布置方案分析、变速器回转件结构参数的确定、同步器的结构及工作原理、各挡齿轮的强度校核、轴的强度校核、轴承的使用寿命计算等。
关键词 齿轮、同步器、变速器
Abstract
This design task is to design a car for five manual shift transmission. Reasonable design and decorate transmission can make the engine power to get the most reasonable use of, so as to improve the dynamic performance and fuel economy cars. Variable speed transmission's main function is to change the torque and speed of numerical and direction; Operation is the main purpose of control transmission mechanism, realize the transmission ratio of the gearbox change, which realize the shift, in order to achieve the change from the speed.
This article refer to the domestic and foreign many papers, and first simply describes the mechanical transmission of the history, the status and effect of the transmission, and discussed its present situation and future development trend. And then we study the basic structure of the mechanical transmission and variable speed principle, which focus on the transmission mechanism (mainly shaft and gear) the basic structure, characteristic and work principle, mechanical transmission of each block transmission line are briefly analyzed. The articles included a large amount of calculation process, and the specific contents: the layout of transmission analysis, the transmission structure paramete determination of turning a synchronizer, the structure and the working principle, each block of the gear axis strength check, the intensity, the service life of the bearings calculations, etc.
Keywords Gear, Shaft, Synchronizer, Three axis five gear
目 录
摘 要I
AbstractII
第1章 绪论1
1.1 本设计的目的和意义1
1.2 变速器的发展1
1.3变速器的设计要求3
1.4设计内容与思路3
1.4.1设计内容3
1.4.2设计思路4
1.5本章小结4
第2章 变速器的整体结构方案设计5
2.1变速器传动机构的型式选择与结构分析5
2.1.1变速器传动方案的比较5
2.1.2倒档的布置方案6
2.2本章小结7
第3章 变速器主要参数的选择与齿轮设计9
3.1变速器主要参数的选择9
3.1.1档位数和传动比9
3.1.2中心距10
3.1.3齿轮模数11
3.1.4压力角α、螺旋角β和齿宽b12
3.1.5齿轮的变位系数13
3.2各档传动比及其齿轮齿数的确定13
3.2.1确定一档齿轮的齿数13
3.2.2确定常啮合齿轮副的齿数14
3.2.3确定其他档位的齿数15
3.2.4确定倒档齿轮的齿数15
3.2.5确定齿轮轮齿尺寸15
3.3本章小结16
第4章 变速器齿轮的强度计算与材料选择17
4.1齿轮的主要失效形式17
4.2齿轮的强度计算及材料接触应力17
4.2.1齿轮弯曲强度计算17
4.2.2齿轮材料接触应力19
4.3本章小结21
第5章 变速器轴的设计与校核22
5.1变速器轴的结构和尺寸22
5.1.1轴的结构22
5.1.2轴的尺寸22
5.2轴的校核23
5.2.1第一轴的强度与刚度校核23
5.2.2第二轴的强度与刚度校核24
5.3本章小结26
第6章 变速器同步器与操纵机构的设计27
6.1同步器设计27
6.1.1同步器的工作原理27
6.1.2同步环主要参数的确定28
6.2变速器的操纵机构30
6.2.1操纵机构的功用30
6.2.2操纵机构的设计要求31
6.2.3变速器的换档位置32
6.3本章小结32
第7章 轴承的选用与寿命计算33
7.1 第一轴轴承选用与计算33
7.2第二轴轴承选用与计算33
7.3本章小结34
结 论41
致 谢42
参考文献43
第1章 绪论
1.1 本设计的目的和意义
随着我国汽车工业不断的壮大,以及汽车行业持续快速的发展,如何设计出经济实惠,工作可靠,性能优良汽车已经是当前汽车设计者的紧迫问题。为了发挥发动机的最佳性能,就必须有一套传动效率高,维修保养成本低,能够带来驾驶乐趣变速装置,来协调发动机的转速和车轮的实际行驶速度。
该课题针对机械专业学生,使学生了解变速器的设计,通过本课题的研究使学生完成理论课程的实践总结,获得一定的工程设计工作方法,可以更好的学习并掌握现代汽车设计与机械设计的全面知识和锻炼学生利用所学知识分析问题和解决问题的能力。
1.2 变速器的发展
在汽车变速箱100多年的历史中,主要经历了从手动到自动的发展过程。目前世界上使用最多的汽车变速器为手动变速器(MT)、自动变速器(AT)、手自一体变速器(AMT)、无级变速器(CVT)、双离合变速器(DCT)五种型式。
(1)手动变速器(MT)
手动变速器(Manual Transmission)采用齿轮组,每档的齿轮组的齿数是固定的,所以各档的变速比是个定值。曾有人断言,繁琐的驾驶操作等缺点,阻碍了汽车高速发展的步伐,手动变速器会在不久被淘汰,从事物发展的角度来说,这话确实有道理。但是从目前市场的需求和适用角度来看,手动变速器不会过早的离开。首先,从商用车的特性上来说,手动变速器的功用是其他变速器所不能替代的。其次,对于老司机和大部分男士司机来说,他们的最爱还是手动变速器。第三,随着生活水平的不断提高现在轿车已经进入了家庭,对于普通工薪阶级的老百姓来说,经济型轿车最为合适,手动变速器以其自身的性价比配套于经济型轿车厂家,而且经济适用型轿车的销量一直在车市名列前茅。
(2)自动变速器(AT)
自动变速器(AutomaticTransmission),利用行星齿轮机构进行变速,它能根据油门踏板程度和车速变化,自动地进行变速。而驾驶者只需操纵加速踏板控制车速即可。虽说自动变速汽车没有离合器,但自动变速器中有很多离合器,这些离合器能随车速变化而自动分离或合闭,从而达到自动变速的目的。
(3)手动/自动变速器(AMT)
此型车在其档位上设有“+”、“-”选择档位。在D档时,可自由变换降档(-)或加档(+),如同手动档一样。自动—手动变速系统向人们提供两种驾驶方式—为了驾驶乐趣使用手动档,而在交通拥挤时使用自动档,这样的变速方式对于我国的现状还是非常适合的。
(4)无级变速器(CVT)
当今汽车产业的发展,是非常迅速的,用户对于汽车性能的要求是越来越高的。汽车变速器的发展也并不仅限于此,无级变速器便是人们追求的“最高境界”。无级变速系统不像手动变速器或自动变速器那样用齿轮变速,而是用两个滑轮和一个钢带来变速,其传动比可以随意变化,没有换档的突跳感觉。它能克服普通自动变速器“突然换档”、油门反应慢、油耗高等缺点。
(5)双离合变速器(DCT)
DCT结合了手动变速器的燃油经济性和自动变速器的舒适性,它是从传统的手动变速器演变而来,目前代表变速器的最高技术。双离合变速器(Dual Clutch Transmission) DCT有别于一般的自动变速器系统,它基于手动变速器而又不是自动变速器,除了拥有手动变速器的灵活性及自动变速器的舒适性外,还能提供无间断的动力输出。而传统的手动变速器使用一台离合器,当换挡时,驾驶员须踩下离合器踏板,使不同挡的齿轮做出啮合动作,而动力就在换挡期间出现间断,令输出表现有所断续。
针对中国变速器市场发展趋势,Global Insight的亚洲区技术分析师段诚武博士阐述了几点自己的见解: 1.3变速器的设计要求
(1)应保证汽车具有高的动力性和经济性指标。在汽车整体设计时,根据汽车载重量、发动机参数及汽车使用要求,选择合理的变速器挡数及传动比,来满足这一要求。
(2)工作可靠,操纵轻便。汽车在行驶过程中,变速器内不应有自动跳挡、乱挡、换挡冲击等现象的发生。为减轻驾驶员的疲劳强度,提高行驶安全性,操纵轻便的要求日益显得重要,这可通过采用同步器和预选气动换挡或自动、半自动换挡来实现。
(3)重量轻、体积小。影响这一指标的主要参数是变速器的中心距。选用优质钢材,采用合理的热处理,设计合适的齿形,提高齿轮精度以及选用圆锥滚柱轴承可以减小中心距。
(4)传动效率高。为减小齿轮的啮合损失,应有直接挡。提高零件的制造精度和安装质量,采用适当的润滑油都可以提高传动效率。
(5)噪声小。采用斜齿轮传动及选择合理的变位系数,提高制造精度和安装刚性可减小齿轮的噪声。
1.4设计内容与思路
1.4.1设计内容
1、齿轮主要参数的选择设计与校核计算
2、齿轮轴的设计与校核计算
3、同步器的设计计算
4、轴承的选择设计与校核计算
5、用CATIA软件进行三维建模
1.4.2设计思路
查看变速器相关资料,理解变速器的结构组成与工作原理,先对变速器进行整体布置,包括整体的传动方案和倒档的布置。其次次变速器中的齿轮和轴进行设计计算,只要确定了齿轮和轴的尺寸就可以用CAD进行草图的绘制,在此基础上对同步器进行设计计算,进一步完善草图。对各个部分进行校核计算,查看其尺寸是否满足使用要求,如果不正确可以对其进行修改。着重分析同步器和操纵机构的工作原理,对其进行细化处理,并出一张的操纵机构图纸。当CAD二维图纸绘制完成后,用CATIA软件进行三维建模,并仿真运动,立体结构能更直观的把变速器呈现出来,也能把内部机构的配合看的更清楚。
1.5本章小结
本章对变速器的发展历史和未来的方向进行了初步了解,我还是对手动变速器的未来比较乐观,因为它有巨大的市场。本章还明确了该设计的目的和意义,设计会严格按照目的去做,保证了不会偏离方向。变速器的设计要求是需要严格遵守的,因为这直接关系到变速器的安全性和舒适性;最后还对本次设计的设计内容和设计思路进行了展开,进一步明确了设计方案。 第2章 变速器的整体结构方案设计
2.1变速器传动机构的型式选择与结构分析
变速器的种类很多,按其传动比的改变方式可以分为有级、无级和综合式的。有级变速器按根据前进档档数的不同,可以分为三、四、五档和多档变速器;而按其轴中心线的位置又分为固定轴线式、螺旋轴线式和综合式的。其中固定轴式应用广泛,有两轴式和三轴式之分,前者多用于发动机前置前轮驱动的汽车上,而后者多用于发动机前置后轮驱动的汽车上。
2.1.1变速器传动方案的比较
图2-3是三轴式五档变速器传动方案。它们的共同特点是:变速器第一轴和第二轴的轴线在同一直线上,经啮合套将它们连接得到直接档。使用直接档,变速器的齿轮和轴承及中间轴均不承载,发动机转矩经变速器第一轴和第二轴直接输出,此时变速器的传动效率高,可达90%以上,噪声低,齿轮和轴承的磨损减少因为直接档的利用率高于其它档位,因而提高了变速器的使用寿命;在其它前进档位工作时,变速器传递的动力需要经过设置在第一轴,中间轴和第二轴上的两对齿轮传递,因此在变速器中间轴与第二轴之间的距离(中心距)不大的条件下,一档仍然有较大的传动比;档位高的齿轮采用常啮合齿轮传动,档位低的齿轮(一档)可以采用或不采用常啮合齿轮传动;多数传动方案中除一档以外的其他档位的换档机构,均采用同步器或啮合套换档,少数结构的一档也采用同步器或啮合套换档,还有各档同步器或啮合套多数情况下装在第二轴上。再除直接档以外的其他档位工作时,三轴式变速器的传动效率略有降低,这是它的缺点。在档数相同的条件下,各种三轴式变速器主要在常啮合齿轮对数,换档方式和倒档传动方案上有差别。第3章 变速器主要参数的选择与齿轮设计
本设计是根据 Polo 2011款劲取 1.6 MT实酷版而开展的,设计中所采用的相关参数均来源于此种车型,如表3-1所示:
表3-1
主减速比3.16最大扭矩155Nm/3750rpm
最高时速188km/h最大功率77kw/5000rpm
轮胎型号185/60R15发动机型号 EA111
整备质量1155Kg
3.1变速器主要参数的选择
3.1.1档位数和传动比
为了降低油耗,提高燃油利用率,变速器的档数应该适当增加。目前,乘用车一般用4--5个档位的变速器。本设计也采用5个档位。
选择最低档传动比时,应根据汽车最大爬坡度、驱动轮与路面的附着力、汽车的最低稳定车速以及主减速比和驱动轮的滚动半径等来综合考虑、确定。
汽车爬陡坡时车速不高,空气阻力可忽略,则最大驱动力用于克服轮胎与路面间的滚动阻力及爬坡阻力。故有
参考文献
[1] 刘惟信. 汽车设计[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2001
[2] 郭新华.汽车构造[M].北京:高等教育出版社.2004
[3] 余志生.汽车理论[M].北京:机械工业出版社.2010
[4] 过学迅/邓亚东.汽车设计[M].北京:人民交通出版社.2008
[5] 王黎钦/陈铁鸣.机械设计[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社.2008
[6] 孙恒/陈作模/葛文杰.机械原理[M]. 北京:高等教育出版社.2006
[7] 张景田/季雅娟/丁建梅.画法几何及机械制图[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社.2005
[8] 刘品/李哲.机械精度设计与检测基础[M].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学出版社.2009
[9] 王宝玺/贾庆祥.汽车制造工艺学[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社.2007
[10] 江洪/李仲兴/陆利锋.CATIA基础教程[M]. 北京:机械工业出版社.2005
[11] 施建/胡建杰.CATIA造型设计项目案例解析. 北京:清华大学出版社,2010
[12] Hans-Hermann Braess, Ulrich Seiffert. Handbook of Automotive Engineering. SAE International, 2004
[13] James D.Halderman, Chase D.Mitchell. Automotive technology: principle, diagnosis, and service. Pearson Education lnc. 2004
 川公网安备: 51019002004831号
川公网安备: 51019002004831号